Communication Campaign
To organize communication with legislators and other involved parties in the War Against Doctors and Patients.Purpose of Communication Campaign
The primary purpose of this website is to end the attacks on drugs, doctors, and pain patients and restore medicine to the control of medical professionals, not the government.
Because Congress is now divided based on party, not what is best for the country, we have the legislators divided into party lists. I recommend you address your communication to each party separately to stress how they can either maintain control or gain control of the government. We have a tremendous opportunity here if we can get one party to take this and run with it.
Everything you need to do the job is here. The posts on the subjects explaining why the Controlled Substance Act should be repealed are all on the Home page.
Communicate with the legislators as an organization of concerned voting citizens, educating them as to the truth and the need to end current drug policies that were created by false information.
In the past, the collective information about Congress was limited to only members of DoctorsofCourage. Now, to accomplish our mission, we share general contact information everyone. Congress now has a rule that representatives can only receive emails from their constituents. But anyone can put posts on FaceBook or X.com (formerly Twitter). So these links are available to you, through the point and click feature on the spread sheet. Copy your message, then bring up the social media page, and post it. You can communicate with 100 legislators per hour. Stop at that limit for an hour or so, and then start another 100. This keeps you from being identified as a spammer.
We are still preserving the complete list of health staffers for only members of Doctorsofcourage. I don’t want the health staffers to be enundated with emails that have nothing to do with healthcare. However, if you are participating in this campaign and agree to follow the directions, communicate with me through the “Who Are My Health Issues Staff” on the right side bar or the Contact Us page, and I will share all the health staffers for the legislators in your state.
The KEY to SUCCESS!
 The Key to Success is Communication. To Legislators, the President, doctors, the media, and to every contact a person has. What needs to be communicated? The truth. And you find that here on Doctors (and Patients) of Courage. Our work is to end government overreach into medicine. But we can’t do that alone. We need YOU!!!
The Key to Success is Communication. To Legislators, the President, doctors, the media, and to every contact a person has. What needs to be communicated? The truth. And you find that here on Doctors (and Patients) of Courage. Our work is to end government overreach into medicine. But we can’t do that alone. We need YOU!!!
Directions
If you are participating as a part of this communication campaign, then I want you to follow simple directions.
- First: Prayer. God does not want man to suffer. It is through our choices that we have brought this atrocity on ourselves. It is only through God and his power to change people’s hearts that we can achieve what, in human minds, appears to be the impossible. So before you write any message, pray to God to lead you in what you need to say. Then give God thanks for what he has done, is doing, and will do to save us.
- Title every email/facebook post/twitter post with “Repeal the CSA”. In that way, even if the reader doesn’t read the email, the title idea will be planted in their head. “Keep it simple, say it often, and they will believe it.” Also, we hope that eventually hundreds or thousands of people will be communicating the same message, and eventually they will want to open the emails up and see what the issue is about.
- Keep the email short and to the point. They won’t read long emails.
- Do not talk about your need for pain medicine. In their mind, a drug user is an addict and that will automatically put your email in the trash bin.
- Do not blame fentanyl or any other illegal drug for the overdose problem. No drug causes addiction. This is the first and foremost fact you must learn. If you blame one drug, you blame them all.
It is imperative that every American communicate with the health issues staff person for their legislators. If you don't have that contact information, you can get it by filling out the contact form below.
For the purpose of this communication campaign, I will provide the health staffer contacts for the entire state. In order to get the health staffer contacts for the entire country, you have to be a supporting member of Doctorsofcourage.
Who Are My Health Issues Staff?
ASSIGNMENTS
- Watch this recording of this webinar: The REAL Cause of Drug Abuse. Learn the truths in the webinar recording and teach them to everyone you know. This is the answer to the attacks on pain management.
- Sign, like, and share the petition to Save Pain Management. https://www.change.org/savepainmanagement. We will be taking this petition in person to Washington. To get more signatures, you can help by contributing $$ to change.org, or ask your more wealthy friends to do it. That way, they share the petition with other active groups in their list. DoC does not benefit from this donation. Only you, the chronic pain patient will, through a bigger petition.
- If you aren’t already, join Doctorsofcourage as a supporting member. Go to Membership Levels to pick the level that best suits you.
Let’s make the first communication of the week go to committee members relating to the subject addressed. Then the second communication of the week will go to groups of legislators, like legislators of color, new members, etc.
January 26-27 Subject Personal Liberty
This week the House is not in session. If you can visit with your legislator face-to-face or through town hall meetings, do so. You can still email them and their health staff as well. The Senate is in session.
For messages about personal liberty with the legislators in the following committees:
House: Judiciary
Senate: Judiciary
The best person to communicate with is the health staffer of this legislator. Read the instructions on this page to get your health staffer contact information and, for a short while, all health staffers of your state. To get all health staffers in the entire Congress, you have to be a member of Doctorsofcourage.
In addition, you need to put a post on these legislators’ FB page, X page, and email them if they are your Congressman/woman. For the Senators, you can email all of them. But they don’t give their health staff information without calling. If we don’t have it, please share it with us.
Email Message:
Repeal the Controlled Substances Act — Restore Personal Liberty and Justice
Dear [Representative/Senator] [Last Name],
When Congress passed the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) in 1970, it did so under the banner of public health and safety. More than fifty years later, that promise has failed. The CSA has not cured addiction, reduced drug abuse, or made communities safer. Instead, it has criminalized personal choice, eroded constitutional rights, and created a vast enforcement system that punishes private, consensual behavior.
At its core, the CSA violates one of the most basic principles of a free society: that every person owns their own body. If we accept “my body, my choice” for medical procedures and end-of-life care, we must also recognize an adult’s right to decide what substances to ingest. What we choose to put into our bodies should never be policed as a matter of criminal law. The role of government should be to educate and protect, not to cage and coerce.
A System Built on Politics, Not Science
The CSA established a rigid hierarchy of drug schedules shaped more by politics than by evidence. Marijuana, for example, remained under Schedule I over 50 years, treated as more dangerous than cocaine despite decades of clinical and real-world data proving otherwise.
We now know from former Nixon administration officials that drug scheduling was used as a political weapon by criminalizing substances associated with certain social groups. In effect, the CSA became a mechanism for criminalizing identity and dissent under the pretext of drug policy.
The War on Drugs: A War on Americans
The CSA gave birth to the “War on Drugs,” a policy that has done immeasurable harm to American citizens. Its enforcement has filled prisons with nonviolent offenders, militarized local police departments, and established an empire of forfeiture that allows law enforcement to seize property without conviction. These actions invert the presumption of innocence and contradict every notion of due process our Constitution upholds.
According to the Department of Justice’s own reports, supply-side enforcement—raids, interdiction, and incarceration—has not reduced the availability of drugs. Instead, it has enriched organized crime, fueled violence, and driven drug use underground. The social costs are enormous: families torn apart, communities destabilized, and health crises exacerbated by fear and stigma.
When the state criminalizes addiction, it doesn’t cure it—it hides it. Substance use disorders are medical and psychological in nature. Drugs do not cause the despair, trauma, or alienation that lead to abuse; they are responses to those conditions. Punishment only deepens the harm.
The Erosion of Liberty
The CSA’s most insidious effect has been the normalization of state control over the body and mind. Under this law, an adult can be imprisoned for ingesting a plant in private. Homes can be invaded by SWAT teams in no-knock raids—for minor possession charges. Entire neighborhoods, particularly those already marginalized, live under constant surveillance and threat.
This is not the behavior of a free republic. The United States was founded on the conviction that individual liberty comes first—that government exists to secure rights, not dictate morality. If liberty means anything, it means the right to decide how to live, what to believe, and what risks to take with one’s own body.
Reclaiming Responsibility and Compassion
Repealing the CSA is not “legalizing drugs” in the reckless sense often portrayed. It is restoring the principle of responsibility. Adults already make choices about alcohol, tobacco, caffeine, prescription medicines, and other potentially harmful substances. The difference is that these are managed through regulation and education—not criminalization.
We can look to Portugal’s example, where decriminalization replaced punishment with treatment and support. The result? Lower overdose deaths, fewer HIV infections, and reduced rates of problematic drug use. When people are treated as human beings instead of criminals, hope replaces fear—and healing becomes possible.
Repealing the CSA would allow the United States to redirect billions from punitive enforcement into evidence-based health care, harm reduction, and education. It would restore fairness to our justice system and reaffirm that personal freedom is not conditional on government approval.
The Moral Imperative of Repeal
After more than half a century, the Controlled Substances Act has failed by every metric—medical, social, and moral. It criminalizes personal behavior without victims. It empowers state intrusion into private life. And it perpetuates a costly, endless war that no one wins.
Our founders envisioned a nation where governance served liberty, not where liberty bent to control. Repealing the CSA would be a profound step toward realigning policy with that founding promise. It would declare that in the United States of America, sovereignty begins with the individual—not the state.
My body, my choice must mean what it says—or it means nothing at all.
Sincerely,
[Your Full Name]
[Your City and State]
[Optional: Amateur Radio Call Sign or Civic Affiliation]
FB Post
Repeal the Controlled Substances Act — Restore Personal Liberty
Over fifty years ago, Congress passed the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) to protect public health. But instead of safety, it gave us mass incarceration, militarized policing, and government control over our own bodies. It’s time to admit the truth: the CSA attacks freedom and must be repealed.
The principle of “my body, my choice” should apply to every adult decision—including what we choose to consume. The government has no rightful authority to criminalize private behavior that harms no one else. Adults already make choices every day about alcohol, caffeine, tobacco, prescription drugs, and more. Why should other substances be treated differently?
The CSA wasn’t built on science—it was built on politics. When enacted in 1970, it created “drug schedules” supposedly based on medical risk. Yet marijuana, safer than alcohol, was labeled Schedule I, alongside heroin. Later, Nixon’s own advisers admitted the classification was used to target political opponents. The result? A “War on Drugs” that became a war on the American people.
Millions have suffered since—jailed for victimless offenses, stripped of voting rights, jobs, and families. Black and poor communities have borne the brunt, even though drug use rates are similar across all groups. Meanwhile, violent cartels, police corruption, and civil asset forfeiture have flourished under prohibition.
Addiction is not caused by drugs themselves—it’s rooted in despair, trauma, and isolation. Treating substance use as a crime only deepens that harm. Real healing comes from compassion, not punishment.
We already have powerful models showing what works. Portugal decriminalized drug use in 2001. Overdose deaths plummeted, HIV rates fell, and recovery rates rose—all without the heavy hand of criminal law.
Repealing the CSA would save billions in wasted enforcement dollars, restore constitutional protections, and affirm a basic truth: our bodies belong to us, not the government. Public policy should be based on education, regulation, and personal responsibility—not fear and coercion.
After half a century of failure, it’s time to choose freedom over fear, compassion over punishment, and truth over control. The Controlled Substances Act has done enough damage.
My body, my choice means what it says.
X.com Post:
Repeal the Controlled Substance Act. It is a violation of our personal and constitutional rights. My body, my choice applies to what I choose to eat or drink. Government–get out of my home. www.doctorsofcourage.org
January 28-29 Personal Liberty to New Members
This week the House is not in session. If you can visit with your legislator face-to-face or through town hall meetings, do so. You can still email them and their health staff as well. The Senate is in session.
The best person to communicate with is the health staffer of this legislator. Read the instructions on this page to get your health staffer contact information and, for a short while, all health staffers of your state. To get all health staffers in the entire Congress, you have to be a member of Doctorsofcourage.
In addition, you need to put a post on these legislators’ FB page, X page, and email them if they are your Congressman/woman. For the Senators, you can email all of them. But they don’t give their health staff information without calling. If we don’t have it, please share it with us.
Email Message:
Repeal the Controlled Substances Act — Restore Personal Liberty and Justice
Dear [Representative/Senator] [Last Name],
When Congress passed the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) in 1970, it did so under the banner of public health and safety. More than fifty years later, that promise has failed. The CSA has not cured addiction, reduced drug abuse, or made communities safer. Instead, it has criminalized personal choice, eroded constitutional rights, and created a vast enforcement system that punishes private, consensual behavior.
At its core, the CSA violates one of the most basic principles of a free society: that every person owns their own body. If we accept “my body, my choice” for medical procedures and end-of-life care, we must also recognize an adult’s right to decide what substances to ingest. What we choose to put into our bodies should never be policed as a matter of criminal law. The role of government should be to educate and protect, not to cage and coerce.
A System Built on Politics, Not Science
The CSA established a rigid hierarchy of drug schedules shaped more by politics than by evidence. Marijuana, for example, remained under Schedule I over 50 years, treated as more dangerous than cocaine despite decades of clinical and real-world data proving otherwise.
We now know from former Nixon administration officials that drug scheduling was used as a political weapon by criminalizing substances associated with certain social groups. In effect, the CSA became a mechanism for criminalizing identity and dissent under the pretext of drug policy.
The War on Drugs: A War on Americans
The CSA gave birth to the “War on Drugs,” a policy that has done immeasurable harm to American citizens. Its enforcement has filled prisons with nonviolent offenders, militarized local police departments, and established an empire of forfeiture that allows law enforcement to seize property without conviction. These actions invert the presumption of innocence and contradict every notion of due process our Constitution upholds.
According to the Department of Justice’s own reports, supply-side enforcement—raids, interdiction, and incarceration—has not reduced the availability of drugs. Instead, it has enriched organized crime, fueled violence, and driven drug use underground. The social costs are enormous: families torn apart, communities destabilized, and health crises exacerbated by fear and stigma.
When the state criminalizes addiction, it doesn’t cure it—it hides it. Substance use disorders are medical and psychological in nature. Drugs do not cause the despair, trauma, or alienation that lead to abuse; they are responses to those conditions. Punishment only deepens the harm.
The Erosion of Liberty
The CSA’s most insidious effect has been the normalization of state control over the body and mind. Under this law, an adult can be imprisoned for ingesting a plant in private. Homes can be invaded by SWAT teams in no-knock raids—for minor possession charges. Entire neighborhoods, particularly those already marginalized, live under constant surveillance and threat.
This is not the behavior of a free republic. The United States was founded on the conviction that individual liberty comes first—that government exists to secure rights, not dictate morality. If liberty means anything, it means the right to decide how to live, what to believe, and what risks to take with one’s own body.
Reclaiming Responsibility and Compassion
Repealing the CSA is not “legalizing drugs” in the reckless sense often portrayed. It is restoring the principle of responsibility. Adults already make choices about alcohol, tobacco, caffeine, prescription medicines, and other potentially harmful substances. The difference is that these are managed through regulation and education—not criminalization.
We can look to Portugal’s example, where decriminalization replaced punishment with treatment and support. The result? Lower overdose deaths, fewer HIV infections, and reduced rates of problematic drug use. When people are treated as human beings instead of criminals, hope replaces fear—and healing becomes possible.
Repealing the CSA would allow the United States to redirect billions from punitive enforcement into evidence-based health care, harm reduction, and education. It would restore fairness to our justice system and reaffirm that personal freedom is not conditional on government approval.
The Moral Imperative of Repeal
After more than half a century, the Controlled Substances Act has failed by every metric—medical, social, and moral. It criminalizes personal behavior without victims. It empowers state intrusion into private life. And it perpetuates a costly, endless war that no one wins.
Our founders envisioned a nation where governance served liberty, not where liberty bent to control. Repealing the CSA would be a profound step toward realigning policy with that founding promise. It would declare that in the United States of America, sovereignty begins with the individual—not the state.
My body, my choice must mean what it says—or it means nothing at all.
Sincerely,
[Your Full Name]
[Your City and State]
[Optional: Amateur Radio Call Sign or Civic Affiliation]
FB Post
Repeal the Controlled Substances Act — Restore Liberty and Justice
Dear Members of Congress,
As you begin your new term, I urge you to take up an issue that strikes at the heart of American freedom and fairness: the repeal of the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) of 1970.
For more than 50 years, the CSA has failed to achieve its stated goal of protecting public health and safety. It hasn’t cured addiction, stopped drug abuse, or made our communities safer. Instead, it has criminalized personal choice, eroded constitutional rights, and empowered a vast machinery of punishment that targets private behavior rather than public harm.
At its core, the CSA denies the most basic liberty of all — ownership of one’s own body. If we affirm “my body, my choice” for medical care and end-of-life decisions, we must also affirm it for what an adult chooses to ingest. Education and compassion heal; coercion and criminalization destroy.
The truth is, drug scheduling under the CSA was built more on politics than science. Marijuana, for decades listed as more dangerous than cocaine, shows how arbitrary and unjust the system has been. It became a tool for political suppression, not public safety.
The War on Drugs has in reality been a war on Americans. Families broken apart, lives ruined by criminal records, property seized without conviction — all while drug availability and addiction rates remain unchanged. We can’t arrest our way out of human suffering.
There’s a better way. Countries like Portugal have shown that when drug use is treated as a health issue, not a crime, outcomes improve: fewer overdoses, lower infection rates, stronger communities. The United States can do the same.
Repealing the CSA isn’t about “legalizing everything” — it’s about ending punishment for personal choices and replacing it with education, regulation, and treatment that work. It’s about restoring the principle that government exists to protect rights, not police morality.
It’s time to end a failed policy and reclaim the promise of liberty.
Repeal the Controlled Substances Act — because my body, my choice must mean what it says.
X.com Post:
Repeal the Controlled Substance Act. It is a violation of our personal and constitutional rights. My body, my choice applies to what I choose to eat or drink. Government–get out of my home. www.doctorsofcourage.org
February 2-3 Subject Healthcare Costs
The best person to communicate with is the health staffer of this legislator. Read the instructions on this page to get your health staffer contact information and, for a short while, all health staffers of your state. To get all health staffers in the entire Congress, you have to be a member of Doctorsofcourage.
In addition, you need to put a post on these legislators’ FB page, X page, and email them if they are your Congressman/woman. For the Senators, you can email all of them. But they don’t give their health staff information without calling. If we don’t have it, please share it with us.
Committees to communicate with:
House: Energy and Commerce, Ways and Means, Education and the Workforce, Appropriations
Senate: Finance, HELP, Special Committee on Aging, Appropriations
Email message:
Repeal the Controlled Substances Act to Cut Healthcare Costs for Everyone
Dear Senator/Representative [Last Name],
Repeal the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) and replace it with a health‑centered framework for all drugs. This is not only a moral and public health imperative—it is also a concrete, data‑supported way to lower healthcare costs for individuals, employers, and government at every level.
The war on drugs has become a driver of medical inflation. By criminalizing drugs and tightly scheduling many medications, the CSA pushes people into high‑cost emergency and hospital care, forces unnecessary office visits, inflates administrative overhead, and blocks cheaper treatment alternatives. Research shows that when we move even one substance out of this punitive model and into a regulated, health‑centered framework, healthcare spending and insurance premiums go down. Ending the CSA would extend those savings across the entire system.
In states that legalized medical cannabis health insurance premiums fell by roughly 1,600 dollars per enrollee per year. If similar medical cannabis policies were adopted nationwide, estimated savings in the individual market alone would reach tens of billions of dollars annually.
Why do premiums drop? When patients can use a relatively low‑cost medicine instead of high‑priced pharmaceuticals and avoid some downstream complications, overall spending falls. Insurers then spread these savings across their risk pools, lowering premiums for all.
Imagine applying that principle across the full spectrum of drugs currently controlled by the CSA. Our current framework concentrates costs in the most expensive part of the system: crisis care. Billions of dollars are spent each year on hospitalizations tied to substance use disorders and their complications—overdoses, injuries, infections, and other crises. Prohibition ensures that many people with problematic use avoid care until their situation becomes an emergency. Fear of arrest, stigma, and the instability created by criminal records all make early, lower‑cost outpatient treatment less likely. That is the most expensive way possible to handle a chronic health condition. By legalizing and regulating all drugs, and repealing the CSA that underpins criminalization, we could redirect resources into early screening, outpatient treatment, and harm reduction—interventions that are far cheaper than repeated emergency visits and hospital stays.
The CSA also drives costs through rigid prescription and administrative rules that have little to do with medical necessity. Patients needing scheduled medications are forced into frequent office visits just to renew prescriptions, even when their conditions are stable. Every visit generates billing, copays, pharmacy interactions, and time costs for both patients and providers. Clinicians must comply with an elaborate apparatus of monitoring and documentation: paper scripts, short refill windows, prior authorizations, urine drug tests, and audits dictated by controlled‑substance status.
These layers of bureaucracy do not come free. They absorb physician time that could be devoted to preventive and complex care, they require back‑office staff and compliance infrastructure, and they ultimately show up in higher insurance premiums and taxes. When drugs are no longer controlled under the CSA, these burdens can be scaled back to what is clinically appropriate.
Importantly, the war on drugs imposes indirect costs that wash back into healthcare. Criminal records make it harder to find stable employment and housing, which are key determinants of health. Communities subjected to aggressive enforcement experience chronic stress, family disruption, and higher rates of untreated mental health needs. All of this increases reliance on public insurance programs and emergency care.
Repealing the CSA would not mean a free‑for‑all. It would allow Congress and the states to design legal markets with age limits, product standards, taxation, and labeling, while shifting public funds from punishment to healthcare.
The fiscal payoff is:
- Lower hospitalization and emergency use for substance‑related crises.
- Fewer unnecessary doctor visits and administrative steps
- Reduced spending on high‑cost prescriptions as cheaper alternatives are available.
- Lower insurance premiums for individuals and employers.
- Lower federal and state outlays for Medicaid, Medicare, and corrections.
At a time when healthcare costs are rising faster than wages and public budgets are strained, it is fiscally irresponsible to maintain a policy framework that makes care more expensive while failing to reduce drug‑related harm. The evidence we already have from medical cannabis is a proof of concept: when we move away from prohibition and toward health, costs go down and outcomes improve.
I urge you to begin the process of repealing the Controlled Substances Act and replacing it with comprehensive, health‑centered regulation of all drugs. This is not only a matter of justice and public health; it is a pragmatic strategy to lower healthcare costs for your constituents and for the nation as a whole.
Thank you for your time and consideration of this urgently needed reform.
Facebook comment:
Repealing the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) isn’t just about ending the “War on Drugs” – it’s about slashing healthcare costs for all of us and finally treating drugs as a health issue instead of a criminal one.
By criminalizing drug use, the CSA drives people away from early, low‑cost care and into the most expensive part of the system: emergency rooms and hospital beds. Substance use disorders are linked to billions of dollars every year in hospital costs for overdoses, infections, injuries, and other crises. Taxpayers pick up a big chunk of that bill through Medicaid and Medicare, and the rest shows up in higher premiums for everyone.
We already have a powerful real‑world experiment: medical cannabis. Studies comparing states show that after medical cannabis laws are passed, individual‑market health insurance premiums dropped by roughly 1,600 dollars per person per year. Employers also see lower premiums. Why? Because patients finally get a safer, cheaper option for pain, sleep, anxiety, nausea, and more – and that means fewer pricey prescriptions, fewer hospitalizations, and fewer specialist visits. When total spending falls, insurers spread those savings across the entire risk pool.
Now imagine we apply that same logic to all drugs.
Repealing the CSA and legalizing drugs would:
- Let stable patients get longer‑term prescriptions and telehealth visits instead of constant, expensive in‑person appointments just to refill controlled meds.
- Cut the massive bureaucracy built around “controlled substances” – paper scripts, rigid refill rules, endless prior authorizations, urine tests – that wastes clinician time and drives up overhead.
- Move money from policing, courts, and prisons into early screening, outpatient treatment, mental health care, and harm reduction that actually prevent crises.
- Reduce emergency‑room dependence by treating addiction like any other chronic condition, not a crime.
This isn’t a call for chaos; it’s a call for smart regulation. We can have age limits, product standards, labeling, and taxes – just like we do for alcohol and tobacco – while shifting our focus from punishment to health.
If you’re tired of skyrocketing premiums and stories of people going broke just to get basic care, it’s time to look honestly at the CSA. Repealing it and legalizing drugs under a health‑centered framework would save individuals, employers, and government billions.
If you agree, share this and tell your legislators: it’s time to repeal the Controlled Substances Act and put health – not the failed drug war – at the center of our policy.
X.com post:
Repealing the Controlled Substance Act would slash healthcare costs by billions per year and provide cheaper, more effective treatment, turning from criminalization to health. Learn more on doctorsofcourage.org.
February 4-5 Healthcare Costs to Medical and Activists
Continue the communications from Monday-Tuesday on FB and X. There were a lot of committees. Also, add the legislators connected to medicine and the activists.
Committees to communicate with:
House: Energy and Commerce, Ways and Means, Education and the Workforce, Appropriations
Senate: Finance, HELP, Special Committee on Aging, Appropriations
Facebook comment:
Repealing the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) isn’t just about ending the “War on Drugs” – it’s about slashing healthcare costs for all of us and finally treating drugs as a health issue instead of a criminal one.
By criminalizing drug use, the CSA drives people away from early, low‑cost care and into the most expensive part of the system: emergency rooms and hospital beds. Substance use disorders are linked to billions of dollars every year in hospital costs for overdoses, infections, injuries, and other crises. Taxpayers pick up a big chunk of that bill through Medicaid and Medicare, and the rest shows up in higher premiums for everyone.
We already have a powerful real‑world experiment: medical cannabis. Studies comparing states show that after medical cannabis laws are passed, individual‑market health insurance premiums dropped by roughly 1,600 dollars per person per year. Employers also see lower premiums. Why? Because patients finally get a safer, cheaper option for pain, sleep, anxiety, nausea, and more – and that means fewer pricey prescriptions, fewer hospitalizations, and fewer specialist visits. When total spending falls, insurers spread those savings across the entire risk pool.
Now imagine we apply that same logic to all drugs.
Repealing the CSA and legalizing drugs would:
- Let stable patients get longer‑term prescriptions and telehealth visits instead of constant, expensive in‑person appointments just to refill controlled meds.
- Cut the massive bureaucracy built around “controlled substances” – paper scripts, rigid refill rules, endless prior authorizations, urine tests – that wastes clinician time and drives up overhead.
- Move money from policing, courts, and prisons into early screening, outpatient treatment, mental health care, and harm reduction that actually prevent crises.
- Reduce emergency‑room dependence by treating addiction like any other chronic condition, not a crime.
This isn’t a call for chaos; it’s a call for smart regulation. We can have age limits, product standards, labeling, and taxes – just like we do for alcohol and tobacco – while shifting our focus from punishment to health.
If you’re tired of skyrocketing premiums and stories of people going broke just to get basic care, it’s time to look honestly at the CSA. Repealing it and legalizing drugs under a health‑centered framework would save individuals, employers, and government billions.
If you agree, share this and tell your legislators: it’s time to repeal the Controlled Substances Act and put health – not the failed drug war – at the center of our policy.
X.com post:
Repealing the Controlled Substance Act would slash healthcare costs by billions per year and provide cheaper, more effective treatment, turning from criminalization to health. Learn more on doctorsofcourage.org.
February 9-10 Subject: Public Health
The best person to communicate with is the health staffer of this legislator. Read the instructions on this page to get your health staffer contact information and, for a short while, all health staffers of your state. To get all health staffers in the entire Congress, you have to be a member of Doctorsofcourage.
In addition, you need to put a post on these legislators’ FB page, X page, and email them if they are your Congressman/woman. For the Senators, you can email all of them. But they don’t give their health staff information without calling. If we don’t have it, please share it with us.
Committees to communicate with:
House: Energy and Commerce, Ways and Means, Education and the Workforce, Appropriations
Senate: Finance, HELP, Special Committee on Aging, Appropriations
Email Message:
Dear [Senator/Representative Last Name],
For more than fifty years, U.S. drug policy has been guided by the Controlled Substances Act of 1970 (CSA)—the cornerstone of the so‑called “War on Drugs.” In hindsight, this policy experiment has been a humanitarian and public health disaster. Its criminal justice approach to substance use has worsened the very problems it set out to solve: rising addiction, record overdose deaths, the spread of infectious disease, racial injustice, and the erosion of family and community health. It is time for Congress to repeal the CSA and replace it with a science‑based, compassionate framework that treats drug use as a health issue, not a crime.
Criminalization Has Fueled a Health Crisis
Five decades of aggressive enforcement have shown that fear of punishment drives people away from lifesaving services far more effectively than it deters drug use. Individuals hesitate to call for help during an overdose or to seek treatment because they fear arrest, loss of employment, or child custody. This fear is fatal. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports overdose deaths reaching 93,000 in 2020, 108,000 in 2021, and roughly 110,500 in 2022—the highest numbers ever recorded.
Drug prohibition also shapes markets in deadly ways. When supply is restricted, traffickers turn to compact, high‑potency substances with greater profit margins and easier concealment. This dynamic transformed a heroin problem into a fentanyl crisis—a synthetic opioid up to 50 times stronger than heroin and now involved in two‑thirds of U.S. overdose deaths. The War on Drugs did not eliminate drugs; it created deadlier ones.
Criminalization Spreads Infectious Disease
Punitive drug laws have also fueled transmission of HIV and hepatitis. The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the World Health Organization have repeatedly warned that outlawing syringe programs and punishing possession of sterile needles pushes people toward unsafe injection practices. The same policies that ban syringe programs also block access to proven therapies such as methadone and buprenorphine, which dramatically reduce overdose deaths and illicit opioid use.
The Broader Public Health Damage
Punitive drug laws do more than fill prisons—they erode the social determinants of health. Research published in the Annals of Medicine (Cohen et al., 2022) shows that criminalization intensifies poverty, unemployment, housing insecurity, and mental health disorders. Arrest records make hiring harder; eviction risks rise; families are torn apart. These consequences are not side effects—they are structural outcomes of a law that treats medical and social vulnerability as criminal behavior.
The results are visible in every neighborhood: overburdened emergency rooms, untreated mental illness, families fractured by incarceration, and billions spent on enforcement instead of treatment.
A Failed Policy by Its Own Standards
Even justice officials knew three decades ago that the War on Drugs could not succeed. The 1990 Justice Department‑funded report Beyond the War on Drugs: Overcoming a Failed Public Policy concluded that supply‑side enforcement was “futile.” Its prediction has proven correct. Drug use continues because psychoactive substances fulfill deep human needs for relief, ritual, and coping. Denying this reality does not solve addiction—it replaces it with stigma, danger, and death.
The Cost of Prohibition: Disease, Overdose, and Lost Freedom
The Alternative World Drug Report (UNODC, 2011) summarized the global fallout of prohibition: empowered cartels, contaminated street drugs, soaring overdoses, and widespread human‑rights abuses. By criminalizing possession and inhibiting harm‑reduction services, the CSA ensures that people consume unregulated substances of unknown potency—conditions unthinkable for any other consumer product. Meanwhile, strict controls on legitimate medical opioids leave millions worldwide without adequate pain relief.
The policy’s irony is tragic: in the name of health and safety, the CSA has caused preventable suffering on an epidemic scale.
A Path Forward: Health, Not Warfare
Repealing the Controlled Substances Act would open the door to a rational public health strategy. Congress could:
- Decriminalize possession and redirect funds from policing to evidence‑based treatment and recovery.
- Implement safe‑supply programs ensuring quality control and reducing poisoning deaths.
- Expand harm‑reduction initiatives such as syringe services, naloxone distribution, and overdose education.
- Support research into drug pharmacology, mental health, and the social roots of addiction without political barriers.
- Rebuild trust between communities and public institutions through transparency and compassion.
These measures save lives, reduce costs, and restore human dignity. Countries such as Portugal, Switzerland, and Canada have already demonstrated that public health approaches can achieve what criminalization never has: stability, recovery, and safety.
From War to Wellness
Half a century after Congress declared the War on Drugs, America faces its most deadly overdose crisis and an exhausted, distrustful public health system. The evidence is overwhelming: criminalization has not protected our communities—it has shattered them.
I urge you to lead in repealing the Controlled Substances Act and replacing it with policies grounded in health, science, and human rights. Doing so would mark the end of a failed war and the beginning of a truly effective strategy: helping people live.
Respectfully,
[Your Full Name]
[City, State]
[Optional Affiliation or Organization]
FB post, generic
For more than fifty years, the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) has fueled the “War on Drugs,” a policy that has done more harm to public health than any drug ever could. What began as an anti-drug effort has become a war on people — especially those struggling with addiction, poverty, or mental illness.
The numbers speak for themselves. The CDC reports over 110,000 overdose deaths in 2022, the highest ever recorded. Far from reducing drug use, criminalization has made it deadlier. When people fear arrest, they delay calling for help or avoid seeking treatment entirely. This fear kills — while communities are torn apart and families are left grieving.
The drug war also reshaped the market, pushing traffickers toward stronger, more compact drugs. That’s how fentanyl, up to 50 times stronger than heroin, became dominant and now drives two-thirds of overdose deaths. Laws meant to protect us have created the most toxic drug supply in U.S. history.
The damage doesn’t stop there. Criminalization spreads HIV and hepatitis by pushing use underground and limiting access to clean syringes. In prisons — where infection rates are many times higher than average — medical care and treatment are often out of reach. Punishment doesn’t heal people; it isolates and endangers them.
Other countries have chosen a smarter path. Portugal decriminalized possession over 20 years ago — and saw massive drops in overdose deaths, HIV infections, and incarceration. By investing in healthcare instead of punishment, they proved that compassion and science save lives where fear and force fail.
Repealing the CSA would let the U.S. finally shift from war to wellness. It would free states and communities to adopt evidence-based strategies:
- Decriminalize possession and redirect funds to treatment and recovery.
- Provide safe supply and quality control to prevent poisonings.
- Expand harm reduction — naloxone, syringes, and overdose education.
- Support medical research without political interference.
Over half a century of evidence is clear: criminalization has failed. Addiction is not a crime — it’s a health condition, and it’s time our laws reflected that truth.
Repeal the Controlled Substances Act. End the War on Drugs. Choose health, compassion, and recovery over punishment.
FB Post Directed to Conservative Legislators
Version 1: Conservative‑leaning audience
Congressman, it’s time to take a serious look at the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) and the broken system it created. After five decades of spending billions on the War on Drugs, America has more addiction, more overdose deaths, and less freedom to handle these problems locally and effectively.
Over 110,000 Americans died from overdoses in 2022, despite rising enforcement costs. Criminalization doesn’t solve addiction — it drives it underground, creating dangerous black markets. When government bans safer options, suppliers turn to smaller, deadlier drugs like fentanyl, which now kills more Americans each year than car crashes.
The CSA strips communities and states of the freedom to experiment with practical, evidence‑based solutions that actually work. It also wastes taxpayer dollars on failed enforcement strategies while families and small towns bear the cost.
Repealing the CSA would return power to states, promote accountability, and allow medical professionals — not bureaucrats — to lead our response. We can protect life, liberty, and local decision‑making while strengthening public health.
Please stand for freedom, fiscal sense, and common‑sense reform. End the federal war on drugs. Repeal the Controlled Substances Act.
FB Post Directed to Progressive Legislators
Representative, I’m urging you to support the repeal of the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) — one of the most damaging laws in modern U.S. history. The War on Drugs has caused immense harm to communities of color, deepened inequality, and turned a public health issue into a criminal justice crisis.
More than 110,000 Americans died from overdoses in 2022. Criminalization doesn’t reduce harm — it multiplies it. People fear calling for help, families are broken apart, and prisons fill with individuals who needed healthcare instead of handcuffs. Meanwhile, punitive laws made drug markets deadlier, fueling the fentanyl crisis.
Portugal and other nations have shown what happens when we treat substance use as a health condition: overdose deaths drop, HIV infections decline, and recovery rates rise. We can do that here — but only if Congress ends the federal barriers that block harm‑reduction and treatment programs.
Repealing the CSA would let us build policies driven by evidence, compassion, and equity — not punishment and fear. Let’s choose health care, not incarceration. End the War on Drugs. Repeal the Controlled Substances Act.
X Post
Repeal the CSA! The War on Drugs is a failure. It costs us lives, untreated disease, overdose, and increased criminalization. Choose health and wellness over war. Doctorsofcourage.org.
February 23-24 Subject Economics
For messages about economy, communicate with the legislators in the following committees:
House: Financial Services, Ways & Means,
Small Business
Senate: Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs, Finance
Joint: Economic Committee
The best person to communicate with is the health staffer of this legislator. Read the instructions on this page to get your health staffer contact information and, for a short while, all health staffers of your state. To get all health staffers in the entire Congress, you have to be a member of Doctorsofcourage.
In addition, you need to put a post on these legislators’ FB page, X page, and email them if they are your Congressman/woman. For the Senators, you can email all of them. But they don’t give their health staff information without calling. If we don’t have it, please share it with us.
Message:
The War on Drugs has been a drain on United States and World Economy for over 50 years and it has done nothing to end substance use disorder because substance use is actually not caused by the drug.
Repealing the CSA entirely would not only dismantle a failed policy—it would open the door to economic growth, new industries, and social reintegration for millions of people, extending far beyond American borders, improving economic stability and justice worldwide.
It is estimated that enforcing drug prohibition costs taxpayers more than $47 billion each year, while the broader costs of incarceration, court expenses, and lost labor productivity may exceed $100 billion annually. Repealing the CSA would end this fiscal sinkhole. Instead of funneling public funds into enforcement and mass incarceration, the U.S. could redirect resources toward addiction treatment, prevention, and economic reintegration. Repealing the Controlled Substances Act, combined with record expungement and restoration of civil rights, would reintegrate millions into the legitimate economy. This reintegration would expand the workforce and increase tax revenue while reducing welfare costs associated with unemployment and recidivism.
Reimagining the Future
The Controlled Substances Act was born of fear and moral panic, not sound economics or evidence-based policy. Its repeal would mark a turning point—an embrace of pragmatic, humane governance that values outcome over ideology.
Economically speaking, repeal would:
- Reduce government spending by tens of billions annually.
- Expand the workforce by removing barriers to employment.
- Create thriving new industries and tax revenues.
- Revitalize rural economies through regulated agricultural production.
- Foster global stability by replacing illicit trade with lawful commerce.
- Correct structural injustices that have suppressed economic mobility for generations.
Like the repeal of alcohol prohibition nearly a century ago, ending the CSA would unleash innovation, entrepreneurship, and social healing. The War on Drugs has too long drained American prosperity into policing and prisons. Economic recovery—true, inclusive recovery—requires abandoning this failed experiment and reimagining a world where policy supports opportunity, not punishment.
For the members of the committee that are democratic, or for your rep or senator that is democratic, add at the end of your message:
This is something that could help the democratic party get a wide margin of control of Congress, both House and Senate, if they would make this a significant part of their 2026 platform.
February 25-26 Subject Against Minorities
Email message:
The War on Drugs has left an indelible scar on America’s communities of color, metastasizing into a system of mass incarceration, economic suppression, and generational trauma. The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) of 1970 must be repealed if we are to dismantle the machinery of injustice that it continues to fuel.
Punitive drug laws have perpetuated racial and economic inequality under the guise of public safety. From their inception, these policies were weaponized against Black, Latino, and poor communities leading to overcrowded prisons and broken families across the nation.
The CSA’s enforcement has disproportionately targeted minority neighborhoods through biased policing, harsh sentencing disparities, and intrusive surveillance. Though Black and White Americans use drugs at comparable rates, people of color are far more likely to be arrested, convicted, and imprisoned for nonviolent drug offenses. These convictions destroy access to housing, employment, education, and healthcare—locking generations in systemic poverty.
The erosion of constitutional rights under the War on Drugs has been profound. Stop-and-frisk tactics, “no-knock” raids, and militarized policing have reduced safety while inflaming fear and mistrust in communities already under siege. Resources wasted on low-level drug enforcement have drained public budgets, diverting funds from education, treatment, and social development—the very tools proven to build stronger, safer neighborhoods.
Meanwhile, drug use and addiction have not declined because the real cause is not being addressed. Instead, deaths from unregulated substances have soared. The CSA does not protect life; it perpetuates death and despair. Other nations that have embraced decriminalization and treatment over punishment have witnessed reduction in overdoses, crime, and incarceration—proof that humane policy saves lives where punishment destroys them.
As a leader, you carry a moral responsibility to end this historical injustice. Repealing the Controlled Substances Act is not about condoning drug use—it is about reclaiming justice, health, and human dignity. America cannot heal until it replaces punishment with compassion and inequality with opportunity.
Now is the moment to act. End the War on Drugs. Repeal the Controlled Substances Act.
Facebook comment:
The War on Drugs didn’t make America safer—it devastated our communities. For over 50 years, the Controlled Substances Act has fueled mass incarceration, torn families apart, and criminalized poverty and color.
Black and Latino Americans are still punished most harshly, despite equal rates of drug use across races. Harsh drug laws eroded constitutional rights, drained public resources, and deepened inequality while addiction and overdose deaths keep rising.
It’s time for justice that heals—not punishes. Repeal the Controlled Substances Act and end the War on Drugs. Our communities deserve health, opportunity, and freedom—not fear.
No drug causes abuse or addiction The War on Drugs is purely a racist, white-supremist agenda. For the truth, visit www.doctorsofcourage.org.
#EndTheWarOnDrugs #RepealCSA #JusticeReform #HealthNotHandcuffs
X.com post:
The War on Drugs is an attack on minorities–a weaponized system of mass incarceration and economic inequality. The CSA does not protect life—it perpetuates death and despair. End the war on Drugs. Repeal the Controlled Substance Act.
March 2-3 Subject: Federal Policing
Because Monday, Jan 19, is a federal holiday, you can use it to send FB and X posts. But save the email to the health staff/legislator for Tuesday or Wednesday.
For Federal regulations and policing responsibility, the committees to address are
House of Representatives
Judiciary Committee; Oversight and Accountability Committee; Homeland Security Committee; Appropriations Committee
Senate
Judiciary Committee; Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs Committee; Appropriations Committee
Message:
Repeal the CSA
The invasions of our cities and the federal attacks on our citizens can be blamed on the Controlled Substance Act, and it needs to be repealed to restore civility in our country.
For more than half a century, the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) has been the cornerstone of a domestic and international “War on Drugs” that has transformed America from a nation of citizens into a nation under surveillance. Originally sold as a measure to protect health and safety, the CSA instead built the foundation for a permanent security apparatus that now extends into every corner of civilian life.
The policing practices that grew from the CSA have blurred the line between military and civilian authority. What began with the militarization of local police through SWAT and drug task forces has now evolved into the deployment of National Guard units and ICE agents in American cities. Under the pretense of drug and border enforcement, these forces operate with military tactics, surveillance equipment, and broad discretionary power over civilians—often without local consent or meaningful oversight. The same logic that once justified raids on small-scale marijuana users now justifies raids in immigrant neighborhoods and the expansion of federal control into local jurisdictions.
The result is an America increasingly governed through force. Communities of color, already devastated by drug sentencing disparities and over-policing, now face layers of enforcement that criminalize poverty, migration, and survival. The CSA’s punitive model fosters dependency on militarized control rather than on public health, education, and opportunity. It erodes trust in law enforcement and turns our cities into training grounds for warfare, not freedom.
Internationally, the U.S. has exported this model, tying foreign aid and military cooperation to drug control. This has spread displacement, rural poverty, and violence across nations, mirroring the harms at home.
Repealing the CSA would be more than a legal reform—it would be a step toward dismantling the war machinery that polices our people. Replacing punishment with healthcare, treatment, and education would not only restore civil liberties but reassert the principle that America is a republic, not an occupied territory.
Ending the CSA is essential to restoring constitutional rights, demilitarizing our cities, and reaffirming a government that serves rather than controls its people.
Facebook Post
For over 50 years, the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) has done more harm than good. It turned a public health issue into a system of punishment, mass incarceration, and militarized policing—devastating families, eroding constitutional rights, and deepening racial inequities.
The CSA gave rise to SWAT raids, racial profiling, and civil asset forfeiture, turning communities—especially Black and Latino neighborhoods—into militarized zones under constant surveillance. Now it is even causing militarized federal agents to invade our cities. Despite decades of enforcement, drug use and deaths have only increased, while millions have lost freedom, opportunity, and trust in government.
Even abroad, U.S. enforcement policies have destroyed livelihoods and fueled violence from Latin America to Asia. This “war” has failed everywhere it’s been waged.
It’s time to repeal the CSA and replace punishment with healthcare, education, and treatment. Let America lead again by ending the policing of poverty and returning to principles of liberty, justice, and human dignity.
X.com post
The militarization of federal agencies and the attacks on our cities and citizens is the result of the Controlled Substance Act. Repeal it. Restore humanity. www.doctorsofcourage.org
March 4-5 To New Members
Continue sending the same message as in March 2-3 but to the new members. Many of the new members have not been added to the committeess. So this is a chance to send this message through their recognition of MLK day on their FB posts.
Message:
Repeal the CSA
The invasions of our cities and the federal attacks on our citizens can be blamed on the Controlled Substance Act, and it needs to be repealed to restore civility in our country.
For more than half a century, the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) has been the cornerstone of a domestic and international “War on Drugs” that has transformed America from a nation of citizens into a nation under surveillance. Originally sold as a measure to protect health and safety, the CSA instead built the foundation for a permanent security apparatus that now extends into every corner of civilian life.
The policing practices that grew from the CSA have blurred the line between military and civilian authority. What began with the militarization of local police through SWAT and drug task forces has now evolved into the deployment of National Guard units and ICE agents in American cities. Under the pretense of drug and border enforcement, these forces operate with military tactics, surveillance equipment, and broad discretionary power over civilians—often without local consent or meaningful oversight. The same logic that once justified raids on small-scale marijuana users now justifies raids in immigrant neighborhoods and the expansion of federal control into local jurisdictions.
The result is an America increasingly governed through force. Communities of color, already devastated by drug sentencing disparities and over-policing, now face layers of enforcement that criminalize poverty, migration, and survival. The CSA’s punitive model fosters dependency on militarized control rather than on public health, education, and opportunity. It erodes trust in law enforcement and turns our cities into training grounds for warfare, not freedom.
Internationally, the U.S. has exported this model, tying foreign aid and military cooperation to drug control. This has spread displacement, rural poverty, and violence across nations, mirroring the harms at home.
Repealing the CSA would be more than a legal reform—it would be a step toward dismantling the war machinery that polices our people. Replacing punishment with healthcare, treatment, and education would not only restore civil liberties but reassert the principle that America is a republic, not an occupied territory.
Ending the CSA is essential to restoring constitutional rights, demilitarizing our cities, and reaffirming a government that serves rather than controls its people.
Facebook Post
For over 50 years, the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) has done more harm than good. It turned a public health issue into a system of punishment, mass incarceration, and militarized policing—devastating families, eroding constitutional rights, and deepening racial inequities.
The CSA gave rise to SWAT raids, racial profiling, and civil asset forfeiture, turning communities—especially Black and Latino neighborhoods—into militarized zones under constant surveillance. Now it is even causing militarized federal agents to invade our cities. Despite decades of enforcement, drug use and deaths have only increased, while millions have lost freedom, opportunity, and trust in government.
Even abroad, U.S. enforcement policies have destroyed livelihoods and fueled violence from Latin America to Asia. This “war” has failed everywhere it’s been waged.
It’s time to repeal the CSA and replace punishment with healthcare, education, and treatment. Let America lead again by ending the policing of poverty and returning to principles of liberty, justice, and human dignity.
X.com post
The militarization of federal agencies and the attacks on our cities and citizens is the result of the Controlled Substance Act. Repeal it. Restore humanity. www.doctorsofcourage.org
SPECIFIC ISSUES
COMMUNICATION TO LEGISLATORS
Example Communication:
Feel free to copy and send as your own. Identify yourself as a member of DoctorsofCourage.
Facebook Post to Medical Professional Legislators
On behalf of all your constituents with untreated pain because of the illegal government overreach into medicine, please make it a goal in Congress to make the DOJ follow the rule of law and stop putting innocent medical professionals in prison for money. The SC has ruled many times that their use of the CSA against physicians is unlawful, and yet they continue. Take away immunity from the DOJ. If they break the law convicting an innocent person, they should be charged. Our country has become a police state, no better than Hitler Germany, just wider targets—all minorities. See www.doctorsofcourage.org for what is happening to innocent people. Pain patients are being forced to the streets. Drugs are NOT the cause of addiction. Learn the REAL cause, and then we can lick it.
Tweet to Medical Professional Legislators
Your job depends on ending the war against doctors and drugs. Learn the truth. Drugs don’t cause addiction. The rogue DOJ is attacking colleagues and patients for money & jobs. End the illegal government overreach into medicine. Repeal the CSA. www.doctorsofcourage.org
From a Chronic Pain Patient to Legislators
Dear Congressman,
I am a chronic pain patient as well as an associate of the patient/doctor advocacy group Doctors (and patients) of Courage (doctorsofcourage.org). There are many people such as myself that are being denied proper pain treatment due to ignorance and misinformation about opioid pain management. Those of us who rely on opioid pain medications are being discriminated against. By preventing trained pain management professionals from doing their job, the government is forcing its own citizens to the street for self-medication, where they most probably will unknowingly receive illegal fentanyl laced pills. More and more suffering patients are forced off their medication and are committing suicide at alarming rates. Since opioid prescriptions are declining, opioid-related deaths are rising rapidly each year. The government solution is not and will not fix the problem, it will only perpetrate it and more people will ultimately die. Most pain patients are not addicts. The opioids that are killing people and contributing to these horrific overdose deaths are not a result of pills diverted from pain management facilities, but are a result of illicit Fentanyl sold on the street. Arresting doctors and forcing people with severe intractable chronic pain to an early grave will not in any way stop the overdose rate from doubling the next few years.
Opioids are not the cause of addiction. Being dependent on a drug does not mean you are addicted. Addiction is caused by toxicity and not by direct exposure to the drug. What does the body do with excess toxins? They have to be stored in the cells. That is genetically determined, and thus you get the genetic propensity to certain diseases. The fact that more people are not addicted that require pain medicines for their diseases actually proves that the medicine itself is not the cause. Restricting opioids from patients with chronic pain has no effect on addiction rates. This is why even though prescriptions have declined deaths have risen and will continue to rise if this war isn’t stopped.
We need to make the DOJ accountable for not following Supreme Court decisions and committing professional misconduct convicting innocent people any way they can. Allowing innocent Americans suffering severe chronic pain to be denied relief will hurt our society. It will force countless of hard working Americans who could function and manage their condition with opioids into a life of misery. This opioid war does nothing to stop addiction. What this all means for those of us who suffer daily. Who will support these people who can no longer support themselves because they can no longer work, care for their kids? These are people who are now out of the workplace and confined to a bed because the pain is so great they can’t work. This so called solution will hurt our economy. SSI/SSDI claims will skyrocket and it will lead to the tax payers having to foot the bill and care for all these people who could have otherwise supported themselves with proper medical care and proper pain management. These laws do nothing to stop addiction. What these laws mean to people like myself. TOTAL DEVASTATION. Loss of job, home, children. I am now forced to live on government assistance. These policies are not good for America. We need to stop this now.
Email/Letter to Medical Professional Legislators
Dear Congressman/Senator___,
Drugs are NOT the cause addiction! This is a government propaganda platform on the same level as Hitler blaming the Jews for the Depression, and your failure to act, allowing this propaganda to form policy, is causing suffering or killing your constituents. As Hitler said, “Make the lie big, make it simple, keep saying it, and eventually they will believe it.” Stop believing it, and stop creating policies based on lies. If you don’t, we, the doctors and patients of courage in the country, will remove you from office.
Did you know your grandparents? Are they all drug addicts? They were more than likely treated with opium as children. Opium has been used medicinally and recreationally for over 6000 years. And yet, when opiates were criminalized in 1914, the percentage of the population who were addicts (and most of that was alcohol), was less than 1%. The percentage is now around 2.% today. It is increasing exponentially, but it is because of other reasons, NOT the drugs! You can learn the real cause on doctorsofcourage.org.
The government’s war against drugs started with a purely racist intent—to disenfranchise the minority populations in America—for political purposes. The definition of insanity: repeating the same action over and over, expecting a different result. Laws have been in effect now against opiates for 100+ years. More people in America are incarcerated for drugs than ever before. Has the use of drugs diminished? Had drug abuse stopped? No. It’s climbing.
Yes, the percentage of drug abuse and addiction is rising, but the cause is not the drugs. Alcohol is one of the drugs most likely abused. But because you might occasionally enjoy a beer or a glass of wine, does that make you an alcoholic? Of course not. Opioids are no different. There is more to addiction than simple exposure. And yet government agencies and people with a position of power are spreading lies such as “Taking an opioid for more than 3 days will make you an addict”. LIES!!!
The cause of addiction is TOXICITY. What does the body do with excess toxins? They have to be stored in the cells. That is genetically determined, and thus you get the genetic propensity to certain diseases. The fact that more people aren’t addicted that require pain medicines for their diseases actually PROVES that the medicine itself is NOT the cause.
Conventional medicine knows nothing about toxicity. Just because you weren’t taught about toxicity in the body during your medical training doesn’t make it unscientific. It just means there wasn’t a pill to treat it. Medical school, as you should know, is purely a pharmaceutical-based sales force. However, there are scientifically-based fields which can explain the cause of addiction, treat it, and even cure it.
The point I want to make is that restricting opioids from patients with chronic pain will have no effect on addiction. But it is obviously leading to increased death. Look at the statistics available:
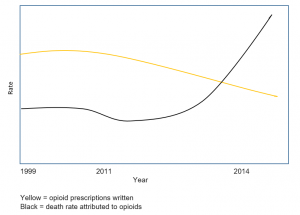
Even though prescriptions have declined, deaths have risen. As Albert Schweitzer said,
“Pain is a more terrible lord of mankind than even death itself”
By stopping legitimate pain management by trained professionals, the government is forcing citizens to the street for self-medication, where they most probably will unknowingly receive illegal fentanyl-laced pills or intentionally commit suicide. The government is also destroying the doctor/patient relationship.
Another problem is that you are allowing rogue agencies to run the government. The rogue DOJ is attacking doctors illegally using the Controlled Substance Act, which was never the intent of that legislation. And the CSA itself is outside the bounds of federal jurisdiction. Please read the CSA, and recognized that doctors treating patients are EXEMPT from prosecution. Start working on legislation to free and exonerate all medical professionals convicted by the rogue Department of Justice’s illegal use of the CSA, especially with statute 841, as per statute 842, only the doctor can determine “legitimate medical practice”, not the government agencies. This has also been reinforced by the SCOTUS decision Ruan & Kahn.
For more information, please visit our website, www.doctorsofcourage.org. Dr. Cheek, the founder, is a physician who once healed patients from disease but who became a target of the government. She is happy to discuss what will really work to help addicts. Save all the wasted taxpayer dollars going down the bottomless pit of special interest groups that will do nothing to end addiction. Learning what we have to offer could make your career. Failure to learn what we offer could be the end of your career.
Communicate with Legislators
The following toggles contain the list s of legislators’ FaceBook, X, and email contact information. They allow point and click to get to the website page. If you are using a phone, move the screen sideways to get to the links.
Use the lists of committee members below to specifically talk about certain issues of the CSA affecting us and the world, as written in the blog and listed on the home page. It is in the committee that actions are taken to proceed with a bill. So those legislators are the most important to understand the effects of the CSA on the citizens, the country, and the world.
For access to all 435 health staffer’s contact information, you have to be a member of Doctorsofcourage. Go HERE for the membership page to choose your level. But I will, for the purpose of this communication campaign, give you access to the health staffer’s contact information for your state if you fill out the “Who Are My Health Issues Staffers” form on the Contact Us page.
This is the first time I’ve shared this work with those who are not supporting DoC members. So I hope people use it.
House of Representatives' Republicans
| State, District | Name | Information | Phone | Room | |||
| Alabama01 | Barry Moore | White, BS ag sci, Nat’l Guard, state rep | RepBarryMoore | repbarrymoore | 2901 | 1511L | |
| Alabama03 | Mike Rogers | White, lawyer, state rep, poli sci and pub admin | Email Rep Rogers | CongressmanMikeDRogers/ | RepMikeRogersAL | 3261 | 2469R |
| Alabama04 | Robert Aderholt | White tea party conservative, lawyer, judge | Email Rep Aderholt | RobertAderholt | Robert_Aderholt | 4876 | 272C |
| Alabama05 | Dale Strong | White, BS Bus Admin, EMT | Email Rep Strong | Dale Strong | RepDaleStrong | 4801 | 449C |
| Alabama06 | Gary Palmer | White, BA operations mgmt, Ala Policy Institute think tank founder | Email Rep Palmer | CongressmanGaryPalmer/ | USRepGaryPalmer | 4921 | 170C |
| Alaska01 | Nick Begich III | White, MBA, owns software dev co | Email Rep Begich | RepNickBegich | RepNickBegich | 5765 | 153C |
| Arizona01 | David Schweikert | White, MBA, state rep, | Email Rep Schweikert | repdavidschweikert/ | RepDavid | 2190 | 166C |
| Arizona02 | Eli Crane | White, Navy Seal. Father pharmacist | Email Rep Crane | rep.elicrane | RepEliCrane | 3361 | 307C |
| Arizona05 | Andy Biggs | White, JD, state rep, state sen, Mormon | Email Rep Biggs | RepAndyBiggs/ | RepAndyBiggsAZ | 2635 | 464C |
| Arizona06 | Juan Ciscomani | Hispanic, | Email Rep Ciscomani | RepCiscomani | 2542 | 461C | |
| Arizona08 | Abraham Hamadeh | Syrian American, JD, prosecutor, USA | Email Rep Hamadeh | RepAbeHamadeh | AbrahamHamadeh | 4576 | 1722L |
| Arizona09 | Paul Gosar | White, dentist, | Email Rep Gosar | repgosar/ | RepGosar | 2315 | 2057R |
| Arkansas01 | Rick Crawford | White, radio announcer, businessman, USArmy | Email Rep Crawford | RepRickCrawford | 4076 | 2422R | |
| Arkansas02 | French Hill | White, BS economics, bank CEO | Email Rep Hill | RepFrenchHill/ | RepFrenchHill | 2506 | 1533L |
| Arkansas03 | Steve Womack | White, USArmy, mayor | Email Rep Womack | rep_stevewomack | 4301 | 2412R | |
| Arkansas04 | Bruce Westerman | White, engineering, forestry, state rep | Email Rep Westerman | RepWesterman/ | RepWesterman | 3772 | 202C |
| California01 | Doug LaMalfa | White, rice farmer, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Lamalfa | RepLaMalfa/ | RepLaMalfa | 3076 | 408C |
| California03 | Kevin Kiley | White, JD, teacher, father physician, state rep | Email Rep Kiley | https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100089382125341 | RepKiley | 2523 | 2445R |
| California05 | Tom McClintock | White, BA, state rep, state sen | Email Rep McClintock | RepMcClintock/ | RepMcClintock | 2511 | 2256R |
| California20 | Vince Fong | Chinese American, MPA, state rep, | Email Rep Fong | RepVinceFong# | RepVinceFong | 2915 | 243C |
| California22 | David Valadao | Portugueze, dairy farmer in lawsuit 2018, state rep, | Email Rep Valadao | CongressmanDavidValadao | RepDavidValadao | 4695 | 2465R |
| California23 | Jay Obernolte | White, businessman, video game developer, state rep, mayor | Email Rep Obernolte | jayobernolte/ | JayObernolte | 5861 | 2433R |
| California40 | Young Kim | South Korean, businesswoman, st. rep, | Email Rep Kim | RepYoungKim | RepYoungKim | 4111 | 2439R |
| California41 | Ken Calvert | White, BA, restauranteur, real estate | Email Rep Calvert | RepKenCalvert/ | KenCalvert | 1986 | 2205R |
| California48 | Darrell Issa | White, Lebanese background, businessman, US Rep 2001-2019 | Email Rep Issa | congressmandarrellissa | repdarrellissa | 5672 | 2108R |
| Colorado03 | Jeff Hurd | White, lawyer | Email Rep Hurd | RepJeffHurd# | RepJeffHurd | 4676 | 1641L |
| Colorado04 | Lauren Boebert | White, businesswoman | Email Rep Boebert | repkenbuck | RepKenBuck | 4761 | 1713L |
| Colorado05 | Jeff Crank | White, radio show host, BA Poli sci, | Email Rep Crank | RepJeffCrank | RepJeffCrank | 4422 | 1029L |
| Colorado08 | Gabe Evans | Hispanic, BA gov’t, USA, Nat’l Guard, Police Dept, state rep | Email Rep Evans | RepGabeEvans | repgabeevans | 5625 | 1229L |
| Florida02 | Neal Dunn | White, MD, surgeon, USArmy Panama City Urological Center and Surgery Center, bank founder | Email Rep Dunn | DrNealDunnFL2/ | DrNealDunnFL2 | 5235 | 466C |
| Florida06 | 2706 | 244C | |||||
| Florida11 | Daniel Webster | White, BS electrical engineering, owns HVAC bus, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Webster | RepWebster/ | RepWebster | 1002 | 2184R |
| Florida12 | Gus Bilirakis | White, lawyer-estate, state rep | Email Rep Bilirakis | GusBilirakis | RepGusBilirakis | 5755 | 2306R |
| Florida13 | Anna Paulina Luna | Hispanic, BS biology, USAF | Email Rep Luna | realAnnaPaulina | RepLuna | 5961 | 226C |
| Florida15 | Laurel Lee | White, lawyer, Asst US Attorney, judge, FL Sec of State | Email Rep Lee | RepLaurelLee | RepLaurelLee | 5626 | 2464R |
| Florida16 | Vern Buchanan | White, MBA, owns auto dealerships, other businesses worth >$100 million | Email Rep Buchanan | CongressmanBuchanan | VernBuchanan | 5015 | 2409R |
| Florida17 | Greg Steube | White, lawyer, USA JAG, father is sheriff; state rep, state sen | Email Rep Stuebe | RepGregSteube/ | RepGregSteube | 5792 | 2457R |
| Florida18 | Scott Franklin | White, USN, MBA, CEO insurance Co | Email Rep Franklin | RepFranklin | RepFranklin | 1252 | 2301R |
| Florida19 | Byron Donalds | Black, BS finance & marketing, state rep | Email Rep Donalds | RepBryonDonalds | RepByronDonalds | 2536 | 1710L |
| Florida21 | Brian Mast | Hispanic, BLA, USArmy bilateral amputee, Homeland Security | Email Rep Mast | RepBrianMast | BrianMastFL | 3026 | 2182R |
| Florida22 | Lois Frankel | White, Jewish, lawyer, state rep, mayor, | Email Rep Frankel | RepLoisFrankel | RepLoisFrankel | 9890 | 2305R |
| Florida26 | Mario Diaz-Balart | Hispanic, BA poli sci, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Diaz-Balart | mdiazbalart | MarioDB | 4211 | 374C |
| Florida27 | Maria Elvira Salazar | Cuban, M Public Admin, journalist, TV anchor | Email Rep Salazar | CongresswomanMariaElviraSalazar | RepMariaSalazar | 3931 | 2162R |
| Florida28 | Carlos Gimenez | Cuban, BA public admin, firefighter, Mayor of Miami-Dade Cty | Email Rep Gimenez | RepCarlosGimenez | RepCarlos | 2778 | 448C |
| Florida3 | Kat Cammack | White, MS National defense, previous rep’s chief of staff | Email Rep Cammack | RepKatCammack | Kat_Cammack | 5744 | 2421R |
| Florida4 | Aaron Bean | White, BS, politician, State sen, state rep | Email Rep Bean | Cong Aaron Bean | RepAaronBean | O123 | 2459R |
| Florida5 | John Rutherford | White, BS criminology, PO, Sheriff | Email Rep Rutherford | RepRutherfordFL/ | RepRutherfordFL | 2501 | 1711L |
| Florida7 | Cory Mills | White, BS health sciences, USA | Email Rep Mills | (5) U.S. Representative Cory Mills | Washington D.C. DC | Facebook | RepMillsPress | 4035 | 346C |
| Florida8 | Mike Haridopolos | White, MA history, teacher, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Haridopolos | RepHaridopolos | 3671 | 1039L | |
| Georgia01 | Buddy Carter | White, BS pharmacy, anti-drugs, state rep, state sen, | Email Rep Carter | CongressmanBuddyCarter/ | RepBuddyCarter | 5831 | 2432R |
| Georgia03 | Brian Jack | White, BA, political advisor to Pres Trump | Email Rep Jack | RepBrianJack | RepBrianJack | 5901 | 1320L |
| Georgia07 | Rich McCormick | White, physician (ER), USMC, USN | Email Rep McCormick | (8) Representative Rich McCormick | Facebook | RepMcCormick | 4272 | 1719L |
| Georgia08 | Austin Scott | White, BBA insurance, Pres. Southern Group, LLC, state rep; father orthopedic surgeon | Email Rep Scott | RepAustinScott/ | AustinScottGA08 | 6531 | 2185R |
| Georgia09 | Andrew Clyde | White, MBA, USN, Won civil asset forfeiture by IRS, Clyde-Hirsch-Sowers RESPECT Act limiting seizures | Email Rep Clyde | Representative Clyde | Rep_Clyde | 9893 | 445C |
| Georgia10 | Mike Collins | White, BA bus, businessman | Email Rep Collins | RepMikeCollinsGA | RepMikeCollins | 4101 | 2351R |
| Georgia11 | Barry Loudermilk | White, BS, state rep, state senate | Email Rep Loudermilk | RepLoudermilk/ | RepLoudermilk | 2931 | 2133R |
| Georgia12 | Rick Allen | White, BS building construction, owner construction co | Email Rep Allen | CongressmanRickAllen | @RepRickAllen | 2823 | 462C |
| Georgia14 | Marjorie Greene | White, BBA, gym owner, construction co, conspiracy theorist | Email Rep Greene | RepMTGreene | RepMTG | 5211 | 2201R |
| Idaho01 | Russ Fulcher | White, MBA, tech business, real estate, state sen | Email Rep Fulcher | RepRussFulcher | RepRussFulcher | 6611 | 1514L |
| Idaho02 | Mike Simpson | White, dentist, state rep | Email Rep Simpson | RepMikeSimpson | CongMikeSimpson | 5531 | 2084R |
| Indiana02 | Rudy Yakym | White, MBA | Email Rep Yakym | RepRudyYakym | RepRudyYakym | 3915 | 349C |
| Indiana03 | Marlin Stutzman | White, farmer, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Stutzman | https://www.facebook.com/repstutzman | RepStutzman | 4436 | 404C |
| Indiana04 | Jim Baird | White, PhD, USA, state rep | Email Rep Baird | RepJimBaird | RepJimBaird | 5037 | 2303R |
| Indiana05 | Victoria Spartz | White, Ukrainian, MBA, real estate & farming businesses, state sen | Email Rep Spartz | RepSpartz | RepSpartz | 2276 | 1609L |
| Indiana06 | Jefferson Shreve | White, MBA, businessman, city council | Email Rep Shreve | RepJeffersonShreve | RepShreve | ||
| Indiana08 | Mark Messmer | White, BS, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Messmer | CongressmanMessmer | RepMessmer | 4636 | 1208L |
| Indiana09 | Erin Houchin | White, MA politics, state sen | Email Rep Houchin | RepHouchin | RepHouchin | 5315 | 342C |
| Iowa01 | Mariannette Miller-Meeks | White, physician, USA, state sen. | Email Rep Miller-Meeks | RepMMM | repMMM | 6576 | 504C |
| Iowa02 | Ashley Hinson | White, BA pub relations, state rep | Email Rep Hinson | RepAshleyHinson | RepAshleyHinson | 2911 | 2458R |
| Iowa03 | Zach Nunn | White, MS Inter Relat, USAF, Nat’l Guard, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Nunn | RepZachNunn | RepZachNunn | 5476 | 1410L |
| Iowa04 | Randy Feenstra | White, M Public Admin, city gov, state sen, univ prof. | Email Rep Feenstra | RepFeenstra | RepFeenstra | 4426 | 2434R |
| Kansas01 | Tracey Mann | White, st.Lt. Gov, real estate broker, farmer | Email Rep Mann | RepTraceyMann | RepMann | 2715 | 344C |
| Kansas02 | Derek Schmidt | White, state AG, lawyer, state sen | Email Rep Schmidt | repderekschmidt | RepDerekSchmidt | 6601 | 1223L |
| Kansas04 | Ron Estes | White, MBA, consultant, state treasurer | Email Rep Estes | RepRonEstes | RepRonEstes | 6216 | 2234R |
| Kentucky01 | James Comer | White, BS agriculture, farmer, bank director, Pres. Chamber of Commerce, state rep | Email Rep Comer | CongresmanComer | RepJamesComer | 3115 | 2410R |
| Kentucky02 | Brett Guthrie | M Public Mgmt, USArmy, VP auto parts co., state sen | Email Rep Guthrie | CongressmanGuthrie/ | RepGuthrie | 3501 | 2161R |
| Kentucky04 | Thomas Massie | MS Mechanical engineering, owned company, farmer, County official | Email Rep Massie | RepThomasMassie/ | RepThomasMassie | 3465 | 2371R |
| Kentucky05 | Hal Rogers | White, lawyer, USANG, Commonwealth Attorney | Email Rep Rogers | CongressmanHalRogers/ | RepHalRogers | 4601 | 2406 R |
| Kentucky06 | Andy Barr | White, lawyer, | Email Rep Barr | RepAndyBarr | RepAndyBarr | 4706 | 2430R |
| Louisiana01 | Steve Scalise | White, BS computer sci, poli sci, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Scalise | RepSteveScalise | SteveScalise | 3015 | 266C |
| Louisiana03 | Clay Higgins | White, USANG, manager car dealerships, City Police officer, Dep Marshall | Email Rep Higgins | CongressmanClayHiggins | RepClayHiggins | 2031 | 572C |
| Louisiana04 | Mike Johnson | White, lawyer-constitutional, non-profit Alliance Defending Freedom, talk radio host, state rep | Email Rep Johnson | RepMikeJohnson/ | RepMikeJohnson | 2777 | 568C |
| Louisiana05 | Julia Letlow | White, PhD communications, Tulane U of Med dir ed & patient safety | Email Rep Letlow | repjulialetlow | RepJuliaLetlow | 8490 | 142C |
| Maryland01 | Andy Harris | White, MD-anesthesiology (father immigrant MD anes from Hungary), USN, state sen | Email Rep Harris | AndyHarrisMD | RepAndyHarrisMD | 5311 | 1536L |
| Michigan01 | Jack Bergman | White, MBA, USMC pilot | Email Rep Bergman | RepJackBergman/ | RepJackBergman | 4735 | 566C |
| Michigan02 | John Moolenaar | White, MPA, chemist Dow Chemical, state house, state sen | Email Rep Moolenaar | RepMoolenaar | RepMoolenaar | 3561 | 246C |
| Michigan04 | Bill Huizenga | White, BA, owner gravel co, real estate, state rep | Email Rep Huizenga | rephuizenga/ | RepHuizenga | 4401 | 2232R |
| Michigan05 | Tim Walberg | White, MA, pastor, state rep | Email Rep Walberg | RepWalberg | RepWalberg | 6276 | 2266R |
| Michigan07 | Tom Barrett | White, USA, BA poli sci, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Barrett | RepTomBarrett | RepTomBarrett | 4872 | 1232L |
| Michigan09 | Lisa McClain | White, BA, catholic | Email Rep McClain | RepLisaMcClain | RepLisaMcClain | 2106 | 562C |
| Michigan10 | John James | Black, MBA, USA | Email Rep James | RepJames | 4961 | 1519L | |
| Minnesota01 | Brad Finstad | White, BS, farmer, Dir Rural Dev, state rep | Email Rep Finstad | RepFinstad | RepFinstad | 2472 | 2418R |
| Minnesota06 | Tom Emmer | White, lawyer, state rep | Email Rep Emmer | reptomemmer | RepTomEmmer | 2331 | 326C |
| Minnesota07 | Michelle Fischbach | White, lawyer, st. lt. gov, st. Sen, Catholic, husband runs Minnesota Citizens Concerned for Life. | Email Rep Fischbach | RepFischbach | RepFischbach | 2165 | 2229R |
| Minnesota08 | Pete Stauber | White, BA criminology, professional hockey, Police officer, cty commissioner | Email Rep Stauber | RepPeteStauber/ | RepPeteStauber | 6211 | 145C |
| Mississippi01 | Trent Kelly | White, lawyer, DA, USANG | Email Rep Kelly | RepTrentKelly/ | RepTrentKelly | 4306 | 2243R |
| Mississippi03 | Michael Guest | White, gay, ambassador to Romania | Email Rep Guest | RepMichaelGuest | RepMichaelGuest | 5031 | 450C |
| Mississippi04 | Mike Ezell | White, BS criminal justice, law enforcement | Email Rep Ezell | RepEzell/ | RepEzell | 5772 | 443C |
| Missouri02 | Ann Wagner | White, Catholic, BSBA, bus. Mngr, US Ambassador | Email Rep Wagner | RepAnnWagner/ | RepAnnWagner | 1621 | 2350R |
| Missouri03 | Bob Onder | White, physician-allergy, asthma, lawyer, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Onder | RepBobOnder | RepBobOnder | 2956 | 1113L |
| Missouri04 | Mark Alford | White, BA, FOX news anchor | Email Rep Alford | MarkAlfordKC | markalfordkc | 2876 | 328C |
| Missouri06 | Sam Graves | White, BS Agronomy, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Graves | RepSamGraves/ | RepSamGraves | 7041 | 1135L |
| Missouri07 | Eric Burlison | White, MBA, CoxHealth bus analyst, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Burlison | (1) Rep. Eric Burlison | Facebook | RepEricBurlison | 6536 | 1108L |
| Missouri08 | Jason Smith | White, lawyer, farmer, state rep | Email Rep Smith | repjasonsmith | RepJasonSmith | 4404 | 1011L |
| Montana01 | Ryan Zinke | White, MBA, MS, Navy Seal, US Sec Interior under Trump, state rep, | Email Rep Zinke | RepRyanZinke | RepRyanZinke | 5628 | 512C |
| Montana02 | Troy Downing | White, USAF, businessman, state auditor | Email Rep Downing | reptroydowning | RepTroyDowning | 3211 | 1529L |
| Nebraska01 | Mike Flood | White, lawyer, owns 15 radio stations and 7 TV stations, state rep | Email Rep Flood | RepMikeFlood | USRepMikeFlood | 4806 | 343C |
| Nebraska02 | Don Bacon | White, MBA, USAF, Comm. Ramstein AFB, | Email Rep Bacon | RepDonBacon | RepDonBacon | 4155 | 2104R |
| Nebraska03 | Adrian Smith | White, BA, state rep | Email Rep Smith | RepAdrianSmith | RepAdrianSmith | 6435 | 502C |
| Nevada02 | Mark Amodei | White, lawyer, USA, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Amodei | MarkAmodeiNV2 | MarkAmodeiNV2 | 6155 | 104C |
| New Jersey02 | Jeff Van Drew | White, dentist, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Van Drew | CongressmanJVD | Congressman_JVD | 6572 | 2447R |
| New Jersey04 | Chris Smith | White, BS | Email Rep Smith | RepChrisSmith/ | ChrisSmithNJCD4 | 3765 | 2373R |
| New Jersey07 | Tom Kean Jr | White, MA in Law & Diplomacy, father past gov of New Jersey, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Kean | CongressmanKean | CongressmanKean | 5361 | 251C |
| New York01 | Nick LaLota | White, lawyer, USN | Email Rep LaLota | replalota | RepLaLota | 3826 | 122C |
| New York02 | Andrew Garbarino | White, lawyer, , catholic, state rep | Email Rep Garbarino | RepAndrewGarbarino | RepGarbarino | 7896 | 2344R |
| New York11 | Nicole Malliotakis | Greek/cuban, MBA, state rep | Email Rep Malliotakis | RepMalliotakis | RepMalliotakis | 3371 | 1124L |
| New York17 | Mike Lawler | White, BS accounting, state rep | Email Rep Lawler | RepMikeLawler | RepMikeLawler | 6506 | 324C |
| New York21 | Elise Stefanik | White, BA gov’t | Email Rep Stefanik | RepStefanik | 4611 | 2211R | |
| New York23 | Nick Langworthy | White, BA Poli sci, politician | Email Rep Langworthy | RepLangworthy | RepLangworthy | 3161 | 422C |
| New York24 | Claudia Tenney | White, lawyer, state rep | Email Rep Tenney | RepClaudiaTenney | RepTenney | 3665 | 2230R |
| North Carolina03 | Greg Murphy | White, MD-urology, medical mission work, state rep | Email Rep Murphy | RepGregMurphy/ | RepGregMurphy | 3415 | 407C |
| North Carolina05 | Virginia Foxx | White, MA, EdD, landscaping business, state sen | Email Rep Foxx | RepVirginiaFoxx | virginiafoxx | 2071 | 2462R |
| North Carolina06 | Addison McDowell | White, BA, BCBS lobbyist, brother died from fentanyl overdose | Email Rep McDowell | RepMcDowell | RepMcDowell | 3065 | 1032L |
| North Carolina07 | David Rouzer | White, BS agriculture, warehouse owner, US Dept Agri, state sen | Email Rep Rouzer | RepRouzer | RepDavidRouzer | 2731 | 2333R |
| North Carolina08 | Mark Harris | White, pastor, BA poli sci | Email Rep Harris | RepMarkHarris | RepMarkHarrisNC | 1976 | 126C |
| North Carolina09 | Richard Hudson | White, BA poli sci, politics | Email Rep Hudson | RepRichHudson | 3715 | 2112R | |
| North Carolina10 | Pat Harrigan | White, USArmy, BS nuclear engineering | Email Rep Harrigan | RepPatHarrigan | RepPatHarrigan | 2576 | 1233L |
| North Carolina11 | Chuck Edwards | White, businessman, state sen | Email Rep Edwards | RepChuckEdwards/ | RepEdwards | 6401 | 1505L |
| North Carolina13 | Brad Knott | White, lawyer, father USAttorney, | Email Rep Knott | RepKnott | RepKnott | 4531 | 1239L |
| North Carolina14 | Tim Moore | White, lawyer, state rep | Email Rep Moore | CongressmanTimMoore | RepTimMooreNC | 5634 | 1424L |
| North Dakota AL | Julie Fedorchak | White, BA journalism | Email Rep Fedorchak | RepJulieFedorchak | RepFedorchak | 2611 | 1607L |
| Ohio02 | David Taylor | White, lawyer, prosecutor, concrete business | Email Rep Taylor | RepDaveTaylor | RepDaveTaylor | 3164 | 325C |
| Ohio04 | Jim Jordan | White, lawyer, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Jordan | repjimjordan | Jim_Jordan | 2676 | 2056R |
| Ohio05 | Bob Latta | White, lawyer, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Latta | boblatta/ | boblatta | 6405 | 2470R |
| Ohio06 | Michael Rulli | White, BA, state sen, family-owned grocery chain store | Email Rep Johnson | RepBillJohnson | RepBillJohnson | 5705 | 2082R |
| Ohio07 | Max Miller | White, BA, USMC, aide to Pres. Trump | Email Rep Max Miller | CongressmanMaxMiller | RepMaxMiller | 3876 | 143C |
| Ohio08 | Warren Davidson | White, MBA, USA | Email Rep Davidson | CongressmanWarrenDavidson | WarrenDavidson | 6205 | 2113R |
| Ohio10 | Mike Turner | White, MBA, lawyer, mayor | Email Rep Turner | RepMikeTurner | RepMikeTurner | 6465 | 2183R |
| Ohio12 | Troy Balderson | White, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Balderson | RepTroyBalderson/ | RepBalderson | 5355 | 2429R |
| Ohio14 | Dave Joyce | White, lawyer, county prosecutor | Email Rep Joyce | RepDaveJoyce | RepDaveJoyce | 5731 | 2065R |
| Ohio15 | Mike Carey | White, BA economics, history, USANG | Email Rep Carey | RepMikeCarey | RepMikeCarey | 2015 | 1433L |
| Oklahoma01 | Kevin Hern | White, MBA, 10 McDonald’s franchises | Email Rep Hern | repkevinhern/ | repkevinhern | 2211 | 171C |
| Oklahoma02 | Josh Brecheen | Native Am, BS, politician, state sen | Email Rep Brecheen | RepBrecheen | RepBrecheen | 2701 | 351C |
| Oklahoma03 | Frank Lucas | White, BS, farmer | Email Rep Lucas | RepFrankLucas | RepFrankLucas | 5565 | 2405R |
| Oklahoma04 | Tom Cole | Native Am, PhD British History, professor, Okla Sec of State | Email Rep Cole | TomColeOK04 | TomColeOK04 | 6165 | 2207R |
| Oklahoma05 | Stephanie Bice | Iranian American, st. sen, business. | Email Rep Bice | RepStephanieBice | RepBice | 2132 | 2402R |
| Oregon02 | Cliff Bentz | White, lawyer, rancher, st. sen, st. rep, | Email Rep Bentz | RepBentz | RepBentz | 6730 | 409C |
| Pennsylvania01 | Brian Fitzpatrick | White, lawyer, FBI agent | Email Rep Fitzpatrick | RepBrianFitz/ | RepBrianFitz | 4276 | 271C |
| Pennsylvania07 | Ryan Mackenzie | White, MBA, state rep, | Email Rep Mackensie | RepMackenzie | RepMackenzie | 5411 | 121C |
| Pennsylvania08 | Rob Bresnahan | White, BA, electrical business CEO | Email Rep Bresnahan | RepBresnahan | RepBresnahan | 5546 | 1133L |
| Pennsylvania09 | Dan Meuser | White, BA, CEO Pride Mobility Products | Email Rep Meuser | RepMeuser | RepMeuser | 6511 | 350C |
| Pennsylvania10 | Scott Perry | White, MS strategic planning, USArmy, state rep | Email Rep Perry | repscottperry | RepScottPerry | 5836 | 2160R |
| Pennsylvania11 | Lloyd Smucker | Amish, construction co, state sen | Email Rep Smucker | RepSmucker | RepSmucker | 2411 | 302C |
| Pennsylvania13 | John Joyce | White, dermatologist | Email Rep Joyce | RepJohnJoyce/ | RepJohnJoyce | 2431 | 2102R |
| Pennsylvania14 | Guy Reschenthaler | White, lawyer, USN JAG, District Judge | Email Rep Reschenthaler | Greschenthaler | GReschenthaler | 2065 | 2209R |
| Pennsylvania15 | Glenn Thompson | White, Med, Nursing Home Admin | Email Rep Thompson | CongressmanGT/ | CongressmanGT | 5121 | 400C |
| Pennsylvania16 | Mike Kelly | White, BA, Car dealership, city Council | Email Rep Kelly | MikeKellyPA/ | MikeKellyPA | 5406 | 1707L |
| South Carolina01 | Nancy Mace | White, consulting business, St. Rep, | Email Rep Mace | RepNancyMace | RepNancyMace | 3176 | 1728L |
| South Carolina02 | Joe Wilson | White, lawyer-real estate, USAR, Judge Advocate in NG, municipal judge, state sen | Email Rep Wilson | JoeWilson | RepJoeWilson | 2452 | 1436L |
| South Carolina03 | Sheri Biggs | White, nurse practitioner, air nat’l guard | Email Rep Biggs | RepSheriBiggs | RepSheriBiggs | 5301 | 1530L |
| South Carolina04 | William Timmons | White, lawyer-prosecutor, small business owner, Army NG, state sen | Email Rep Timmons | RepTimmons/ | reptimmons | 6030 | 267C |
| South Carolina05 | Ralph Norman | White, BS, real estate developer, state rep | Email Rep Norman | RepRalphNorman/ | RepRalphNorman | 5501 | 569C |
| South Carolina07 | Russell Fry | White, lawyer, state rep | Email Rep Fry | reprussellfry | RepRussellFry | 9895 | 345C |
| South Dakota | Dusty Johnson | White, MPA, Governor’s Chief of Staff | Email Rep Johnson | RepDustyJohnson/ | RepDustyJohnson | 2801 | 1714L |
| Tennessee01 | Diana Harshbarger | Pharmacist, compounding pharmacy, focus: fixing opioid crisis | Email Rep Harshbarger | RepDianaHarshbarger | RepHarshbarger | 6356 | 167C |
| Tennessee02 | Tim Burchett | White, BS ed, state rep, state sen, mayor | Email Rep Burchett | RepTimBurchett/ | RepTimBurchett | 5435 | 1122L |
| Tennessee03 | Chuck Fleischmann | White, Catholic, lawyer | Email Rep Fleischmann | repchuck | RepChuck | 3271 | 2187R |
| Tennessee04 | Scott DesJarlais | White, physician (gen. med) | Email Rep DesJarlais | ScottDesJarlaisTN04 | DesJarlaisTN04 | 6831 | 2304R |
| Tennessee05 | Andy Ogles | White, BS poli sci, businessman, mayor | Email Rep Ogles | andyogles | RepOgles | 4311 | 151C |
| Tennessee06 | John Rose | White, lawyer, State Ag Commissioner | Email Rep Rose | repjohnrose | RepJohnRose | 4231 | 2238L |
| Tennessee07 | Mark Green | White, MD, USArmy, state sen | Email Rep Green | RepMarkGreenTN/ | RepMarkGreen | 2811 | 2446R |
| Tennessee08 | David Kustoff | White, Jewish, lawyer, US Attorney | Email Rep Kustoff | RepDavidKustoff/ | RepDavidKustoff | 4714 | 560C |
| Texas01 | Nathaniel Moran | White, lawyer, judge, city council | Email Rep Moran | RepNateMoran | RepNateMoran | 3035 | 1605L |
| Texas02 | Dan Crenshaw | White, MPA, USN medically retired–lost eye | Email Rep Crenshaw | RepDanCrenshaw/ | RepDanCrenshaw | 6565 | 248C |
| Texas03 | Keith Self | White, MA, USA, county judge | Email Rep Self | RepKeithSelf | RepKeithSelf | 4201 | 1030L |
| Texas04 | Pat Fallon | Catholic, businessman, USAF, St. sen, St. rep | Email Rep Fallon | RepPatFallon | RepPatFallon | 6673 | 2416R |
| Texas05 | Lance Gooden | White, BBA, UT, state rep | Email Rep Gooden | RepGooden | Lancegooden | 3484 | 2431R |
| Texas06 | Jake Ellzey | White, BS, USN, airline pilot, state rep | Email Rep Ellzey | RepJakeEllzey | RepEllzey | 2002 | 1721L |
| Texas08 | Morgan Luttrell | White, MS applied cognition neuroscience. Professor, USN Seal | Email Rep Luttrell | Congressman Morgan Luttrell | RepLuttrell | 4901 | 444C |
| Texas10 | Michael McCaul | White, lawyer, federal prosecutor, | Email Rep McCaul | michaeltmccaul | RepMcCaul | 2401 | 2300R |
| Texas11 | August Pfluger | White, USAF pilot, Nat’l security Council | Email Rep Pfluger | RepAugustPfluger | RepPfluger | 3605 | 2202R |
| Texas12 | Craig Goldman | White, Jewish, BA Poli sci, real estate | Email Rep Goldman | RepCraigGoldman | RepCraigGoldman | 5071 | 1716L |
| Texas13 | Ronny Jackson | White, physician, Chief Medical Advisor to Pres, USN | Email Rep Jackson | RepRonnyJackson | RepRonnyJackson | 3706 | 125C |
| Texas14 | Randy Weber | White, BS Pub Affairs, owns HVAC co, state rep | Email Rep Weber | TXRandy14 | TXRandy14 | 2831 | 107C |
| Texas15 | Monica De la Cruz | Hispanic, Aviation Bus. Admin, lawyer | Email Rep De La Cruz | monicaforcongress | RepMonicaDLC | 9901 | 1415L |
| Texas17 | Pete Sessions | White, father FBI director | Email Rep Sessions | petesessions | PeteSessions | 6105 | 2204R |
| Texas18 | |||||||
| Texas19 | Jodey Arrington | White, MPA, WH staff | Email Rep Arrington | RepJodeyArrington/ | RepArrington | 4005 | 1111L |
| Texas21 | Chip Roy | White, lawyer, US Attorney, ghostwriter for Rick Perry’s book Fed Up | Email Rep Roy | RepChipRoyPress/ | RepChipRoy | 4236 | 103C |
| Texas22 | Troy Nehls | White, Cty Sheriff, USAR, M. Criminal Justice. | Email Rep Nehls | RepTroyNehls/ | RepTroyNehls | 5951 | 1104L |
| Texas23 | Tony Gonzales | Hispanic, USN, | Email Rep Gonzalez | RepTonyGonzales | RepTonyGonzales | 4511 | 2239R |
| Texas24 | Beth Van Duyne | White, Mayor | Email Rep Duyne | RepBethVanDuyne | RepBethVanDuyne | 6605 | 1725L |
| Texas25 | Roger Williams | White, BA, prof baseball, car dealership, Sec of State of Texas | Email Rep Williams | RepRogerWilliams | RepRWilliams | 9896 | 2336R |
| Texas26 | Brandon Gill | White, investment banker, extreme Trumpster | Email Rep Gill | RepBrandonGill | RepBrandonGill | 7772 | 1305L |
| Texas27 | Michael Cloud | White, BS, | Email Rep Cloud | RepCloudTX/ | RepCloudTX | 7742 | 304C |
| Texas31 | John Carter | White, lawyer, UT, judge | Email Rep Carter | judgecarter | JudgeCarter | 3864 | 2208R |
| Texas36 | Brian Babin | White, dentist-UT, USAF | Email Rep Babin | RepBrianBabin | RepBrianBabin | 1555 | 2236R |
| Texas38 | Wesley Hunt | Black, MBA, MPA, USA, helicopter pilot | Email Rep Hunt | RepWesleyHunt/ | RepWesleyHunt | 5646 | 1520L |
| Utah01 | Blake Moore | Mormon, US Dept of State | Email Rep Moore | RepBlakeMoore | RepBlakeMoore | O453 | 1131L |
| Utah02 | Celeste Maloy | Lawyer, cty atty, Mormon | Email Rep Malloy | RepMaloyUtah | 9730 | 249C | |
| Utah03 | Mike Kennedy | White, MD, Morman, lawyer, state sen, state rep | Email Rep Kennedy | RepMikeKennedy | RepMikeKennedy | 7751 | 1626L |
| Utah04 | Burgess Owens | Black, football, non-profit exec for troubled & incarcerated youth | Email Rep Owens | CongressmanBurgessOwens/ | RepBurgessOwens | 3011 | 309C |
| Virginia01 | Rob Wittman | White, M Pub Health, VA Dept of Health, town council, mayor | Email Rep Wittman | RepRobWittman | RobWittman | 4261 | 2055R |
| Virginia02 | Jen Kiggans | White, Geriatric nurse practitioner at Eastern VA med school, state sen, husband Navy pilot | Email Rep Kiggans | repjenkiggans/ | RepJenKiggans | 4215 | 152C |
| Virginia05 | John McGuire | White, USN Seal, State sen, state rep, businessman | Email Rep McQuire | RepJohnMcGuire | RepJohnMcGuire | 4711 | 1013L |
| Virginia06 | Ben Cline | White, lawyer, Commonwealth’s Attorney, state rep | Email Rep Cline | RepBenCline | RepBenCline | 5431 | 2443R |
| Virginia09 | Morgan Griffith | White, lawyer, state rep | Email Rep Griffith | RepMorganGriffith | RepMGriffith | 3861 | 2110R |
| Washington04 | Dan Newhouse | White, BA agri econ, state rep | Email Rep Newhouse | RepNewhouse | RepNewhouse | 5816 | 460C |
| Washington05 | Michael Baumgartner | White, state sen, MAPub Admin, | Email Rep Baumgartner | RepBaumgartner | RepBaumgartner | 2006 | 124C |
| West Virginia01 | Carol Miller | White, BA poli sci, state rep | Email Rep Miller | RepCarolMiller | RepCarolMiller | 3452 | 465C |
| West Virginia02 | Riley Moore | White, WV Treas, state rep, Catholic, aunt Shelley Moore Capito, welder | Email Rep Moore | Congressman-Riley-M-Moore | RepRileyMoore | 2711 | 1337L |
| Wisconsin01 | Bryan Steil | White, lawyer | Email Rep Steil | RepBryanSteil/ | RepBryanSteil | 3031 | 1526L |
| Wisconsin03 | Derrick Van Orden | White, US Navy Seal, businessman, actor | Email Rep Van Orden | RepVanOrden | RepVanOrden | 5506 | 1513L |
| Wisconsin05 | Scott Fitzgerald | White, USAR, St. sen, newspaper publisher | Email Rep Fitzgerald | CongressmanScottFitzgerald | RepFitzgerald | 5101 | 2444R |
| Wisconsin06 | Glenn Grothman | White, lawyer, state rep, state sen | Email Rep Grothman | RepGrothman | RepGrothman | 2476 | 1211L |
| Wisconsin07 | Tom Tiffany | White, businessman, st. sen, st. rep | Email Rep Tiffany | RepTiffany | RepTiffany | 3365 | 451C |
| Wisconsin08 | Tony Wied | White, BA, businessman | Email Rep Wied | RepMikeGallagher | RepGallagher | 5665 | 424C |
| Wyoming | Harriet Hageman | White, lawyer, | Email Rep Hageman | RepHageman | RepHagemanWY | 2311 | 1227L |
Senate Republicans
| State | Name | Information | Phone 202-224 | Address | |||
| Alabama | Tommy Tuberville | White, BS (PE), retired football coach | Email Sen. Tuberville | SenatorTuberville | @SenTuberville | 4124 | 142 R |
| Alabama | Katie Britt | White, lawyer, politician | Email Sen. Britt | senkatiebritt | @SenKatieBritt | 5744 | B40A |
| Alaska | Lisa Murkowski | White, lawyer, state rep | Email Sen. Murkowski | SenLisaMurkowksi/ | @lisamurkowski | 6665 | 522 H |
| Alaska | Dan Sullivan | White, USMC, lawyer, Attorney General | Email Sen. Sullivan | SenDanSullivan | @SenDanSullivan | 3004 | 302 H |
| Arkansas | John Boozman | White, optometrist for low-income families, advocate for drug policy issues, state rep | Email Sen. Boozman | JohnBoozman | @JohnBoozman | 4843 | 141 H |
| Arkansas | Tom Cotton | White, lawyer, USA, rancher | Email Sen. Cotton | SenatorTomCotton | @SenTomCotton | 2353 | 326 R |
| Florida | Rick Scott | White, lawyer, USN, owner Columbia HCA, Gov FL | Email Sen. Scott | RickScottSenOffice/ | @SenRickScott | 5274 | 502 H |
| Florida | Ashley Moody | White, lawyer, State AG, Circuit Court Judge, | Email Sen. Moody | SenAshleyMoody | 3041 | B40-B | |
| Idaho | Jim Risch | White, lawyer, prosecuting attorney, Lt Gov & Gov Idaho, state sen | Email Sen. Risch | SenatorJimRisch/ | @SenatorRisch | 2752 | 483 R |
| Idaho | Mike Crapo | White, lawyer, US Rep, state sen, | Email Sen. Crapo | mikecrapo | @MikeCrapo | 6142 | 239 D |
| Indiana | Jim Banks | White, MBA, Real estate and construction, USNR, County Council, state sen | Email Senator Banks | SenatorJimBanks | SenatorBanks | 4814 | B85 R |
| Indiana | Todd Young | White, lawyer, USMC, business, US rep | Email Sen. Young | SenatorToddYoung | @SenToddYoung | 5623 | 185 D |
| Iowa | Chuck Grassley | White, BA, MA, professor, US rep, State rep, | Email Sen. Grassley | grassley | @ChuckGrassley | 3744 | 135 H |
| Iowa | Joni Ernst | White, BA psych, MPubAdmin, USANG, State Sen | Email Sen. Ernst | senjoniernst | @SenJoniErnst | 3254 | 730 H |
| Kansas | Jerry Moran | White, lawyer, asst attorney general, US rep, state sen | Email Sen. Moran | jerrymoran | @JerryMoran | 6521 | 521 D |
| Kansas | Roger Marshall | White, MD, OB/Gyn, USA US Rep | Email Sen. Marshall | RogerMarshallMD | @RogerMarshallMD | 4774 | 479A R |
| Kentucky | Rand Paul | White, physician–ophthalmology | Email Sen. Paul | SenatorRandPaul/ | @SenRandPaul | 4343 | 167 R |
| Louisiana | Bill Cassidy, MD | White, physician-liver specialist, uninsured clinics, nonprofit Health Centers, US Rep, state sen | Email Sen. Cassidy | SenBillCassidy/ | @SenBillCassidy | 5824 | 520 H |
| Louisiana | John Neely Kennedy | White, lawyer, professor, US rep, state treas | Email Sen. Kennedy | SenatorJohnKennedy/ | @SenJohnKennedy | 4623 | 416 R |
| Maine | Susan Collins | White, BA-gov, politician | Email Sen. Collins | susancollins | @SenatorCollins | 2523 | 413 D |
| Mississippi | Roger F. Wicker | White, lawyer, USAF, US Rep, state Sen, | Email Sen. Wicker | SenatorWicker | @SenatorWicker | 6253 | 555 D |
| Mississippi | Cindy Hyde-Smith | White, BA poli sci, politician, State Sen, | Email Sen. Hyde-Smith | SenatorCindyHydeSmith/ | @SenHydeSmith | 5054 | 702 H |
| Missouri | Josh Hawley | White, lawyer, State Attorney Gen, | Email Sen. Hawley | SenatorHawley | @SenHawleyPress | 6154 | 115 Russell |
| Missouri | Eric Schmitt | White, lawyer, State Attorney Gen, state treas, state sen | Email Sen. Schmitt | SenEricSchmitt/ | @SenEricSchmitt | 5721 | B11 R |
| Montana | Steve Daines | White, BS Chem Eng, Proctor & Gamble, RightNow Technologies, US Rep | Email Sen. Daines | SteveDainesMT | @SteveDaines | 2651 | 320 H |
| Montana | Tim Sheehy | White, USN Seal, | Email Sen. Sheehy | Tim Sheehy | TimSheehyMT | 2644 | G55 D |
| Nebraska | Pete Ricketts | White, MBA, businessman, Governor | Email Sen. Ricketts | SenateGOP | @SenateGOP | 4224 | 139 R |
| Nebraska | Deb Fischer | White, BS ed, state rep, | Email Sen. Fischer | senatordebfischer | @SenatorFischer | 6551 | 454 R |
| North Carolina | Ted Budd | White, MBA, owns gun shop, US rep | Email Sen. Budd | SenTedBudd | @SenTedBuddNC | 3154 | B85 R |
| North Carolina | Thom Tillis | White, BA techmgmt, ins co, computer co, accting & consulting, IBM, state rep | Email Sen. Tillis | SenatorThomTillis | @SenThomTillis | 6342 | 113 D |
| North Dakota | Kevin Cramer | White, MA management, politician, chair ND Rep Party, US Rep, | Email Sen. Cramer | SenatorKevinCramer | @SenKevinCramer | 2043 | 330 H |
| North Dakota | John Hoeven | White, MBA, St. Governor, banker, pres Bank of North Dakota | Email Sen. Hoeven | SenatorJohnHoeven | @SenJohnHoeven | 2551 | 338 R |
| Ohio | Jon Husted | White, state lt.gov, sen and rep, MA communications | Email Sen. Husted | SenJonHusted | SenJonHusted | 3353 | 198 R |
| Ohio | Bernie Moreno | Hispanic, BA Bus Admin, father Columbian physician | Email Sen. Moreno | Sen. Bernie Moreno | berniemoreno | 2315 | B33 R |
| Oklahoma | Markwayne Mullin | White, AS construction, businessman, US Rep | Email Sen. Mullin | SenMullin/ | @SenMullin | 4721 | B33 R |
| Oklahoma | James Lankford | White, BS ed UT, MDiv, Christian camp program director, US Rep | Email Sen. Lankford | SenatorLankford | @SenatorLankford | 5754 | 316 H |
| Pennsylvania | Dave McCormick | White, USA, PhD Intern’l relations | Email Sen. McCormick | Sen Dave McCormick | SenMcCormickPA | 6324 | B40C D |
| South Carolina | Tim Scott | Black, BA Poli sci, Owner insurance agency, Charleston County Council, US Rep, state rep, | Email Sen. Scott | SenatorTimScott | @SenatorTimScott | 6121 | 104 H |
| South Carolina | Lindsey Graham | White, lawyer, AF Judge Advocate, state rep, US Rep, advocates strong national defense, leadership in world affairs, | Email Sen. Graham | LindseyGrahamSC/ | @LindseyGrahamSC | 5972 | 290 R |
| South Dakota | Mike Rounds | White, BS poli sci, partner insurance and real estate firm, state sen, State Gov, | Email Sen. Rounds | SenatorMikeRounds | @SenatorRounds | 5842 | 716 H |
| South Dakota | John Thune | White, MBA, Exec state republican party, US Rep | Email Sen. Thune | johnthune/ | @SenJohnThune | 2321 | 511 D |
| Tennessee | Bill Hagerty | White, lawyer, Ambassador to Japan | Email Sen. Hagerty | SenatorBillHagerty | @SenatorHagerty | 4944 | 248 R |
| Tennessee | Marsha Blackburn | White, BS home ec, politician, US Rep, State Sen, | Email Sen. Blackburn | marshablackburn/ | @MarshaBlackburn | 3344 | 357 D |
| Texas | John Cornyn | White, Lawyer, Texas Attorney Gen, San Antonio Dist. Judge, Assoc Justice Texas Supreme Court | Email Sen. Cornyn | SenJohnCornyn/ | @JohnCornyn | 2934 | 517 H |
| Texas | Ted Cruz | Hispanic, Lawyer, Texas Solicitor General, Law professor | Email Sen. Cruz | SenatorTedCruz | @SenTedCruz | 5922 | 127A R |
| Utah | Mike Lee | White, Mormon, lawyer, Asst US Attorney, private practice focusing on courtroom advocacy and constitutional law. | Email Sen. Lee | senatormikelee | @SenMikeLee | 5444 | 363 R |
| Utah | John Curtis | White, US rep, mayor, BS | Email Sen. Curtis | SenJohnCurtis | SenJohnCurtis | 5251 | B11 R |
| West Virginia | Shelley Moore Capito | White, MA ed, member Main Street Partnership, US rep, | Email Sen. Capito | senshelley | @SenCapito | 6472 | 172 R |
| West Virginia | Jim Justice | White, Gov, MBA, owns Greenbriar, coal companies | Email Sen. Justice | Sen. Jim Justice | |||
| Wisconsin | Ron Johnson | White, BA business & accounting | Email Sen. Johnson | senronjohnson/ | @SenRonJohnson | 5323 | 328 H |
| Wyoming | Cynthia Lummis | White, lawyer, State rep. US Rep | Email Sen. Lummis | sencynthialummis/ | @SenLummis | 3424 | 124 R |
| Wyoming | John Barrasso | White, physician-orthopedics, state sen, | Email Sen. Barrasso | johnbarrasso | @SenJohnBarrasso | 6441 | 307 D |
House of Representatives' Democrats & Independents
| State | Name | Information about | Phone 202-224 | Address Line 1 | |||
| Arizona | Mark Kelly | White, astronaut, USN, husband of Gabby Giffords, | Email Sen. Kelly | SenMarkKelly | @SenMarkKelly | 2235 | 516 H |
| Arizona | Ruben Gallego | Hispanic, US Rep, state rep, BA gov’t, USMC | Email Sen. Gallego | SenRubenGallego | SenRubenGallego | 4521 | 302 H |
| California | Adam Schiff | White, Jewish, lawyer, US attorney, state sen, vegan, | Email Sen. Schiff | SenAdamSchiff | SenAdamSchiff | 3841 | 112 H` |
| California | Alex Padilla | Hispanic, BS, mech eng, Sec of State, State sen, city council | Email Sen. Padilla | SenAlexPadella/ | @SenAlexPadilla | 3553 | 331 H |
| Colorado | John Hickenlooper | White, MS, Governor, Mayor | Email Sen. Hickenlooper | SenatorHick | @SenatorHick | 5941 | 316 H |
| Colorado | Michael Bennet | White, Jewish, Lawyer, Anschutz Investment Co, super of Schools | Email Sen. Bennet | senbennetco/ | @SenatorBennet | 5852 | 261 R |
| Connecticut | Chris Murphy | White, lawyer, US Rep, state sen, state rep | Email Sen. Murphy | senchrismurphy/ | @ChrisMurphyCT | 4041 | 136 H |
| Connecticut | Richard Blumenthal | White, Jewish, USMR, Lawyer, US Attorney, state Attorney General, state sen, state rep, US Attorney | Email Sen. Blumenthal | SenBlumenthal | @SenBlumenthal | 2823 | 503 H |
| Delaware | Chris Coons | White, lawyer, nonprofits, missions | Email Sen. Coons | senatorchriscoons | @ChrisCoons | 5042 | 218 R |
| Delaware | Lisa Blunt Rochester | Black, US Rep, MA public policy, CEO Urban League | Email Sen. Blunt Rochester | SenLBR | SenLBR | 2441 | 513 H |
| Georgia | Jon Ossoff | White, Jewish, MS int’l pol, filmmaker | Email Sen. Ossoff | SenOssoff | @SenOssoff | 3521 | 317 H |
| Georgia | Raphael G. Warnock | Black, Mdiv, pastor, activist | Email Sen. Warnock | SenatorWarnock | @SenatorWarnock | 3643 | 717 R |
| Hawaii | Brian Schatz | White, Jewish, Lt. Gov, State rep, CEO Helping Hands Hawaii, | Email Sen. Schatz | SenBrianSchatz | @SenBrianSchatz | 3934 | 722 H |
| Hawaii | Mazie Hirono | Asian, non-practicing Buddhist, Lawyer, State rep, Lt. Gov, US rep | Email Sen. Hirono | senatorhirono | @maziehirono | 6361 | 109 H |
| Illinois | Dick Durbin | White, lawyer, Sen Maj whip, US rep | Email Sen. Durbin | SenatorDurbin | @SenatorDurbin | 2152 | 711 H |
| Illinois | Tammy Duckworth | Asian, MA int’l affairs, PhD human services, USA helio pilot, bilateral amputee, Dept Veterans Affairs, US Rep, | Email Sen. Duckworth | SenDuckworth | @SenDuckworth | 2854 | 524 H |
| Maine | Angus King | White, lawyer, private practice, state gov, Subcommittee on Alcoholism & Narcotics. | Email Sen. King | SenatorAngusSKingJr | @SenAngusKing | 5344 | 133 H |
| Maryland | Angela Alsobrooks | Black, lawyer, State attorney | Email Sen. Alsobrooks | SenatorAlsobrooks | Sen_Alsobrooks | 4524 | B40E D |
| Maryland | Chris Van Hollen | White, lawyer, BA in philos, M. Public Policy, US Rep, state sen, state rep | Email Sen. Van Hollen | chrisvanhollen/ | @ChrisVanHollen | 4654 | 730 H |
| Massachusetts | Ed Markey | White, lawyer, USAR, US Rep, state rep, liberal, focus on energy policy | Email Sen. Markey | EdJMarkey | @SenMarkey | 2742 | 255 D |
| Massachusetts | Elizabeth Warren | White, lawyer, law prof, consumer protection advocate | Email Sen. Warren | senatorelizabethwarren | @SenatorWarren | 4543 | 311 H |
| Michigan | Elissa Slotkin | Jewish, US Rep, MA Intern’l Affairs, CIA, DoD | Email Sen. Slotkin | SenElissaSlotkin | SenatorSlotkin | 4822 | 825B/C H |
| Michigan | Gary Peters | White, lawyer, MBA, USNR, investment advisor, Asst VP at Merrill Lynch, then Paine Webber VP, US rep | Email Sen. Peters | SenGaryPeters | @SenGaryPeters | 6221 | 724 H |
| Minnesota | Amy Klobuchar | White, lawyer, County attorney | Email Sen. Klobuchar | amyklobuchar | @SenAmyKlobuchar | 3244 | 425 D |
| Minnesota | Tina Smith | White, MBA-Poli Sci, Lt. Gov | Email Sen. Smith | USSenTinaSmith/ | @SenTinaSmith | 5641 | 720 H |
| Nevada | Catherine Cortez Masto | Hispanic, Lawyer, At Gen, possible misconduct. Attacked Bank of America | Email Sen. Cortez Masto | SenatorCortezMasto/ | @SenCortezMasto | 3542 | 309 H |
| Nevada | Jacky Rosen | White, Jewish, BA psych, business-IT, US Rep, | Email Sen. Rosen | SenJackyRosen/ | @SenJackyRosen | 6244 | 713 H |
| New Hampshire | Jeanne Shaheen | White, MA Poli Sci, taught HS, owned jewelry store, St. Governor, state sen | Email Sen. Shaheen | SenatorShaheen | @SenatorShaheen | 2841 | 506 H |
| New Hampshire | Maggie Hassan | White, lawyer, Governor, state sen | Email Sen. Hassan | SenatorHassan | @SenatorHassan | 3324 | 324 H |
| New Jersey | Andy Kim | Korean American, US Rep, MA | Email Sen. Kim | SenatorAndyKim | SenatorAndyKim | 4744 | B-40 D |
| New Jersey | Cory Booker | Black, lawyer, MA sociology, Mayor, city councilor | Email Sen. Booker | SenatorCoryBooker | @SenBooker | 3224 | 306 H |
| New Mexico | Ben Ray Lujan | Hispanic, US Rep, state public service | Email Sen. Lujan | SenatorLujan | @SenatorLujan | 6621 | 498 R |
| New Mexico | Martin Heinrich | White, BA mech eng, worked AmeriCorps fellow, Cottonwood Gulch Foundation (NP), founded his own public affairs consulting firm, US Rep, City Council | Email Sen. Heinrich | MartinHeinrich | @MartinHeinrich | 5521 | 709 H |
| New York | Chuck Schumer | White, Jewish, lawyer, Sen Maj. Leader, US Rep, state rep | Email Sen. Schumer | senschumer/ | @SenSchumer | 6542 | 322 H |
| New York | Kirsten Gillibrand | White, lawyer-Private, defense for tobacco co Philip Morris, abused women & children, pro bono, Women’s Leadership Forum, US Rep | Email Sen. Gillibrand | SenKirstenGillibrand | @gillibrandny | 4451 | 478 R |
| Oregon | Jeff Merkley | White, M. Pub Pol, director Portland Hapbitat for Humanity, initiated “YouthBuild” for young offenders, State rep, | Email Sen. Merkley | jeffmerkley | @SenJeffMerkley | 3753 | 531 H |
| Oregon | Ron Wyden | White, Jewish, Lawyer, taught gerontology, founded Oregon chapter of Gray Panthers, directed nonprofit law service, US Rep, | Email Sen. Wyden | senatorronwyden/ | @RonWyden | 5244 | 221 D |
| Pennsylvania | John Fetterman | White, M pub Policy, MBA, Lt. gov, Mayor | Email Sen. Fetterman | @SenFettermanPA | 4254 | 142 R | |
| Rhode Island | Jack Reed | White, lawyer- private practice, focused on education & health care, USArmy, US Rep | Email Sen. Reed | SenJackReed/ | @SenJackReed | 4642 | 728 H |
| Rhode Island | Sheldon Whitehouse | White, USAF, lawyer, clerk Appeals Court Judge West VA, State Attorney General, US Attorney | Email Sen. Whitehouse | SenatorWhitehouse | @SenWhitehouse | 2921 | 530 H |
| Vermont | Bernie Sanders | White, Jewish, BA Poli sci, social democracy, Young People’s Socialist League, mayor, US rep, | Email Sen. Sanders | senatorsanders/ | @SenSanders | 5141 | 332 D |
| Vermont | Peter Welch | White, lawyer, law clerk, State sen, US rep | Email Sen. Welch | PeterWelch | @PeterWelch | 4242 | 124 R |
| Virginia | Mark Warner | White, lawyer (never practiced), Gov VA, mobile phone franchise licenses broker, Capital Cellular Corp, wealthiest US Senator. | Email Sen. Warner | MarkRWarner | @MarkWarner | 2023 | 703 H |
| Virginia | Tim Kaine | White, lawyer, BA economics, chair Nat’l Dem Comm, Gov VA, Lt Gov VA, Mayor | Email Sen. Kaine | SenatorKaine | @SenKaineTeam | 4024 | 231 R |
| Washington | Maria Cantwell | White, BA Public Admin, state rep, US rep | Email Sen. Cantwell | senatorcantwell | @SenatorCantwell | 3441 | 511 H |
| Washington | Patty Murray | White, BA-PE, preschool teacher, welfare as teen, dad with MS, state sen, | Email Sen. Murray | pattymurray/ | @PattyMurray | 2621 | 154 R |
| Wisconsin | Tammy Baldwin | White, lesbian, lawyer, Wisc state assembly, US Rep, | Email Sen. Baldwin | senatortammybaldwin | @SenatorBaldwin | 5653 | 141 H |
Senate Democrats & Independents
| State | Name | Information about | Phone 202-224 | Address Line 1 | |||
| Arizona | Mark Kelly | White, astronaut, USN, husband of Gabby Giffords, | Email Sen. Kelly | SenMarkKelly | @SenMarkKelly | 2235 | 516 H |
| Arizona | Ruben Gallego | Hispanic, US Rep, state rep, BA gov’t, USMC | Email Sen. Gallego | SenRubenGallego | SenRubenGallego | 4521 | 302 H |
| California | Adam Schiff | White, Jewish, lawyer, US attorney, state sen, vegan, | Email Sen. Schiff | SenAdamSchiff | SenAdamSchiff | 3841 | 112 H` |
| California | Alex Padilla | Hispanic, BS, mech eng, Sec of State, State sen, city council | Email Sen. Padilla | SenAlexPadella/ | @SenAlexPadilla | 3553 | 331 H |
| Colorado | John Hickenlooper | White, MS, Governor, Mayor | Email Sen. Hickenlooper | SenatorHick | @SenatorHick | 5941 | 316 H |
| Colorado | Michael Bennet | White, Jewish, Lawyer, Anschutz Investment Co, super of Schools | Email Sen. Bennet | senbennetco/ | @SenatorBennet | 5852 | 261 R |
| Connecticut | Chris Murphy | White, lawyer, US Rep, state sen, state rep | Email Sen. Murphy | senchrismurphy/ | @ChrisMurphyCT | 4041 | 136 H |
| Connecticut | Richard Blumenthal | White, Jewish, USMR, Lawyer, US Attorney, state Attorney General, state sen, state rep, US Attorney | Email Sen. Blumenthal | SenBlumenthal | @SenBlumenthal | 2823 | 503 H |
| Delaware | Chris Coons | White, lawyer, nonprofits, missions | Email Sen. Coons | senatorchriscoons | @ChrisCoons | 5042 | 218 R |
| Delaware | Lisa Blunt Rochester | Black, US Rep, MA public policy, CEO Urban League | Email Sen. Blunt Rochester | SenLBR | SenLBR | 2441 | 513 H |
| Georgia | Jon Ossoff | White, Jewish, MS int’l pol, filmmaker | Email Sen. Ossoff | SenOssoff | @SenOssoff | 3521 | 317 H |
| Georgia | Raphael G. Warnock | Black, Mdiv, pastor, activist | Email Sen. Warnock | SenatorWarnock | @SenatorWarnock | 3643 | 717 R |
| Hawaii | Brian Schatz | White, Jewish, Lt. Gov, State rep, CEO Helping Hands Hawaii, | Email Sen. Schatz | SenBrianSchatz | @SenBrianSchatz | 3934 | 722 H |
| Hawaii | Mazie Hirono | Asian, non-practicing Buddhist, Lawyer, State rep, Lt. Gov, US rep | Email Sen. Hirono | senatorhirono | @maziehirono | 6361 | 109 H |
| Illinois | Dick Durbin | White, lawyer, Sen Maj whip, US rep | Email Sen. Durbin | SenatorDurbin | @SenatorDurbin | 2152 | 711 H |
| Illinois | Tammy Duckworth | Asian, MA int’l affairs, PhD human services, USA helio pilot, bilateral amputee, Dept Veterans Affairs, US Rep, | Email Sen. Duckworth | SenDuckworth | @SenDuckworth | 2854 | 524 H |
| Maine | Angus King | White, lawyer, private practice, state gov, Subcommittee on Alcoholism & Narcotics. | Email Sen. King | SenatorAngusSKingJr | @SenAngusKing | 5344 | 133 H |
| Maryland | Angela Alsobrooks | Black, lawyer, State attorney | Email Sen. Alsobrooks | SenatorAlsobrooks | Sen_Alsobrooks | 4524 | B40E D |
| Maryland | Chris Van Hollen | White, lawyer, BA in philos, M. Public Policy, US Rep, state sen, state rep | Email Sen. Van Hollen | chrisvanhollen/ | @ChrisVanHollen | 4654 | 730 H |
| Massachusetts | Ed Markey | White, lawyer, USAR, US Rep, state rep, liberal, focus on energy policy | Email Sen. Markey | EdJMarkey | @SenMarkey | 2742 | 255 D |
| Massachusetts | Elizabeth Warren | White, lawyer, law prof, consumer protection advocate | Email Sen. Warren | senatorelizabethwarren | @SenatorWarren | 4543 | 311 H |
| Michigan | Elissa Slotkin | Jewish, US Rep, MA Intern’l Affairs, CIA, DoD | Email Sen. Slotkin | SenElissaSlotkin | SenatorSlotkin | 4822 | 825B/C H |
| Michigan | Gary Peters | White, lawyer, MBA, USNR, investment advisor, Asst VP at Merrill Lynch, then Paine Webber VP, US rep | Email Sen. Peters | SenGaryPeters | @SenGaryPeters | 6221 | 724 H |
| Minnesota | Amy Klobuchar | White, lawyer, County attorney | Email Sen. Klobuchar | amyklobuchar | @SenAmyKlobuchar | 3244 | 425 D |
| Minnesota | Tina Smith | White, MBA-Poli Sci, Lt. Gov | Email Sen. Smith | USSenTinaSmith/ | @SenTinaSmith | 5641 | 720 H |
| Nevada | Catherine Cortez Masto | Hispanic, Lawyer, At Gen, possible misconduct. Attacked Bank of America | Email Sen. Cortez Masto | SenatorCortezMasto/ | @SenCortezMasto | 3542 | 309 H |
| Nevada | Jacky Rosen | White, Jewish, BA psych, business-IT, US Rep, | Email Sen. Rosen | SenJackyRosen/ | @SenJackyRosen | 6244 | 713 H |
| New Hampshire | Jeanne Shaheen | White, MA Poli Sci, taught HS, owned jewelry store, St. Governor, state sen | Email Sen. Shaheen | SenatorShaheen | @SenatorShaheen | 2841 | 506 H |
| New Hampshire | Maggie Hassan | White, lawyer, Governor, state sen | Email Sen. Hassan | SenatorHassan | @SenatorHassan | 3324 | 324 H |
| New Jersey | Andy Kim | Korean American, US Rep, MA | Email Sen. Kim | SenatorAndyKim | SenatorAndyKim | 4744 | B-40 D |
| New Jersey | Cory Booker | Black, lawyer, MA sociology, Mayor, city councilor | Email Sen. Booker | SenatorCoryBooker | @SenBooker | 3224 | 306 H |
| New Mexico | Ben Ray Lujan | Hispanic, US Rep, state public service | Email Sen. Lujan | SenatorLujan | @SenatorLujan | 6621 | 498 R |
| New Mexico | Martin Heinrich | White, BA mech eng, worked AmeriCorps fellow, Cottonwood Gulch Foundation (NP), founded his own public affairs consulting firm, US Rep, City Council | Email Sen. Heinrich | MartinHeinrich | @MartinHeinrich | 5521 | 709 H |
| New York | Chuck Schumer | White, Jewish, lawyer, Sen Maj. Leader, US Rep, state rep | Email Sen. Schumer | senschumer/ | @SenSchumer | 6542 | 322 H |
| New York | Kirsten Gillibrand | White, lawyer-Private, defense for tobacco co Philip Morris, abused women & children, pro bono, Women’s Leadership Forum, US Rep | Email Sen. Gillibrand | SenKirstenGillibrand | @gillibrandny | 4451 | 478 R |
| Oregon | Jeff Merkley | White, M. Pub Pol, director Portland Hapbitat for Humanity, initiated “YouthBuild” for young offenders, State rep, | Email Sen. Merkley | jeffmerkley | @SenJeffMerkley | 3753 | 531 H |
| Oregon | Ron Wyden | White, Jewish, Lawyer, taught gerontology, founded Oregon chapter of Gray Panthers, directed nonprofit law service, US Rep, | Email Sen. Wyden | senatorronwyden/ | @RonWyden | 5244 | 221 D |
| Pennsylvania | John Fetterman | White, M pub Policy, MBA, Lt. gov, Mayor | Email Sen. Fetterman | @SenFettermanPA | 4254 | 142 R | |
| Rhode Island | Jack Reed | White, lawyer- private practice, focused on education & health care, USArmy, US Rep | Email Sen. Reed | SenJackReed/ | @SenJackReed | 4642 | 728 H |
| Rhode Island | Sheldon Whitehouse | White, USAF, lawyer, clerk Appeals Court Judge West VA, State Attorney General, US Attorney | Email Sen. Whitehouse | SenatorWhitehouse | @SenWhitehouse | 2921 | 530 H |
| Vermont | Bernie Sanders | White, Jewish, BA Poli sci, social democracy, Young People’s Socialist League, mayor, US rep, | Email Sen. Sanders | senatorsanders/ | @SenSanders | 5141 | 332 D |
| Vermont | Peter Welch | White, lawyer, law clerk, State sen, US rep | Email Sen. Welch | PeterWelch | @PeterWelch | 4242 | 124 R |
| Virginia | Mark Warner | White, lawyer (never practiced), Gov VA, mobile phone franchise licenses broker, Capital Cellular Corp, wealthiest US Senator. | Email Sen. Warner | MarkRWarner | @MarkWarner | 2023 | 703 H |
| Virginia | Tim Kaine | White, lawyer, BA economics, chair Nat’l Dem Comm, Gov VA, Lt Gov VA, Mayor | Email Sen. Kaine | SenatorKaine | @SenKaineTeam | 4024 | 231 R |
| Washington | Maria Cantwell | White, BA Public Admin, state rep, US rep | Email Sen. Cantwell | senatorcantwell | @SenatorCantwell | 3441 | 511 H |
| Washington | Patty Murray | White, BA-PE, preschool teacher, welfare as teen, dad with MS, state sen, | Email Sen. Murray | pattymurray/ | @PattyMurray | 2621 | 154 R |
| Wisconsin | Tammy Baldwin | White, lesbian, lawyer, Wisc state assembly, US Rep, | Email Sen. Baldwin | senatortammybaldwin | @SenatorBaldwin | 5653 | 141 H |
Communicate with Democratic and Independent Legislators
Copy any of the communications in the toggles below and send to all of the democratic and independent legislators. If you have a letter you would like to add to the collection, please send it to me through the Contact Us page.
When going to the Facebook pages for legislators, look for a post from our constituents, and then add your comments. Mix your posts to them up, and repeat often. Remember Hitler’s philosophy: Keep it simple, say it often, and soon they will believe it.
If you get any responses from the candidates, please share them with me so I can post them
Emails
Number 1:
I am a representative of Doctorsofcourage.org and represent a large population in your state, of doctors illegally attacked for treating legitimate pain and patients now suffering and dying because of illegal government overreach into medicine. It is imperative that Democrats take over the House, and we want to support you.
I can tell you a way to gather the majority of your state voters around you. Democrats are rallying around the cry of reproductive freedom for women, saying that the government has no right to decide what a woman does with her own body. We say there is even a more important area of freedom that has been usurped by the government. That is the freedom of every American to decide what to eat, drink, or smoke.
The War on Drugs is unconstitutional, and we need you to stand on that for your campaign. The War on Drugs has created the black market, the poisonous illicit drugs, the overdoses, and the border crisis. All of these problems will end with the legalization of all drugs in addition to the savings of billions of taxpayer dollars chasing the rabbits. Learn from prohibition. If you will stand on ending the use of the Controlled Substance Act against physicians and pain patients, you will win the election.
If you need to understand that no drug causes addiction, to fight the propaganda created by previous Republican administrations, you can find the truth on our website. I do hope that you use this to achieve a win so that we can create a democratic Congress that will then pass laws to end the government overreach in medicine, for the future of this country and the world. Thank you.
Number 2:
On Sept 4, 2024, a 14 y/o boy went on a shooting rampage at a Georgia high school. The cause of this behavior can be explained. It is the same cause as the increase in addiction and other chronic diseases in the country and the world. It is explained though my videos on www.doctorsofcourage.org/videos.
The cause of these increases in abnormal behavior in the world is toxicity. It isn’t explained through conventional medicine and cannot be cured with conventional medicine. It is explained through the most scientific medicine ever studied, but we in America ignore it. The science is homeopathy. I also explain this in my videos.
Attacking guns isn’t the answer. Sick people will find a gun. Just like attacking abortion isn’t the answer. Women with unwanted pregnancies will find an abortion doctor in a back alley, like it was 50 years ago.
If you would recognize the things I’ve passed on to you, the freedom of choice when it comes to drugs, food, drink, etc., and the importance of learning more about how toxicity affects our health and future, you could win a lot of votes.
If you need more information from me on this, I would be happy to give a personal presentation to a group of 10 interested people, or more.
Linda Cheek, MD
Number 3:
Illegal Use of the Law Against Innocent Citizens
On behalf of all of your constituents being affected by the illegal government attacks on the most compassionate, professional physicians in your state, we, Doctorsofcourage.org, ask you to hear our complaints, share them with others, and hopefully Congress will act to end this atrocity. Doing so will end a lot of problems we are currently having. I’m happy to explain this to you further if you are interested.
During the Cavanaugh hearings, over and over Senators and Congressmen bemoaned the current state of Congress—that you no longer do what you were elected to do, but allow agencies to determine the laws. One of the greatest failures is in the area of allowing the Department of Justice to misrepresent the law in court in order to confiscate assets of innocent citizens. This has got to stop, and we ask you to support an investigation into this illegal activity. As a result of this rogue agency’s actions, innocent people are going to prison and innocent citizens are suffering and dying.
As Albert Schweitzer said,
“Pain is a more terrible lord of mankind than even death itself”
So by stopping legitimate pain management by trained professionals, you are forcing your citizens to the street for self-medication, where they most probably will be faced with illegal fentanyl-laced pills, or to committing suicide. Is that really the direction you want your citizens to go?
Here is a list of our concerns and demands:
DOCTORS OF COURAGE (DoC)
www.doctorsofcourage.org
Concerns-1. The “Opioid Epidemic” is a fake, government-created situation to falsely blame on legal prescriptions written by physicians in order to confiscate assets through illegal use of the Controlled Substance Act. As a result, innocent citizens are suffering and dying.
- The disproportionate and discriminatory over-prosecution of black and other ethnic physicians of color by the DOJ, DEA, criminal justice system and state medical boards
- The alarming increase in the death rate of chronic pain patients, who are opioid non-abusers, through DOJ persecution of treating physicians. This has created an epidemic of suicides, especially by veterans, through physician abandonment and limiting needed medications by pharmacies
- The increase in the horrendous death rate of sickle cell anemia chronic pain patients, who are mostly African American. The denial of National Institute of Health (NIH) standard of care treatment guidelines by emergency room and hospital providers, using CDC guidelines to excuse “medical manslaughter” and “black genocide”
- The cost of human suffering and loss of quality of life of chronic pain patients, who are opioid non-abusers
- Government overreach leading to non-medical government agencies practicing medicine without a license
- Violation of Doctors’ Constitutional Rights
a 4th amendment through illegal search and seizure, use of warrants without just cause.
b 5th amendment through lack of due process.
c 6th amendment rights of a speedy and public trial, an impartial jury, the right to be informed of the charges, the right to confront and call witnesses, and the right to an attorney.
d 14th amendment through loss of property. A doctor’s profession is his property.
- Misuse of the forfeiture statute of the CSA
Demands
- The investigation of the DOJ by the U.S. Congress for the prosecution of physicians through the illegal application of the Controlled Substance Act.
- Doctors that have been charged or convicted based on Title 21, The Controlled Substance Act, be immediately released from prison and exonerated from any federal charges, including Medicare/Medicaid fraud charges, as that is simply a door-opener.
- Doctors have their licenses and DEA certificates restored
- The CSA be amended or new law written to permanently exempt doctors from charges related to controlled substance prescriptions in words that even US Attorneys can understand.
- Remove the actual immunity from prosecutors. If they break the law to convict an innocent person, they should be prosecuted, not protected.
- Defendants should have first option of witnesses. The government should not be allowed to declare everyone a government witness and leave the defendant with no one.
- Allow doctors who have been denied DEA certification without cause a means of civil action to be remunerated for their loss of their 14th amendment rights.
- A search warrant into a doctor’s office must be served with actual charges in mind, based on the criminal standard of actual sale of prescriptions for resale or abuse, not for patient treatment.
- Stop asset forfeiture prior to conviction.
- Investigate National Data Banks for publishing false allegations against medical professionals. Information should not be public until proven.
Facebook Posts
Post 1: Democrats can’t be hypocrites. Declaring “freedom” and “get the government out of the doctor’s office” when innocent doctors are in prison cells and patients are dying doesn’t cut it. So let’s get on the freedom train for ALL! We must end the War on Drugs, repeal the CSA, exonerate all those illegally attacked by the government through unconstitutional attack. No drug causes addiction. The constitution does not give the federal government control of our body. Learn the truth on Doctorsofcourage(dot)org.
Post 2:
Please learn the REAL Cause of Drug Abuse because it is also the cause of the increased gun violence and other abnormal behavior problems we now face in America. We must accept this knowledge and learn the solution. Chasing gun restriction isn’t the answer. Putting 14 y/o boys in prison for life isn’t the answer. Getting to the cause and treating it before violence occurs is the answer. We hold the key on DoC.
Responses
House Committees
Agriculture
Appropriations
Armed Services
Budget
| Name | State, District | Party | Phone 202-225- | |||
| Mark DeSaulnier | California10 | D | Email Rep DeSaulner | RepMarkDeSaulnier/ | RepDeSaulnier | 2095 |
| Michael Guest | Mississippi03 | R | Email Rep Guest | RepMichaelGuest | RepMichaelGuest | 5031 |
Education & Workforce
Energy & Commerce
Ethics
Financial Services
Foreign Affairs
Homeland Security
House Administration
| Name | State, District | Party | Phone 202-225- | |||
| Barry Loudermilk | Georgia11 | R | Email Rep Loudermilk | RepLoudermilk/ | RepLoudermilk | 2931 |
| Bryan Steil | Wisconsin01 | R | Email Rep Steil | RepBryanSteil/ | RepBryanSteil | 3031 |
| Greg Murphy | North Carolina03 | R | Email Rep Murphy | RepGregMurphy/ | RepGregMurphy | 3415 |
| Joseph Morelle | New York25 | D | Email Rep Morelle | RepJoeMorelle/ | RepJoeMorelle | 3615 |
| Julie Johnson | Texas32 | D | Email Rep Johnson | RepJulieJohnson | RepJulieJohnson | 2231 |
| Laurel Lee | Florida15 | R | Email Rep Lee | RepLaurelLee | RepLaurelLee | 5626 |
| Mary Miller | Illinois15 | D | Email Rep Mary Miller | RepMaryMiller | RepMaryMiller | 5271 |
| Mike Carey | Ohio15 | R | Email Rep Carey | RepMikeCarey | RepMikeCarey | 2015 |
| Morgan Griffith | Virginia09 | R | Email Rep Griffith | RepMorganGriffith | RepMGriffith | 3861 |
| Norma Torres | California35 | D | Email Rep Torres | RepNormaTorres/ | NormaJTorres | 6161 |
| Stephanie Bice | Oklahoma05 | R | Email Rep Bice | RepStephanieBice | RepBice | 2132 |
| Terri Sewell | Alabama07 | D | Email Rep Sewell | RepSewell | RepTerriSewell | 2665 |
Judiciary
Natural Resources
Oversight & Government
Rules
| Name | State, District | Party | Phone 202-225- | |||
| Austin Scott | Georgia08 | R | Email Rep Scott | RepAustinScott/ | AustinScottGA08 | 6531 |
| Brian Jack | Georgia03 | R | Email Rep Jack | RepBrianJack | RepBrianJack | 5901 |
| Chip Roy | Texas21 | R | Email Rep Roy | RepChipRoyPress/ | RepChipRoy | 4236 |
| Erin Houchin | Indiana09 | R | Email Rep Houchin | RepHouchin | RepHouchin | 5315 |
| James McGovern | Massachusetts02 | D | Email Rep McGovern | RepJimMcGovern/ | RepMcGovern | 6101 |
| Joe Neguse | Colorado2 | D | Email Rep Neguse | RepJoeNeguse | RepJoeNeguse | 2161 |
| Mary Gay Scanlon | Pennsylvania05 | D | Email Rep Scanlon | RepMGS/ | RepMGS | 2011 |
| Michelle Fischbach | Minnesota07 | R | Email Rep Fischbach | RepFischbach | RepFischbach | 2165 |
| Morgan Griffith | Virginia09 | R | Email Rep Griffith | RepMorganGriffith | RepMGriffith | 3861 |
| Nick Langworthy | New York23 | R | Email Rep Langworthy | RepLangworthy | RepLangworthy | 3161 |
| Ralph Norman | South Carolina05 | R | Email Rep Norman | RepRalphNorman | RRepRalphNorman | 5501 |
| Teresa Leger Fernandez | New Mexico03 | D | Email Rep Fernandez | RepTeresaLF | RepTeresaLF | 6190 |
| Virginia Foxx | North Carolina05 | R | Email Rep Foxx | RepVirginiaFoxx | virginiafoxx | 2071 |
Science, Space, & Technology
Small Business
Transportation
Veteran's Affairs
Ways & Means
Senate Committees
Agriculture
Appropriations
Armed Services
Banking, Housing & Urban Affairs
Budget
Commerce, Science & Transportation
Energy & Natural Resources
Foreign Relations
Finance
Environment & Public Works
HELP: Health, Education. Labor & Pensions
Homeland Security & Government Affairs
Judiciary
Rules & Administration
Small Business
Veteran's Affairs

Groups of House Representatives
Medicine Connection
Medically connected legislators (the legislators that are connected to medicine, either through themselves, or a family member):
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Phone | |||
| Arizona09 | Paul Gosar | White, dentist, | repgosar/ | RepGosar | Email Rep Gosar | 2315 |
| California06 | Ami Bera, MD | India, MD, Sch of Med Dean, | RepAmiBera/ | RepBera | Email Rep Bera | 5716 |
| California07 | Doris Matsui | Asian, BA psych, took husband’s seat | doris.matsui/ | DorisMatsui | Email Rep Matsui | 7163 |
| California25 | Raul Ruiz | Hispanic, emergency MD, MPH, | RepRaulRuizMD/ | CongressmanRuiz | Email Rep Ruiz | 5330 |
| Florida2 | Neal Dunn | White, MD, surgeon, USArmy Panama City Urological Center and Surgery Center, bank founder | DrNealDunnFL2/ | DrNealDunnFL2 | Email Rep Dunn | 5235 |
| Georgia01 | Buddy Carter | White, BS pharmacy, anti-drugs, state rep, state sen, | CongressmanBuddyCarter/ | RepBuddyCarter | Email Rep Carter | 5831 |
| Georgia06 | Lucy McBath | Black, BA poli sci, flight attendant, son was shot; father dentist. | replucymcbath/ | RepLucyMcBath | Email Rep McBath | 4501 |
| Georgia08 | Austin Scott | White, BBA insurance, Pres. Southern Group, LLC, state rep; father orthopedic surgeon | RepAustinScott/ | AustinScottGA08 | Email Rep Scott | 6531 |
| Idaho02 | Mike Simpson | White, dentist, state rep | RepMikeSimpson | CongMikeSimpson | Email Rep Simpson | 5531 |
| Illinois02 | Robin Kelly | Black, BA psych, MA counseling, PhD Poli Sci, Pres Unity Coalition, state rep | reprobinkelly | RepRobinKelly | Email Rep Kelly | O773 |
| Illinois14 | Lauren Underwood | Black, RN, MPH, DHHS | repunderwood/ | RepUnderwood | Email Rep Underwood | 2976 |
| Indiana01 | Frank J. Mrvan | White, BS journalism, mortgage broker, pharmaceutical sales rep | RepMrvan | RepMrvan | Email Rep Mrvan | 2461 |
| Iowa01 | Mariannette Miller-Meeks | White, physician, USA, state sen. | RepMMM | repMMM | Email Rep Miller-Meeks | 6576 |
| Maryland01 | Andy Harris | White, MD-anesthesiology (father immigrant MD anes from Hungary), USN, state sen | AndyHarrisMD | RepAndyHarrisMD | Email Rep Harris | 5311 |
| Minnesota03 | Kelly Morrison | White, physician OB-GYN, state sen, state rep | repkellymorrison | KellyMorrisonMN | Email Rep Morrison | 2871 |
| Minnesota05 | Ilhan Omar | Black, (Somali), Muslim, BA poli sci, nutrition educator, state rep | RepIlhan/ | Ilhan | Email Rep Omar | 4755 |
| Missouri03 | Bob Onder | White, physician-allergy, asthma, lawyer, state sen, state rep | RepBobOnder | RepBobOnder | Email Rep Onder | 2956 |
| New Jersey01 | Donald Norcross | White, BA criminal justice, (Wife echocardiographer, brother psychologist), state rep | DonaldNorcrossNJ | DonaldNorcross | Email Rep Norcross | 6501 |
| New Jersey02 | Jeff Van Drew | White, dentist, state rep, state sen | CongressmanJVD | Congressman_JVD | Email Rep Van Drew | 6572 |
| New Jersey03 | Herb Conaway | Black, MD int med, lawyer, USAF med corps, state rep | RepHerbConaway | Email Rep Conaway | 4765 | |
| New York26 | Tim Kennedy | White, occupational therapy, mother nurse | https://www.facebook.com/RepTimKennedy | RepTimKennedy | Email Rep Tim Kennedy | 3306 |
| North Carolina02 | Deborah K. Ross | White, lawyer, st. rep, father a physician in AF in Viet Nam | RepDeborahRoss | RepDeborahRoss | Email Rep Ross | 3032 |
| North Carolina03 | Greg Murphy | White, MD-urology, medical mission work, state rep | RepGregMurphy/ | RepGregMurphy | Email Rep Murphy | 3415 |
| Ohio03 | Joyce Beatty | Black, MS psychology, state rep | RepJoyceBeatty/ | RepBeatty | Email Rep Beatty | 4324 |
| Oregon03 | Maxine Dexter | White, MD, pulmonologist, state rep | RepDexterOR | RepDexterOR | Email Rep Dexter | 4811 |
| Pennsylvania13 | John Joyce | White, dermatologist | RepJohnJoyce/ | RepJohnJoyce | Email Rep Joyce | 2431 |
| Pennsylvania15 | Glenn Thompson | White, Med, Nursing Home Admin | CongressmanGT/ | CongressmanGT | Email Rep Thompson | 5121 |
| South Carolina03 | Sheri Biggs | White, nurse practitioner, air nat’l guard | RepSheriBiggs | RepSheriBiggs | Email Rep Biggs | 5301 |
| Tennessee01 | Diana Harshbarger | Pharmacist, compounding pharmacy, focus: fixing opioid crisis | RepDianaHarshbarger | RepHarshbarger | Email Rep Harshbarger | 6356 |
| Tennessee04 | Scott DesJarlais | White, physician (gen. med) | ScottDesJarlaisTN04 | DesJarlaisTN04 | Email Rep DesJarlais | 6831 |
| Tennessee07 | Mark Green | White, MD, USArmy, state sen | RepMarkGreenTN/ | RepMarkGreen | Email Rep Green | 2811 |
| Texas13 | Ronny Jackson | White, physician, Chief Medical Advisor to Pres, USN | RepRonnyJackson | RepRonnyJackson | Email Rep Jackson | 3706 |
| Texas36 | Brian Babin | White, dentist-UT, USAF | RepBrianBabin | RepBrianBabin | Email Rep Babin | 1555 |
| Utah03 | Mike Kennedy | White, MD, Morman, lawyer, state sen, state rep | RepMikeKennedy | RepMikeKennedy | Email Rep Kennedy | 7751 |
| Virginia01 | Rob Wittman | White, M Pub Health, VA Dept of Health, town council, mayor | RepRobWittman | RobWittman | Email Rep Wittman | 4261 |
| Washington08 | Kim Schrier, MD | Jewish, pediatrician | RepKimSchrier/ | RepKimSchrier | Email Rep Schrier | 7761 |
Legislators of Color
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Phone | Room | |||
| Alabama02 | Shomari Figures | Black | congressman.shomari.figures | Email Rep Figures | 4931 | 225C | |
| Alabama07 | Terri Sewell | Black | RepSewell | RepTerriSewell | Email Rep Sewell | 2665 | 1035L |
| Arizona08 | Abraham Hamadeh | Syrian | RepAbeHamadeh | AbrahamHamadeh | Email Rep Hamadeh | 4576 | 1722L |
| Arizona03 | Yassamin Ansari | Iranian | repyassansari | RepYassAnsari | Email Yassamin Ansari | 4065 | 1432L |
| Arizona06 | Juan Ciscomani | Hispanic | RepCiscomani | Email Rep Ciscomani | 2542 | 461C | |
| California12 | Lateefah Simon | Black | replsimon | RepLSimon | Email Rep Simon | 2661 | 1023L |
| California06 | Ami Bera, MD | India | RepAmiBera/ | RepBera | Email Rep Bera | 5716 | 172C |
| California07 | Doris Matsui | Asian | doris.matsui/ | DorisMatsui | Email Rep Matsui | 7163 | 2206R |
| California08 | John Garamendi | Hispanic | repgaramendi/ | RepGaramendi | Email Rep Garamendi | 1880 | 2428R |
| California17 | Ro Khanna | India | RepRoKhanna/ | RepRoKhanna | Email Rep Khanna | 2631 | 306C |
| California20 | Vince Fong | Chinese | RepVinceFong# | RepVinceFong | Email Rep Fong | 2915 | 243C |
| California22 | David Valadao | Portugueze | CongressmanDavidValadao | RepDavidValadao | Email Rep Valadao | 4695 | 2465R |
| California24 | Salud Carbajal | Hispanic | repsaludcarbajal/ | RepCarbajal | Email Rep Carbajal | 3601 | 2331R |
| California25 | Raul Ruiz | Hispanic | RepRaulRuizMD/ | CongressmanRuiz | Email Rep Ruiz | 5330 | 2342R |
| California28 | Judy Chu | Asian | RepJudyChu/ | RepJudyChu | Email Rep Chu | 5464 | 2423R |
| California29 | Luz Rivas | Hispanic | congresswomanluzrivas | RepLuzRivas | Email Rep Rivas | 6131 | 1319L |
| Califonria31 | Gil Cisneros | Hispanic | RepGilCisneros | RepGilCisneros | Email Rep Cisneros | 5256 | 2463R |
| California33 | Pete Aguilar | Hispanic | reppeteaguilar/ | RepPeteAguilar | Email Rep Aguilar | 3201 | 108C |
| California34 | Jimmy Gomez | Hispanic | RepJimmyGomez/ | RepJimmyGomez | Email Rep Gomez | 6235 | 506C |
| California35 | Norma Torres | Hispanic | RepNormaTorres/ | NormaJTorres | Email Rep Torres | 6161 | 2227R |
| California36 | Ted Lieu | Asian | RepTedLieu/ | RepTedLieu | Email Rep Lieu | 3976 | 2454R |
| California37 | Sydney Kamlager-Dove | Black | House Democrats | RepKamlagerDove | Email Rep Kamlager-Dove | 7084 | 144C |
| California38 | Linda Sanchez | Hispanic | RepLindaSanchez/ | RepLindaSanchez | Email Rep Sanchez | 6676 | 2428R |
| California39 | Mark Takano | Asian | RepMarkTakano | RepMarkTakano | Email Rep Takano | 2305 | 2078R |
| California40 | Young Kim | South Korean | RepYoungKim | RepYoungKim | Email Rep Kim | 4111 | 2439R |
| California42 | Robert Garcia | Hispanic | reprobertgarcia | RepRobertGarcia | Email Rep Garcia | 7924 | 109C |
| California43 | Maxine Waters | Black | MaxineWaters | RepMaxineWaters | Email Rep Waters | 2201 | 2221R |
| California44 | Nanette Barragan | Hispanic | CongresswomanBarragan | RepBarragan | Email Rep Barragan | 8220 | 2312R |
| California45 | Derek Tran | Vietnamese | CongressmanTran | RepDerekTranCA | Email Rep Tran | 2415 | 1127L |
| California46 | Lou Correa | Hispanic | RepLouCorrea | RepLouCorrea | Email Rep Correa | 2965 | 2082R |
| California47 | Dave Min | Korean | thecongressmin | CongressMin | Email Rep Min | 5611 | 1034L |
| California49 | Mike Levin | Hispanic | RepMikeLevin | RepMikeLevin | Email Rep Levin | 3906 | 2352R |
| California52 | Juan Vargas | Hispanic | RepJuanVargas | RepJuanVargas | Email Rep Vargas | 8045 | 2467R |
| Colorado08 | Gabe Evans | Hispanic | RepGabeEvans | repgabeevans | Email Rep Evans | 5625 | 1229L |
| Colorado02 | Joe Neguse | Black | RepJoeNeguse | RepJoeNeguse | Email Rep Neguse | 2161 | 2400L |
| Connecticut05 | Jahana Hayes | Black | RepJahanaHayes | RepJahanaHayes | Email Rep Hayes | 4476 | 2049R |
| D.C. | Eleanor Holmes Norton | Black | CongresswomanNorton | EleanorNorton | Email Rep Norton | 8050 | 2136R |
| Florida10 | Maxwell Frost | Hispanic/Black Haiti | RepMaxwellFrost | RepMaxwellFrost | Email Rep Frost | 2176 | 1224L |
| Florida13 | Anna Paulina Luna | Hispanic | realAnnaPaulina | RepLuna | Email Rep Luna | 5961 | 226C |
| Florida19 | Byron Donalds | Black | RepDonaldsPress | RepByronDonalds | Email Rep Donalds | 2536 | 1710L |
| Florida20 | Sheila Cherfilus-McCormick | Black | CongresswomanSCM | CongresswomanSC | Email Rep Cherifilus-McCormick | 1313 | 2442R |
| Florida21 | Brian Mast | Hispanic | RepBrianMast | BrianMastFL | Email Rep Mast | 3026 | 2182R |
| Florida24 | Frederica Wilson | Black | RepWilson | @RepWilson | Email Rep Wilson | 4506 | 2080R |
| Florida26 | Mario Diaz-Balart | Hispanic | mdiazbalart | MarioDB | Email Rep Diaz-Balart | 4211 | 374C |
| Florida27 | Maria Elvira Salazar | Cuban | CongresswomanMariaElviraSalazar | RepMariaSalazar | Email Rep Salazar | 3931 | 2162R |
| Florida28 | Carlos Gimenez | Cuban | RepCarlosGimenez | RepCarlos | Email Rep Gimenez | 2778 | 448C |
| Florida09 | Darren Soto | Hispanic | RepDarrenSoto/ | RepDarrenSoto | Email Rep Soto | 9889 | 2353R |
| Georgia02 | Sanford Bishop | Black | sanfordbishop | SanfordBishop | Email Rep Bishop | 3631 | 2407R |
| Georgia04 | Hank Johnson | Black | RepHankJohnson/ | RepHankJohnson | Email Rep Johnson | 1605 | 2240R |
| Georgia05 | Nikema Williams | Black | RepNikemaWilliams | RepNikema | Email Rep Williams | 3801 | 1406L |
| Georgia06 | Lucy McBath | Black | replucymcbath/ | RepLucyMcBath | Email Rep McBath | 4501 | 2246R |
| Georgia13 | David Scott | Black | RepDavidScott | repdavidscott | Email Rep Scott | 2939 | 468C |
| Hawaii02 | Jill Tokuda | Asian | RepJillTokuda | RepJillTokuda | Email Rep Tokuda | 4906 | 1005L |
| Illinois01 | Jonathan Jackson | Black | Email Rep Jackson | 4372 | 1632L | ||
| Illinois02 | Robin Kelly | Black | reprobinkelly | RepRobinKelly | Email Rep Kelly | O773 | 2329R |
| Illinois03 | Delia Ramirez | Hispanic | repdeliaramirez | repdeliaramirez | Email Rep Ramirez | 5701 | 1523L |
| Illinois04 | Chuy Garcia | Hispanic | RepChuyGarcia/ | RepChuyGarcia | Email Rep Garcia | 8203 | 2334R |
| Illinois07 | Danny Davis | Black | OfficialRepDannyDavis/ | RepDannyDavis | Email Rep Davis | 5006 | 2159R |
| Illinois08 | Raja Krishnamoorthi | India | CongressmanRaja | CongressmanRaja | Email Rep Krishnamoorthi | 3711 | 2367R |
| Illinois14 | Lauren Underwood | Black | repunderwood/ | RepUnderwood | Email Rep Underwood | 2976 | 2228R |
| Indiana07 | Andre Carson | Black | CongressmanAndreCarson | RepAndreCarson | Email Rep Carson | 4011 | 2135R |
| Kansas03 | Sharice Davids | Native American | RepDavids | RepDavids | Email Rep Davids | 2865 | 2435R |
| Louisiana02 | Troy Carter | Black | RepTroyCarter | RepTroyCarter | Email Rep Carter | 6636 | 442C |
| Louisiana06 | Cleo Fields | Black | Congressman-Cleo-Fields | RepFields | Email Rep Fields | 2349 | 2349R |
| Maryland04 | Glenn Ivey | Black | RepGlennIvey | RepGlennIvey | Email Rep Ivey | 8699 | 1610L |
| Maryland07 | Kweisi Mfume | Black | RepKweisiMfume | RepKweisiMfume | Email Rep Mfume | 4741 | 2263R |
| Massachusetts03 | Lori Trahan | Hispanic | RepLoriTrahan/ | RepLoriTrahan | Email Rep Trahan | 3411 | 2233R |
| Massachusetts07 | Ayanna Pressley | Black | RepAyannaPressley | RepPressley | Email Rep Pressley | 5111 | 402C |
| Michigan10 | John James | Black | RepJohnJames | RepJames | Email Rep James | 4961 | 1519L |
| Michigan12 | Rashida Tlaib | Black | RepRashida | RepRashida | Email Rep Tlaib | 5126 | 2438R |
| Michigan13 | Shri Thanedar | India | CongressmanShriThanedar | RepShriThanedar | Email Rep Thanedar | 5802 | 154C |
| Minnesota05 | Ilhan Omar | Black | RepIlhan/ | Ilhan | Email Rep Omar | 4755 | 1730L |
| Mississippi02 | Bennie Thompson | Black | CongressmanBennieGThompson/ | BennieGThompson | Email Rep Thompson | 5876 | 2466R |
| Missouri01 | Wesley Bell | Black | repwesleybell | RepWesleyBellMO | Email Rep Bell | 2406 | 1429L |
| Missouri05 | Emanuel Cleaver | Black | emanuelcleaverii/ | repcleaver | Email Rep Cleaver | 4535 | 2217R |
| Nevada04 | Steven Horsford | Black | RepHorsford/ | RepHorsford | Email Rep Horsford | 9894 | 406C |
| New Jersey03 | Herb Conaway | Black | Repherbconaway | RepHerbConaway | Email Rep Conaway | 4765 | 1022L |
| New Jersey08 | Rob Menendez | Hispanic | repmenendez | RepMenendez | Email Rep Menendez | 7919 | 2453R |
| New Jersey09 | Nellie Pou | Hispanic | CongresswomanNelliePou | RepNellie | Email Rep Pou | 5751 | 1007L |
| New Jersey10 | LaMonica McIver | Black | RepLaMonica | 3436 | 426C | ||
| New Jersey12 | Bonnie Watson Coleman | Black | RepBonnie | RepBonnie | Email Rep Watson Coleman | 5801 | 168C |
| New Mexico01 | Melanie Stansbury | Native American | RepStansbury | Rep_Stansbury | Email Rep Stansbury | 6316 | 1421L |
| New Mexico02 | Gabe Vasquez | Native American | https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100089328694464 | RepGabeVasquez | Email Rep Vasquez | 2365 | 322C |
| New Mexico03 | Teresa Leger Fernandez | Hispanic | RepTeresaLF | RepTeresaLF | Email Rep Fernandez | 6190 | 2417R |
| New York05 | Gregory Meeks | Black | RepGregoryMeeks/ | RepGregoryMeeks | Email Rep Meeks | 3461 | 2310R |
| New York06 | Grace Meng | Asian | repgracemeng | RepGraceMeng | Email Rep Meng | 2601 | 2468R |
| New York07 | Nydia Velazquez | Hispanic | RepNydiaVelazquez/ | NydiaVelazquez | Email Rep Velazquez | 2361 | 2302R |
| New York08 | Hakeem Jeffries | Black | RepJeffries | RepJeffries | Email Rep Jeffries | 5936 | 2267R |
| New York09 | Yvette Clarke | Black | repyvetteclarke/ | RepYvetteClarke | Email Rep Clarke | 6231 | 2058R |
| New York11 | Nicole Malliotakis | Greek/cuban | RepMalliotakis | RepMalliotakis | Email Rep Malliotakis | 3371 | 1124L |
| New York13 | Adriano Espaillat | Hispanic | RepEsaillat/ | RepEspaillat | Email Rep Espaillat | 4365 | 2332R |
| New York14 | Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez | Hispanic | repAOC/ | AOC | Email Rep Ocasio-Cortez | 3965 | 250C |
| New York15 | Ritchie Torres | Black/Hispanic | RepRitchie | RepRitchie | Email Rep Torres | 4361 | 1414L |
| North Carolina01 | Don Davis | Black | RepDonDavis | RepDonDavis | Email Rep Davis | 3101 | 1123L |
| North Carolina04 | Valerie Foushee | Black | RepValerieFoushee | ValerieFoushee | Email Rep Foushee | 1784 | 2452R |
| North Carolina12 | Alma Adams | Black | CongresswomanAdams/ | RepAdams | Email Rep Adams | 1510 | 2436R |
| Ohio03 | Joyce Beatty | Black | RepJoyceBeatty/ | RepBeatty | Email Rep Beatty | 4324 | 2079R |
| Ohio11 | Shontel Brown | Black | RepShontelBrown | RepShontelBrown | Email Rep Brown | 7032 | 2455R |
| Ohio13 | Emilia Sykes | Black | repemiliasykes | RepEmiliaSykes | Email Rep Sykes | 6265 | 1217L |
| Oklahoma02 | Josh Brecheen | Native American | RepBrecheen | RepBrecheen | Email Rep Brecheen | 2701 | 351C |
| Oklahoma04 | Tom Cole | Native American | TomColeOK04 | TomColeOK04 | Email Rep Cole | 6165 | 2207R |
| Oklahoma05 | Stephanie Bice | Iranian | RepStephanieBice | RepBice | Email Rep Bice | 2132 | 2402R |
| Oregon05 | Janelle Bynum | Black | repbynum | RepBynum | Email Rep Bynum | 5711 | 1508L |
| Pennsylvania03 | Dwight Evans | Black | RepDwightEvans/ | RepDwightEvans | Email Rep Evans | 4001 | 1105L |
| Rhode Island01 | Gabe Amo | Black | RepGabeAmo | RepGabeAmo | Email Rep Cicilline | 4911 | 1119L |
| South Carolina06 | Jim Clyburn | Black | RepJamesClyburn | RepJamesClyburn | Email Rep Clyburn | 3315 | 274C |
| Texas15 | Monica De la Cruz | Hispanic | monicaforcongress | RepMonicaDLC | Email Rep De La Cruz | 9901 | 1415L |
| Texas16 | Veronica Escobar | Hispanic | RepEscobar/ | RepEscobar | Email Rep Escobar | 4831 | 2448L |
| Texas20 | Joaquin Castro | Hispanic | JoaquinCastroTX/ | JoaquinCastrotx | Email Rep Castro | 3236 | 2241R |
| Texas23 | Tony Gonzales | Hispanic | RepTonyGonzales | RepTonyGonzales | Email Rep Gonzalez | 4511 | 2239R |
| Texas28 | Henry Cuellar | Hispanic | repcuellar/ | RepCuellar | Email Rep Cuellar | 1640 | 2308R |
| Texas29 | Sylvia Garcia | Hispanic | RepSylviaGarcia | RepSylviaGarcia | Email Rep Garcia | 1688 | 2419R |
| Texas30 | Jasmine Crockett | Black | RepJasmine | RepJasmine | Email Rep Crockett | 8885 | 1616L |
| Texas33 | Marc Veasey | Black | CongressmanMarcVeasey | RepVeasey | Email Rep Veasey | 9897 | 2186R |
| Texas34 | Vincente Gonzalez | Hispanic | RepVincenteGonzalez | RepGonzalez | Email Rep Gonzalez | 2531 | 1201L |
| Texas35 | Greg Casar | Hispanic | repcasar/ | RepCasar | Email Rep Casar | 5645 | 446C |
| Texas38 | Wesley Hunt | Black | RepWesleyHunt/ | RepWesleyHunt | Email Rep Hunt | 5646 | 1520L |
| Utah04 | Burgess Owens | Black | CongressmanBurgessOwens/ | RepBurgessOwens | Email Rep Owens | 3011 | 309C |
| Virginia03 | Bobby Scott | Black | RepBobbyScott/ | BobbyScott | Email Rep Scott | 8351 | 2328R |
| Virginia04 | Jennifer McClellan | Black | Congresswoman Jennifer MCClellan | RepMcClellan | Email Rep McClellan | 6365 | 1628L |
| Virginia10 | Suhas Subramanyam | India | RepSuhasSubramanyam/ | RepSuhas | Email Rep Subramanyam | 5136 | 1009L |
| Washington03 | Marie Gluesenkamp Perez | Hispanic | RepMGP | RepMGP | Email Rep Gluesenkamp-Perez | 3536 | 1431L |
| Washington06 | Emily Randall | Hispanic | RepEmilyRandall | Email Rep Randall | 5916 | 1531L | |
| Washington07 | Pramila Jayapal | India | RepJayapal/ | RepJayapal | Email Rep Jayapal | 3106 | 2346R |
| Washington10 | Marilyn Strickland | Black/Korean | RepStricklandWA | RepStricklandWA | Email Rep Strickland | 9740 | 1724L |
| Wisconsin04 | Gwen Moore | Black | GwenSMoore | RepGwenMoore | Email Rep Moore | 4572 | 2252R |
Black Legislators
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Phone | Room | |||
| Alabama02 | Shomari Figures | Black | congressman.shomari.figures | Email Rep Figures | 4931 | 225C | |
| Alabama07 | Terri Sewell | Black | RepSewell | RepTerriSewell | Email Rep Sewell | 2665 | 1035L |
| California12 | Lateefah Simon | Black | replsimon | RepLSimon | Email Rep Simon | 2661 | 1023L |
| California37 | Sydney Kamlager-Dove | Black | House Democrats | RepKamlagerDove | Email Rep Kamlager-Dove | 7084 | 144C |
| California43 | Maxine Waters | Black | MaxineWaters | RepMaxineWaters | Email Rep Waters | 2201 | 2221R |
| Colorado02 | Joe Neguse | Black | RepJoeNeguse | RepJoeNeguse | Email Rep Neguse | 2161 | 2400L |
| Connecticut05 | Jahana Hayes | Black | RepJahanaHayes | RepJahanaHayes | Email Rep Hayes | 4476 | 2049R |
| D.C. | Eleanor Holmes Norton | Black | CongresswomanNorton | EleanorNorton | Email Rep Norton | 8050 | 2136R |
| Florida19 | Byron Donalds | Black | RepBryonDonalds | RepByronDonalds | Email Rep Donalds | 2536 | 1710L |
| Florida20 | Sheila Cherfilus-McCormick | Black | CongresswomanSCM | CongresswomanSC | Email Rep Cherifilus-McCormick | 1313 | 2442R |
| Florida24 | Frederica Wilson | Black | RepWilson | @RepWilson | Email Rep Wilson | 4506 | 2080R |
| Georgia02 | Sanford Bishop | Black | sanfordbishop | SanfordBishop | Email Rep Bishop | 3631 | 2407R |
| Georgia04 | Hank Johnson | Black | RepHankJohnson/ | RepHankJohnson | Email Rep Johnson | 1605 | 2240R |
| Georgia05 | Nikema Williams | Black | RepNikemaWilliams | RepNikema | Email Rep Williams | 3801 | 1406L |
| Georgia06 | Lucy McBath | Black | replucymcbath/ | RepLucyMcBath | Email Rep McBath | 4501 | 2246R |
| Georgia13 | David Scott | Black | RepDavidScott/ | repdavidscott | Email Rep Scott | 2939 | 468C |
| Illinois01 | Jonathan Jackson | Black | rep_jackson | Email Rep Jackson | 4372 | 1632L | |
| Illinois02 | Robin Kelly | Black | reprobinkelly | RepRobinKelly | Email Rep Kelly | O773 | 2329R |
| Illinois07 | Danny Davis | Black | OfficialRepDannyDavis/ | RepDannyDavis | Email Rep Davis | 5006 | 2159R |
| Illinois14 | Lauren Underwood | Black | repunderwood/ | RepUnderwood | Email Rep Underwood | 2976 | 2228R |
| Indiana07 | Andre Carson | Black | CongressmanAndreCarson | RepAndreCarson | Email Rep Carson | 4011 | 2135R |
| Louisiana02 | Troy Carter | Black | RepTroyCarter | RepTRoyCarter | Email Rep Carter | 6636 | 442C |
| Louisiana06 | Cleo Fields | Black | Congressman-Cleo-Fields | RepFields | Email Rep Fields | 2349 | 2349R |
| Maryland04 | Glenn Ivey | Black | RepGlennIvey | RepGlennIvey | Email Rep Ivey | 8699 | 1610L |
| Maryland07 | Kweisi Mfume | Black | RepKweisiMfume | RepKweisiMfume | Email Rep Mfume | 4741 | 2263R |
| Massachusetts07 | Ayanna Pressley | Black | RepAyannaPressley | RepPressley | Email Rep Pressley | 5111 | 402C |
| Michigan10 | John James | Black | RepJames | Email Rep James | 4961 | 1519L | |
| Michigan12 | Rashida Tlaib | Black | RepRashida | RepRashida | Email Rep Tlaib | 5126 | 2438R |
| Michigan13 | Shri Thanedar | India | repshrithanedar | RepShriThanedar | Email Rep Thanedar | 5802 | 154C |
| Minnesota05 | Ilhan Omar | Black | RepIlhan/ | Ilhan | Email Rep Omar | 4755 | 1730L |
| Mississippi02 | Bennie Thompson | Black | CongressmanBennieGThompson/ | BennieGThompson | Email Rep Thompson | 5876 | 2466R |
| Missouri01 | Wesley Bell | Black | RepWesleyBellMO | Email Rep Bell | 2406 | 1429L | |
| Missouri05 | Emanuel Cleaver | Black | emanuelcleaverii/ | repcleaver | Email Rep Cleaver | 4535 | 2217R |
| Nevada04 | Steven Horsford | Black | RepHorsford/ | RepHorsford | Email Rep Horsford | 9894 | 406C |
| New Jersey03 | Herb Conaway | Black | RepHerbConaway | Email Rep Conaway | 4765 | 1022L | |
| New Jersey10 | LaMonica McIver | Black | DonaldPayneJr | RepDonaldPayne | Email Rep Payne | 3436 | 426C |
| New Jersey12 | Bonnie Watson Coleman | Black | RepBonnie | RepBonnie | Email Rep Watson Coleman | 5801 | 168C |
| New York05 | Gregory Meeks | Black | RepGregoryMeeks/ | RepGregoryMeeks | Email Rep Meeks | 3461 | 2310R |
| New York08 | Hakeem Jeffries | Black | RepJeffries | RepJeffries | Email Rep Jeffries | 5936 | 2267R |
| New York09 | Yvette Clarke | Black | repyvetteclarke/ | RepYvetteClarke | Email Rep Clarke | 6231 | 2058R |
| New York15 | Ritchie Torres | Black/Hispanic | RepRitchie | RepRitchie | Email Rep Torres | 4361 | 1414L |
| North Carolina01 | Don Davis | Black | RepDonDavis | RepDonDavis | Email Rep Davis | 3101 | 1123L |
| North Carolina04 | Valerie Foushee | Black | RepValerieFoushee | ValerieFoushee | Email Rep Foushee | 1784 | 2452R |
| North Carolina12 | Alma Adams | Black | CongresswomanAdams/ | RepAdams | Email Rep Adams | 1510 | 2436R |
| Ohio03 | Joyce Beatty | Black | RepJoyceBeatty/ | RepBeatty | Email Rep Beatty | 4324 | 2079R |
| Ohio11 | Shontel Brown | Black | RepShontelBrown | RepShontelBrown | Email Rep Brown | 7032 | 2455R |
| Ohio13 | Emilia Sykes | Black | repemiliasykes | RepEmiliaSykes | Email Rep Sykes | 6265 | 1217L |
| Oregon05 | Janelle Bynum | Black | repbynum | RepBynum | Email Rep Bynum | 5711 | 1508L |
| Pennsylvania03 | Dwight Evans | Black | RepDwightEvans/ | RepDwightEvans | Email Rep Evans | 4001 | 1105L |
| Rhode Island01 | Gabe Amo | Black | CongressmanDavidCicilline/ | RepCicilline | Email Rep Cicilline | 4911 | 1119L |
| South Carolina06 | Jim Clyburn | Black | RepJamesClyburn | RepJamesClyburn | Email Rep Clyburn | 3315 | 274C |
| Texas30 | Jasmine Crockett | Black | RepJasmine | RepJasmine | Email Rep Crockett | 8885 | 1616L |
| Texas33 | Marc Veasey | Black | CongressmanMarcVeasey | RepVeasey | Email Rep Veasey | 9897 | 2186R |
| Texas38 | Wesley Hunt | Black | RepWesleyHunt/ | RepWesleyHunt | Email Rep Hunt | 5646 | 1520L |
| Utah04 | Burgess Owens | Black | CongressmanBurgessOwens/ | RepBurgessOwens | Email Rep Owens | 3011 | 309C |
| Virginia03 | Bobby Scott | Black | RepBobbyScott/ | BobbyScott | Email Rep Scott | 8351 | 2328R |
| Virginia04 | Jennifer McClellan | Black | Congresswoman Jennifer MCClellan | RepMcClellan | Email Rep McClellan | 6365 | 1628L |
| Wisconsin04 | Gwen Moore | Black | GwenSMoore | RepGwenMoore | Email Rep Moore | 4572 | 2252R |
Hispanic Legislators
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Phone | Room | |||
| Arizona06 | Juan Ciscomani | Hispanic | RepCiscomani | Email Rep Ciscomani | 2542 | 461C | |
| California08 | John Garamendi | Hispanic | repgaramendi/ | RepGaramendi | Email Rep Garamendi | 1880 | 2428R |
| California24 | Salud Carbajal | Hispanic | repsaludcarbajal/ | RepCarbajal | Email Rep Carbajal | 3601 | 2331R |
| California25 | Raul Ruiz | Hispanic | RepRaulRuizMD/ | CongressmanRuiz | Email Rep Ruiz | 5330 | 2342R |
| California29 | Luz Rivas | Hispanic | congresswomanluzrivas | RepLuzRivas | Email Rep Rivas | 6131 | 1319L |
| Califonria31 | Gil Cisneros | Hispanic | RepGilCisneros | RepGilCisneros | Email Rep Cisneros | 5256 | 2463R |
| California33 | Pete Aguilar | Hispanic | reppeteaguilar/ | RepPeteAguilar | Email Rep Aguilar | 3201 | 108C |
| California34 | Jimmy Gomez | Hispanic | RepJimmyGomez/ | RepJimmyGomez | Email Rep Gomez | 6235 | 506C |
| California35 | Norma Torres | Hispanic | RepNormaTorres/ | NormaJTorres | Email Rep Torres | 6161 | 2227R |
| California38 | Linda Sanchez | Hispanic | RepLindaSanchez/ | RepLindaSanchez | Email Rep Sanchez | 6676 | 2428R |
| California42 | Robert Garcia | Hispanic | reprobertgarcia | RepRobertGarcia | Email Rep Garcia | 7924 | 109C |
| California44 | Nanette Barragan | Hispanic | CongresswomanBarragan | RepBarragan | Email Rep Barragan | 8220 | 2312R |
| California46 | Lou Correa | Hispanic | RepLouCorrea | RepLouCorrea | Email Rep Correa | 2965 | 2082R |
| California49 | Mike Levin | Hispanic | RepMikeLevin | RepMikeLevin | Email Rep Levin | 3906 | 2352R |
| California52 | Juan Vargas | Hispanic | RepJuanVargas | RepJuanVargas | Email Rep Vargas | 8045 | 2467R |
| Colorado08 | Gabe Evans | Hispanic | RepGabeEvans | repgabeevans | Email Rep Evans | 5625 | 1229L |
| Florida10 | Maxwell Frost | Hispanic/Black Haiti | RepMaxwellFrost | RepMaxwellFrost | Email Rep Frost | 2176 | 1224L |
| Florida13 | Anna Paulina Luna | Hispanic | realAnnaPaulina | RepLuna | Email Rep Luna | 5961 | 226C |
| Florida21 | Brian Mast | Hispanic | RepBrianMast | BrianMastFL | Email Rep Mast | 3026 | 2182R |
| Florida26 | Mario Diaz-Balart | Hispanic | mdiazbalart | MarioDB | Email Rep Diaz-Balart | 4211 | 374C |
| Florida27 | Maria Elvira Salazar | Cuban | CongresswomanMariaElviraSalazar | RepMariaSalazar | Email Rep Salazar | 3931 | 2162R |
| Florida28 | Carlos Gimenez | Cuban | RepCarlosGimenez | RepCarlos | Email Rep Gimenez | 2778 | 448C |
| Florida09 | Darren Soto | Hispanic | RepDarrenSoto/ | RepDarrenSoto | Email Rep Soto | 9889 | 2353R |
| Illinois03 | Delia Ramirez | Hispanic | repdeliaramirez | Email Rep Ramirez | 5701 | 1523L | |
| Illinois04 | Chuy Garcia | Hispanic | RepChuyGarcia/ | RepChuyGarcia | Email Rep Garcia | 8203 | 2334R |
| Massachusetts03 | Lori Trahan | Hispanic | RepLoriTrahan/ | RepLoriTrahan | Email Rep Trahan | 3411 | 2233R |
| New Jersey08 | Rob Menendez | Hispanic | repmenendez | RepMenendez | Email Rep Menendez | 7919 | 2453R |
| New Jersey09 | Nellie Pou | Hispanic | RepNellie | Email Rep Pou | 5751 | 1007L | |
| New Mexico03 | Teresa Leger Fernandez | Hispanic | RepTeresaLF | RepTeresaLF | Email Rep Fernandez | 6190 | 2417R |
| New York07 | Nydia Velazquez | Hispanic | RepNydiaVelazquez/ | NydiaVelazquez | Email Rep Velazquez | 2361 | 2302R |
| New York13 | Adriano Espaillat | Hispanic | RepEsaillat/ | RepEspaillat | Email Rep Espaillat | 4365 | 2332R |
| New York14 | Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez | Hispanic | repAOC/ | AOC | Email Rep Ocasio-Cortez | 3965 | 250C |
| Texas15 | Monica De la Cruz | Hispanic | monicaforcongress | RepMonicaDLC | Email Rep De La Cruz | 9901 | 1415L |
| Texas16 | Veronica Escobar | Hispanic | RepEscobar/ | RepEscobar | Email Rep Escobar | 4831 | 2448L |
| Texas20 | Joaquin Castro | Hispanic | JoaquinCastroTX/ | JoaquinCastrotx | Email Rep Castro | 3236 | 2241R |
| Texas23 | Tony Gonzales | Hispanic | RepTonyGonzales | RepTonyGonzales | Email Rep Gonzalez | 4511 | 2239R |
| Texas28 | Henry Cuellar | Hispanic | repcuellar/ | RepCuellar | Email Rep Cuellar | 1640 | 2308R |
| Texas29 | Sylvia Garcia | Hispanic | RepSylviaGarcia | RepSylviaGarcia | Email Rep Garcia | 1688 | 2419R |
| Texas34 | Vincente Gonzalez | Hispanic | RepVincenteGonzalez | RepGonzalez | Email Rep Gonzalez | 2531 | 1201L |
| Texas35 | Greg Casar | Hispanic | repcasar/ | RepCasar | Email Rep Casar | 5645 | 446C |
| Washington03 | Marie Gluesenkamp Perez | Hispanic | RepMGP | RepMGP | Email Rep Gluesenkamp-Perez | 3536 | 1431L |
| Washington06 | Emily Randall | Hispanic | RepEmilyRandall | Email Rep Randall | 5916 | 1531L | |
Asian Legislators
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Phone | Room | |||
| California07 | Doris Matsui | Asian | doris.matsui/ | DorisMatsui | Email Rep Matsui | 7163 | 2206R |
| California20 | Vince Fong | Chinese | RepVinceFong# | RepVinceFong | Email Rep Fong | 2915 | 243C |
| California28 | Judy Chu | Asian | RepJudyChu/ | RepJudyChu | Email Rep Chu | 5464 | 2423R |
| California36 | Ted Lieu | Asian | RepTedLieu/ | RepTedLieu | Email Rep Lieu | 3976 | 2454R |
| California39 | Mark Takano | Asian | RepMarkTakano | RepMarkTakano | Email Rep Takano | 2305 | 2078R |
| California40 | Young Kim | South Korean | RepYoungKim | RepYoungKim | Email Rep Kim | 4111 | 2439R |
| California45 | Derek Tran | Vietnamese | RepDerekTranCA | Email Rep Tran | 2415 | 1127L | |
| California47 | Dave Min | Korean | thecongressmin | CongressMin | Email Rep Min | 5611 | 1034L |
| Hawaii02 | Jill Tokuda | Asian | RepJillTokuda | RepJillTokuda | Email Rep Tokuda | 4906 | 1005L |
| New York06 | Grace Meng | Asian | repgracemeng | RepGraceMeng | Email Rep Meng | 2601 | 2468R |
| Washington10 | Marilyn Strickland | Black/Korean | RepStricklandWA | RepStricklandWA | Email Rep Strickland | 9740 | 1724L |
Veterans
Legislators who have served in the armed forces:
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Phone | Room | |||
| Alabama01 | Barry Moore | White, BS ag sci, Nat’l Guard, state rep | RepBarryMoore | repbarrymoore | 2901 | 1511L | |
| Arizona02 | Eli Crane | White, Navy Seal. Father pharmacist | rep.elicrane | RepEliCrane | Email Rep Crane | 3361 | 307C |
| Arkansas01 | Rick Crawford | White, radio announcer, businessman, USArmy | RepRickCrawford | Email Rep Crawford | 4076 | 2422R | |
| Arkansas03 | Steve Womack | White, USArmy, mayor | rep_stevewomack | Email Rep Womack | 4301 | 2412R | |
| California04 | Mike Thompson | White, Mpub Admin, USArmy, state sen | RepMikeThompson/ | RepThompson | Email Rep Thompson | 3311 | 268C |
| California19 | Jimmy Panetta | White, Catholic, USNR, dep. Dist. Attorney. Father was WH Chief of Staff, Dir CIA, wife is Cty SC judge | RepJimmyPanetta/ | RepJimmyPanetta | Email Rep Panetta | 2861 | 200C |
| California24 | Salud Carbajal | Hispanic, M Organization Management, USMR | repsaludcarbajal/ | RepCarbajal | Email Rep Carbajal | 3601 | 2331R |
| California31 | Gil Cisneros | Hispanic, USN, MBA | RepGilCisneros | RepGilCisneros | Email Rep Cisneros | 5256 | 2463R |
| California36 | Ted Lieu | Asian, lawyer, USAF, JAG, state rep, state sen | RepTedLieu/ | RepTedLieu | Email Rep Lieu | 3976 | 2454R |
| Colorado06 | Jason Crow | White, lawyer, USArmy ranger, VA board | RepJasonCrow | RepJasonCrow | Email Rep Crow | 7882 | 1323L |
| Colorado08 | Gabe Evans | Hispanic, BA gov’t, USA, Nat’l Guard, Police Dept, state rep | RepGabeEvans | repgabeevans | Email Rep Evans | 5625 | 1229L |
| Florida02 | Neal Dunn | White, MD, surgeon, USArmy Panama City Urological Center and Surgery Center, bank founder | DrNealDunnFL2/ | DrNealDunnFL2 | Email Rep Dunn | 5235 | 466C |
| Florida13 | Anna Paulina Luna | Hispanic, BS biology, USAF | realAnnaPaulina | RepLuna | Email Rep Luna | 5961 | 226C |
| Florida17 | Greg Steube | White, lawyer, USA JAG, father is sheriff; state rep, state sen | RepGregSteube/ | RepGregSteube | Email Rep Stuebe | 5792 | 2457R |
| Florida18 | Scott Franklin | White, USN, MBA, CEO insurance Co | RepFranklin | RepFranklin | Email Rep Franklin | 1252 | 2301R |
| Florida21 | Brian Mast | Hispanic, BLA, USArmy bilateral amputee, Homeland Security | RepBrianMast | BrianMastFL | Email Rep Mast | 3026 | 2182R |
| Florida7 | Cory Mills | White, BS health sciences, USA | (5) U.S. Representative Cory Mills | Washington D.C. DC | Facebook | RepMillsPress | Email Rep Mills | 4035 | 346C |
| Georgia02 | Sanford Bishop | Black, lawyer, USArmy, state rep, state sen, lymphoma survivor, | sanfordbishop | SanfordBishop | Email Rep Bishop | 3631 | 2407R |
| Georgia07 | Rich McCormick | White, physician (ER), USMC, USN | (8) Representative Rich McCormick | Facebook | RepMcCormick | Email Rep McCormick | 4272 | 1719L |
| Georgia09 | Andrew Clyde | White, MBA, USN, Won civil asset forfeiture by IRS, Clyde-Hirsch-Sowers RESPECT Act limiting seizures | Representative Clyde | Rep_Clyde | Email Rep Clyde | 9893 | 445C |
| Illinois12 | Mike Bost | White, firefighter, USMC, owner Beauty Salon, state rep | RepBost | RepBost | Email Rep Bost | 5661 | 352C |
| Indiana04 | Jim Baird | White, PhD, USA, state rep | RepJimBaird | RepJimBaird | Email Rep Baird | 5037 | 2303R |
| Iowa01 | Mariannette Miller-Meeks | White, physician, USA, state sen. | RepMMM | repMMM | Email Rep Miller-Meeks | 6576 | 504C |
| Iowa03 | Zach Nunn | White, MS Inter Relat, USAF, Nat’l Guard, state sen, state rep | RepZachNunn | RepZachNunn | Email Rep Nunn | 5476 | 1410L |
| Kentucky02 | Brett Guthrie | M Public Mgmt, USArmy, VP auto parts co., state sen | CongressmanGuthrie/ | RepGuthrie | Email Rep Guthrie | 3501 | 2161R |
| Kentucky05 | Hal Rogers | White, lawyer, USANG, Commonwealth Attorney | CongressmanHalRogers/ | RepHalRogers | Email Rep Rogers | 4601 | 2406 R |
| Louisiana03 | Clay Higgins | White, USANG, manager car dealerships, City Police officer, Dep Marshall | CongressmanClayHiggins | RepClayHiggins | Email Rep Higgins | 2031 | 572C |
| Maine02 | Jared Golden | White, BA, USMC, state rep | RepGolden | RepGolden | Email Rep Golden | 6306 | 1107L |
| Maryland01 | Andy Harris | White, MD-anesthesiology (father immigrant MD anes from Hungary), USN, state sen | AndyHarrisMD | RepAndyHarrisMD | Email Rep Harris | 5311 | 1536L |
| Massachusetts04 | Jake Auchincloss | White, Jewish, USMC, father Dr. Fauci’s deputy | RepAuchincloss | RepAuchincloss | Email Rep Auchincloss | 5931 | 1524L |
| Massachusetts06 | Seth Moulton | White, MPP, business, USMC | RepMoulton | RepMoulton | Email Rep Moulton | 8020 | 1126L |
| Michigan01 | Jack Bergman | White, MBA, USMC pilot | RepJackBergman/ | RepJackBergman | Email Rep Bergman | 4735 | 566C |
| Michigan07 | Tom Barrett | White, USA, BA poli sci, state sen, state rep | RepTomBarrett | RepTomBarrett | Email Rep Barrett | 4872 | 1232L |
| Michigan10 | John James | Black, MBA, USA | RepJohnJames | RepJames | Email Rep James | 4961 | 1519L |
| Mississippi01 | Trent Kelly | White, lawyer, DA, USANG | RepTrentKelly/ | RepTrentKelly | Email Rep Kelly | 4306 | 2243R |
| Montana01 | Ryan Zinke | White, MBA, MS, Navy Seal, US Sec Interior under Trump, state rep, | RepRyanZinke | RepRyanZinke | Email Rep Zinke | 5628 | 512C |
| Montana02 | Troy Downing | White, USAF, businessman, state auditor | reptroydowning | RepTroyDowning | Email Rep Downing | 3211 | 1529L |
| Nebraska02 | Don Bacon | White, MBA, USAF, Comm. Ramstein AFB, | RepDonBacon | RepDonBacon | Email Rep Bacon | 4155 | 2104R |
| Nevada02 | Mark Amodei | White, lawyer, USA, state rep, state sen | MarkAmodeiNV2 | MarkAmodeiNV2 | Email Rep Amodei | 6155 | 104C |
| New Jersey03 | Herb Conaway | Black, MD int med, lawyer, USAF med corps, state rep | Repherbconaway | RepHerbConaway | Email Rep Conaway | 4765 | 1022L |
| New Jersey11 | Mikie Sherrill | White, lawyer, USN helio pilot | RepMikieSherrill/ | RepSherrill | Email Rep Sherrill | 5034 | 1427L |
| New York01 | Nick LaLota | White, lawyer, USN | replalota | RepLaLota | Email Rep LaLota | 3826 | 122C |
| New York18 | Pat Ryan | White, MA, USA, businessman | RepPatRyan | RepPatRyanNY | Email Rep Ryan | 5614 | 1708L |
| North Carolina01 | Don Davis | Black, EdD, USAF, state sen | RepDonDavis | RepDonDavis | Email Rep Davis | 3101 | 1123L |
| North Carolina10 | Pat Harrigan | White, USArmy, BS nuclear engineering | RepPatHarrigan | RepPatHarrigan | Email Rep Harrigan | 2576 | 1233L |
| Ohio07 | Max Miller | White, BA, USMC, aide to Pres. Trump | CongressmanMaxMiller | RepMaxMiller | Email Rep Max Miller | 3876 | 143C |
| Ohio08 | Warren Davidson | White, MBA, USA | CongressmanWarrenDavidson | WarrenDavidson | Email Rep Davidson | 6205 | 2113R |
| Ohio15 | Mike Carey | White, BA economics, history, USANG | RepMikeCarey | RepMikeCarey | Email Rep Carey | 2015 | 1433L |
| Pennsylvania06 | Chrissy Houlahan | M Tech & Policy, USAF, business CEO | RepChrissyHoulahan/ | RepHoulahan | Email Rep Houlahan | 4315 | 1727L |
| Pennsylvania10 | Scott Perry | White, MS strategic planning, USArmy, state rep | repscottperry | RepScottPerry | Email Rep Perry | 5836 | 2160R |
| Pennsylvania14 | Guy Reschenthaler | White, lawyer, USN JAG, District Judge | Greschenthaler | GReschenthaler | Email Rep Reschenthaler | 2065 | 2209R |
| Pennsylvania17 | Chris Deluzio | White, lawyer, USN | RepChrisDeluzio | RepDeluzio | Email Rep Deluzio | 2301 | 1222L |
| South Carolina02 | Joe Wilson | White, lawyer-real estate, USAR, Judge Advocate in NG, municipal judge, state sen | JoeWilson | RepJoeWilson | Email Rep Wilson | 2452 | 1436L |
| South Carolina03 | Sheri Biggs | White, nurse practitioner, air nat’l guard | RepSheriBiggs | RepSheriBiggs | Email Rep Biggs | 5301 | 1530L |
| South Carolina04 | William Timmons | White, lawyer-prosecutor, small business owner, Army NG, state sen | RepTimmons/ | reptimmons | Email Rep Timmons | 6030 | 267C |
| Tennessee07 | Mark Green | White, MD, USArmy, state sen | RepMarkGreenTN/ | RepMarkGreen | Email Rep Green | 2811 | 2446R |
| Texas02 | Dan Crenshaw | White, MPA, USN medically retired–lost eye | RepDanCrenshaw/ | RepDanCrenshaw | Email Rep Crenshaw | 6565 | 248C |
| Texas03 | Keith Self | White, MA, USA, county judge | RepKeithSelf | RepKeithSelf | Email Rep Self | 4201 | 1030L |
| Texas04 | Pat Fallon | Catholic, businessman, USAF, St. sen, St. rep | RepPatFallon | RepPatFallon | Email Rep Fallon | 6673 | 2416R |
| Texas06 | Jake Ellzey | White, BS, USN, airline pilot, state rep | RepJakeEllzey | RepEllzey | Email Rep Ellzey | 2002 | 1721L |
| Texas08 | Morgan Luttrell | White, MS applied cognition neuroscience. Professor, USN Seal | Congressman Morgan Luttrell | RepLuttrell | Email Rep Luttrell | 4901 | 444C |
| Texas11 | August Pfluger | White, USAF pilot, Nat’l security Council | RepAugustPfluger | RepPfluger | Email Rep Pfluger | 3605 | 2202R |
| Texas13 | Ronny Jackson | White, physician, Chief Medical Advisor to Pres, USN | RepRonnyJackson | RepRonnyJackson | Email Rep Jackson | 3706 | 125C |
| Texas22 | Troy Nehls | White, Cty Sheriff, USAR, M. Criminal Justice. | RepTroyNehls/ | RepTroyNehls | Email Rep Nehls | 5951 | 1104L |
| Texas23 | Tony Gonzales | Hispanic, USN, | RepTonyGonzales | RepTonyGonzales | Email Rep Gonzalez | 4511 | 2239R |
| Texas36 | Brian Babin | White, dentist-UT, USAF | RepBrianBabin | RepBrianBabin | Email Rep Babin | 1555 | 2236R |
| Texas38 | Wesley Hunt | Black, MBA, MPA, USA, helicopter pilot | RepWesleyHunt/ | RepWesleyHunt | Email Rep Hunt | 5646 | 1520L |
| Virginia02 | Jen Kiggans | White, Geriatric nurse practitioner at Eastern VA med school, state sen, husband Navy pilot | repjenkiggans/ | RepJenKiggans | Email Rep Kiggans | 4215 | 152C |
| Virginia03 | Bobby Scott | Black, lawyer, USANG, USAR, state rep, state sen, | RepBobbyScott/ | BobbyScott | Email Rep Scott | 8351 | 2328R |
| Virginia05 | John McGuire | White, USN Seal, State sen, state rep, businessman | RepJohnMcGuire | RepJohnMcGuire | Email Rep McQuire | 4711 | 1013L |
| Virginia07 | Eugene Vindman | Ukranian, Jewish, lawyer, USA | CongressmanEugeneVindman | RepVindman | Email Rep Vindman | 2815 | 1005L |
| Wisconsin03 | Derrick Van Orden | White, US Navy Seal, businessman, actor | RepVanOrden | RepVanOrden | Email Rep Van Orden | 5506 | 1513L |
| Wisconsin05 | Scott Fitzgerald | White, USAR, St. sen, newspaper publisher | CongressmanScottFitzgerald | RepFitzgerald | Email Rep Fitzgerald | 5101 | 2444R |
Activists
Legislators who have a history of activism in some area:
| State, district | Name | Party | 1st term | Characteristics | X | Phone 202-225- | ||
| Alabama06 | Gary Palmer | R | 2015 | White, BA operations mgmt, Ala Policy Institute think tank founder | CongressmanGaryPalmer/ | USRepGaryPalmer | Email Rep Palmer | 4921 |
| California02 | Jared Huffman | D | 2013 | White, lawyer, public interest, state rep | RepHuffman/ | RepHuffman | Email Rep Huffman | 5161 |
| California17 | Ro Khanna | D | 2017 | India, lawyer, professor, Dept of Commerce, pro bono legal activity | RepRoKhanna/ | RepRoKhanna | Email Rep Khanna | 2631 |
| Colorado01 | Diana DeGette | D | 1997 | White, lawyer-civil rights, state rep | DianaDeGette | RepDianaDeGette | Email Rep DeGette | 4431 |
| Colorado07 | Brittany Pettersen | D | 2023 | White, BA poli sci, non-profit political advocacy group, state sen, state rep | RepBrittanyPettersen | RepPettersen | Email Rep Pettersen | 2645 |
| D.C. | Eleanor Holmes Norton | 1991 | Black, lawyer, civil rights movement, | CongresswomanNorton | EleanorNorton | Email Rep Norton | 8050 | |
| Florida10 | Maxwell Frost | D | 2023 | Hispanic/Black Haiti, civil liberty activist | RepMaxwellFrost | RepMaxwellFrost | Email Rep Frost | 2176 |
| Illinois01 | Jonathan Jackson | D | 2023 | Black, son of Jesse Jackson, MBA, human rights activist | rep_jackson | Email Rep Jackson | 4372 | |
| Illinois06 | Sean Casten | D | 2019 | M. Engineering, scientist at Tufts Sch of Med. Civic advocate. | RepSeanCasten/ | RepCasten | Email Rep Casten | 4561 |
| Louisiana04 | Mike Johnson | R | 2017 | White, lawyer-constitutional, non-profit Alliance Defending Freedom, talk radio host, state rep | RepMikeJohnson/ | RepMikeJohnson | Email Rep Johnson | 2777 |
| Maine01 | Chellie Pingree | D | 2009 | White, BS Human ecology, knitting business, leader of Common Cause, state sen | ChelliePingree/ | chelliepingree | Email Rep Pingree | 6116 |
| Maryland07 | Kweisi Mfume | D | 2020 | Black, US rep, Pres NAACP, Baltimore City Council, past Chair Black Caucus | RepKweisiMfume | RepKweisiMfume | Email Rep Mfume | 4741 |
| Maryland08 | Jamie Raskin | D | 2017 | Jewish, lawyer, professor constitutional law, state sen | RepRaskin | RepRaskin | Email Rep Raskin | 5341 |
| Massachusetts08 | Stephen Lynch | D | 2001 | White, iron worker, lawyer, pro bono, state rep, state sen | repstephenlynch/ | RepStephenLynch | Email Rep Lynch | 8273 |
| Minnesota07 | Michelle Fischbach | R | 2021 | White, lawyer, st. lt. gov, st. Sen, Catholic, husband runs Minnesota Citizens Concerned for Life. | RepFischbach | RepFischbach | Email Rep Fischbach | 2165 |
| Nebraska01 | Mike Flood | R | 2022 | White, lawyer, owns 15 radio stations and 7 TV stations, state rep | RepMikeFlood | USRepMikeFlood | Email Rep Flood | 4806 |
| New Mexico03 | Teresa Leger Fernandez | D | 2021 | White or hispanic, lawyer in community development, civil rights, social justice | RepTeresaLF | RepTeresaLF | Email Rep Fernandez | 6190 |
| North Carolina03 | Greg Murphy | R | 2019 | White, MD-urology, medical mission work, state rep | RepGregMurphy/ | RepGregMurphy | Email Rep Murphy | 3415 |
| Oregon01 | Suzanne Bonamici | D | 2012 | White, Jewish, lawyer, consumer protection, FTC, state rep, state sen | CongresswomanBonamici | RepBonamici | Email Rep Bonamici | O855 |
| Pennsylvania03 | Dwight Evans | D | 2016 | Black, BA, teacher, community activist, Urban League, state rep | RepDwightEvans/ | RepDwightEvans | Email Rep Evans | 4001 |
| Pennsylvania04 | Madeleine Dean | D | 2019 | White, lawyer, professor, writer, journalist, state rep | RepMadeleineDean | RepDean | Email Rep Dean | 4731 |
| Pennsylvania05 | Mary Gay Scanlon | D | 2018 | White, lawyer-Public interest, | RepMGS/ | RepMGS | Email Rep Scanlon | 2011 |
| South Carolina06 | Jim Clyburn | D | 1993 | Black, BA history, teacher, ancestors fought racism | RepJamesClyburn | RepJamesClyburn | Email Rep Clyburn | 3315 |
| Tennessee01 | Diana Harshbarger | R | 2021 | Pharmacist, compounding pharmacy, focus: fixing opioid crisis | RepDianaHarshbarger | RepHarshbarger | Email Rep Harshbarger | 6356 |
| Texas20 | Joaquin Castro | D | 2013 | Hispanic, lawyer-health care, San Antonio, parent taught at Edgewood, state rep | JoaquinCastroTX/ | JoaquinCastrotx | Email Rep Castro | 3236 |
| Texas21 | Chip Roy | R | 2019 | White, lawyer, US Attorney, ghostwriter for Rick Perry’s book Fed Up | RepChipRoyPress/ | RepChipRoy | Email Rep Roy | 4236 |
| Texas30 | Jasmine Crockett | D | 2023 | Black, lawyer, civil rights attorney, state rep | RepJasmine | RepJasmine | Email Rep Crockett | 8885 |
| Utah04 | Burgess Owens | R | 2021 | Black, football, non-profit exec for troubled & incarcerated youth | CongressmanBurgessOwens/ | RepBurgessOwens | Email Rep Owens | 3011 |
| Washington07 | Pramila Jayapal | D | 2017 | India, MBA, civil rights activist, state sen | RepJayapal/ | RepJayapal | Email Rep Jayapal | 3106 |
New Members
Legislators who are new to Congress:
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Room | Phone (202)-225- | |||
| Alabama02 | Shomari Figures | Black, JD, worked for Loretta Lynch, Merrick Garland. | congressman.shomari.figures | repscfigures | Email Rep Figures | 225C | 4931 |
| Alaska01 | Nick Begich III | White, MBA, owns software dev co | RepNickBegich | RepNickBegich | Email Rep Begich | 153C | 5765 |
| Arizona03 | Yassamin Ansari | Iranian American, M Intern’l relat. | repyassansari | RepYassAnsari | Email Yassamin Ansari | 1432L | 4065 |
| Arizona07 | Adelita Grijalva | Hispanic, BA poli sci | repadelitasgrijalva | rep_grijalva | Not available | 1203L | 2435 |
| Arizona08 | Abraham Hamadeh | Syrian American, JD, prosecutor, USA | RepAbeHamadeh | AbrahamHamadeh | Email Rep Hamadeh | 1722L | 4576 |
| California12 | Lateefah Simon | Black, M Pub Admin | replsimon | RepLSimon | Email Rep Simon | 1023L | 2661 |
| California13 | Adam Gray | White, BA poli sci, state rep, | repadamgrayca | RepAdamGrayCA | Email Rep Gray | 1230L | 1947 |
| California16 | Sam Liccardo | White, JD, prosecutor, Mayor | repliccardo | RepLiccardo | Email Rep Liccardo | 1117L | 8104 |
| California20 | Vince Fong | Chinese American, MPA, state rep, | RepVinceFong# | RepVinceFong | Email Rep Fong | 243C | 2915 |
| California27 | George Whitesides | White, NASA chief of staff, Mphil, CEO Virgin Galactic | RepWhitesides | Rep_Whitesides | Email Rep Whitesides | 1504L | 1956 |
| California29 | Luz Rivas | Hispanic, BS electrical engineer, Med, state rep | congresswomanluzrivas | RepLuzRivas | Email Rep Rivas | 1319L | 6131 |
| California30 | Laura Friedman | Jewish, BA, state rep, Hollywood producer | RepLauraFriedman | RepFriedmanCA | Email Rep Friedman | 1517L | 4176 |
| California31 | Gil Cisneros | Hispanic, USN, MBA | RepGilCisneros | RepGilCisneros | Email Rep Cisneros | 2463R | 5256 |
| California45 | Derek Tran | Vietnamese, USA, lawyer | CongressmanTran | RepDerekTranCA | Email Rep Tran | 1127L | 2415 |
| California47 | Dave Min | Korean, lawyer, state sen | thecongressmin | CongressMin | Email Rep Min | 1034L | 5611 |
| Colorado03 | Jeff Hurd | White, lawyer | RepJeffHurd# | RepJeffHurd | Email Rep Hurd | 1641L | 4676 |
| Colorado05 | Jeff Crank | White, radio show host, BA Poli sci, | RepJeffCrank | RepJeffCrank | Email Rep Crank | 1029L | 4422 |
| Colorado08 | Gabe Evans | Hispanic, BA gov’t, USA, Nat’l Guard, Police Dept, state rep | RepGabeEvans | repgabeevans | Email Rep Evans | 1229L | 5625 |
| Delaware | Sarah McBride | White, trans, political activist | CongresswomanSarahMcBride | Rep_McBride | Email Rep McBride | 1306L | 4165 |
| Florida01 | Jimmy Patronis | White, BS poli sci | PatronisFL/ | PatronisFL | Email Rep Patronis | 2021R | 4136 |
| Florida06 | Randy Fine | White, Jewish, state sen, MBA | RepFine/ | RepFine | Email Rep Fine | 244C | 2706 |
| Florida8 | Mike Haridopolos | White, MA history, teacher, state sen, state rep | Mike Haridopolos | RepHaridopolos | Email Rep Haridopolos | 1039L | 3671 |
| Georgia03 | Brian Jack | White, BA, political advisor to Pres Trump | RepBrianJack | RepBrianJack | Email Rep Jack | 1320L | 5901 |
| Indiana03 | Marlin Stutzman | White, farmer, state sen, state rep | repstutzman | RepStutzman | Email Rep Stutzman | 404C | 4436 |
| Indiana06 | Jefferson Shreve | White, MBA, businessman, city council | RepJeffersonShreve | RepShreve | Email Rep Shreve | ||
| Indiana08 | Mark Messmer | White, BS, state sen, state rep | CongressmanMessmer | RepMessmer | Email Rep Messmer | 1208L | 4636 |
| Kansas02 | Derek Schmidt | White, state AG, lawyer, state sen | repderekschmidt | RepDerekSchmidt | Email Rep Schmidt | 1223L | 6601 |
| Louisiana06 | Cleo Fields | Black, lawyer, state sen | Congressman-Cleo-Fields | RepFields | Email Rep Fields | 2349R | 2349 |
| Maryland02 | Johnny Olszewski | White, PhD, BS poli sci, state rep | RepJohnnyOlszewski | RepJohnnyO | Email Rep Olszewski | 1339L | 3061 |
| Maryland03 | Sarah Elfreth | White, M Pub Policy, state sen | RepSarahElfreth/ | RepSarahElfreth | Email Rep Elfreth | 1213L | 4016 |
| Maryland06 | April McClain-Delaney | White, lawyer, wife of John Delaney | RepAprilDelaney | RepAprilDelaney | Email Rep McClain-Delaney | 1130L | 2721 |
| Michigan07 | Tom Barrett | White, USA, BA poli sci, state sen, state rep | RepTomBarrett | RepTomBarrett | Email Rep Barrett | 1232L | 4872 |
| Michigan08 | Kristen McDonald Rivet | White, MPA, state sen | repmcdonaldrivet | repkmr | Email Rep McDonald-Rivet | 1408L | 3611 |
| Minnesota03 | Kelly Morrison | White, physician OB-GYN, state sen, state rep | repkellymorrison | KellyMorrisonMN | Email Rep Morrison | 1205L | 2871 |
| Missouri01 | Wesley Bell | Black, lawyer, prosecuting attorney father police officer | repwesleybell | RepWesleyBellMO | Email Rep Bell | 1429L | 2406 |
| Missouri03 | Bob Onder | White, physician-allergy, asthma, lawyer, state sen, state rep | RepBRepBobOnderobOnder | RepBobOnder | Email Rep Onder | 1113L | 2956 |
| Montana02 | Troy Downing | White, USAF, businessman, state auditor | reptroydowning | RepTroyDowning | Email Rep Downing | 1529L | 3211 |
| New Hampshire02 | Maggie Goodlander | White, lawyer USDoJ, USN res, | RepGoodlander/ | RepGoodlander | Email Rep Goodlander | 223C | 5206 |
| New Jersey03 | Herb Conaway | Black, MD int med, lawyer, USAF med corps, state rep | Repherbconaway | RepHerbConaway | Email Rep Conaway | 1022L | 4765 |
| New Jersey09 | Nellie Pou | Hispanic, state sen, state rep | CongresswomanNelliePou | RepNellie | Email Rep Pou | 1007L | 5751 |
| New Jersey10 | LaMonica McIver | Black, MA, Town Council | DonaldPayneJr | RepDonaldPayne | Email Rep Payne | 426C | 3436 |
| New York04 | Laura Gillen | White, lawyer, law school professor | replauragillen | RepLauraGillen | Email Rep Gillen | 428C | 5516 |
| New York16 | George Latimer | White, MPA, state sen, state rep | RepGLatimer | RepGLatimer | Email Rep Latimer | 1507L | 2464 |
| New York19 | Josh Riley | White, lawyer, | RepRileyNY | RepRileyNY | Email Rep Riley | 128C | 5441 |
| New York22 | John Mannion | White, MS sci ed, teacher, state sen | CongressmanJohnMannion | JohnMannionNY22 | Email Rep Mannion | 1516L | 3701 |
| North Carolina06 | Addison McDowell | White, BA, BCBS lobbyist, brother died from fentanyl overdose | RepMcDowell | RepMcDowell | Email Rep McDowell | 1032L | 3065 |
| North Carolina08 | Mark Harris | White, pastor, BA poli sci | RepMarkHarris | RepMarkHarrisNC | Email Rep Harris | 126C | 1976 |
| North Carolina10 | Pat Harrigan | White, USArmy, BS nuclear engineering | RepPatHarrigan | RepPatHarrigan | Email Rep Harrigan | 1233L | 2576 |
| North Carolina13 | Brad Knott | White, lawyer, father USAttorney, | RepKnott | RepKnott | Email Rep Knott | 1239L | 4531 |
| North Carolina14 | Tim Moore | White, lawyer, state rep | CongressmanTimMoore | RepTimMooreNC | Email Rep Moore | 1424L | 5634 |
| North Dakota AL | Julie Fedorchak | White, BA journalism | RepJulieFedorchak | RepFedorchak | Email Rep Fedorchak | 1607L | 2611 |
| Ohio02 | David Taylor | White, lawyer, prosecutor, concrete business | RepDaveTaylor | RepDaveTaylor | Email Rep Taylor | 325C | 3164 |
| Oregon03 | Maxine Dexter | White, MD, pulmonologist, state rep | RepDexterOR | RepDexterOR | Email Rep Dexter | 1207L | 4811 |
| Oregon05 | Janelle Bynum | Black, state rep, MBA, businesswoman | repbynum | RepBynum | Email Rep Bynum | 1508L | 5711 |
| Pennsylvania07 | Ryan Mackenzie | White, MBA, state rep, | RepMackenzie | RepMackenzie | Email Rep Mackensie | 121C | 5411 |
| Pennsylvania08 | Rob Bresnahan | RepBresnahan | RepBresnahan | Email Rep Bresnahan | 1133L | 5546 | |
| Puerto Rico | Pablo Hernandez Rivera | Hispanic, lawyer | RepHernandez | RepPabloJose | Email Rep Hernandez | 1419L | 2615 |
| South Carolina03 | Sheri Biggs | White, nurse practitioner, air nat’l guard | RepSheriBiggs | RepSheriBiggs | Email Rep Biggs | 1530L | 5301 |
| Tennessee07 | Matt Van Epps | White, MPA, USArmy | RepVanEpps | repvanepps | Email Rep Van Epp | 2446R | 2811 |
| Texas12 | Craig Goldman | White, Jewish, BA Poli sci, real estate | RepCraigGoldman | RepCraigGoldman | Email Rep Goldman | 1716L | 5071 |
| Texas26 | Brandon Gill | White, investment banker, extreme Trumpster | RepBrandonGill | RepBrandonGill | Email Rep Gill | 1305L | 7772 |
| Texas32 | Julie Johnson | White, lawyer, state rep, lesbian (married) | RepJulieJohnson | RepJulieJohnson | Email Rep Johnson | 221C | 2231 |
| Utah03 | Mike Kennedy | White, MD, Morman, lawyer, state sen, state rep | RepMikeKennedy | RepMikeKennedy | Email Rep Kennedy | 1626L | 7751 |
| Virginia05 | John McGuire | White, USN Seal, State sen, state rep, businessman | RepJohnMcGuire | RepJohnMcGuire | Email Rep McQuire | 1013L | 4711 |
| Virginia07 | Eugene Vindman | Ukranian, Jewish, lawyer, USA | CongressmanEugeneVindman | RepVindman | Email Rep Vindman | 1005L | 2815 |
| Virginia10 | Suhas Subramanyam | India, Hindu, lawyer, state sen, state rep | RepSuhasSubramanyam/ | RepSuhas | Email Rep Subramanyam | 1009L | 5136 |
| Virginia11 | James Walkinshaw | White, BA politics | RepJamesWalkinshaw/ | Rep_Walkinshaw | Email Rep Walkinshaw | 2265R | 1492 |
| Washington05 | Michael Baumgartner | White, state sen, MAPub Admin, | RepBaumgartner | RepBaumgartner | Email Rep Baumgartner | 124C | 2006 |
| Washington06 | Emily Randall | Hispanic, sister with disability, state sen, LGBTQ, no religion | RepEmilyRandall | Email Rep Randall | 1531L | 5916 | |
| West Virginia02 | Riley Moore | White, WV Treas, state rep, Catholic, aunt Shelley Moore Capito, welder | Congressman-Riley-M-Moore | RepRileyMoore | Email Rep Moore | 1337L | 2711 |
| Wisconsin08 | Tony Wied | White, BA, businessman | RepMikeGallagher | RepGallagher | Email Rep Wied | 424C | 5665 |
Long-Term Members (1980-2005)
-Legislators who have served in Congress for 20+ years (1980-2005)
Before 1997
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Phone | Room | |||
| California11 | Nancy Pelosi | White, Catholic, BA poli Sci, | NancyPelosi/ | SpeakerPelosi | Email Rep Pelosi | 4965 | 1236L |
| California18 | Zoe Lofgren | White, lawyer, | zoelofgren/ | RepZoeLofgren | Email Rep Lofgren | 3072 | 1401L |
| California41 | Ken Calvert | White, BA, restauranteur, real estate | RepKenCalvert/ | KenCalvert | Email Rep Calvert | 1986 | 2205R |
| California43 | Maxine Waters | Black, BA Sociology, state rep | MaxineWaters | RepMaxineWaters | Email Rep Waters | 2201 | 2221R |
| Connecticut3 | Rosa DeLauro | White, MA Economics | CongresswomanRosaDeLauro | Rosa_DeLauro | Email Rep DeLauro | 3661 | 2413R |
| D.C. | Eleanor Holmes Norton | Black, lawyer, civil rights movement, | CongresswomanNorton | EleanorNorton | Email Rep Norton | 8050 | 2136R |
| Georgia02 | Sanford Bishop | Black, lawyer, USArmy, state rep, state sen, lymphoma survivor, | sanfordbishop | SanfordBishop | Email Rep Bishop | 3631 | 2407R |
| Kentucky05 | Hal Rogers | White, lawyer, USANG, Commonwealth Attorney | CongressmanHalRogers/ | RepHalRogers | Email Rep Rogers | 4601 | 2406 R |
| Maryland05 | Steny Hoyer | White, lawyer, state sen, | RepStenyHoyer | RepStenyHoyer | Email Rep Hoyer | 4131 | 1705L |
| Massachusetts01 | Richard Neal | White, Mpub Admin, history teacher, Mayor, | reprichardneal/ | RepRichardNeal | Email Rep Neal | 5601 | 372C |
| Mississippi02 | Bennie Thompson | Black, BA poli sci, MS educ admin, mayor, | CongressmanBennieGThompson/ | BennieGThompson | Email Rep Thompson | 5876 | 2466R |
| New Jersey04 | Chris Smith | White, BS | RepChrisSmith/ | ChrisSmithNJCD4 | Email Rep Smith | 3765 | 2373R |
| New Jersey06 | Frank Pallone | White, lawyer, state sen, | RepFrankPallone/ | FrankPallone | Email Rep Pallone | 4671 | 2107R |
| New York07 | Nydia Velazquez | Hispanic, MA poli sci, teacher, city council | RepNydiaVelazquez/ | NydiaVelazquez | Email Rep Velazquez | 2361 | 2302R |
| New York12 | Jerrold Nadler | White, Jewish, lawyer, state rep | CongressmanNadler | RepJerryNadler | Email Rep Nadler | 5635 | 2132R |
| Ohio09 | Marcy Kaptur | White, M Urban Planning | RepMarcyKaptur/ | RepMarcyKaptur | Email Rep Kaptur | 4146 | 2314R |
| Oklahoma03 | Frank Lucas | White, BS, farmer | RepFrankLucas | RepFrankLucas | Email Rep Lucas | 5565 | 2405R |
| South Carolina06 | Jim Clyburn | Black, BA history, teacher, ancestors fought racism | RepJamesClyburn | RepJamesClyburn | Email Rep Clyburn | 3315 | 274C |
| Texas37 | Lloyd Doggett | White, lawyer, UT, state sen, State SC justice, | RepLloydDoggett/ | RepLloydDoggett | Email Rep Doggett | 4865 | 2307R |
| Virginia03 | Bobby Scott | Black, lawyer, USANG, USAR, state rep, state sen, | RepBobbyScott/ | BobbyScott | Email Rep Scott | 8351 | 2328R |
1997-2005
| State, District | Name | Characteristics | Phone | Room | |||
| Alabama03 | Mike Rogers | White, lawyer, state rep, poli sci and pub admin | CongressmanMikeDRogers/ | RepMikeRogersAL | Email Rep Rogers | 3261 | 2469R |
| Alabama04 | Robert Aderholt | White tea party conservative, lawyer, judge | RobertAderholt | Robert_Aderholt | Email Rep Aderholt | 4876 | 272C |
| Arizona07 | Raul Grijalva | Hispanic, sociology, school board, | peopleforgrijalva | RepRaulGrijalva | Email Rep Grijalva | 2435 | 1203L |
| California04 | Mike Thompson | White, Mpub Admin, USArmy, state sen | RepMikeThompson/ | RepThompson | Email Rep Thompson | 3311 | 268C |
| California07 | Doris Matsui | Asian, BA psych, took husband’s seat | doris.matsui/ | DorisMatsui | Email Rep Matsui | 7163 | 2206R |
| California21 | Jim Costa | White, BA, farmer, state rep, state sen | RepJimCosta/ | RepJimCosta | Email Rep Costa | 3341 | 2081R |
| California32 | Brad Sherman | White, Jewish, lawyer-tax, CPA | CongressmanBradSherman/ | BradSherman | Email Rep Sherman | 5911 | 2365R |
| California38 | Linda Sanchez | Hispanic, lawyer-labor, | RepLindaSanchez/ | RepLindaSanchez | Email Rep Sanchez | 6676 | 2428R |
| California48 | Darrell Issa | White, Lebanese background, businessman, US Rep 2001-2019 | congressmandarrellissa | repdarrellissa | Email Rep Issa | 5672 | 2108R |
| Colorado01 | Diana DeGette | White, lawyer-civil rights, state rep | DianaDeGette | RepDianaDeGette | Email Rep DeGette | 4431 | 2111R |
| Connecticut1 | John Larson | White, BA, history teacher, owner insurance agency, state sen | RepJohnLarson | RepJohnLarson | Email Rep Larson | 2265 | 1501L |
| Florida25 | Debbie Wasserman Schultz | White, Jewish, MA poli sci; brother USA for DC; state rep, state sen, chair Dem Nat’l Comm, breast CA survivor | RepDWS | RepDWStweets | Email Rep Schultz | 7931 | 270C |
| Florida26 | Mario Diaz-Balart | Hispanic, BA poli sci, state rep, state sen | mdiazbalart | MarioDB | Email Rep Diaz-Balart | 4211 | 374C |
| Georgia13 | David Scott | Black, MBA, state rep, state sen, | RepDavidScott/ | repdavidscott | Email Rep Scott | 2939 | 468C |
| Idaho02 | Mike Simpson | White, dentist, state rep | RepMikeSimpson | CongMikeSimpson | Email Rep Simpson | 5531 | 2084R |
| Illinois07 | Danny Davis | Black, PhD Public Admin. City Council, Board of Commissioners. | OfficialRepDannyDavis/ | RepDannyDavis | Email Rep Davis | 5006 | 2159R |
| Illinois09 | Jan Schakowsky | Jewish, BS elem ed, | janschakowsky | RepSchakowsky | Email Rep Schakowsky | 2111 | 2408R |
| Massachusetts02 | James McGovern | White, Mpub Admin, | RepJimMcGovern/ | RepMcGovern | Email Rep McGovern | 6101 | 370C |
| Massachusetts08 | Stephen Lynch | White, iron worker, lawyer, pro bono, state rep, state sen | repstephenlynch/ | RepStephenLynch | Email Rep Lynch | 8273 | 2109R |
| Minnesota04 | Betty McCollum | White, BA, teacher, sales manager, state rep | repbettymccollum/ | BettyMcCollum04 | Email Rep McCollum | 6631 | 2426R |
| Missouri05 | Emanuel Cleaver | Black, Mdiv, pastor, Mayor | emanuelcleaverii/ | repcleaver | Email Rep Cleaver | 4535 | 2217R |
| Missouri06 | Sam Graves | White, BS Agronomy, state rep, state sen | RepSamGraves/ | RepSamGraves | Email Rep Graves | 7041 | 1135L |
| New York05 | Gregory Meeks | Black, lawyer, Ass’t DA, NY Narcotics Prosecutor, state rep | RepGregoryMeeks/ | RepGregoryMeeks | Email Rep Meeks | 3461 | 2310R |
| North Carolina05 | Virginia Foxx | White, MA, EdD, landscaping business, state sen | RepVirginiaFoxx | virginiafoxx | Email Rep Foxx | 2071 | 2462R |
| Ohio10 | Mike Turner | White, MBA, lawyer, mayor | RepMikeTurner | RepMikeTurner | Email Rep Turner | 6465 | 2183R |
| Oklahoma04 | Tom Cole | Native Am, PhD British History, professor, Okla Sec of State | TomColeOK04 | TomColeOK04 | Email Rep Cole | 6165 | 2207R |
| Texas09 | Al Green | White, lawyer, Justice of Peace | repalgreen | RepAlGreen | Email Rep Green | 7508 | 2347R |
| Texas10 | Michael McCaul | White, lawyer, federal prosecutor, | michaeltmccaul | RepMcCaul | Email Rep McCaul | 2401 | 2300R |
| Texas17 | Pete Sessions | White, father FBI director | petesessions | PeteSessions | Email Rep Sessions | 6105 | 2204R |
| Texas28 | Henry Cuellar | Hispanic, lawyer, customs broker, professor, state rep, Sec of State of Texas, | repcuellar/ | RepCuellar | Email Rep Cuellar | 1640 | 2308R |
| Texas31 | John Carter | White, lawyer, UT, judge | judgecarter | JudgeCarter | Email Rep Carter | 3864 | 2208R |
| Washington02 | Rick Larsen | White, MPA, city director of development | RepRickLarsen | RepRickLarsen | Email Rep Larsen | 2605 | 2163R |
| Washington09 | Adam Smith | White, lawyer, state sen | RepAdamSmith | RepAdamSmith | Email Rep Smith | 8901 | 2264R |
| Wisconsin04 | Gwen Moore | Black, BA poli sci, civil service, state rep, state sen | GwenSMoore | RepGwenMoore | Email Rep Moore | 4572 | 2252R |
Groups of Senators
Medicine Connection
Medically connected legislators (the legislators that are connected to medicine, either through themselves, or a family member:
| State | Name | Information | Phone | |||
| Arkansas | John Boozman | White, optometrist for low-income families, advocate for drug policy issues, state rep | Email Sen. Boozman | JohnBoozman | JohnBoozman | 4843 |
| Kansas | Roger Marshall | White, MD, OB/Gyn, USA US Rep | Email Sen. Marshall | RogerMarshallMD | RogerMarshallMD | 4774 |
| Kentucky | Rand Paul | White, physician–ophthalmology | Email Sen. Paul | SenatorRandPaul/ | SenRandPaul | 4343 |
| Louisiana | Bill Cassidy, MD | White, physician-liver specialist, uninsured clinics, nonprofit Health Centers, US Rep, state sen | Email Sen. Cassidy | SenBillCassidy/ | SenBillCassidy | 5824 |
| Michigan | Elissa Slotkin | White, Jewish, US Rep, MA Intern’l Affairs, CIA, DoD, husband USA pilot, stepdaughter physician. | Email Sen. Slotkin | SenElissaSlotkin | SenatorSlotkin | 4822 |
| Ohio | Bernie Moreno | Hispanic, BA Bus Admin, father Columbian physician | Email Sen. Moreno | Sen. Bernie Moreno | berniemoreno | 2315 |
| Wyoming | John Barrasso | White, physician-orthopedics, state sen, | Email Sen. Barrasso | johnbarrasso | SenJohnBarrasso | 6441 |
Senators of Color
| State | Name | Information | Phone | |||
| Arizona | Ruben Gallego | Hispanic, US Rep, state rep, BA gov’t, USMC | Email Sen. Gallego | SenRubenGallego | SenRubenGallego | 4521 |
| California | Alex Padilla | Hispanic, BS, mech eng, Sec of State, State sen, city council | Email Sen. Padilla | SenAlexPadella/ | SenAlexPadilla | 3553 |
| Delaware | Lisa Blunt Rochester | Black, US Rep, MA public policy, CEO Urban League | Email Sen. Rochester | SenLBR | SenLBR | 2441 |
| Georgia | Raphael G. Warnock | Black, Mdiv, pastor, activist | Email Sen. Warnock | SenatorWarnock | SenatorWarnock | 3643 |
| Hawaii | Mazie Hirono | Asian, non-practicing Buddhist, Lawyer, State rep, Lt. Gov, US rep | Email Sen. Hirono | senatorhirono | maziehirono | 6361 |
| Illinois | Tammy Duckworth | Asian, MA int’l affairs, PhD human services, USA helio pilot, bilateral amputee, Dept Veterans Affairs, US Rep, | Email Sen. Duckworth | SenDuckworth | SenDuckworth | 2854 |
| Maryland | Angela Alsobrooks | Black, lawyer, State attorney | Email Senator Alsobrooks | SenatorAlsobrooks | Sen_Alsobrooks | 4524 |
| Nevada | Catherine Cortez Masto | Hispanic, Lawyer, At Gen, possible misconduct. Attacked Bank of America | Email Sen. Cortez Masto | SenatorCortezMasto/ | SenCortezMasto | 3542 |
| New Jersey | Andy Kim | Korean American, US Rep, MA | Email Sen. Kim | SenatorAndyKim | SenatorAndyKim | 4744 |
| New Jersey | Cory Booker | gloria_nunez@booker.senate.gov | anybody | SenatorCoryBooker | @SenBooker | 3224 |
| New Mexico | Ben Ray Lujan | Hispanic, US Rep, state public service | Email Sen. Lujan | SenatorLujan | SenatorLujan | 6621 |
| Ohio | Bernie Moreno | Hispanic, BA Bus Admin, father Columbian physician | Email Sen. Moreno | Sen. Bernie Moreno | berniemoreno | 2315 |
| South Carolina | Tim Scott | Black, BA Poli sci, Owner insurance agency, Charleston County Council, US Rep, state rep, | Email Sen. Scott | SenatorTimScott | SenatorTimScott | 6121 |
| Texas | Ted Cruz | Hispanic, Lawyer, Texas Solicitor General, Law professor | Email Sen. Cruz | SenatorTedCruz | SenTedCruz | 5922 |
Black Senators
| State | Name | Health Staff Email | Phone | |||
| Delaware | Lisa Blunt Rochester | Black, US Rep, MA public policy, CEO Urban League | Email Sen. Rochester | SenLBR | SenLBR | 2441 |
| Georgia | Raphael G. Warnock | Black, Mdiv, pastor, activist | Email Sen. Warnock | SenatorWarnock | SenatorWarnock | 3643 |
| Maryland | Angela Alsobrooks | Black, lawyer, State attorney | Email Senator Alsobrooks | SenatorAlsobrooks | Sen_Alsobrooks | 4524 |
| New Jersey | Cory Booker | gloria_nunez@booker.senate.gov | anybody | SenatorCoryBooker | @SenBooker | 3224 |
| South Carolina | Tim Scott | Black, BA Poli sci, Owner insurance agency, Charleston County Council, US Rep, state rep, | Email Sen. Scott | SenatorTimScott | SenatorTimScott | 6121 |
Hispanic Senators
| State | Name | Health Staff Email | Phone | |||
| California | Alex Padilla | Hispanic, BS, mech eng, Sec of State, State sen, city council | Email Sen. Padilla | SenAlexPadella/ | SenAlexPadilla | 3553 |
| Nevada | Catherine Cortez Masto | Hispanic, Lawyer, At Gen, possible misconduct. Attacked Bank of America | Email Sen. Cortez Masto | SenatorCortezMasto/ | SenCortezMasto | 3542 |
| New Mexico | Ben Ray Lujan | Hispanic, US Rep, state public service | Email Sen. Lujan | SenatorLujan | SenatorLujan | 6621 |
| Ohio | Bernie Moreno | Hispanic, BA Bus Admin, father Columbian physician | Email Sen. Moreno | Sen. Bernie Moreno | berniemoreno | 2315 |
| Texas | Ted Cruz | Hispanic, Lawyer, Texas Solicitor General, Law professor | Email Sen. Cruz | SenatorTedCruz | SenTedCruz | 5922 |
Asian Senators
| Hawaii | Mazie Hirono | Asian, non-practicing Buddhist, Lawyer, State rep, Lt. Gov, US rep | Email Sen. Hirono | senatorhirono | maziehirono | 6361 |
| Illinois | Tammy Duckworth | Asian, MA int’l affairs, PhD human services, USA helio pilot, bilateral amputee, Dept Veterans Affairs, US Rep, | Email Sen. Duckworth | SenDuckworth | SenDuckworth | 2854 |
Veterans
Senators who have served in the armed forces:
| State | Name | Health Staff Email | Phone | |||
| Alaska | Dan Sullivan | White, USMC, lawyer, Attorney General | Email Sen. Sullivan | SenDanSullivan | SenDanSullivan | 3004 |
| Arizona | Mark Kelly | White, astronaut, USN, husband of Gabby Giffords, | Email Sen. Kelly | SenMarkKelly | SenMarkKelly | 2235 |
| Arizona | Ruben Gallego | Hispanic, US Rep, state rep, BA gov’t, USMC | Email Sen. Gallego | SenRubenGallego | SenRubenGallego | 4521 |
| Arkansas | Tom Cotton | White, lawyer, USA, rancher | Email Sen. Cotton | SenatorTomCotton | SenTomCotton | 2353 |
| Connecticut | Richard Blumenthal | White, Jewish, USMR, Lawyer, US Attorney, state Attorney General, state sen, state rep, US Attorney | Email Sen. Blumenthal | SenBlumenthal | SenBlumenthal | 2823 |
| Florida | Rick Scott | jared_honts@rickscott.senate.gov | anybody | RickScottSenOffice/ | @SenRickScott | 5274 |
| Illinois | Tammy Duckworth | Asian, MA int’l affairs, PhD human services, USA helio pilot, bilateral amputee, Dept Veterans Affairs, US Rep, | Email Sen. Duckworth | SenDuckworth | SenDuckworth | 2854 |
| Indiana | Jim Banks | White, MBA, Real estate and construction, USNR, County Council, state sen | Email Senator Banks | SenatorJimBanks | SenatorBanks | 4814 |
| Indiana | Todd Young | White, lawyer, USMC, business, US rep | Email Sen. Young | SenatorToddYoung | SenToddYoung | 5623 |
| Iowa | Joni Ernst | White, BA psych, MPubAdmin, USANG, State Sen | Email Sen. Ernst | senjoniernst | SenJoniErnst | 3254 |
| Kansas | Roger Marshall | White, MD, OB/Gyn, USA US Rep | Email Sen. Marshall | RogerMarshallMD | RogerMarshallMD | 4774 |
| Massachusetts | Ed Markey | White, lawyer, USAR, US Rep, state rep, liberal, focus on energy policy | Email Sen. Markey | EdJMarkey | SenMarkey | 2742 |
| Michigan | Elissa Slotkin | White, Jewish, US Rep, MA Intern’l Affairs, CIA, DoD, husband USA pilot, stepdaughter physician. | Email Sen. Slotkin | SenElissaSlotkin | SenatorSlotkin | 4822 |
| Michigan | Gary Peters | White, lawyer, MBA, USNR, investment advisor, Asst VP at Merrill Lynch, then Paine Webber VP, US rep | Email Sen. Peters | SenGaryPeters | SenGaryPeters | 6221 |
| Mississippi | Roger F. Wicker | White, lawyer, USAF, US Rep, state Sen, | Email Sen. Wicker | SenatorWicker | SenatorWicker | 6253 |
| Montana | Tim Sheehy | White, USN Seal, | Email Sen. Sheehy | Tim Sheehy | TimSheehyMT | 2644 |
| Pennsylvania | Dave McCormick | White, USA, PhD Intern’l relations | Email Sen. McCormick | Sen Dave McCormick | SenMcCormickPA | 6324 |
| Rhode Island | Sheldon Whitehouse | White, USAF, lawyer, clerk Appeals Court Judge West VA, State Attorney General, US Attorney | Email Sen. Whitehouse | SenatorWhitehouse | SenWhitehouse | 2921 |
| Rhode Island | Jack Reed | White, lawyer- private practice, focused on education & health care, USArmy, US Rep | Email Sen. Reed | SenJackReed/ | SenJackReed | 4642 |
Activists
Legislators who have a history of activism in some area:
| State | Name | Health Staff Email | Phone | |||
| Arkansas | John Boozman | White, optometrist for low-income families, advocate for drug policy issues, state rep | Email Sen. Boozman | JohnBoozman | JohnBoozman | 4843 |
| Delaware | Chris Coons | White, lawyer, nonprofits, missions | Email Sen. Coons | senatorchriscoons | ChrisCoons | 5042 |
| Delaware | Lisa Blunt Rochester | Black, US Rep, MA public policy, CEO Urban League | Email Sen. Rochester | SenLBR | SenLBR | 2441 |
| Georgia | Raphael G. Warnock | Black, Mdiv, pastor, activist | Email Sen. Warnock | SenatorWarnock | SenatorWarnock | 3643 |
| Hawaii | Brian Schatz | White, Jewish, Lt. Gov, State rep, CEO Helping Hands Hawaii, | Email Sen. Schatz | SenBrianSchatz | SenBrianSchatz | 3934 |
| Illinois | Tammy Duckworth | Asian, MA int’l affairs, PhD human services, USA helio pilot, bilateral amputee, Dept Veterans Affairs, US Rep, | Email Sen. Duckworth | SenDuckworth | SenDuckworth | 2854 |
| Louisiana | Bill Cassidy, MD | White, physician-liver specialist, uninsured clinics, nonprofit Health Centers, US Rep, state sen | Email Sen. Cassidy | SenBillCassidy/ | SenBillCassidy | 5824 |
| Massachusetts | Elizabeth Warren | White, lawyer, law prof, consumer protection advocate | Email Sen. Warren | senatorelizabethwarren | SenatorWarren | 4543 |
| Montana | Steve Daines | White, BS Chem Eng, Proctor & Gamble, RightNow Technologies, US Rep | Email Sen. Daines | SteveDainesMT | SteveDaines | 2651 |
| New Mexico | Ben Ray Lujan | Hispanic, US Rep, state public service | Email Sen. Lujan | SenatorLujan | SenatorLujan | 6621 |
| New Mexico | Martin Heinrich | White, BA mech eng, worked AmeriCorps fellow, Cottonwood Gulch Foundation (NP), founded his own public affairs consulting firm, US Rep, City Council | Email Sen. Heinrich | MartinHeinrich | MartinHeinrich | 5521 |
| New York | Kirsten Gillibrand | White, lawyer-Private, defense for tobacco co Philip Morris, abused women & children, pro bono, Women’s Leadership Forum, US Rep | Email Sen. Gillibrand | SenKirstenGillibrand | gillibrandny | 4451 |
| Oregon | Jeff Merkley | White, M. Pub Pol, director Portland Hapbitat for Humanity, initiated “YouthBuild” for young offenders, State rep, | Email Sen. Merkley | jeffmerkley | SenJeffMerkley | 3753 |
| Oregon | Ron Wyden | White, Jewish, Lawyer, taught gerontology, founded Oregon chapter of Gray Panthers, directed nonprofit law service, US Rep, | Email Sen. Wyden | senatorronwyden/ | RonWyden | 5244 |
| Rhode Island | Jack Reed | White, lawyer- private practice, focused on education & health care, USArmy, US Rep | Email Sen. Reed | SenJackReed/ | SenJackReed | 4642 |
| Rhode Island | Jack Reed | steve_keenan@reed.senate.gov | anybody | SenJackReed/ | @SenJackReed | 4642 |
| Utah | Mike Lee | White, Mormon, lawyer, Asst US Attorney, private practice focusing on courtroom advocacy and constitutional law. | Email Sen. Lee | senatormikelee | SenMikeLee | 5444 |
New Members
Senators who are new to Congress:
| State | Name | Health Staff Email | Phone | |||
| Arizona | Ruben Gallego | Hispanic, US Rep, state rep, BA gov’t, USMC | Email Sen. Gallego | SenRubenGallego | SenRubenGallego | 4521 |
| California | Adam Schiff | White, Jewish, lawyer, US attorney, state sen, vegan, | Email Sen. Schiff | SenAdamSchiff | SenAdamSchiff | 3841 |
| Delaware | Lisa Blunt Rochester | Black, US Rep, MA public policy, CEO Urban League | Email Sen. Rochester | SenLBR | SenLBR | 2441 |
| Florida | Ashley Moody | White, lawyer, State AG, Circuit Court Judge, | Email Sen. Moody | SenAshleyMoody | 3041 | |
| Indiana | Jim Banks | White, MBA, Real estate and construction, USNR, County Council, state sen | Email Senator Banks | SenatorJimBanks | SenatorBanks | 4814 |
| Maryland | Angela Alsobrooks | Black, lawyer, State attorney | Email Senator Alsobrooks | SenatorAlsobrooks | Sen_Alsobrooks | 4524 |
| Michigan | Elissa Slotkin | White, Jewish, US Rep, MA Intern’l Affairs, CIA, DoD, husband USA pilot, stepdaughter physician. | Email Sen. Slotkin | SenElissaSlotkin | SenatorSlotkin | 4822 |
| Montana | Tim Sheehy | White, USN Seal, | Email Sen. Sheehy | Tim Sheehy | TimSheehyMT | 2644 |
| Ohio | Bernie Moreno | Hispanic, BA Bus Admin, father Columbian physician | Email Sen. Moreno | Sen. Bernie Moreno | berniemoreno | 2315 |
| Ohio | Jon Husted | White, state lt.gov, sen and rep, MA communications | Email Sen. Husted | SenJonHusted | SenJonHusted | 3353 |
| Pennsylvania | Dave McCormick | White, USA, PhD Intern’l relations | Email Sen. McCormick | Sen Dave McCormick | SenMcCormickPA | 6324 |
| Utah | John Curtis | White, US rep, mayor, BS | Email Sen. Curtis | SenJohnCurtis | SenJohnCurtis | 5251 |
| West Virginia | Jim Justice | White, Gov, MBA, owns Greenbriar, coal companies | Email Sen. Justice | Sen. Jim Justice |
Long-Term Members (1980-2005)
-Legislators who have served in Congress for 20+ years (1980-2005)
Before 1997
| State | Name | Health Staff Email | Phone | |||
| Iowa | Chuck Grassley | White, BA, MA, professor, US rep, State rep, | Email Sen. Grassley | grassley | ChuckGrassley | 3744 |
| Oregon | Ron Wyden | White, Jewish, Lawyer, taught gerontology, founded Oregon chapter of Gray Panthers, directed nonprofit law service, US Rep, | Email Sen. Wyden | senatorronwyden/ | RonWyden | 5244 |
| Washington | Patty Murray | White, BA-PE, preschool teacher, welfare as teen, dad with MS, state sen, | Email Sen. Murray | pattymurray/ | PattyMurray | 2621 |
1997-2005
| State | Name | Health Staff Email | Phone | |||
| Alaska | Lisa Murkowski | White, lawyer, state rep | Email Sen. Murkowski | SenLisaMurkowksi/ | lisamurkowski | 6665 |
| Idaho | Mike Crapo | White, lawyer, US Rep, state sen, | Email Sen. Crapo | mikecrapo | MikeCrapo | 6142 |
| Illinois | Dick Durbin | White, lawyer, Sen Maj whip, US rep | Email Sen. Durbin | SenatorDurbin | SenatorDurbin | 2152 |
| Maine | Susan Collins | White, BA-gov, politician | Email Sen. Collins | susancollins | SenatorCollins | 2523 |
| New York | Chuck Schumer | White, Jewish, lawyer, Sen Maj. Leader, US Rep, state rep | Email Sen. Schumer | senschumer/ | SenSchumer | 6542 |
| Rhode Island | Jack Reed | White, lawyer- private practice, focused on education & health care, USArmy, US Rep | Email Sen. Reed | SenJackReed/ | SenJackReed | 4642 |
| South Carolina | Lindsey Graham | White, lawyer, AF Judge Advocate, state rep, US Rep, advocates strong national defense, leadership in world affairs, | Email Sen. Graham | LindseyGrahamSC/ | LindseyGrahamSC | 5972 |
| South Dakota | John Thune | White, MBA, Exec state republican party, US Rep | Email Sen. Thune | johnthune/ | SenJohnThune | 2321 |
| Texas | John Cornyn | White, Lawyer, Texas Attorney Gen, San Antonio Dist. Judge, Assoc Justice Texas Supreme Court | Email Sen. Cornyn | SenJohnCornyn/ | JohnCornyn | 2934 |
| Washington | Maria Cantwell | White, BA Public Admin, state rep, US rep | Email Sen. Cantwell | senatorcantwell | SenatorCantwell | 3441 |
Email Letter to Health Staff
Send the letter(s) below (or modify them to your own situation) to the health staffer when legislators are in Washington. Repeat as necessary.
Repeal the CSA
Repeal the CSA Why is it important to repeal the CSA? The war on drugs has failed. The government transferring the attacks to doctors has simply increased deaths due to opioids because legitimate patients are forced to the street.
As shown in prohibition, making a drug illegal simply worsens the problem. When Congress finally realizes this and ends the war on drugs, we will save billions of dollars in running down wasted rabbit holes, end the black market, end the border crisis, and make billions of dollars in taxes from legitimate sales.
The war on drugs was a racist agenda created by a government to make the United States a world power. Minorities have been affected for 120 years. This needs to stop.
We have the answer. Just go to our website, www.doctorsofcourage.org and watch the webinar recording on the top menu bar for a short insight into the solution.
Facebook post to Representatives
The War on Drugs is a failure. Understand that no drug causes addiction. Learn the REAL cause on doctorsofcourage(dot)org. We must get the Controlled Substance Act repealed, all citizens charged with drug crimes exonerated, and stop the waste of taxpayer dollars.
Twitter Post
End the defunct war on drugs & repeal the CSA! Save taxes, end overdoses & the border crisis. No drug causes addiction. Alcohol, most abused, is legal. The war on drugs is a government agenda against minorities. Restore pain management! doctorsofcourage.org
Email, FB and tweet to New Legislators
Email:
We, Doctors and Patients of Courage, represent the 100 million Americans who have legitimate pain or the doctors who are trying to treat them. We are looking for legislators—of which you could be one—who will put the country’s interest over his/her own. As a newly-elected representative, we would like to help you understand a major problem the government has caused. We are asking you to help fix the ignorance of the government and the standard jumping into a quagmire of ineffective solutions that they are so good at creating. The problem, as we see it, is one of money. More money is being spent than is being recovered, but the organizations recovering the money spread the lies and throw the blame on others, to justify their own existence.
We are throwing money away because of a government-created, fake “crisis” with the only intent of making money for special interest law enforcement groups and agencies. Read Ronald Libby’s masterpiece “The Criminalization of Medicine” and learn the history of what you have walked into. Learn the truth on www.doctorsofcourage.org. The government is
actually creating addiction by the increased anxiety of legitimate patients who need legitimate medicines to maintain a quality of life. We can give you the information on how government ignorance and mishandling of the facts is actually creating the problem you are attempting to control, and won’t with your current methods. The centuries-old percentage of addiction has always been 1%. It was 1% when the fake government agencies decided to criminalize the legitimate use of opioids in the 1990’s. It is now climbing (slightly, to 1.3%) due to government-created anxiety (the #1 acidifier of the body) in legitimate patients now being tortured with lack of treatment.
Please become a supporter of stopping this never-ending waste of taxpayer’s money. Learn what WILL work. Stop destroying the lives of 33% of the citizens over the 1% that you aren’t helping anyway. Learn how you can help be learning the REAL cause of Addiction and Drug Abuse, which can be seen on a video on https://www.doctorsofcourage.org/videos/.
Linda Cheek, MD, the president of Doctors of Courage, is happy to speak to any group that would like to get together to work on what will really solve the problem. Her website is www.lindacheekmd.com
Respectfully,
FB post:
The country needs a legislator—maybe you—who puts the country’s interest over his/her own. We are throwing money away because of a government-created, fake “crisis” with the only intent of making money for special interest law enforcement groups and agencies. Read Ronald Libby’s masterpiece “The Criminalization of Medicine” and learn the history of what you have walked into. Learn the truth on www.doctorsofcourage.org. The government is actually creating addiction by the increased anxiety of legitimate patients who need legitimate medicines to maintain a quality of life. We can give you the information on how government ignorance and mishandling of the facts is actually creating the problem you are attempting to control, and won’t with your current methods. The centuries-old percentage of addiction has always been 1%. It was 1% when the fake government agencies decided to criminalize the legitimate use of opioids in the 1990’s. It is now climbing (slightly, to 1.3%) due to government-created anxiety (the #1 acidifier of the body) in legitimate patients now being tortured with lack of treatment.
Please become a supporter of stopping this never-ending waste of taxpayer’s money. Learn what WILL work. Stop destroying the lives of 33% of the citizens over the 1% that you aren’t helping anyway. Learn how you can help be learning the REAL cause of Addiction and Drug Abuse, which can be seen on a video on https://www.doctorsofcourage.org/videos/. Linda Cheek, MD, the president of Doctors of Courage, can speak to any group to work on what will really solve the problem. Her website is: www.lindacheekmd.com
Tweet:
Needed: decrease the deficit and stop attacks on citizens by rogue agencies supporting themselves with US tax dollars. For the truth about the fake, government-created “opioid crisis”, go to www.doctorsofcourage.org. Stop
throwing money down a bottomless pit.
Tips for Writing Your Patient Testimony
Tips for Writing Your Patient Testimony (PT):
We ARE being judged – although affected by our pain or disability, we may be thought to be impaired by ‘drugs’ if our letters are rambling, lengthy or off topic.
- Be brief as possible, polite, clear, concise.
- Explain your pain condition/diagnosis – 3 or 4 which most affect your life
- Discuss failed treatments: PT, OT, Chiro, Devices, Surgeries, Procedures, etc,
- Non opioids ineffective – Nsaids, mood stabilizers, anti epileptics, etc
- Discuss how your function/life affected – work, driving, chores, entertainment, self care, travel, finance, family, etc.
- Explain all treatments, non opioids failed and medication/PM was a last resort and that you are incurable and your condition will likely worsen with aging
- Mention if inadequate pain control has been detrimental to your health – high BP, stroke, other physiological problems.
- Share how you have been a model patient on a strict pain contract with regular UAs, pill counts, utilizing one pharmacy, etc.
- Explain if you have to travel long distances, difficulties with paying for additional appointments and pharmacy co-pays
- If cut from meds/dropped by doctor – explain the above and how your function and life has been affected
- If you still have meds, discuss what your function/life would be like without
- Please do NOT use the words ‘drugs’, ‘narcotics’ or ‘addicts’. It’s been suggested to us that we use ‘people with addiction’. *Avoid ‘opioid’ or ‘opiate’ when possible, using ‘pain reliever’ or ‘pain relief’. Try not to use acronyms (UA, PM, etc.) as others may not understand.
To all letter writers, the guidelines above were about patient testimonies. What we are communicating may be a little different.
Think of WHO you’re writing and what you’re trying to convey to them while remembering, in the guidelines above, the basic rules that must apply, ex.(no profanity, clear & concise, not too lengthy). If you’re mentioning your diseases or injuries don’t write a novel. State the main ones and move on, or you risk losing the reader.
Remember that this first letter will be the most difficult to compose. It may take some time to think about what you’re trying to convey.
But once you’re done, the hard part is over. If you compose this on your computer or phone SAVE YOUR WORK!!
Then with the next target, if changes are needed, it’s easy to change it and SAVE!
In the above guidelines where it’s telling you how to write a testimony, for this project you may want to do that or you may have other information you’re trying to convey.
An Open Letter to Legislators by a CPP on Medium
Here is a letter by Heather on Medium that is worth copying and using by both chronic pain patients and professionals. I would break it down, however, and send it in several separate letters. A letter this long would not be read by health staff or the legislator. Put the main point you want to get across in the first paragraph. Then expand on it, but not more than a page long.
An Open Letter To All Who Hold Public Office in America From Painful Disease Patients
Effects of Chronic Pain by Doug Marsh
Described by Doug Marsh of Chronic Pain Sufferer Rights Leadership Commission. Feel free to use any of these descriptions in your letters to Congress.
Chronic Pain touches us all in so many different ways.
Physical Effects
Far too often after an illness or pain caused by an injury, we believe the treatment or therapy originally given to us has cured us. But then later on down the road the pain starts again, most of the time as a dull and periodic annoyance, just slightly more irritating than a common headache or another pain we might take an Aspirin for. As time progresses this inconvenience starts to become a more noticeable annoyance happening more and more frequently. To deal with this pain we start taking more and stronger over-the-counter pain relievers like Ibuprofen, Tylenol and Aleve to deal with this irritation or simply just to do our jobs, or even play with our children.
Eventually, the irritating pain starts becoming an interference effecting how we all do even simple tasks like making the bed or carrying out the garbage or even taking a walk. We start do things like favoring different parts of our bodies, posturing or carrying ourselves differently in an attempt to feel less pain. Most of the time we do not even realize that we are walking bent over or slouching while we are standing or sitting. All we know is that we don’t hurt as much at this time.
Next this interference caused by our pain starts to become a disruption, effecting our lives in various ways until one morning we wake up and can’t move without experiencing excruciating pain. We start missing work or backing out of social activities because we just don’t feel well enough to participate. We don’t know what’s happening to us—all we know is that the pain we are feeling has been getting worse every day.
Our employers start to become disappointed with our performance along with our work attendance and we can’t explain it to them. Now, every aspect of our lives has become difficult and our abilities and actions become more difficult and life itself is interrupted. What was once a reflex or a simple action now takes thought and planning to do because we want to avoid the pain every action now causes.
We want answers. We want an explanation other than “as we get older our aches and pains get worse”. So we seek the explanation by going to doctor after doctor to have tests done and seek relief. We subject ourselves to torture simply to find out what is causing our everyday pain. We are jabbed to the bone with needles that they then put an electrical current though in order to test our nervous systems. We are given steroid and epidural injections, spinal cord stimulator implants and other surgical procedures in an attempt to alleviate the pain and get our lives back to normal. Then, after all that fails we are prescribed everything from massive amounts of ibuprofen, gabapentin or Lyrica to opioid pain medications to manage our pain. But still no one can fix our ailments or injuries. Finally we succumb to our ailment or injury because we have come to the realization that pain now controls our lives.
Financial Effects
For years we took pride in our jobs and worked as hard as possible to get raises and promotions. We always showed up to work, even sick at times because we had families to support. There is no way we will ever ask them to go without.
Then one day our pain starts causing us to miss work, or it starts effecting our job performance. Our paychecks start suffering and our medical bills start adding up. We have family medical leave (FMLA) and short term disability, but that starts running out after 90 days. So we beg our doctors to release us and attempt to return to work so we don’t lose our jobs.
What we find out is that these injections and surgical procedures that were supposed to alleviate our pain only succeeded in making it worse and we start having to go home early and calling off work once again. Then when our employers can no longer afford to carry us anymore, we lose our jobs.
So now we have lost our employer sponsored health insurance, our income, and our sense of self-worth. Our pain won’t allow us to work and we have to go to court and fight tooth and nail for what is rightfully ours. Our Social Security Disability that we have paid into for all the years we were in the workforce often takes years to get. So now we are disabled, have no income and no health insurance. Our medical bills are adding up, and we have spent through our savings nest eggs or cashed in our 402k retirement, but still we have to wait on the federal government for our SSDI and do back flips through hoops to get what is rightfully ours. We are both physically and financially broken at this time.
Emotional effects
Because we are stubborn, we refuse to let pain slow us down. We stay positive and hopeful even though we are miserable. We force ourselves out of bed every day and go to work in agony. While at work, we put on our best, “I’m ok face and work through the pain but fight internally with ourselves daily on how much longer we can work.
We are gullible by believing and going through painful and expensive testing, along with surgical procedures that are supposed to make our lives great again.
We see the ads on television and we believe what pain doctors tell us about miracle surgeries and magical implants so we agree to it all.
We are embarrassed by being taken by these doctors who promise us a pain free future.
We start feeling helpless when we can’t work anymore because of our pain. Our desperation grows when we can’t earn the money to pay our bills.
We get depressed and we start feeling as if we are letting our families down.
We feel inadequate and irritated because we have to spend our life savings to put a dent in the medical bills. Then we feel anger at ourselves and depressed because we feel we are the cause of all the above.
Finally beaten by the pain, the financial and the emotional problems caused by our pain, we accept our future no matter what the outcome.
We are entirely broken now and totally unsure of our future.
Our bank accounts suffer and our relationships are stressed. Our lives are in complete turmoil and we are finding out that few really care.
Letter from Patient With Chronic Pancreatitis
Here is a copy of a letter that can be modified to fit your needs and sent to your representatives:
(To whom it may concern)
Dear____
My name is ______ and I am writing this letter on behalf of myself and the countless others I am connected with who also suffer from Chronic Pancreatitis (ChP). According to Dr. David Whitcomb from the University of PA, Chronic pancreatitis is more painful than cancer, diabetes, and most other chronic illnesses. I have suffered from this disease due to gallstones for 14 years and I can attest to the debilitating level of pain it incurs. But more than just pain, ChP affects other organs sharing nerves with the heart and a blood supply with the spleen.
Any time we have a flare it can mean death for those of us who suffer with pancreatitis. We also suffer with mal-nutrition, PTSD and many have other conditions like GERD, diabetes, etc as well.
There is no curative treatment for pancreatitis other than transplant surgery which is not covered by most insurance companies. Controlling the symptoms is the only way to have ANY quality of life I no longer have the pain relief needed to allow me to function even in the most minimal part time job. every day,. I am actively being harmed by the unscientific and biased treatment standards being forced on my doctors, insurance companies and pharmacies by both the federal and state levels of government. I want to live a productive life despite the challenge of a very painful disease. However, my quality of life has been taken away from me due to government overreach. The current “opioid epidemic” has been vastly mischaracterized and misdirected in the dominant public narrative.
The federal government, in deciding to stop people from becoming addicted to opioids, has chosen to make it extremely difficult for people with chronic pain conditions to continue getting the very medications that make life tolerable and worth living. There are many politicians and government departments who have made our lives miserable. For example, the CDC has written opioid treatment guidelines which are now known to be fraudulent. (Cite?) The guidelines were based on “research” that was deliberately biased to over-emphasize the real risks of treating chronic pain with opioids (Cite?). Thus, it denied the reality that opioids are currently the MOST effective means of safely and reliably treating millions of people who would otherwise be totally disabled by pain.
The guidelines are also being enshrined in highly restrictive state laws with a record of malicious and unwarranted prosecution of doctors by the DEA. (Cite) The DEA has completely ruined the “doctor-patient relationship” that I used to receive in treating my painful disease. Now doctors fear for their licenses instead of caring for patients. The FDA and Dept. of Health & Human Services have also become involved in this travesty. There are legislators and lobbyists that have become involved as well, and all of them are directly responsible for denial of effective pain management to tens of thousands of patients. Chronic pain patients are being involuntary denied medications that have been effective and safe for them for decades. They face reluctant doctors, wary pharmacists and insurance companies, and the frequent demand to prove that they are not addicts.
Suicides due to overwhelming pain have already happened and more are anticipated. (Give examples) It is not fair to punish one group of society in an effort to improve another group that chooses to abuse the medications we need to live our lives in a productive way. Our lives literally depend on these medications to function. All of this has also caused undue financial stress on an already stressful situation which intensifies our symptoms. My last Urine Analysis was $1500.00, twice a year makes it $3000.00 more on top of an already tight budget. It is $220.00 every time I walk into my pain specialist office. In addition, now my state wants to make us get our medications filled every 7 days which again places undue financial burden upon my family as well as stress on my already weary body. We are not criminals, we are only seeking relief from severe pain.
It is my plea that you do everything possible to stop the war against chronic pain patients immediately. The only ethically and medically sound way forward is immediate withdrawal of the CDC guidelines. They then need to be immediately replaced by better qualified stakeholder groups including both pain management specialists and chronic pain patients. The DEA should also be required by Congress to cease prosecution of doctors whose only “crime” is an attempt to serve the medical needs of their patients.
I have been advocating for and supporting those with chronic pain for 10 years and it is my conviction that those who have no experience suffering from debilitating pain have no right legislate pain management restrictions. Because for us, it is not about getting high, it is about getting by.

Meet with Your Legislator Face-to-Face
The most effective communication is meeting with your legislator face-to-face. Here is how to arrange that and how to best use your time together. Be sure and print off and take the Concerns and Demands that you can download from the button here:
How to Get a Meeting With Your Legislator
Meeting with your members of congress is one of the most effective ways that you can influence the legislative process. Members are more likely to support positions that their constituents feel strongly about, and there is no better way to display your passion for an issue than by taking the time to have a face-to-face meeting. This is especially important on issues where the opposition, such as the Department of Justice and DEA, is lobbying strongly against legislation you support, or on issues that are relatively new, complex, and sometimes controversial, such as the “opioid crisis” where there is an opportunity to educate policy makers. Meeting with your legislators can be easy and fun. You can meet one-on-one or you can plan a meeting with other activists in your area.
Setting up a meeting
- Plan, Plan, Plan. If you are willing to invest the time to get a face-to-face meeting with your legislator, be willing to think through what you hope to accomplish from the meeting and how best to go about reaching your goal. Consider what issue you most want to focus on and what your main message on this issue is. What is your legislator’s position on that issue and what do you want your legislator to do after the meeting? It is also important to consider whether having other people join you in the meeting would help you to convey your main message. Bring any relevant materials regarding your topic to leave behind.
- Find a date and location. If you are meeting with a federal legislator, you will need to find out when your legislator is back in the district. Check their website for the most current information about when they are on recess. If you plan to meet with a state or local legislator, be sure to check their website for details about where the office is.
- Request the meeting.Your request for a meeting should be initiated by mailing or faxing a letter to the legislator’s scheduler. Call the local office and ask for the names of the legislator’s scheduler. Next, fax or mail a letter requesting a meeting, putting it to the attention of the scheduler. You should indicate how flexible you are with the time of the meeting, as this will increase your chances of getting a meeting during busier days. In a toggle below there is a sample meeting request letter
- Follow-up by phone. Within 24 hours of sending the fax or when you think the letter will have arrived, call the scheduler and confirm his or her receipt of the note. If you have not heard back in three to four days, call the scheduler again and ask if a meeting has been arranged.
Additional tips and resources
- Consider meeting with the health issues staff person. If the legislator is unavailable to meet, you could actually benefit by meeting with the health issues staff person instead, especially as more people join the cause and also communicate with him/her. The health issues staff person is the office “expert” on the issue and thus has influence with the legislator. If you are persistent and effective, you may be able to parlay a first meeting with an aide into a long-term relationship with that office and/or a meeting directly with the legislator.
- Have Reasonable Expectations. Don’t expect your legislator to change his/her position after your 20-minute meeting. You should view your meeting as one critical step among many to engage your legislator on the issue.
Sample Meeting Request Letter
Sample Meeting Request Letter
Date
Legislator title and name
Address
ATTN: Scheduler’s Name, fax number
Dear [Title Last Name]: I am writing to request a meeting with you and your aides on the subject of the opioid epidemic. [If appropriate, briefly mention any credentials that would convince the scheduler to make you a priority.]
[Discuss the reasons for your current request for a meeting—e.g., developments in a piece of legislation you’re concerned about. For example:] I wish to request a few minutes of your time to discuss the recently introduced bill, [bill name].
I will be available to meet with you anytime on the [date(s)] and would be delighted to talk with you then about [the bill]. I would like to bring with me [list colleagues, or other are activists if applicable], also from [your state/district]].
I can be reached at the phone number (s) below, and look forward to hearing from you soon. Respectfully yours,
Dr./Mr./Mrs. _____________
Institution (if appropriate, and you may use DoctorsofCourage as an organization)
Address
Phone Numbers
Now That You've Got the Meeting Set, What's Next?
How to Have an Effective Visit With Your Policy Maker
Once you have your meeting set, you’ll need to prepare and know what to expect. Here are some tips to ensure you have a productive meeting:
Getting the most out of your meeting
- Identify your main message. Before the meeting, determine what the main message that you want to convey to your legislator is. For instance, “please play a leadership role in advancing policies to stop government overreach into medicine” or “please vote for bills that will ensure proper pain management for chronic pain patients.”
- Determine roles for participants. If more than one person is meeting with the legislator designate a group leader to open and close the meeting and a different person to present each issue or main message.
- Prepare and practice for the meeting. It’s always a good idea to run-through what you intend to say before the meeting itself. If you are meeting with a group of people, have each person practice their part in front of the group. Time permitting—hold a dry run of the entire meeting. Remember to dress nicely, business attire is appropriate. If you are meeting in Washington, D.C. business/formal dress is required in the Capitol building.
- Introduce yourself. Tell your legislator or staff person your name, where you are from, and that you are a constituent. If you represent an organization, note its name, where the group is located, and the size of its membership. If you are associated with a specific institution, identify it and your field of study (i.e. pain management). If you have any family, social, business, or political ties to the legislator, mention them as well. If possible, thank the member for a good stand they recently took on an issue and/or mention if you voted for the member. At a minimum, thank them for taking the time to meet with you.
- Take the initiative. State clearly and concisely what issue you want to discuss, what your position is, and what action you want the member to take. Follow this with facts about why they should take your position. Ask questions the legislator can respond “yes” or “no.” Press politely for a commitment, unless the member is clearly opposed to your position or to making a commitment.
- Make a local connection. Stress how the issue will affect the legislator’s district or state and, if possible, tell a personal story that highlights your experience with the issue and why you care about it.
Additional Tools and Resources
Additional tools and resources
- Follow up. Always follow up with a prompt thank you letter. In the letter, reiterate your key points and any commitments the legislator made to you. Include all follow-up information you promised to provide.
- Let us know how it went. Be sure to let us know the results of your meeting. The more details you can provide us with the better.
- Bring a “leave-behind” document. Give the legislator a brief fact sheet (one to two pages) that outlines your position and explains what the bill does (if there is one) and why they should support your viewpoint.
- Drop names. Mention any other organizations, important individuals, government officials, and legislators that support your position.
- Don’t answer what you don’t know. It’s okay to not know all the answers. Answer questions to the best of your ability, and if you don’t know an answer, admit it. This ensures you maintain credibility and it provides an opportunity for a relevant follow-up letter to provide any additional information.
- Don’t get discouraged. Members of the legislature are very busy and could be called out of the meeting—or not available at all—leaving you with their legislative aide that handles the issue. Don’t let this discourage you. Meeting with a staff member can be equally or even more productive than meeting with the member. Staff can have tremendous influence over legislators and in many cases know far more about the legislation than the legislators themselves. Be sure to ask the staff person to convey your views and legislative requests to their boss.
Stay on topic. The legislator may hijack the agenda or waste valuable time by bringing up unrelated issues. While it is important to be cordial and flexible, this is a meeting for you to relay your concerns to an elected official. Quickly acknowledge and address their issue and redirect the discussion back to the agenda. Don’t let them take you off-course for more than a moment.
Communicate With the White House
We do need to include the President and his staff in our communications. The most important thing is to tell them the REAL Cause of Drug Abuse, and how the medical profession has become victims of a witchhunt. He can relate to that.

Donald J. Trump
President
Call the President:
202-456-1111
Email the President:
https://www.whitehouse.gov/contact/
Write a letter:
The White House
1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW
Washington, DC 20500

Alina Saad Habba
Counselor to the President
Email at:
https://www.whitehouse.gov/contact
Write a letter:
Alina Habba
The White House
1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW
Washington, DC 20500
MEET YOUR LEGISLATOR FACE TO FACE:
Identify yourself as a member of DoctorsofCourage.
It is really important to make an appointment with your legislators and meet them face to face.
Be sure you are prepared and have your talking points listed as described below.
Here are the calendars for House and Senate. They will be in their districts during the times on the calendar when they are not in session.
For the House, the representatives might be visiting the district on the days that are clear or blue.
For the Senate, the senators might be visiting the district on the days that are clear or pink.
Below this calendar is a more detailed calendar for the Senate showing district work days. For the House, go to https://www.majorityleader.gov/uploadedfiles/full-calendar-2023-house-calendar.pdf
Call their local office and make an appointment to meet with them on a day they will be available. If you would like for me to join you virtually, just connect with me when you have the appointment set. I’ll be happy to hang out with you through zoom or google meet, or just on your phone.
Points to make when talking to legislators:
Opioids have been used by man for 6000 years. At the turn of the 19th century, when governments turned on opioids for the first time, the percentage of the population addicted was 1-5%.
For 100 years, the same policies have been attempted and failed multiple times because:
- Opioids do not cause addiction.
- Conventional medicine doesn’t know the cause of addiction.
- Being dependent on a medicine does not mean you are addicted. The study done on Viet Nam veterans coming back hooked on heroin shows that. 80% came back having used heroin, 20% came back hooked. But on their own, most stopped using and were not addicts. The final % that stayed addicted was 6%–slightly more than the general population at 1%
- Treating pain patients like addicts was done in the 1920’s-30’s without success. Learn from history and stop doing it today. Same with treating addicts like criminals.
Pain patients are being forced to the street for self-treatment because of the propagandized blame on opioids today for addiction. THIS is the reason for the increased deaths, not legitimate prescriptions. Doctors are being illegally attacked as “drug-pushers” using the Controlled Substance Act which actually exempts doctors from persecution. The DOJ is rogue, though, and creates crime where there is no crime. Innocent doctors are going to prison for the government to confiscate their assets which are then dispersed among the law enforcement agencies breaking the law convicting them.
If you want to make a difference in the country:
- At least amend the Controlled Substance Act so that even the DOJ can’t charge a doctor with a crime for treating a patient. A medical chart of any description is enough to establish a doctor/patient relationship, and make the doctor exempt. As is stated in the Controlled Substance Act 802(56)(c), only the DOCTOR can determine what is legitimate medical practice. Consider repealing the CSA. Talk with Dr. Linda Cheek to understand why this is needed.
- Make the DOJ accountable for not following Supreme Court decisions and professional misconduct convicting innocent people any way they can.
- Stop sending money down an empty chute. Learn the REAL cause of drug abuse, and establish trials to bring this to the attention of the medical profession. The REAL cause of drug abuse can be learned on the video on doctorsofcourage.org/videos.
- Restore our doctor/patient relationship. Medicine is not under the jurisdiction of the federal government. For the government to be interfering with patient care in the doctor’s office is gross government overreach.
For any questions, feel free to mention my name and tell them that their Washington health staff person has my email and I am willing to come to Washington to discuss these points with any group.
Contact Form for Comments:
How to Create Emails & Letters
- Create your email to COPY and Paste to send to many elected officials
- Keep your letter under one page in length.
- Comment that you are a Chronic Pain Patient and BRIEFLY tell about your conditions and procedures you have tried for relief.
- Do you currently have pain control options. If so, what benefit does this allow you. What functions or quality of life does pain relief give you. If you are losing pain control or have lost it, describe your quality of life now.
- Ask for help to restore the dr/patient relationship, stating how government attack has destroyed it.
- Define the real problem. Drugs do not cause addiction. Point them to the REAL cause on the video (link https://www.doctorsofcourage/videos/)
- Sign your email with your name, cell phone # and organization memberships
- Then copy and paste into your elected officials’ emails. Send to state reps, state senators, governor, state department of social services, State Medical Associations, State Attorney General, Federal Reps, Federals Senators, Attorney General, President.
Useful Information for Your Communication
Letter from DCBA Law & Policy LLP: which demands the president act on these illegal actions against MAT prescribing doctors. Rephrase to include ALL pain management providers:
Need for Organization
If you have a family member who is incarcerated or a felon because of the government use of the Controlled Substance Act, then we need to organize our efforts at this communication. Please contact us at doctorsofcourage so we can work together for the best effect.
Bills Introduced in Congress by Subject:
These bills were listed in early 2025. They will be reviewed, changed, and added to. So many of these bills are anti-American and anti-democratic. It is important to fire those legislators that back those bills, as they are picking party over country (and you). So if you live in the district of one of these legislators, you need to start working now to get them replaced.
House of Representatives Bills:
Ridiculous MAGA Bills
H.J.Res.14 – Proposing an amendment to the Constitution of the United States to repeal the sixteenth article of amendment.
Summary: This joint resolution proposes a constitutional amendment repealing the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution. The Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution, ratified in 1913, specifies that Congress may collect federal income taxes.
JOINT RESOLUTION
Proposing an amendment to the Constitution of the United States to repeal the sixteenth article of amendment.
Resolved by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America in Congress assembled (two-thirds of each House concurring therein),
section 1. That the following article is proposed as an amendment to the Constitution of the United States, which shall be valid to all intents and purposes as part of the Constitution when ratified by the legislatures of three-fourths of the several States within seven years after the date of its submission for ratification:
“article —
“ section 1. The sixteenth article of amendment to the Constitution of the United States is hereby repealed, and the Congress shall have no power to lay and collect taxes on incomes, from whatever source derived, except in time of war declared by the Congress.
“ section 2. Section 1 of this article shall take effect beginning 2 years after ratification of this article. Not later than 180 days after such ratification, the Secretary of the Treasury shall submit a report to the Congress containing recommendations for any legislation that may be necessary to implement this article.”.
H.R.52 – Stop Woke Investing Act
Summary: This bill requires the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to amend regulations to limit the inclusion of shareholder proposals in proxy statements. A proxy statement is provided to shareholders prior to a public company holding a shareholder meeting and contains information relevant to a shareholder vote. Under current SEC rules, certain qualifying shareholder proposals must be included on a company’s proxy statement, including proposals that raise significant social policy issues.
Under the bill, a shareholder proposal must have a material effect on the financial performance of the company to be included in a proxy statement. The bill also establishes a cap on the number of shareholder proposals required to be included in a shareholder meeting, depending on the size and type of the company. In addition, a proposal submitted by a member of the board of directors is prohibited from inclusion as a shareholder proposal.
SEC. 2. Shareholder proposals.
(a) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) ACCELERATED FILER; LARGE ACCELERATED FILER.—The terms “accelerated filer” and “large accelerated filer” have the meanings given the terms in section 240.12b–2 of title 17, Code of Federal Regulations, or any successor regulation.
(2) COMMISSION.—The term “Commission” means the Securities and Exchange Commission.
(3) MATERIAL.—The term “material”, when used to qualify a financial risk or financial return—
(A) means a financial risk or financial return in which there is a substantial likelihood that a reasonable investor would attach importance when—
(i) evaluating the potential financial risks or returns of an existing or prospective investment; or
(ii) exercising, or declining to exercise, any rights with respect to securities; and
(B) does not include—
(i) furthering nonpecuniary, environmental, social, political, ideological, or other goals or objectives; or
(ii) any portion of a financial risk or financial return that primarily relates to events that—
(I) involve a high degree of uncertainty regarding what may occur in the long-term future; and
(II) are systemic, general, or not investment-specific in nature.
(4) NON-ACCELERATED FILER.—The term “non-accelerated filer” means an issuer that is not an accelerated filer or a large accelerated filer.
(b) Amendments required.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this Act, the Commission shall amend section 240.14a–8 of title 17, Code of Federal Regulations, or any successor regulation, to provide that the shareholder proposals that a company includes on the proxy card of the company, and includes along with any supporting statement in the proxy statement of the company, shall be determined in accordance with the following:
(1) A company shall determine the proposals to include with respect to any 1 annual or special meeting of shareholders as follows:
(A) Subject to paragraph (2), if the company is a non-accelerated filer, the company shall not be required to include more than 2 proposals submitted by shareholders.
(B) Subject to paragraph (2), if the company is an accelerated filer, the company shall not be required to include more than 4 proposals submitted by shareholders.
(C) Subject to paragraph (2), if the company is a large accelerated filer, the company shall not be required to include more than 7 proposals submitted by shareholders.
(2) A proposal may not be included under paragraph (1) unless the proposal has a material effect on the financial performance of the applicable company.
(3) The method for determining which proposals to include under subparagraphs (A), (B), and (C) of paragraph (1) shall be—
(A) determined by the company; and
(B) disclosed to the Commission.
(4) The order in which the company receives the proposals shall have no bearing in determining whether a proposal is so included.
(5) If any 2 or more proposals submitted are substantially similar, all such proposals shall be considered to be a single proposal for the purposes of this subsection.
(6) No proposal submitted by a member of the board of directors of the company may be so included.
(c) Rules of construction.—Nothing in this section may be construed—
(1) to require a company to include a shareholder proposal in the proxy statement of the company if, under rules prescribed by the Commission, the proposal otherwise is not required to be included in the proxy statement;
(2) to authorize or approve any Commission rule or claim of authority to require a company to include the proposal of a shareholder in the proxy statement of the company; or
(3) to restrict the ability of the Commission to repeal any rule requiring a company to include the proposal of a shareholder in the proxy statement of the company.
H.R.54 – WHO Withdrawal Act
SEC. 2. Withdrawal of United States from the Constitution of the World Health Organization; prohibition on use of funds.
Effective on the date of the enactment of this Act—
(1) the President shall withdraw the United States from the Constitution of the World Health Organization (62 Stat. 2679; 14 U.N.T.S 186); and
(2) no funds available to any Federal department or agency may used to provide for the participation of the United States in the World Health Organization or any successor organization.
SEC. 3. Repeal of the Act of June 14, 1948.
The Act of June 14, 1948 (Public Law 806–43; 62 Stat. 441; 22 U.S.C. 290 et seq.), providing for membership and participation by the United States in the World Health Organization and authorizing an appropriation therefor, is repealed.
H.R.62 – WILLIS Act or “Withholding Investments from Lawless Litigators In States Act”
To prohibit Federal funds from being awarded or otherwise made available to the Fulton County District Attorney’s Office.
SEC. 2. Prohibition on Federal funding with respect to Fulton County District Attorney.
(a) Prohibition on Federal funding.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, no Federal funds may be awarded or otherwise made available to the Fulton County District Attorney’s Office.
(b) Rescission and repayment of Federal funding.—The unobligated balances of all amounts allocated for or otherwise made available to the Fulton County District Attorney’s Office is hereby rescinded, and the Attorney General shall take such steps as may be necessary and practicable to require the Fulton County District Attorney’s Office to reimburse the Federal Government for all amounts expended for such Office after the date of January 1, 2021.
H.R.63 – ALVIN Act Accountability for Lawless Violence In our Neighborhoods Act or the ALVIN Act
To prohibit Federal funds from being awarded or otherwise made available to the Manhattan District Attorney’s Office.
SEC. 2. Prohibition on Federal funding with respect to Manhattan District Attorney.
(a) Prohibition on Federal funding.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, no Federal funds may be awarded or otherwise made available to the Manhattan District Attorney’s Office.
(b) Recision and repayment of Federal funding.—The unobligated balances of all amounts allocated for or otherwise made available to the Manhattan District Attorney’s Office is hereby rescinded, and the Attorney General shall take such steps as may be necessary and practicable to require the Manhattan District Attorney’s Office to reimburse the Federal Government for all amounts expended for such Office after the date of January 1, 2022.
H.R.75 – HOUSE Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Energy efficiency standards for housing.
(a) In general.—The Secretary of Housing and Urban Development and the Secretary of Agriculture—
(1) shall withdraw the final determination announced in the notice of final determination entitled “Adoption of Energy Efficiency Standards for New Construction of HUD- and USDA-Financed Housing” (89 Fed. Reg. 33112);
(2) may not take any action or use any Federal funds to implement or enforce the final determination described in paragraph (1) or any substantially similar final determination; and
(3) shall revert energy efficiency standards for covered programs under such final determination to the energy efficiency standards required before such final determination.
(b) Action by additional agencies.—
(1) DEPARTMENT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS.—The Secretary of Veterans Affairs may not take any action or use any Federal funds to implement or enforce a final determination that is substantially similar to the final determination described in subsection (a)(1).
(2) FEDERAL HOUSING FINANCE AGENCY.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Director of the Federal Housing Finance Agency may not finalize, implement, or enforce a determination or rule relating to energy efficiency standards for single and multifamily housing.
(c) Consideration of State standards.—Section 109(d) of the Cranston-Gonzalez National Affordable Housing Act (42 U.S.C. 12709(d)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1), by striking “and” at the end;
(2) in paragraph (2), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(3) not less than 26 States have adopted an energy efficiency code or standard that meets or exceeds the requirements of the revised code or standard.”.
H.R.77 – Midnight Rules Relief Act
Summary: This bill allows Congress to disapprove multiple regulations under one joint resolution of disapproval if the regulations were submitted for review during a portion of the final year of a President’s term.
Under current law, the Congressional Review Act generally provides for a period of additional review during the succeeding Congress for regulations that were submitted during the last 60 legislative days of the prior Congress. However, each joint resolution may disapprove of only one regulation.
SEC. 2. En bloc consideration of resolutions of disapproval pertaining to “midnight rules”.
(a) In general.—Section 801(d) of title 5, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(4) In applying section 802 to rules described under paragraph (1), a joint resolution of disapproval may contain one or more such rules if the report under subsection (a)(1)(A) for each such rule was submitted during the final year of a President’s term.”.
(b) Text of resolving clause.—Section 802(a) of title 5, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by inserting after “resolving clause of which is” the following: “(except as otherwise provided in this subsection)”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following: “In the case of a joint resolution under section 801(d)(4), the matter after the resolving clause of such resolution shall be as follows: ‘That Congress disapproves the following rules: the rule submitted by the __ relating to __; and the rule submitted by the __ relating to __. Such rules shall have no force or effect.’ (The blank spaces being appropriately filled in and additional clauses describing additional rules to be included as necessary).”.
Passed the House of Representatives February 12, 2025.
H.R.117 – Fourth Amendment Restoration Act
To repeal the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act.
SEC. 2. Repeal of foreign surveillance authorities.
The Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act of 1978 (50 U.S.C. 1801 et seq.) is repealed.
SEC. 3. Definitions.
For the purposes of this Act—
(a) Pen register and trap and trace device.—The terms “pen register” and “trap and trace device” have the meanings given such terms in section 3127 of title 18, United States Code.
(b) United States citizen.—The term “United States citizen” means an individual who is a citizen of the United States.
(c) Foreign intelligence information.—The term “foreign intelligence information” means—
(1) information that relates to, and if concerning a United States citizen is necessary to, the ability of the United States to protect against—
(A) actual or potential attack or other grave hostile acts of a foreign power or an agent of a foreign power;
(B) sabotage, international terrorism, or the intentional proliferation of weapons of mass destruction by a foreign power or an agent of a foreign power; or
(C) clandestine intelligence activities by an intelligence service or network of a foreign power or by an agent of a foreign power; or
(2) information with respect to a foreign power or foreign territory that relates to, and if concerning a United States citizen, is necessary to—
(A) the national defense or the security of the United States; or
(B) the conduct of the foreign affairs of the United States.
(d) Electronic surveillance.—The term “electronic surveillance” means—
(1) the acquisition by an electronic, mechanical, or other surveillance device of the contents of any wire or radio communication sent by or intended to be received by a particular, known United States citizen who is in the United States, if the contents are acquired by intentionally targeting that United States citizen, under circumstances in which a citizen has a reasonable expectation of privacy and a warrant would be required for law enforcement purposes; or
(2) the installation or use of an electronic, mechanical, or other surveillance device in the United States for monitoring to acquire information, other than from a wire or radio communication, under circumstances in which a citizen has a reasonable expectation of privacy and a warrant would be required for law enforcement purposes.
(e) Wire communication.—The term “wire communication” means any communication while it is being carried by a wire, cable, or other like connection furnished or operated by any person engaged as a common carrier in providing or operating such facilities for the transmission of interstate or foreign communications.
SEC. 4. Prohibitions on surveilling United States citizens.
(a) An officer of the United States must obtain a warrant issued using the procedures described in the Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure by a Federal court in order to conduct or request—
(1) electronic surveillance of a United States citizen;
(2) a physical search of a premises, information, material, or property used exclusively by, or under the open and exclusive control of, a United States citizen;
(3) approval of the installation and use of a pen register or trap and trace device, a sole or significant purpose of which is to obtain foreign intelligence information concerning a United States citizen;
(4) the production of tangible things (including books, records, papers, documents, and other items) concerning a United States citizen to obtain foreign intelligence information; or
(5) the targeting of a United States citizen for the acquisition of foreign intelligence information.
(b) Any information concerning a United States citizen acquired under Executive Order 12333 (50 U.S.C. 3001 note; relating to United States intelligence activities) shall not be used in evidence against that United States citizen in any criminal, civil, or administrative proceeding or as part of any criminal, civil, or administrative investigation.
SEC. 5. Limitation on use of information concerning United States citizens.
Any information concerning a United States citizen acquired during surveillance of a non-United States citizen shall not be used in evidence against that United States citizen in any criminal, civil, or administrative proceeding or as part of any criminal, civil, or administrative investigation.
SEC. 6. Criminal sanctions.
(a) A person is guilty of an offense if he intentionally—
(1) engages in any of the offenses described in section 4, except as authorized by this Act, title 18, or any express statutory authorization that is an additional exclusive means for conducting electronic surveillance under section 1812 of title 50; or
(2) discloses or uses information obtained under color of law by any of the methods described in section 4, paragraph (1), knowing or having reason to know that the information was obtained without authorization by this chapter, title 18, or any express statutory authorization that is an additional exclusive means for conducting electronic surveillance under section 1812 of title 50.
(b) It is a defense to prosecution under subsection (a) that the defendant was a law enforcement officer or investigative officer engaging in the course of his official duties and the conduct was authorized and conducted pursuant to a search warrant or court order of a court of competent jurisdiction.
(c) An offense described in this section is punishable by a fine of not more than $10,000 or imprisonment for not less than five years, or both.
(d) There is a Federal jurisdiction over an offense under this section if the person committing the offense was an officer or employee of the United States at the time the offense was committed.
H.R.118 – No Federal Funds for Political Prosecutions Act
To prohibit the use of forfeited funds made available to certain State or local law enforcement agencies pursuant to equitable sharing for certain purposes.
SEC. 2. Limitation on use of forfeited funds made available pursuant to equitable sharing.
(a) In general.—No funds or property received pursuant to section 511(e) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 811(e)), section 981 of title 18, United States Code, or section 524 of title 28, United States Code, by a State or local law enforcement agency with the authority to prosecute a criminal case may be used to investigate or prosecute the President or Vice President, a former President or Vice President, or a candidate for the office of President.
(b) Certification.—A State or local law enforcement agency referred to in subsection (a) shall certify to the Attorney General that the law enforcement agency will comply with subsection (a).
(c) Disqualification.—In the case of a State or local law enforcement agency that the Attorney General determines has failed to comply with this section, the Attorney General may not transfer, under section 511(e) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 811(e)), section 981 of title 18, United States Code, or section 524 of title 28, United States Code, any property seized by the Attorney General and forfeited to the United States, or any of the proceeds from the sale of such property to such State or local law enforcement agency.
(d) Definition.—In this section, the term “candidate” has the meaning given such term in section 301 of the Federal Election Campaign Act of 1971 (52 U.S.C. 30101).
H.R.125 – Limiting Emergency Powers Act of 2025
To amend the National Emergencies Act to provide that a national emergency declared by the President terminates 30 days after the declaration unless a joint resolution affirming such declaration is enacted into law, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Limitation on duration of national emergency without congressional approval.
(a) In general.—Section 202 of the National Emergencies Act (50 U.S.C. 1622) is amended—
(1) by striking subsection (a) and inserting the following:
“(a) Any national emergency declared by the President in accordance with this title shall terminate if—
“(1) there has not been enacted into law a joint resolution affirming the declaration of such national emergency before the date that is 30 days after the date on which such national emergency is declared;
“(2) there is enacted into law a joint resolution terminating the emergency; or
“(3) the President issues a proclamation terminating the emergency.”;
(2) by striking subsection (b) and inserting the following:
“(b) (1) The date on which a national emergency is terminated pursuant to subsection (a) shall be the first occurrence of any of the following dates:
“(A) The last date of the period described in subsection (a)(1).
“(B) The date specified in any joint resolution referred to in subsection (a)(2).
“(C) The date specified in a proclamation by the President terminating the emergency as provided in subsection (a)(3).
“(2) Effective on the date of the termination of a national emergency under paragraph (1)—
“(A) any amounts reprogrammed or transferred under any provision of law with respect to the emergency that remain unobligated on that date shall be returned and made available for the purpose for which such amounts were appropriated;
“(B) any contracts entered into under any provision of law for construction relating to the emergency shall be terminated unless construction commenced under the contract before that date; and
“(C) any powers or authorities exercised by reason of said emergency shall cease to be exercised after that date, except that a termination shall not affect—
“(i) any action taken or proceeding pending not finally concluded or determined on such date;
“(ii) any action or proceeding based on any act committed prior to such date; or
“(iii) any rights or duties that matured or penalties that were incurred prior to such date.”;
(3) in subsection (c)—
(A) in paragraph (1) by inserting “or affirm” after “terminate”; and
(B) in paragraph (5) by striking “, subsection (b) of this section,”; and
(4) by striking subsection (d) and inserting the following:
“(d) A national emergency declared by the President under section 201, affirmed by a joint resolution under subsection (a)(1), and not otherwise previously terminated, shall terminate on the date that is 2 years after the President transmitted to Congress the proclamation declaring the emergency under section 201(a) or Congress affirms a previous renewal pursuant to this subsection, unless—
“(1) the President publishes in the Federal Register and transmits to Congress an Executive order renewing the emergency; and
“(2) there is enacted into law a joint resolution affirming the renewal of the declaration, according to the requirements of subsection (c), before the termination of the emergency or previous renewal of the emergency.”.
(b) Application to national emergencies previously declared.—A national emergency declared under section 201 of the National Emergencies Act (50 U.S.C. 1621 et seq.) before the date of the enactment of this Act shall be unaffected by the amendments made by this Act except that such emergencies shall terminate on the date that is 2 years after such date of enactment unless the emergency is renewed under section 201(d) of the National Emergencies Act, as amended by this Act.
H.R.151 – Equal Representation Act
To require a citizenship question on the decennial census, to require reporting on certain census statistics, and to modify apportionment of Representatives to be based on United States citizens instead of all persons.
SEC. 2. Citizenship status on decennial census.
(a) In general.—Section 141 of title 13, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by redesignating subsection (g) as subsection (h); and
(2) by inserting after subsection (f) the following:
“(g) (1) In conducting the 2030 decennial census and each decennial census thereafter, the Secretary shall include in any questionnaire distributed or otherwise used for the purpose of determining the total population by States a checkbox or other similar option for the respondent to indicate, for the respondent and for each of the members of the household of the respondent, whether that individual is—
“(A) a citizen of the United States;
“(B) a national of the United States but not a citizen of the United States;
“(C) an alien lawfully residing in the United States; or
“(D) an alien unlawfully residing in the United States.
“(2) Not later than 120 days after completion of a decennial census of the population under subsection (a), the Secretary shall make publicly available the number of persons per State, disaggregated by each of the 4 categories described in subparagraphs (A) through (D) of paragraph (1), as tabulated in accordance with this section.”.
SEC. 3. Exclusion of noncitizens from number of persons used to determine apportionment of representatives and number of electoral votes.
(a) Exclusion.—Section 22(a) of the Act entitled “An Act to provide for the fifteenth and subsequent decennial censuses and to provide for an apportionment of Representatives in Congress”, approved June 18, 1929 (2 U.S.C. 2a(a)), is amended by inserting after “not taxed” the following: “and individuals who are not citizens of the United States”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by subsection (a) shall apply with respect to the apportionment of Representatives carried out pursuant to the decennial census conducted during 2030 and any succeeding decennial census.
SEC. 4. Severability clause.
If any provision of this Act or amendment made by this Act, or the application thereof to any person or circumstance, is held to be unconstitutional, the remainder of the provisions of this Act and amendments made by this Act, and the application of the provision or amendment to any other person or circumstance, shall not be affected.
- R. 162 “First Amendment Accountability Act”
To provide for a right of action against Federal employees for violations of First Amendment rights.
SEC. 2. Right of action against Federal employees for violations of First Amendment rights.
(a) In general.—A Federal employee who, under color of any statute, ordinance, regulation, custom, or usage, of the United States, subjects, or causes to be subjected, any citizen of the United States or any person within the jurisdiction thereof to the deprivation of any rights, privileges, or immunities secured by the First Amendment, shall be liable to the party injured in an action at law, suit in equity, or other proper proceeding for redress.
(b) Exception.—This section does not authorize a Federal employee to bring a suit against their Federal employer or the Federal Government for conduct that is within the scope of the employment relationship.
(c) Attorney’s fees.—In any action or proceeding to enforce this Act, the court, in its discretion, may allow the prevailing party, other than the United States, a reasonable attorney’s fee as part of the costs.
(d) Definition.—In this section, the term “Federal employee” means an individual, other than the President or the Vice President, who occupies a position in any agency or instrumentality of the executive branch (including any independent agency).
(e) Severability.—If any provision of this Act or the application of a provision of this Act to any person or circumstance is held to be unconstitutional, the remainder of this Act, and the application of the provisions to any person or circumstance, shall not be affected thereby.
H. R. 191 Inflation Reduction Act of 2025
This bill repeals the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 and rescinds any unobligated funds made available by the act.
SEC. 2. Repeal of Inflation Reduction Act of 2022.
(a) In general.—Public Law 117–169 (commonly referred to as the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022) is repealed.
(b) Rescissions.—The unobligated balances of any amounts made available under Public Law 117–169 are rescinded.
H.R.236 – Federal Employee Return to Work Act
To prohibit certain telework employees from receiving certain annual adjustments to pay schedules, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Definitions.
In this Act:
(1) COVERED EMPLOYEE.—The term “covered employee”—
(A) means an employee who teleworks not fewer than 1 day, or in the case of an alternative work schedule, not less than 20 percent, a week; and
(B) does not include an employee who—
(i) teleworks not fewer than 1 day a week; and
(ii) is—
(I) is disabled and receives reasonable accommodations;
(II) a member of the Foreign Service of the United States;
(III) a Federal law enforcement officer;
(IV) a member of the Armed Forces on active duty; or
(V) any other employee, the official worksite of whom is not described in section 531.605(a)(1) of title 5, Code of Federal Regulations (or any corresponding similar regulation or ruling).
(2) EMPLOYEE.—The term “employee” has the meaning given the term in section 2105 of title 5, United States Code.
(3) TELEWORK.—The term “telework” has the meaning given the term in section 6501 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 3. Annual adjustments to pay schedules.
No covered employee may receive an annual adjustment under section 5303 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 4. Pay localities.
Each covered employee shall be paid at the rate of basic pay under the applicable grade and step for that employee under the locality pay area designated as “Rest of U.S.”—
(1) as of the date on which the employee becomes a covered employee; and
(2) which shall not be adjusted under section 5304 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 5. Effective date.
This Act shall take effect on the first day of the first full fiscal year beginning after the date of enactment of this Act.
H.R.276 – Gulf of America Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Renaming of Gulf of Mexico as “Gulf of America”.
(a) Renaming.—The Gulf of Mexico shall be known as the “Gulf of America”.
(b) References.—Any reference in a law, map, regulation, document, paper, or other record of the United States to the Gulf of Mexico shall be deemed to be a reference to the “Gulf of America”.
(c) Implementation.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary of the Interior, acting through the Chairman of the Board on Geographic Names, shall oversee the implementation of the renaming described in subsection (a) with respect to each Federal document and map.
(2) REQUIREMENT.—Not later than 180 days after the date of the enactment of this section, the head of each Federal agency shall update each document and map of the Federal agency in accordance with the renaming described in subsection (a).
H.R.283 – Panama Canal Repurchase Act of 2025
To authorize the President to enter into negotiations for the reacquisition of the Panama Canal from the Republic of Panama.
SEC. 2. Authorization to negotiate.
(a) Authorization.—The President, acting in coordination with the Secretary of State, is authorized to initiate and conduct negotiations with appropriate counterparts of the Government of the Republic of Panama to reacquire the Panama Canal.
(b) Report.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this Act, the President shall submit a report to Congress detailing the progress of the negotiations authorized by subsection (a), potential challenges, and anticipated outcomes.
H.R.361 – Make Greenland Great Again Act
SEC. 2. Authorization to enter into negotiations with the Kingdom of Denmark.
(a) In general.—Congress hereby authorizes the President, beginning at 12:01 p.m. Eastern Standard Time on January 20, 2025, to seek to enter into negotiations with the Kingdom of Denmark to secure the acquisition of Greenland by the United States.
(b) Transmission of agreement.—Not later than 5 calendar days after reaching an agreement with the Kingdom of Denmark relating to the acquisition of Greenland by the United States, the President shall transmit to the appropriate congressional committees the agreement, including all related materials and annexes.
(c) Period of review by Congress of agreement.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The period for congressional review for any agreement described in subsection (a) shall be 60 calendar days from the date on which the President transmits to the appropriate Congressional committees the agreement for the acquisition of Greenland from the Kingdom of Denmark.
(2) EFFECTIVE DATE.—If no joint resolution of disapproval is enacted by Congress within the 60-calendar day period, the agreement described in subsection (a) shall be in effect and take the full force of law.
(d) Appropriate congressional committees defined.—In this section, the term “appropriate congressional committees” means—
(1) the Committee on Foreign Affairs of the House of Representatives; and
(2) the Committee on Foreign Relations of the Senate.
H.R.377 – Regulation Reduction Act of 2025
To require agencies to repeal three existing regulations before issuing a new regulation, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Repeal of regulations required before issuance of a new rule.
(1) REQUIREMENT FOR RULE.—An agency may not issue a rule unless such agency has repealed three or more rules described in paragraph (4) that, to the extent practicable, are related to the rule.
(2) REQUIREMENT FOR MAJOR RULE.—
(A) REPEAL REQUIRED.—An agency may not issue a major rule unless—
(i) such agency has repealed three or more rules described in paragraph (4) that, to the extent practicable, are related to the major rule; and
(ii) the cost of the new major rule is less than or equal to the cost of the rules repealed.
(B) CERTIFIED COST.—For any rule issued in accordance with subparagraph (A), the Administrator of the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs of the Office of Management and Budget must have certified that the cost of the new major rule is equal to or less that the cost of the rules repealed.
H.R.396 – TRUST in Congress Act or Transparent Representation Upholding Service and Trust in Congress Act
This bill requires a Member of Congress, as well as any spouse or dependent child of a Member, to place specified investments into a qualified blind trust (i.e., an arrangement in which certain financial holdings are placed in someone else’s control to avoid a possible conflict of interest) until 180 days after the end of their tenure as a Member of Congress.
H.R.401 – No Taxpayer Funding for the World Health Organization Act
SEC. 2. Prohibition on assessed and voluntary contributions to the World Health Organization.
Notwithstanding any other provision of law, effective on the date of the enactment of this Act, the United States may not provide any assessed or voluntary contributions to the World Health Organization.
H.R.465 – Old Glory Only Act
To prohibit the flying of any flag other than the United States flag over United States diplomatic and consular posts, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Prohibition on flying of certain flags over United States diplomatic and consular posts.
The Secretary of State shall ensure that no United States diplomatic or consular post flies any flag other than the United States flag over such post.
H.R.472 – Restore VA Accountability Act of 2025
To amend title 38, United States Code, to modify personnel action procedures with respect to employees of the Department of Veterans Affairs, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Supervisors: removal, demotion, or suspension based on performance or misconduct.
(a) Discipline of supervisors.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Title 38, United States Code, is amended by inserting after section 711 the following:
Ҥ 712. Supervisors: removal, demotion, or suspension based on performance or misconduct
“(a) In general.—The Secretary may remove from civil service, demote, or suspend a covered individual who is an employee of the Department if the Secretary determines by substantial evidence that the performance or misconduct of the covered individual warrants such action.
“(b) Rights and procedures.— (1) (A) When making an initial decision under subsection (a) with respect to determining whether a covered individual should be removed, demoted, or suspended, the deciding employee of the Department shall exclusively apply the following factors:
“(i) The nature and seriousness of the offense, and its relation to the covered individual’s duties, position, and responsibilities, including whether the offense was intentional or technical or inadvertent, or was committed maliciously or for gain, or was frequently repeated.
“(ii) The covered individual’s job level and type of employment, including supervisory or fiduciary role, and prominence of the position.
“(B) The Secretary shall review the initial decision and uphold such decision if it is supported by substantial evidence.
“(2) A covered individual subject to an action under subsection (a) is entitled to—
“(A) advance notice of the action and a file containing all evidence in support of the proposed action;
“(B) be represented by an attorney or other representative of the covered individual’s choice; and
“(C) grieve the action in accordance with an internal grievance process that the Secretary, in consultation with the Assistant Secretary for Accountability and Whistleblower Protection, shall establish for purposes of this subsection.
“(3) A final decision by the Secretary under paragraph (1)(B) that is not grieved, and a grievance decision under paragraph (2)(C), shall be final and conclusive.
“(4) The procedures under chapter 43 of title 5 shall not apply to a removal, demotion, or suspension under this section, and the Secretary may carry out such a removal, demotion, or suspension without first placing a covered individual on a performance improvement plan.
“(c) Timing.— (1) (A) The aggregate period for notice, response, and final decision by the Secretary of an action under this section may not exceed 15 business days.
“(B) The period for the response of a covered individual to a notice under subsection (b)(2)(A) shall be 7 business days.
“(C) The final decision by the Secretary under subsection (b)(1)(B) shall—
“(i) be issued not later than 15 business days after notice is provided under subsection (b)(2)(A); and
“(ii) be in writing and shall include the specific reasons for the decision.
“(D) The Secretary shall ensure that the grievance process established under paragraph (2)(C) takes fewer than 21 days after the final decision.
“(d) Judicial review.— (1) A covered individual adversely affected by a final decision under this section that is not grieved, or by a grievance decision under subsection (b)(2)(C), may obtain judicial review of such decision.
“(2) Any removal, demotion, or suspension under this section is not appealable to the Merit Systems Protection Board, or to any administrative judge or other person appointed by the Merit Systems Protection Board.
“(3) In any case in which judicial review is sought under paragraph (1), the court shall review the record and may set aside any Department action found to be—
“(A) arbitrary, capricious, an abuse of discretion, or otherwise not in accordance with a provision of law;
“(B) obtained without procedures required by a provision of law having been followed; or
“(C) unsupported by substantial evidence.
“(4) Except to the extent that an appeal under this subsection presents a constitutional issue, such court may not review a challenge to the penalty imposed against the covered individual or mitigate such penalty.
“(e) Demoted individuals.— (1) A demotion under subsection (a) shall be carried out as a reduction in grade for which the covered individual is qualified, that the Secretary determines is appropriate, and that reduces the annual rate of pay of the covered individual.
“(2) Notwithstanding any other provision of law, any covered individual so demoted—
“(A) shall, beginning on the date of such demotion, receive the annual rate of pay applicable to such grade;
“(B) may not be placed on administrative leave during the period during which an appeal (if any) under this section is ongoing, and may only receive pay if the covered individual reports for duty or is approved to use accrued unused annual, sick, family medical, military, or court leave; and
“(C) who does not report for duty or receive approval to use accrued unused leave shall not receive pay or other benefits.
“(f) Whistleblower protection.— (1) In the case of a covered individual seeking corrective action (or on behalf of whom corrective action is sought) from the Office of Special Counsel based on an alleged prohibited personnel practice described in section 2302(b) of title 5, the Secretary may not remove, demote, or suspend such covered individual under subsection (a) without the approval of the Special Counsel under section 1214(f) of title 5.
“(2) In the case of a covered individual who has made a whistleblower disclosure to the Assistant Secretary for Accountability and Whistleblower Protection, the Secretary may not remove, demote, or suspend such covered individual under subsection (a) until—
“(A) in the case in which the Assistant Secretary determines to refer the whistleblower disclosure under section 323(c)(1)(D) of this title to an office or other investigative entity, a final decision with respect to the whistleblower disclosure has been made by such office or other investigative entity; or
“(B) in the case in which the Assistant Secretary determines not to refer the whistleblower disclosure under such section, the Assistant Secretary makes such determination.
“(g) Termination of investigations by office of special counsel.— (1) Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Special Counsel (established by section 1211 of title 5) may terminate an investigation of a prohibited personnel practice alleged by an employee or former employee of the Department after the Special Counsel provides to the employee or former employee a written statement of the reasons for the termination of the investigation.
“(2) Such statement may not be admissible as evidence in any judicial or administrative proceeding without the consent of such employee or former employee.
“(h) Application.—This section shall apply to any performance or misconduct of a covered individual beginning on the date of enactment of the Department of Veterans Affairs Accountability and Whistleblower Protection Act of 2017 (Public Law 115–41).
“(i) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) The term ‘civil service’ has the meaning given that term in section 2101 of title 5.
“(2) The term ‘covered individual’ means an employee of the Department who is a supervisor or management official as defined in section 7103(a) of title 5 occupying a position at the Department, including individuals appointed pursuant to this title, title 5, and hybrid employees appointed pursuant to section 7401 of this title, but does not include—
“(A) an individual occupying a senior executive position (as defined in section 713(d) of this title);
“(B) an individual appointed pursuant to section 7306, 7401(1), 7401(4), or 7405 of this title;
“(C) an individual who has not completed a probationary or trial period; or
“(D) a political appointee.
“(3) The term ‘grade’ has the meaning given such term in section 7511(a) of title 5.
“(4) The term ‘misconduct’ includes neglect of duty, malfeasance, or failure to accept a directed reassignment or to accompany a position in a transfer of function.
“(5) The term ‘political appointee’ means an individual who is—
“(A) employed in a position described under sections 5312 through 5316 of title 5 (relating to the Executive Schedule);
“(B) a limited term appointee, limited emergency appointee, or noncareer appointee in the Senior Executive Service, as defined under paragraphs (5), (6), and (7), respectively, of section 3132(a) of title 5; or
“(C) employed in a position of a confidential or policy-determining character under schedule C of subpart C of part 213 of title 5, Code of Federal Regulations, or successor regulation.
“(6) The term ‘suspend’ means the placing of an employee, for disciplinary reasons, in a temporary status without duties and pay for a period in excess of 14 days.
“(7) The term ‘whistleblower disclosure’ has the meaning given such term in section 323(g) of this title.”.
(2) CLERICAL AMENDMENT.—The table of contents for title 38, United States Code, is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 711 the following:
“712. Supervisors: removal, demotion, or suspension based on performance or misconduct.”.
SEC. 3. Senior executives: modification of procedures to remove, demote, or suspend based on performance or misconduct.
Section 713 of title 38, United States Code, is amended—
(1) in subsection (a)—
(A) after “determines”, insert “by substantial evidence”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following:
“(3) When making an initial decision under this subsection with respect to determining whether a covered individual should be reprimanded or suspended, involuntarily reassigned, demoted, or removed, the deciding employee of the Department shall exclusively apply the following factors:
“(A) The nature and seriousness of the offense, and its relation to the covered individual’s duties, position, and responsibilities, including whether the offense was intentional or technical or inadvertent, or was committed maliciously or for gain, or was frequently repeated.
“(B) The covered individual’s job level and type of employment, including supervisory or fiduciary role, and prominence of the position.
“(4) The Secretary shall review the initial decision and uphold such decision if it is supported by substantial evidence.”;
(2) in subsection (b)—
(A) in paragraph (3), by inserting “after the final decision” after “21 days”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following:
“(7) Except to the extent that an appeal under this subsection presents a constitutional issue, such court may not review a challenge to the penalty imposed against the covered individual or mitigate such penalty.”; and
(3) insert after subsection (c) the following (and redesignate subsection (d) as subsection (e)):
“(d) Application.—This section shall apply to any misconduct or performance of a covered individual beginning on the date of enactment of the Department of Veterans Affairs Accountability and Whistleblower Protection Act of 2017 (Public Law 115–41).”.
SEC. 4. Modification of disciplinary procedures for employees of the Department of Veterans Affairs.
(a) Department of Veterans Affairs employee discipline modifications.—Section 714 of title 38, United States Code, is amended—
(1) in subsection (a),
(A) in paragraph (1), by inserting “by substantial evidence” after “the Secretary determines”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following:
“(3) (A) When making an initial decision under this subsection with respect to determining whether a covered individual should be removed, demoted, or suspended, the deciding employee of the Department shall exclusively apply the following factors:
“(i) The nature and seriousness of the offense, and its relation to the covered individual’s duties, position, and responsibilities, including whether the offense was intentional or technical or inadvertent, or was committed maliciously or for gain, or was frequently repeated.
“(ii) The covered individual’s job level and type of employment, including supervisory or fiduciary role, and prominence of the position.
“(iii) The covered individual’s past disciplinary record.
“(iv) The covered individual’s past work record, including length of service, performance on the job, ability to get along with fellow workers, and dependability.
“(v) Mitigating circumstances surrounding the offense such as unusual job tensions, personality problems, mental impairment, harassment, or bad faith, malice, or provocation on the part of others involved in the matter.
“(B) The Secretary shall review the initial decision and uphold such decision if it is supported by substantial evidence.”.
(2) in subsection (c)—
(A) by striking paragraph (1)(D); and
(B) in paragraph (3), by inserting before the period the following: “, and the Secretary may carry out such a removal, demotion, or suspension without first placing a covered individual on a performance improvement plan”;
(3) in subsection (d)—
(A) in paragraph (2), by adding at the end the following:
“(C) Except to the extent that an appeal under this subsection presents a constitutional issue, the administrative judge may not review a challenge to the penalty imposed against the covered individual.”;
(B) in paragraph (3), by adding at the end the following:
“(D) Except to the extent that an appeal under this subsection presents a constitutional issue, the Merit Systems Protection Board may not review a challenge to the penalty imposed against the covered individual.”;
(C) in paragraph (5), by adding at the end the following:
“(C) Except to the extent that an appeal under this subsection presents a constitutional issue, such Court may not review a challenge to the penalty imposed against the covered individual or mitigate such penalty.”; and
(D) by striking paragraph (10);
(4) by redesignating subsection (h) as subsection (j);
(5) by inserting after subsection (g) the following:
“(h) Collective bargaining agreements.—The procedures in this section shall supersede any collective bargaining agreement to the extent that such agreement is inconsistent with such procedures.
“(i) Application.—This section shall apply to any performance or misconduct of a covered individual beginning on the date of enactment of the Department of Veterans Affairs Accountability and Whistleblower Protection Act of 2017 (Public Law 115–41).”; and
(6) in paragraph (1) of subsection (j), as redesignated by paragraph (4)—
(A) by inserting “including individuals appointed pursuant to this title, title 5, and hybrid employees appointed pursuant to section 7401 of this title” after “Department”;
(B) in subparagraph (D), by striking the period and inserting “; or”; and
(C) by adding after subparagraph (D) the following:
“(E) a supervisor or management official as defined in section 7103(a) of title 5.”.
(b) VHA employee discipline modifications.—Section 7403(f)(3) of such title is amended—
(1) by striking “Notwithstanding any other provision of this title or other law,” and inserting “(A) Notwithstanding any other provision of this title or other law, and consistent with subparagraph (B),”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following:
“(B) With respect to any covered individual (as that term is defined in section 712 or 714) appointed to such positions, such matters shall be resolved, at the Secretary’s sole discretion, under—
“(i) section 712;
“(ii) section 714; or
“(iii) title 5 as though such individuals had been appointed under that title.”.
H.R.473 – SHOW UP Act of 2025
To restore in-person work at Federal agencies to not less than pre-pandemic levels, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Reinstatement of pre-pandemic telework policies, practices, and levels for Executive agencies.
Not later than 30 days after the date of enactment of this Act, each agency shall adopt and apply telework policies, practices, and levels at the agency that are equivalent to, or otherwise permit no additional levels of telework than, those which were in effect on December 31, 2019, and may not expand any such policy, practice, or level until the date that an agency plan is submitted to Congress with a certification by the Director of the Office of Personnel Management under section 3.
SEC. 3. Study, plan, and certification regarding Executive agency telework policies, practices, and levels for Executive agencies.
(a) In general.—Not later than 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act, the head of each agency, in consultation with the Director, shall submit to Congress—
(1) a study on the impacts on the agency and its mission of expanding telework by its employees during the SARS–CoV–2 pandemic that commenced in 2019 and maintaining such expanded telework thereafter, including an analysis of—
(A) any adverse impacts of that expansion on the agency’s performance of its mission, including the performance of customer service by the agency;
(B) any costs to the agency during that expansion attributable to—
(i) owning, leasing, or maintaining underutilized real property; or
(ii) paying higher rates of locality pay to teleworking employees as a result of incorrectly classifying such employees as teleworkers rather than remote workers;
(C) any degree to which the agency failed during that expansion to provide teleworking employees with secure network capacity, communications tools, necessary and secure access to appropriate agency data assets and Federal records, and equipment sufficient to enable each such employee to be fully productive;
(D) any degree to which that expansion facilitated dispersal of the agency workforce around the Nation; and
(E) any other impacts of that expansion that the agency or the Director considers appropriate;
(2) any agency plan to expand telework policies, practices, or levels beyond those in place as a result of section 2; and
(3) a certification by the Director that such plan will—
(A) have a substantial positive effect on—
(i) the performance of the agency’s mission, including the performance of customer service;
(ii) increasing the level of dispersal of agency personnel throughout the Nation; and
(iii) the reversal of any adverse impact set forth pursuant to paragraph (1)(D);
(B) substantially lower the agency’s costs of owning, leasing, or maintaining real property;
(C) substantially lower the agency’s costs attributable to paying locality pay to agency personnel working from locations outside the pay locality of their position’s official worksite; and
(D) ensure that teleworking employees will be provided with secure network capacity, communications tools, necessary and secure access to appropriate agency data assets and Federal records, and equipment sufficient to enable each such employee to be fully productive, without substantially increasing the agency’s overall costs for secure network capacity, communications tools, and equipment.
(b) Limitation.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—An agency may not implement the plan submitted under subsection (a)(2) unless a certification by the Director was issued under subsection (a)(3).
(2) SUBSEQUENT PLANS.—In the event an initial agency plan submitted under subsection (a)(2) fails to receive such certification, the agency may submit to the Director subsequent plans until such certification is received, and submit such plan and certification to Congress.
(c) Definitions.—In this Act—
(1) the term “agency” has the meaning given the term “Executive agency” in section 105 of title 5, United States Code, except that such term does not include the Government Accountability Office;
(2) the term “Director” means the Director of the Office of Personnel Management;
(3) the term “locality pay” means locality pay provided for under section 5304 or 5304a of such title; and
(4) the terms “telework” and “teleworking” have the meaning given those terms in section 6501 of such title, and include remote work.
H.R.576 – To codify Executive Order 14096 relating to revitalizing our Nation’s commitment to environmental justice for all.
SECTION 1. Codification of Executive Order 14096.
Executive Order 14096 (88 Fed. Reg. 25251; relating to revitalizing our Nation’s commitment to environmental justice for all) shall have the force and effect of law.
H.R.589 – FACE Act Repeal Act of 2025
To amend title 18, United States Code, to repeal prohibitions relating to freedom of access to clinic entrances, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Repeal of prohibitions relating to freedom of access to clinic entrances.
(a) In general.—Section 248 of title 18, United States Code, is repealed.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for chapter 13 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking the item relating to section 248.
(c) Applicability.—The repeal made in subsection (a) shall apply to any prosecution of an offense that is pending on, or commenced on or after, the date of enactment of this Act.
My addition:
Section 248 of Title 18 states:
(a)Prohibited Activities.—Whoever—
(1)
by force or threat of force or by physical obstruction, intentionally injures, intimidates or interferes with or attempts to injure, intimidate or interfere with any person because that person is or has been, or in order to intimidate such person or any other person or any class of persons from, obtaining or providing reproductive health services;
(2)
by force or threat of force or by physical obstruction, intentionally injures, intimidates or interferes with or attempts to injure, intimidate or interfere with any person lawfully exercising or seeking to exercise the First Amendment right of religious freedom at a place of religious worship; or
(3)
intentionally damages or destroys the property of a facility, or attempts to do so, because such facility provides reproductive health services, or intentionally damages or destroys the property of a place of religious worship,
H.R.643 – Federal Insurance Office Elimination Act
SEC. 2. Elimination of Federal Insurance Office.
(a) In general.—The Federal Insurance Office of the Department of the Treasury, and the position of the Director of the Federal Insurance Office, are hereby eliminated.
(b) Amendment.—Title 31, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by striking section 313; and
(2) in the table of sections for subchapter I of chapter 3, by striking the item relating to section 313.
(c) Treasury authority.—This section, and the amendment made by this section, may not be construed to repeal or otherwise limit any authority of the Secretary of the Treasury with respect matters relating to insurance.
H.R.687 – MERIT Act of 2025
To amend title 5, United States Code, to provide for an alternative removal for performance or misconduct for Federal employees.
Sec. 2. Termination of authority for chapter 43 performance-based actions.
Sec. 3. Adverse actions based on performance or conduct.
Sec. 4. Prohibition on grieving adverse actions and reductions in force.
Sec. 5. Actions against senior executives for performance or conduct.
Sec. 6. Actions against supervisors for performance or conduct.
Sec. 7. Modification of procedures for furlough.
Sec. 8. Reduction of annuity of employee convicted of a felony for which an adverse action is or would have been taken.
Sec. 9. Authority to recoup bonuses or awards paid to employees.
Sec. 10. Extension of probationary period for positions within the Senior Executive Service.
Sec. 11. Extension of probationary period for employees in the competitive service.
Sec. 12. Application.
A long bill. For the rest of it go to: uscongress.gov
H.R.734 – To amend the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 with respect to the issuance of quality control guidance issued by the Secretary of Agriculture.
SECTION 1. Public comment on quality control guidance.
Section 16(c) of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 2025(c)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(10) PUBLIC COMMENT ON QUALITY CONTROL GUIDANCE.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary shall provide notice and make available for public comment for a period of not fewer than 60 days any new or updated guidance proposing substantive changes for conducting quality control reviews prior to any such guidance being finalized.
“(B) SCOPE.—The requirement in (A) shall be applicable to any proposed guidance reasonably expected to require state agencies to make changes to systems, procedures, or staffing pertaining to quality control reviews or that impact verification requirements for supplemental nutrition assistance program recipients.
“(C) EXCEPTION.—In the case of an urgent and immediate need, the Secretary may issue interim final guidance simultaneous with the notice and comment requirements required in (A).”.
H.R.735 – United States Reciprocal Trade Act
To authorize the President to take certain actions relating to reciprocal trade, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) The United States maintains an open market for goods, with relatively low tariffs, and has long encouraged trading partners, both bilaterally and in multilateral fora, to liberalize their markets.
(2) The United States is the world’s largest importer of goods.
(3) Trading partners of the United States in many instances impose significantly higher tariffs on United States goods than the United States imposes on the same or similar goods imported from those same countries.
(4) Europeans have continued to protect their auto markets from United States automotive companies through high tariffs while dumping cheap European cars into the United States, undermining our automotive industry.
(5) Canadian and Mexican authorities have flooded American markets with cheap goods while simultaneously allowing for illegal migrants and poisonous fentanyl to pour into the United States.
(6) United States trading partners in many instances impose significant nontariff barriers that greatly undermine the value of negotiated tariff concessions.
(7) The lack of reciprocity in tariff levels and disproportionate use of nontariff barriers by United States trading partners facilitates foreign imports, discourages United States exports, and puts United States producers, farmers, and workers at a competitive disadvantage.
(8) The lack of reciprocity in tariff levels and nontariff barriers contributes to the large and growing United States trade deficit in goods, which is a drag on economic growth and undermines economic prosperity.
(9) Tariffs under the Trump presidency substantially shrank the trade deficit with China.
(10) The President must be able to levy tariffs on our global competitors. Preferential treatment of adversaries, such as China’s Most Favored Nation trading status, undermines American national security interests domestically and around the world.
(11) To date a number of United States trading partners have been unwilling, including in multilateral negotiations, to reduce tariffs and eliminate nontariff barriers applied to United States exports.
(12) The United States should seek action by United States trading partners to lower tariffs and eliminate nontariff barriers, to promote efficiency in those markets and enhance opportunities for United States producers, farmers, and workers.
(13) For the United States to maintain its economic dominance globally, the President must have the authority to levy reciprocal tariffs against unfair trading partners.
(14) The President should have a wide array of tools to open the markets of United States trading partners and encourage participation in negotiations to liberalize trade in goods on a fair and reciprocal basis, including the authority to adjust tariff rates to reciprocal levels.
SEC. 3. Authority to take certain actions relating to reciprocal trade.
(a) In general.—If the President determines that—
(1) the rate of duty imposed by a foreign country with respect to a particular good, when imported from the United States, is significantly higher than the rate of duty imposed by the United States on that good, when imported from that country, or
(2) the nontariff barriers applied by a foreign country with respect to a particular good, when imported from the United States, impose significantly higher burdens, alone or in combination with any tariffs imposed by that country on that good, than the burdens of the nontariff barriers applied by the United States with respect to that good, alone or in combination with any tariffs imposed by the United States on that good, when imported from that country,
the President may take one or more of the actions authorized under subsection (b).
(b) Actions authorized.—The actions authorized under this subsection are the following:
(1) To negotiate and seek to enter into an agreement with the foreign country that commits the country to reduce the rate of duty or reduce or eliminate nontariff barriers on the good that is the subject of the determination under subsection (a).
(2) To impose a rate of duty on imports of the good that is equal to—
(A) the rate of duty imposed by the foreign country with respect to the good, in the case of a determination described in subsection (a)(1); or
(B) the effective rate of duty of the nontariff barriers applied by the foreign country with respect to the good, alone or in combination with any tariffs imposed by that country on that good, in the case of a determination described in subsection (a)(2).
(c) Factors.—In taking an action authorized under subsection (b), the President shall consider the following factors:
(1) The tariff classification of the good by the United States and the tariff classification of the good by the foreign country.
(2) The rate of duty applied by the United States with respect to the good and the rate of duty applied by the foreign country with respect to the good.
(3) The physical characteristics of the good.
(4) The end uses and existence of a competitive relationship between the good—
(A) as exported from the United States to the foreign country; and
(B) as imported from the country to the United States.
(5) The level of exports of the good by the country to the United States and to other countries.
(6) In the case of a determination described in subsection (a)(1), the extent to which the rate of duty applied by the foreign country with respect to the good is impeding or distorting trade.
(7) In the case of a determination described in subsection (a)(2)—
(A) the extent of the nontariff barriers applied by the foreign country with respect to the good and the extent of the nontariff barriers applied by the United States with respect to the good;
(B) the extent to which the nontariff barriers applied by the country with respect to the good, alone or in combination with any tariffs imposed by that country on that good, are impeding or distorting trade;
(C) the identified purpose of the nontariff barriers applied by the country with respect to the good, if any, and the extent to which the nontariff barriers are more restrictive than necessary to meet that purpose; and
(D) the degree of transparency of the process by which the country adopted the nontariff barriers.
(8) Other factors, as the President determines appropriate.
(d) Role of USTR.—The United States Trade Representative, in consultation with the Secretary of Treasury, the Secretary of Commerce, and the heads of other relevant Federal agencies, shall advise the President in determining the effective rate of duty imposed by the nontariff barriers applied by a foreign country with respect to a good, alone or in combination with any tariffs imposed by that country on that good, in the case of a determination described in subsection (a)(2).
(e) Lower rate of duty.—The President may impose a rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country that is lower than the rate of duty described in subsection (b)(2)(A) or lower than the effective rate of duty described in subsection (b)(2)(B), as the case may be, if the President determines that application of such lower rate of duty is necessary and appropriate.
(f) Higher rate of duty.—If the President imposes a rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country under subsection (b)(2), and the country further increases its rate of duty on imports of the good from the United States, the President may further increase the rate of duty on imports of the good from the country to a rate that is equal to the rate of duty applied by that country.
(g) Termination.—The President shall terminate the imposition of any increase in the rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country under subsection (b)(2) effective on the date on which the President determines that—
(1) the foreign country is no longer—
(A) imposing a rate of duty with respect to the good, as described in subsection (a)(1); or
(B) applying nontariff barriers with respect to the good, as described in subsection (a)(2); or
(2) continued imposition of the increased rate of duty on imports of the good from the foreign country is not in the economic or public interest of the United States.
SEC. 4. Notice and consultation.
(a) In general.—Before taking any action authorized under section 3(b)(1), the President shall provide notice to and consult with the Committee on Ways and Means of the House of Representatives and the Committee on Finance of the Senate regarding the proposed action.
(b) Notice.—Before taking any action authorized under section 3(b)(2), the President shall—
(1) not less than 30 days before the date on which imposition of an increased rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country is to take effect, publish notice in the Federal Register of, and allow for public comment on, the proposed imposition and level of such increased rate of duty; and
(2) seek advice regarding the proposed action from the advisory committees established under section 135 of the Trade Act of 1974 (19 U.S.C. 2155).
(c) Additional notice.—The President shall promptly publish in the Federal Register notice of any action taken pursuant to section 3(f) or 3(g).
SEC. 5. CONGRESSIONAL DISAPPROVAL OF PRESIDENTIAL IMPOSITION OF RATES OF DUTY ON IMPORTS OF GOODS FROM FOREIGN COUNTRIES UNDER SECTION 3(b)(2); DISAPPROVAL RESOLUTION.
(a) In general.—An action taken by the President under section 3(b)(2) to impose a rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country shall cease to have force and effect upon the enactment of a disapproval resolution, provided for in subsection (b), relating to that action.
(b) Congressional rulemaking power; disapproval resolution.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—This section is enacted by the Congress—
(A) as an exercise of the rulemaking power of the House of Representatives and the Senate, respectively, and as such is deemed a part of the rules of each House, respectively, but applicable only with respect to the procedures to be followed in that House in the case of disapproval resolutions and such procedures supersede other rules only to the extent that they are inconsistent therewith; and
(B) with the full recognition of the constitutional right of either House to change the rules (so far as relating to the procedure of that House) at any time, in the same manner, and to the same extent as any other rule of that House.
(2) DISAPPROVAL RESOLUTION.—For purposes of this section, the term “disapproval resolution” means only a joint resolution of either House of Congress the matter after the resolving clause of which is as follows: “That the Congress disapproves the action taken under section 3(b)(2) of the United States Reciprocal Trade Act with respect to the imposition of a rate of duty on imports of __ from __ under such section 3(b)(2).”, the first blank space being filled with a description of the good with respect to which the duty is imposed under section 3(b)(2) and the second blank being filled with the name of the foreign country from which the good is imported into the United States.
(3) CONSIDERATION.—
(A) INTRODUCTION.—All disapproval resolutions introduced in the House of Representatives shall be referred to the Committee on Ways and Means and all disapproval resolutions introduced in the Senate shall be referred to the Committee on Finance.
(B) AMENDMENTS PROHIBITED; MOTIONS TO SUSPEND APPLICATION OF THIS SUBPARAGRAPH PROHIBITED.—No amendment to a disapproval resolution shall be in order in either the House of Representatives or the Senate, and no motion to suspend the application of this subparagraph shall be in order in either House nor shall it be in order in either House for the Presiding Officer to entertain a request to suspend the application of this subparagraph by unanimous consent.
(C) MAJORITY REQUIRED FOR ADOPTION.—A disapproval resolution considered under this subsection shall require an affirmative vote of two-thirds of the Members, duly chosen and sworn, for adoption.
SEC. 6. Report.
Before entering into an agreement with a foreign country under section 3(b)(1), the United States Trade Representative shall submit to the appropriate congressional committees and leadership a report that describes—
(1) the implementation of the agreement, including how it is consistent with and does not materially differ from or otherwise affect Federal or State laws or regulations;
(2) the impact on the competitiveness of United States businesses; and
(3) the impact on United States consumers.
SEC. 7. SUNSET OF PRESIDENTIAL IMPOSITION OF RATES OF DUTY ON IMPORTS OF GOODS FROM FOREIGN COUNTRIES UNDER SECTION 3(b)(2) BY DISAPPROVAL RESOLUTION.
(a) In general.—The authority of the President to take an action under section 3(b)(2) to impose a rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country—
(1) shall be effective for the period ending on the date that is three years after the date of the enactment of this Act; and
(2) shall be extended for an additional period of three years if (and only if)—
(A) the President requests such extension under subsection (b); and
(B) a disapproval resolution is not enacted into law as provided for under subsection (c).
(b) Report to Congress.—If the President is of the opinion that the authority of the President to take an action under section 3(b)(2) to impose a rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country should be extended for the additional period described in subsection (a)(2), the President shall submit to Congress, not later than the date that is three months before the end of the period described in subsection (a)(1), a written report that contains a request for such extension, together with a description of all actions taken under section 3(b)(2) to date.
(c) Disapproval resolution.—
(1) CONGRESSIONAL RULEMAKING POWER.—This section is enacted by the Congress—
(A) as an exercise of the rulemaking power of the House of Representatives and the Senate, respectively, and as such is deemed a part of the rules of each House, respectively, but applicable only with respect to the procedures to be followed in that House in the case of disapproval resolutions and such procedures supersede other rules only to the extent that they are inconsistent therewith; and
(B) with the full recognition of the constitutional right of either House to change the rules (so far as relating to the procedure of that House) at any time, in the same manner, and to the same extent as any other rule of that House.
(2) DISAPPROVAL RESOLUTION.—For purposes of subsection (a), the term “disapproval resolution” means only a joint resolution of either House of Congress the matter after the resolving clause of which is as follows: “That the Congress disapproves the request of the President for the extension, under section 7(a)(2)(A) of the United States Reciprocal Trade Act, of the authority of the President to take an action under section 3(b)(2) of such Act to impose a rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country after the period ending on the date that is three years after the date of the enactment of such Act.”.
(3) INTRODUCTION; REFERRAL.—A disapproval resolution—
(A) may be introduced in either House of Congress by any member of such House; and
(B) shall be referred, in the House of Representatives, to the Committee on Ways and Means and, in addition, to the Committee on Rules.
(4) FLOOR CONSIDERATION.—The provisions of subsections (d) and (e) of section 152 of the Trade Act of 1974 (19 U.S.C. 2192) (relating to the floor consideration of certain resolutions in the House and Senate) apply to a disapproval resolution.
(5) LIMITATIONS ON CONSIDERATION.—It is not in order for—
(A) the House of Representatives to consider any disapproval resolution not reported by the Committee on Ways and Means and, in addition, by the Committee on Rules;
(B) the Senate to consider any disapproval resolution not reported by the Committee on Finance; or
(C) either House of Congress to consider a disapproval resolution after the date that is three years after the date of the enactment of this Act.
(d) Rules of construction.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—An action authorized under section 3(b)(2) to impose a rate of duty on imports of a good from a foreign country that is taken before the end of the period described in subsection (a)(1) or the end of the period described in subsection (a)(2) shall remain in effect after the end of such respective period.
(2) ADDITIONAL AUTHORITIES.—The President may exercise the authorities of subsections (e), (f), and (g) of section 3 with respect to an action described in paragraph (1) after the end of the period described in such paragraph that is applicable to such action.
SEC. 8. Definitions.
In this Act:
(1) APPROPRIATE CONGRESSIONAL COMMITTEES AND LEADERSHIP.—The term “appropriate congressional committees and leadership” means—
(A) the Committee on Ways and Means of the House of Representatives and the Committee on Finance of the Senate; and
(B) the Speaker of the House of Representatives, the minority leader of the House of Representatives, the majority leader of the Senate, and the minority leader of the Senate.
(2) NONTARIFF BARRIER.—The term “nontariff barrier” includes any government-imposed measure or policy, other than a customs duty, that restricts, prevents, or impedes international trade in goods, including import policies, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, technical barriers to trade, government procurement, export subsidies, lack of intellectual property protection, digital trade barriers, and government-tolerated anticompetitive conduct of state-owned or private firms.
(3) RATE OF DUTY.—The term “rate of duty” means the rate of customs duty applied on imports of a good, but does not include an antidumping or countervailing duty or a duty applied under a preferential tariff arrangement.
H.R.899 – To terminate the Department of Education.
H.R.908 – To amend section 230 of the Communications Act of 1934 (commonly referred to as the Communications Decency Act) to stop censorship, and for other purposes.
H.R.909 – To temporarily provide additional deposits into the Crime Victims Fund.
H.R.989 – To codify Executive Order 11246 titled “Equal Employment Opportunity”.
H.R.1029 – To abolish the United States Agency for International Development.
H.R. 1180 Repeal Impoundment Control Act
H.R. 1216 No NPR funding
H.R.1243 – To prohibit United States assistance to foreign countries that oppose the position of the United States in the United Nations
H.R.1251 – To provide Members of Congress access to Federal buildings, and for other purposes.
H.R.1295 – To amend chapter 9 of title 5, United States Code, to reauthorize the executive reorganization authority of the President and to ensure efficient executive reorganization, and for other purposes.
H.R.1351 – To amend the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 to require the recitation of the Pledge of Allegiance and the display of the American Flag in certain federally funded elementary and secondary schools, and for other purposes.
Abortion
H. R. 7 No Taxpayer Funding for Abortion and Abortion Insurance Full Disclosure Act of 2025
Summary: This bill modifies provisions relating to federal funding for, and health insurance coverage of, abortions.
Specifically, the bill prohibits the use of federal funds for abortions or for health coverage that includes abortions. Additionally, abortions may not be provided in a federal health care facility or by a federal employee.
Historically, language has been included in annual appropriations bills for the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) that prohibits the use of federal funds for abortions—such language is commonly referred to as the Hyde Amendment. Similar language is also frequently included in appropriations bills for other federal agencies and the District of Columbia. The bill makes these restrictions permanent and extends the restrictions to all federal funds (rather than specific agencies).
The bill’s restrictions regarding the use of federal funds do not apply in cases of rape, incest, or where a physical disorder, injury, or illness endangers a woman’s life unless an abortion is performed. The Hyde Amendment provides the same exceptions.
The bill also prohibits qualified health plans from including coverage for abortions. Currently, qualified health plans may cover abortion, but the portion of the premium attributable to abortion coverage is not eligible for subsidies.
SECTION 1. table of contents.
(b) Table of contents.
Sec. 1. Short title; table of contents.
TITLE I—PROHIBITING FEDERALLY FUNDED ABORTIONS
Sec. 101. Prohibiting taxpayer funded abortions.
Sec. 102. Amendment to table of chapters.
TITLE II—APPLICATION UNDER THE AFFORDABLE CARE ACT
Sec. 201. Clarifying application of prohibition to premium credits and cost-sharing reductions under ACA.
Sec. 202. Revision of notice requirements regarding disclosure of extent of health plan coverage of abortion and abortion premium surcharges.
TITLE I—Prohibiting Federally Funded Abortions
SEC. 101. Prohibiting taxpayer funded abortions.
Title 1, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following new chapter:
“CHAPTER 4—PROHIBITING TAXPAYER FUNDED ABORTIONS
“301. Prohibition on funding for abortions.
“302. Prohibition on funding for health benefits plans that cover abortion.
“303. Limitation on Federal facilities and employees.
“304. Construction relating to separate coverage.
“305. Construction relating to the use of non-Federal funds for health coverage.
“306. Non-preemption of other Federal laws.
“307. Construction relating to complications arising from abortion.
“308. Treatment of abortions related to rape, incest, or preserving the life of the mother.
“309. Application to District of Columbia.
Ҥ 301. Prohibition on funding for abortions
“No funds authorized or appropriated by Federal law, and none of the funds in any trust fund to which funds are authorized or appropriated by Federal law, shall be expended for any abortion.
Ҥ 302. Prohibition on funding for health benefits plans that cover abortion
“None of the funds authorized or appropriated by Federal law, and none of the funds in any trust fund to which funds are authorized or appropriated by Federal law, shall be expended for health benefits coverage that includes coverage of abortion.
Ҥ 303. Limitation on Federal facilities and employees
“No health care service furnished—
“(1) by or in a health care facility owned or operated by the Federal Government; or
“(2) by any physician or other individual employed by the Federal Government to provide health care services within the scope of the physician’s or individual’s employment,
may include abortion.
Ҥ 304. Construction relating to separate coverage
“Nothing in this chapter shall be construed as prohibiting any individual, entity, or State or locality from purchasing separate abortion coverage or health benefits coverage that includes abortion so long as such coverage is paid for entirely using only funds not authorized or appropriated by Federal law and such coverage shall not be purchased using matching funds required for a federally subsidized program, including a State’s or locality’s contribution of Medicaid matching funds.
Ҥ 305. Construction relating to the use of non-Federal funds for health coverage
“Nothing in this chapter shall be construed as restricting the ability of any non-Federal health benefits coverage provider from offering abortion coverage, or the ability of a State or locality to contract separately with such a provider for such coverage, so long as only funds not authorized or appropriated by Federal law are used and such coverage shall not be purchased using matching funds required for a federally subsidized program, including a State’s or locality’s contribution of Medicaid matching funds.
Ҥ 306. Non-preemption of other Federal laws
“Nothing in this chapter shall repeal, amend, or have any effect on any other Federal law to the extent such law imposes any limitation on the use of funds for abortion or for health benefits coverage that includes coverage of abortion, beyond the limitations set forth in this chapter.
Ҥ 307. Construction relating to complications arising from abortion
“Nothing in this chapter shall be construed to apply to the treatment of any infection, injury, disease, or disorder that has been caused by or exacerbated by the performance of an abortion. This rule of construction shall be applicable without regard to whether the abortion was performed in accord with Federal or State law, and without regard to whether funding for the abortion is permissible under section 308.
Ҥ 308. Treatment of abortions related to rape, incest, or preserving the life of the mother
“The limitations established in sections 301, 302, and 303 shall not apply to an abortion—
“(1) if the pregnancy is the result of an act of rape or incest; or
“(2) in the case where a woman suffers from a physical disorder, physical injury, or physical illness that would, as certified by a physician, place the woman in danger of death unless an abortion is performed, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself.
Ҥ 309. Application to District of Columbia
“(1) Any reference to funds appropriated by Federal law shall be treated as including any amounts within the budget of the District of Columbia that have been approved by an Act of Congress pursuant to section 446 of the District of Columbia Home Rule Act (or any applicable successor Federal law).
“(2) The term ‘Federal Government’ includes the Government of the District of Columbia.”.
SEC. 102. Amendment to table of chapters.
The table of chapters for title 1, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following new item:
- “4. Prohibiting taxpayer funded abortions 301”.
TITLE II—Application under the Affordable Care Act
SEC. 201. Clarifying application of prohibition to premium credits and cost-sharing reductions under ACA.
(a) In general.—
(1) DISALLOWANCE OF REFUNDABLE CREDIT AND COST-SHARING REDUCTIONS FOR COVERAGE UNDER QUALIFIED HEALTH PLAN WHICH PROVIDES COVERAGE FOR ABORTION.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—Subparagraph (A) of section 36B(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by inserting before the period at the end the following: “or any health plan that includes coverage for abortions (other than any abortion or treatment described in section 307 or 308 of title 1, United States Code)”.
(B) OPTION TO PURCHASE OR OFFER SEPARATE COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Paragraph (3) of section 36B(c) of such Code is amended by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(C) SEPARATE ABORTION COVERAGE OR PLAN ALLOWED.—
“(i) OPTION TO PURCHASE SEPARATE COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall be construed as prohibiting any individual from purchasing separate coverage for abortions described in such subparagraph, or a health plan that includes such abortions, so long as no credit is allowed under this section with respect to the premiums for such coverage or plan.
“(ii) OPTION TO OFFER COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall restrict any non-Federal health insurance issuer offering a health plan from offering separate coverage for abortions described in such subparagraph, or a plan that includes such abortions, so long as premiums for such separate coverage or plan are not paid for with any amount attributable to the credit allowed under this section (or the amount of any advance payment of the credit under section 1412 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act).”.
(2) DISALLOWANCE OF SMALL EMPLOYER HEALTH INSURANCE EXPENSE CREDIT FOR PLAN WHICH INCLUDES COVERAGE FOR ABORTION.—Subsection (h) of section 45R of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended—
(A) by striking “Any term” and inserting the following:
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Any term”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(2) EXCLUSION OF HEALTH PLANS INCLUDING COVERAGE FOR ABORTION.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The term ‘qualified health plan’ does not include any health plan that includes coverage for abortions (other than any abortion or treatment described in section 307 or 308 of title 1, United States Code).
“(B) SEPARATE ABORTION COVERAGE OR PLAN ALLOWED.—
“(i) OPTION TO PURCHASE SEPARATE COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall be construed as prohibiting any employer from purchasing for its employees separate coverage for abortions described in such subparagraph, or a health plan that includes such abortions, so long as no credit is allowed under this section with respect to the employer contributions for such coverage or plan.
“(ii) OPTION TO OFFER COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall restrict any non-Federal health insurance issuer offering a health plan from offering separate coverage for abortions described in such subparagraph, or a plan that includes such abortions, so long as such separate coverage or plan is not paid for with any employer contribution eligible for the credit allowed under this section.”.
(3) CONFORMING ACA AMENDMENTS.—Section 1303(b) of Public Law 111–148 (42 U.S.C. 18023(b)) is amended—
(A) by striking paragraph (2);
(B) by striking paragraph (3), as amended by section 202(a); and
(C) by redesignating paragraph (4) as paragraph (2).
(b) Application to multi-State plans.—Paragraph (6) of section 1334(a) of Public Law 111–148 (42 U.S.C. 18054(a)) is amended to read as follows:
“(6) COVERAGE CONSISTENT WITH FEDERAL ABORTION POLICY.—In entering into contracts under this subsection, the Director shall ensure that no multi-State qualified health plan offered in an Exchange provides health benefits coverage for which the expenditure of Federal funds is prohibited under chapter 4 of title 1, United States Code.”.
(c) Effective date.—The amendments made by subsection (a) shall apply to taxable years ending after December 31, 2025, but only with respect to plan years beginning after such date, and the amendment made by subsection (b) shall apply to plan years beginning after such date.
SEC. 202. Revision of notice requirements regarding disclosure of extent of health plan coverage of abortion and abortion premium surcharges.
(a) In general.—Paragraph (3) of section 1303(b) of Public Law 111–148 (42 U.S.C. 18023(b)) is amended to read as follows:
“(3) RULES RELATING TO NOTICE.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The extent of coverage (if any) of services described in paragraph (1)(B)(i) or (1)(B)(ii) by a qualified health plan shall be disclosed to enrollees at the time of enrollment in the plan and shall be prominently displayed in any marketing or advertising materials, comparison tools, or summary of benefits and coverage explanation made available with respect to such plan by the issuer of the plan, by an Exchange, or by the Secretary, including information made available through an Internet portal or Exchange under sections 1311(c)(5) and 1311(d)(4)(C).
“(B) SEPARATE DISCLOSURE OF ABORTION SURCHARGES.—In the case of a qualified health plan that includes the services described in paragraph (1)(B)(i) and where the premium for the plan is disclosed, including in any marketing or advertising materials or any other information referred to in subparagraph (A), the surcharge described in paragraph (2)(B)(i)(II) that is attributable to such services shall also be disclosed and identified separately.”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by subsection (a) shall apply to materials, tools, or other information made available more than 30 days after the date of the enactment of this Act.
H.R.49 – No Pro-Abortion Task Force Act
SEC. 2. Prohibition against use of Federal funds for HHS Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force.
No Federal funds may be used for—
(1) the HHS Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force, announced by the Secretary of Health and Human Services on January 21, 2022; or
(2) any successor or substantially similar task force.
- R. 73 Abortion Is Not Health Care Act of 2025
Summary: This bill excludes amounts paid for an abortion from the itemized tax deduction for qualified medical and dental expenses.
Under current law, individuals who itemize their tax deductions may deduct qualified medical and dental expenses to the extent that such expenses exceed 7.5% of the individual’s adjusted gross income for the tax year. Further, under current law, the calculation of the itemized tax deduction for medical and dental expenses may include amounts paid for a legal abortion.
SEC. 2. Amounts paid for abortion not taken into account in determining deduction for medical expenses.
(a) In general.—Section 213 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(f) Amounts paid for abortion not taken into account.—An amount paid during the taxable year for an abortion shall not be taken into account under subsection (a).”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by this section shall apply to taxable years beginning after the date of the enactment of this Act.
H.R.78 – Pregnant Women Health and Safety Act of 2025
Summary: This bill establishes requirements for physicians who perform abortions and abortion clinics. Specifically, the bill requires a physician who performs an abortion (1) to have admitting privileges at a nearby hospital; and (2) at the time of the abortion, to notify the patient of the hospital location where the patient can receive follow-up care if complications arise.
A physician who fails to comply is subject to criminal penalties—a fine, a prison term of up to two years, or both. A woman who undergoes an abortion may not be prosecuted.
The bill also requires an abortion clinic, in order to receive federal funds or assistance, to (1) be licensed by the state in which it is located, and (2) be in compliance with federal standards for ambulatory surgical centers.
SEC. 2. Requirement for physicians relating to the performance of abortions.
(a) In general.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) in the chapter heading by striking “Partial-Birth”; and
(2) by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Prohibition on certain procedures
“(a) Definition.—In this section, the term ‘physician’ means a doctor of medicine or osteopathy legally authorized to practice medicine and surgery by the State in which the doctor performs such activity, or any other individual legally authorized by the State to perform abortions.
“(b) Requirements.—A physician who performs an abortion shall—
“(1) have admitting privileges at a hospital located within 15 miles from the principal medical office of the physician and the location in which the abortion is being performed; and
“(2) at the time of the abortion, notify the patient involved of the hospital location where the patient can receive follow-up care by the physician if complications resulting from the abortion arise.
“(c) Offense.—It shall be unlawful for a physician, in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce, to knowingly perform an abortion and, in doing so, fail to comply with subsection (b).
“(d) Penalty.—Any physician who violates subsection (c) shall be fined under this title, imprisoned not more than 2 years, or both.
“(e) Limitation.—A woman upon whom a procedure described in subsection (c) is performed may not be prosecuted under this section, for a conspiracy to violate this section, or for an offense under section 2, 3, or 4 of this title based on a violation of this section.”.
(b) Technical and conforming amendments.—
(1) CHAPTER 74.—The table of sections for such chapter is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 1531 the following:
“1532. Prohibition on certain procedures.”.
(2) PART I.—The table of chapters for part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking the item relating to chapter 74 and inserting the following:
- “74. Abortions 1531”
SEC. 3. Requirement of abortion clinics.
(a) In general.—Subject to subsection (b), as a condition for receiving any Federal funds or assistance, an abortion clinic shall—
(1) be licensed by the State in which it is located; and
(2) be in compliance with the requirements for ambulatory surgery centers under title XVIII of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395 et seq.), except for any requirement relating to a certificate of public need for State licensing purposes.
(b) Waiver.—For purposes of complying with subsection (a)(2) with respect to an abortion clinic, a State board of health may waive the application of certain structural requirements (as the Secretary of Health and Human Services determines appropriate).
(c) Definition.—In this section, the term “abortion clinic” means a facility, other than a hospital or ambulatory surgery center, in which first, second, or third trimester abortions are performed during any 12-month period.
H.R.599 – Protect Funding for Women’s Health Care Act
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds as follows:
(1) State and county health departments, community health centers, hospitals, physicians’ offices, and other entities currently provide, and will continue to provide, health services to women. Such health services include relevant diagnostic laboratory and radiology services, well-child care, prenatal and postpartum care, immunization, family planning services including contraception, sexually transmitted disease testing, cervical and breast cancer screenings, and referrals.
(2) Many such entities provide services to all persons, regardless of the person’s ability to pay, and provide services in medically underserved areas and to medically underserved populations.
(3) All funds no longer available to Planned Parenthood Federation of America will continue to be made available to other eligible entities to provide women’s health care services.
SEC. 3. Prohibition.
(a) In general.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, no Federal funds may be made available to Planned Parenthood Federation of America, or to any of its affiliates, subsidiaries, successors, or clinics.
(b) Rules of construction.—Nothing in this Act shall be construed to—
(1) affect any limitation contained in an appropriations Act relating to abortion; or
(2) reduce overall Federal funding available in support of women’s health.
H.R.629 – Ending Chemical Abortions Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) In 2000, the Food and Drug Administration approved chemical abortion drugs for use in the United States. The agency illegally categorized pregnancy as an illness and asserted chemical abortion drugs provide a meaningful therapeutic benefit.
(2) In 2016, the Food and Drug Administration reduced the number of doctor visits required for administration of chemical abortion drugs from 3 visits to 1 visit. The agency also removed the requirement for both the in-person administration of misoprostol and a subsequent follow-up appointment. At this time, the agency also expanded the availability of inducing a chemical abortion from 7 to 10 weeks.
(3) In 2021, the Food and Drug Administration eliminated the in-person dispensing requirement for chemical abortion drugs, purporting to allow these drugs to be dispensed by mail in violation of longstanding Federal law.
(4) When compared to surgical abortions, chemical abortions are consistently more likely to result in complications that are miscoded as a spontaneous abortion or “miscarriage”.
(5) According to the Guttmacher Institute, the Abortion Industry’s think tank, since 2000, the administration of mifepristone and misoprostol has grown to comprise over 50 percent of all induced abortions in the United States.
(6) There is a four times higher risk of experiencing complications due to a chemical abortion than a surgical abortion.
SEC. 3. Renaming chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code.
The table of chapters for part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking the item related to chapter 74 and inserting the following:
“74. Abortion crimes.”.
SEC. 4. Chemical abortions prohibited.
(a) In general.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Chemical abortions
“(a) Prohibition.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, whoever prescribes, dispenses, distributes, or sells, any drug, medication, or chemical for the purpose of procuring or performing an abortion on any woman, shall be imprisoned for not more than 25 years, fined under this title, or both.
“(b) Exceptions.—Subsection (a) shall not apply to any of the following:
“(1) The sale, use, prescription or administration of any contraceptive agent administered before conception or before pregnancy can be confirmed through conventional testing.
“(2) The treatment of a miscarriage according to medical guidelines as accepted as of the date of the miscarriage.
“(3) In the case where a woman suffers from a physical disorder, physical injury, or physical illness, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, that would, as certified by a physician, place the woman in danger of death.
“(c) Bar to prosecution.—A woman upon whom a chemical abortion is performed or attempted may not be criminally prosecuted under this section.
“(d) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) ABORTION.—The term ‘abortion’ means intentionally terminating the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(A) to produce a live birth;
“(B) to remove a dead unborn child caused by miscarriage; or
“(C) to treat an ectopic or molar pregnancy.
“(2) PREGNANT; PREGNANCY.—The term ‘pregnant’ or ‘pregnancy’ refers to the human female reproductive condition of having a living unborn child within her body throughout the entire embryonic and fetal stages from fertilization to full gestation and childbirth.
“(3) UNBORN CHILD.—The term ‘unborn child’ means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b) of title 1, United States Code.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 1531 the following:
“1532. Chemical abortions.”.
H.R.682 – Heartbeat Protection Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Abortions prohibited without a check for fetal heartbeat, or if a fetal heartbeat is detectable.
(a) Abortions prohibited without a check for fetal heartbeat, or if a fetal heartbeat is detectable.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) in the chapter heading, by striking “Partial-Birth”;
(2) by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Abortions prohibited without a check for fetal heartbeat, or if a fetal heartbeat is detectable
“(a) Offense.—Any physician who knowingly performs an abortion and thereby kills a human unborn child—
“(1) without determining, according to standard medical practice, whether the unborn child has a detectable heartbeat;
“(2) without informing the mother of the results of that determination; or
“(3) after determining, according to standard medical practice, that the unborn child has a detectable heartbeat,
shall be fined under this title or imprisoned not more than 5 years, or both. This subsection does not apply to an abortion that is necessary to save the life of a mother whose life is endangered by a physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, but not including psychological or emotional conditions.
“(b) Exceptions.—Subsection (a) shall not apply if—
“(1) in reasonable medical judgment, the abortion is necessary to save the life of a pregnant woman whose life is endangered by a physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, but not including psychological or emotional conditions;
“(2) the pregnancy is the result of rape against an adult woman, and at least 48 hours prior to the abortion—
“(A) she has obtained counseling for the rape; or
“(B) she has obtained medical treatment for the rape or an injury related to the rape; or
“(3) the pregnancy is a result of rape against a minor or incest against a minor, and the rape or incest has been reported at any time prior to the abortion to either—
“(A) a government agency legally authorized to act on reports of child abuse; or
“(B) a law enforcement agency.
“(c) Documentation requirements.—
“(1) DOCUMENTATION PERTAINING TO ADULTS.—A physician who performs or attempts to perform an abortion under an exception provided by subsection (b)(2) shall, prior to performing the abortion, place in the patient medical file documentation from a hospital licensed by the State or operated under authority of a Federal agency, a medical clinic licensed by the State or operated under authority of a Federal agency, from a personal physician licensed by the State, a counselor licensed by the State, or a victim’s rights advocate provided by a law enforcement agency that the adult woman seeking the abortion obtained medical treatment or counseling for the rape or an injury related to the rape.
“(2) DOCUMENTATION PERTAINING TO MINORS.—A physician who performs or attempts to perform an abortion under an exception provided by subsection (b)(3) shall, prior to performing the abortion, place in the patient medical file documentation from a government agency legally authorized to act on reports of child abuse that the rape or incest was reported prior to the abortion; or, as an alternative, documentation from a law enforcement agency that the rape or incest was reported prior to the abortion.
“(d) Requirement for data retention.—Paragraph (j)(2) of section 164.530 of title 45, Code of Federal Regulations, shall apply to documentation required to be placed in a patient’s medical file pursuant to paragraph (6) of such section and a consent form required to be retained in a patient’s medical file pursuant to paragraph (7) of such section in the same manner and to the same extent as such paragraph applies to documentation required by paragraph (j)(1) of such section.
“(e) Additional exceptions and requirements.—
“(1) EXCLUSION OF CERTAIN FACILITIES.—Notwithstanding the definitions set forth in subsection (j), the counseling described in subsection (b)(2)(A) and subsection (c)(1) or medical treatment may not be provided by a facility that performs abortions (unless that facility is a hospital).
“(2) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION IN CASES OF REPORTS TO LAW ENFORCEMENT.—The requirements of subsection (b)(2) do not apply if the rape has been reported at any time prior to the abortion to a law enforcement agency or Department of Defense victim assistance personnel.
“(f) Defendant may seek hearing.—A defendant indicted for an offense under this section may seek a hearing before the State Medical Board on whether the physician’s conduct was necessary to save the life of the mother whose life was endangered by a physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, but not including psychological or emotional conditions. The findings on that issue are admissible on that issue at the trial of the defendant. Upon a motion of the defendant, the court shall delay the beginning of the trial for not more than 30 days to permit such a hearing to take place.
“(g) No liability for the mother on whom abortion is performed.—A mother upon whom an abortion is performed may not be prosecuted under this section, for a conspiracy to violate this section, or for an offense under section 2, 3, or 4 of this title based on a violation of this section.
“(h) Requirement for data retention.—The physician shall include in the medical file of the mother documentation of the determination, according to standard medical practice, of whether the unborn child has a detectable heartbeat, the results of that determination, notification of the mother of those results, and any information entered into evidence in any proceedings under subsection (b). Paragraph (j)(2) of section 164.530 of title 45, Code of Federal Regulations, shall apply to such documentation.
“(i) Severability.—If any provision of this section or the application of such provision to any person or circumstance is held to be invalid, the remainder of this section and the application of the provisions of the remainder to any person or circumstance shall not be affected thereby.
“(j) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) The term ‘counseling’ means counseling provided by a counselor licensed by the State, or a victims rights advocate provided by a law enforcement agency.
“(2) The term ‘medical treatment’ means treatment provided at a hospital licensed by the State or operated under authority of a Federal agency, at a medical clinic licensed by the State or operated under authority of a Federal agency, or from a personal physician licensed by the State.
“(3) The term ‘abortion’ means the use or prescription of any instrument, medicine, drug, or any other substance or device—
“(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) after viability to produce a live birth and preserve the life and health of the child born alive; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
“(4) The term ‘attempt’, with respect to an abortion, means conduct that, under the circumstances as the actor believes them to be, constitutes a substantial step in a course of conduct planned to culminate in performing an abortion.
“(5) The term ‘facility’ means any medical or counseling group, center or clinic and includes the entire legal entity, including any entity that controls, is controlled by, or is under common control with such facility.
“(6) The term ‘perform’, with respect to an abortion, includes inducing an abortion through a medical or chemical intervention including writing a prescription for a drug or device intended to result in an abortion.
“(7) The term ‘physician’ means a person licensed to practice medicine and surgery or osteopathic medicine and surgery, or otherwise legally authorized to perform an abortion.
“(8) The term ‘reasonable medical judgment’ means a medical judgment that would be made by a reasonably prudent physician, knowledgeable about the case and the treatment possibilities with respect to the medical conditions involved.
“(9) The term ‘unborn child’ means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b) of title 1.
“(10) The term ‘woman’ means a female human being whether or not she has reached the age of majority.
“(k) Rules of construction.—
“(1) GREATER PROTECTIONS.—Nothing in this section may be construed to pre-empt or limit any Federal, State, or local law that provides greater protections for an unborn child than those provided in this section.
“(2) CREATION OF RECOGNITION OF RIGHT.—Nothing in this section may be construed to create or recognize a right to abortion or to make lawful an abortion that is unlawful on the effective date of this section.”; and
(3) in the table of sections, by inserting after the item pertaining to section 1841 the following:
“1532. Abortions prohibited without a check for fetal heartbeat, or if a fetal heartbeat is detectable.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of chapters for part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended, in the item relating to chapter 74, to read as follows:
- “74. Abortions 1531”.
H.R.685 – SAVE Moms and Babies Act of 2025
To amend the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act to prohibit the approval of new abortion drugs, to prohibit investigational use exemptions for abortion drugs, and to impose additional regulatory requirements with respect to previously approved abortion drugs, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Abortion drugs prohibited.
(a) In general.—Section 505 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355) (as amended by Public Law 117–328) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(aa) Abortion drugs.—
“(1) PROHIBITIONS.—The Secretary shall not approve—
“(A) any application submitted under subsection (b) or (j) for marketing an abortion drug; or
“(B) grant an investigational use exemption under subsection (i) for—
“(i) an abortion drug; or
“(ii) any investigation in which the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant is knowingly destroyed.
“(2) PREVIOUSLY APPROVED ABORTION DRUGS.—If an approval described in paragraph (1) is in effect for an abortion drug as of the date of enactment of the Support And Value Expectant Moms and Babies Act of 2025, the Secretary shall—
“(A) not approve any labeling change—
“(i) to approve the use of such abortion drug after 70 days gestation; or
“(ii) to approve the dispensing of such abortion drug by any means other than in-person administration by the prescribing health care practitioner;
“(B) treat such abortion drug as subject to section 503(b)(1); and
“(C) require such abortion drug to be subject to a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy under section 505–1 that at a minimum—
“(i) requires health care practitioners who prescribe such abortion drug—
“(I) to be certified in accordance with the strategy; and
“(II) to not be acting in their capacity as a pharmacist;
“(ii) as part of the certification process referred to in clause (i), requires such practitioners—
“(I) to have the ability to assess the duration of pregnancy accurately;
“(II) to have the ability to diagnose ectopic pregnancies;
“(III) to have the ability to provide surgical intervention in cases of incomplete abortion or severe bleeding;
“(IV) to have the ability to ensure patient access to medical facilities equipped to provide blood transfusions and resuscitation, if necessary; and
“(V) to report any deaths or other adverse events associated with the use of such abortion drug to the Food and Drug Administration and to the manufacturer of such abortion drug, identifying the patient by a non-identifiable reference and the serial number from each package of such abortion drug;
“(iii) limits the dispensing of such abortion drug to patients—
“(I) in a clinic, medical office, or hospital by means of in-person administration by the prescribing health care practitioner; and
“(II) not in pharmacies or any setting other than the health care settings described in subclause (I);
“(iv) requires the prescribing health care practitioner to give to the patient documentation on any risk of serious complications associated with use of such abortion drug and receive acknowledgment of such receipt from the patient;
“(v) requires all known adverse events associated with such abortion drug to be reported, excluding any individually identifiable patient information, to the Food and Drug Administration by the—
“(I) manufacturers of such abortion drug; and
“(II) prescribers of such abortion drug; and
“(vi) requires reporting of administration of the abortion drug as required by State law, or in the absence of a State law regarding such reporting, in the same manner as a surgical abortion.
“(3) REPORTING ON ADVERSE EVENTS BY OTHER HEALTH CARE PRACTITIONERS.—The Secretary shall require all other health care practitioners to report to the Food and Drug Administration any adverse events experienced by their patients that are connected to use of an abortion drug, excluding any individually identifiable patient information.
“(4) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to restrict the authority of the Federal Government, or of a State, to establish, implement, and enforce requirements and restrictions with respect to abortion drugs under provisions of law other than this section that are in addition to the requirements and restrictions under this section.
“(5) DEFINITIONS.—In this section:
“(A) The term ‘abortion drug’ means any drug, substance, or combination of drugs or substances that is intended for use or that is in fact used (irrespective of how the product is labeled) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant, or to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) to produce a live birth;
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child; or
“(iii) to treat an ectopic pregnancy.
“(B) The term ‘adverse event’ includes each of the following:
“(i) A fatality.
“(ii) An ectopic pregnancy.
“(iii) A hospitalization.
“(iv) A blood loss requiring a transfusion.
“(v) An infection, including endometritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and pelvic infections with sepsis.
“(vi) A severe infection.
“(C) The term ‘gestation’ means the period of days beginning on the first day of the last menstrual period.
“(D) The term ‘health care practitioner’ means any individual who is licensed, registered, or otherwise permitted, by the United States or the jurisdiction in which the individual practices, to prescribe drugs subject to section 503(b)(1).
“(E) The term ‘unborn child’ means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b) of title 1, United States Code.”.
(b) Ongoing investigational use.—In the case of any investigational use of a drug pursuant to an investigational use exemption under section 505(i) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355(i)) that was granted before the date of enactment of this Act, such exemption is deemed to be rescinded as of the day that is 3 years after the date of enactment of this Act if the Secretary would be prohibited by section 505(aa)(1)(B) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, as added by subsection (a), from granting such exemption as of such day.
H.R.722 – To implement equal protection under the 14th article of amendment to the Constitution for the right to life of each born and preborn human person.
Text not available
H.R.729 – Teleabortion Prevention Act of 2025
To prohibit chemical abortions performed without the presence of a healthcare provider, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Chemical abortions prohibited without a healthcare provider present.
(a) Chemical abortions prohibited without a physician present.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) in the chapter heading by striking “Partial-Birth”; and
(2) by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Chemical abortions prohibited without a healthcare provider physically present
“(a) Offense.—Any healthcare provider who, in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce, who knowingly provides or attempts to provide a chemical abortion—
“(1) without physically examining the patient;
“(2) without being physically present at the location of the chemical abortion; and
“(3) without scheduling a follow-up visit for the patient to occur not more than 14 days after the administration or use of the drug to assess the patient’s physical condition,
shall be fined not more than $1,000 or imprisoned not more than 2 years, or both. This subsection does not apply to a chemical abortion that is necessary to save the life of a mother whose life is endangered by a physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself.
“(b) No liability of the patient.—A patient upon whom an abortion is performed may not be prosecuted under this section or for a conspiracy to violate this section.
“(c) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) ABORTION DRUG.—The term ‘abortion drug’ means any medicine, drug or any other substance, or any combination of drugs, medicines or substances, when it is used—
“(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) to produce a live birth; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
“(2) ATTEMPTS TO PROVIDE.—In this section, the term ‘attempts to provide’, means conduct that, under the circumstances as the actor believes them to be, constitutes a substantial step in a course of conduct planned to culminate in a chemical abortion.
“(3) HEALTHCARE PROVIDER.—The term ‘healthcare provider’ means any person licensed to prescribe prescription drugs under applicable Federal and State laws.
“(4) PROVIDE.—In this section, the term ‘provide’, means to dispense or prescribe an abortion drug, or to otherwise make an abortion drug available to a patient.
“(5) CHEMICAL ABORTION.—The term ‘chemical abortion’ refers to the use of an abortion drug to—
“(A) intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) to produce a live birth; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
“(6) UNBORN CHILD.—The term ‘unborn child’ means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b).
“(d) Rule of construction regarding ectopic pregnancy.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to have any impact on the treatment of a verified ectopic pregnancy.
“(e) Severability.—If any provision of this section or the application of such provision to any person or circumstance is held to be invalid, the remainder of this section and the application of the provisions of the remainder to any person or circumstance shall not be affected thereby.”.
(b) Clerical amendments.—
(1) CHAPTER 74.—The table of sections for such chapter is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 1531 the following:
“1532. Chemical abortions prohibited without a healthcare provider physically present.”.
(2) PART I.—The table of chapters for part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking the item relating to chapter 74, and inserting the following:
- “74. Abortions 1531”.
H.R.796 – Second Chance for Moms Act
To amend the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act to require a warning label advising that the effects of mifepristone can be counteracted, to amend the Public Health Service Act to establish a hotline to provide information to women seeking to counteract the effects of mifepristone, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Mifepristone warning label and hotline.
(a) Warning label.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 502 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 352) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(hh) If it is the drug mifepristone, and its labeling does not bear the following statement printed in conspicuous text: ‘WARNING: Medical evidence suggests that the abortifacient effects of mifepristone can be counteracted by natural progesterone, which can increase the chance of fetal survival. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine has determined that natural progesterone is safe in the first trimester of pregnancy. For more information, call [___].’ (with the blank filled in to refer to the appropriate number for the hotline under section 1009 of the Public Health Service Act).”.
(2) EFFECTIVE DATE.—Section 502(hh) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (as added by paragraph (1)) applies beginning on the date that is 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act.
(b) Hotline.—Title X of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 300 et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 1009. Hotline for reversal of effects of mifepristone.
“(a) In general.—The Secretary shall establish or maintain, directly or by grant or contract, a toll-free hotline to provide support for 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, for women seeking to reverse the effects of the drug mifepristone.
“(b) Referrals to APR providers only.—A referral through the hotline described in subsection (a) may only be made to a health care provider that provides abortion pill reversal services.”.
H.R.797 – Ultrasounds Save Lives Act of 2025
To ensure that women seeking an abortion are notified, before giving informed consent to receive an abortion, of the medical risks associated with the abortion procedure and the major developmental characteristics of the unborn child.
SEC. 2. Requirement of informed consent.
(a) In general.—
(1) REQUIREMENT OF COMPLIANCE BY PROVIDERS.—Any abortion provider, acting in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce, who knowingly performs, or attempts to perform, any abortion shall comply with the requirements of this section.
(2) REVIEW OF MEDICAL RISKS AND UNBORN HEALTH STATUS.—Except in the case of a medical emergency, an abortion provider who intends to perform, or attempt to perform, an abortion may not perform any part of the abortion procedure without first—
(A) performing an ultrasound on the woman seeking the abortion, using whichever method the physician and patient agree is best under the circumstance, and sharing the results of such ultrasound with the woman; and
(B) obtaining a signed Informed Consent Authorization form in accordance with this subsection.
(3) INFORMED CONSENT AUTHORIZATION FORM.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—The Informed Consent Authorization form required under this subsection shall—
(i) be presented in person by the abortion provider 24 hours prior to performing, or attempting to perform, the abortion to the woman seeking the abortion; and
(ii) consist of—
(I) a statement by the abortion provider indicating—
(aa) the probable gestational age, in completed days, of the child;
(bb) all medical risks associated with abortion-inducing drugs or the specific abortion procedure; and
(cc) the major developmental characteristics of unborn children at such gestational age, including the presence of a heartbeat, the ability to react to painful stimuli, and the development of organs, appendages, and facial features;
(II) a statement by the abortion provider that an ultrasound has been performed, and the results of such ultrasound have been shared, as required by paragraph (2)(A);
(III) a statement that the requirements of this subsection are binding upon the abortion provider and all other medical personnel, that such abortion providers and medical personnel are subject to criminal and civil penalties for violations of these requirements, and that a woman on whom an abortion has been performed may take civil action if these requirements are not followed; and
(IV) an affirmation that each individual signing the Informed Consent Authorization form has filled out the form to the best of his or her knowledge and understands the information contained in the form.
(B) SIGNATORIES REQUIRED.—The Informed Consent Authorization form required under this subsection shall be signed in person by the woman seeking the abortion, the abortion provider performing or attempting to perform the abortion, and a witness.
(C) RETENTION OF CONSENT FORM.—The abortion provider performing or attempting to perform an abortion shall retain the signed Informed Consent Authorization form required under this subsection in the patient’s medical file.
(D) REQUIREMENT FOR DATA RETENTION.—Paragraph (j)(2) of section 164.530 of title 45, Code of Federal Regulations, shall apply to the Informed Consent Authorization form required to be placed in a patient’s medical file pursuant to subparagraph (C) in the same manner and to the same extent as such paragraph applies to documentation required by paragraph (j)(1) of such section.
(4) EXCEPTIONS.—The requirements of this subsection shall not apply if, in reasonable medical judgment, compliance with paragraph (2) would pose a greater risk of—
(A) the death of the pregnant woman; or
(B) the substantial and irreversible physical impairment of a major bodily function, not including psychological or emotional conditions, of the pregnant woman.
(b) Penalty for failure To comply.—
(1) CIVIL PENALTY.—
(A) ENFORCEMENT BY ATTORNEY GENERAL.—The Attorney General shall commence a civil action in an appropriate district court of the United States under this subsection against any abortion provider who knowingly commits a violation of subsection (a).
(B) PENALTY.—In a civil action under subparagraph (A), the court may, to vindicate the public interest, assess a civil penalty against the abortion provider in an amount—
(i) not less than $100,000 and not more than $150,000, for each such violation that is adjudicated in the first proceeding against such abortion provider under this subsection; or
(ii) not less than $150,001 and not more than $250,000, for each such violation that is adjudicated in a subsequent proceeding against such abortion provider under this subsection.
(C) NOTIFICATION.—Upon the assessment of a civil penalty under subparagraph (B), the Attorney General shall notify the appropriate State medical licensing authority.
(D) NO PENALTIES FOR PREGNANT WOMEN.—A pregnant woman shall not be subject to any penalty under this section.
(2) PRIVATE RIGHT OF ACTION.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—A woman or a parent of a minor upon whom an abortion has been performed in violation of subsection (a) may commence a civil action against the abortion provider for appropriate relief.
(B) APPROPRIATE RELIEF.—
(i) IN GENERAL.—Subject to clause (ii), appropriate relief in a civil action under this paragraph includes—
(I) objectively verifiable money damages for all injuries, psychological and physical, occasioned by the violation;
(II) statutory damages equal to 3 times the cost of the abortion; and
(III) punitive damages.
(ii) EXCEPTION.—No damages may be awarded to a plaintiff in a civil action under this paragraph if the pregnancy in relation to which an abortion was performed in violation of subsection (a) resulted from the plaintiff’s criminal conduct.
(C) ATTORNEY’S FEES FOR PLAINTIFF.—The court shall award a reasonable attorney’s fee as part of the costs to a prevailing plaintiff in a civil action under this paragraph.
(D) ATTORNEY’S FEES FOR DEFENDANT.—If a defendant in a civil action under this paragraph prevails and the court finds that the plaintiff’s suit was frivolous, the court shall award a reasonable attorney’s fee in favor of the defendant against the plaintiff.
(E) AWARDS AGAINST WOMAN.—In any civil action under this paragraph, no damages or other monetary relief, and no attorney’s fees except as provided under subparagraph (D), may be assessed against the woman upon whom the abortion was performed or attempted.
(c) Preemption.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to preempt any provision of State law to the extent that such State law establishes, implements, or continues in effect disclosure requirements regarding abortion or penalties for failure to comply with such requirements that are more extensive than those provided under this section.
(d) Rule of construction.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to prohibit an abortion provider from presenting the information required under subsection (a) to a pregnant woman at the same time as acquiring informed consent for an abortion from such woman in accordance with State law, provided that the presentation of such information occurs at least 24 hours before the abortion.
(e) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) ABORTION.—The term “abortion” means the use or prescription of any instrument, medicine, drug, or any other substance or device—
(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
(i) after viability to produce a live birth and preserve the life and health of the child born alive; or
(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
(2) ABORTION PROVIDER.—The term “abortion provider” means a person—
(A) licensed to practice medicine and surgery or osteopathic medicine and surgery; or
(B) otherwise legally authorized to perform an abortion.
(3) ATTEMPT.—The term “attempt”, with respect to an abortion, means conduct that, under the circumstances as the actor believes them to be, constitutes a substantial step in a course of conduct planned to culminate in performing an abortion.
(4) MINOR.—The term “minor” means an individual who has not attained the age of 18 years.
(5) PERFORM.—The term “perform”, with respect to an abortion, includes inducing an abortion through a medical or chemical intervention including writing a prescription for a drug or device intended to result in an abortion.
(6) REASONABLE MEDICAL JUDGMENT.—The term “reasonable medical judgment” means a medical judgment that would be made by a reasonably prudent abortion provider, knowledgeable about the case and the treatment possibilities with respect to the medical conditions involved.
(7) UNBORN CHILD.—The term “unborn child” means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b) of title 1, United States Code.
(8) WOMAN.—The term “woman” means a female human being whether or not she has reached the age of majority.
H.R.798 – Dignity for Aborted Children Act
To protect the dignity of fetal remains, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Constitutional authority.
Congress enacts the following pursuant to Congress’ power under—
(1) the Interstate Commerce Clause of section 8 of article I of the Constitution;
(2) section 5 of the 14th Amendment to the Constitution of the United States, including the power to enforce the prohibition on government action denying equal protection of the laws; and
(3) section 8 of article I of the Constitution of the United States to make all laws necessary and proper for the carrying into execution of powers vested by the Constitution in the Government of the United States.
SEC. 3. Protection of fetal remains.
(a) In general.—Part H of title IV of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 289 et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 498F. Protection of fetal remains.
“(a) Consent requirement.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Any abortion provider, after performing an abortion, shall provide the patient with an informed consent form, offering the patient the following options for disposal of the human fetal tissue from the abortion:
“(A) The patient may take possession of the human fetal tissue and may choose to transfer the tissue to an entity providing interment or cremation services.
“(B) The patient may elect to release the human fetal tissue to the abortion provider, who shall be subject to the requirements of subsection (b).
“(2) CONSENT REQUIREMENTS.—An abortion provider described in paragraph (1) shall—
“(A) obtain a patient signature on each consent form required under paragraph (1); and
“(B) retain each such form in the patient’s file.
“(b) Provider disposal requirement.—It shall be unlawful for any abortion provider who, after performing an abortion in which the woman on whom the abortion was performed elects, pursuant to subsection (a)(1)(B), to release the human fetal tissue to the abortion provider, to fail to provide for the final disposition of the human fetal tissue through interment or cremation, consistent with State law regarding the disposal of human remains, not later than 7 days after the date on which the abortion procedure was performed. Such final disposition of human fetal tissue may be carried out through interment or cremation of tissue from more than one abortion procedure collectively.
“(c) Penalties.—
“(1) INFORMED CONSENT VIOLATIONS.—An abortion provider who fails to maintain the documentation required under subsection (a)(2)(B) shall be subject to civil monetary penalties in an amount not to exceed $50,000.
“(2) DISPOSAL VIOLATIONS.—Any abortion provider who violates subsection (b) shall be fined in accordance with title 18, United States Code, imprisoned not more than 5 years, or both.
“(3) BAR TO PROSECUTION.—A patient upon whom an abortion in violation of subsection (b) is performed or attempted may not be prosecuted under, or for a conspiracy to violate, paragraph (1), or for an offense under section 2, 3, or 4 of title 18, United States Code, based on such a violation.
“(d) Reporting.—Each abortion provider described in subsection (a)(1) shall submit annual reports to the Secretary indicating, with respect to the reporting period—
“(1) the aggregate number of abortion procedures performed by such abortion provider;
“(2) the gestational age at the time of each such procedure; and
“(3) for abortions carried out using an abortion method other than chemical abortion, the aggregate number of fetal remains transferred for interment or cremation and the number released to patients.
“(e) Annual reports by the Secretary.—The Secretary shall submit to Congress an annual report on the number of abortions by State, procedure type, and method of disposal of human fetal tissue.
“(f) Non-Preemption.—Nothing in this section shall preempt any State requirement that, at a minimum, requires interment or cremation in the same manner that other human remains are required to be treated in such State.
“(g) Definitions.—In this section—
“(1) the term ‘abortion’ means the use or prescription of any instrument, medicine, drug, or any other substance or device—
“(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) after viability to produce a live birth and preserve the life and health of the child born alive; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child;
“(2) the term ‘abortion provider’ means an individual or entity that performs abortions; and
“(3) the term ‘human fetal tissue’ has the meaning given the term in section 498A(g).”.
H.R.799 – Parental Notification and Intervention Act of 2025
To provide for parental notification and intervention in the case of an unemancipated minor seeking an abortion.
SEC. 2. Parental notification.
(a) In general.—It shall be unlawful for any person or organization in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce or who solicits or accepts Federal funds to perform any abortion on an unemancipated minor under the age of 18, to permit the facilities of the person or organization to be used to perform any abortion on such a minor, or to assist in the performance of any abortion on such a minor if the person or organization has failed to comply with all of the following requirements:
(1) The provision of written notification to the parents (as defined in subsection (e)) of the minor informing the parents that an abortion has been requested for the minor, except that such notification is not required for a parent if the physician is presented with documentation showing with a reasonable degree of certainty that a court of record in the minor’s State of residence has waived any parental notification. The court of record shall not waive any parental notification requirement unless there is clear and convincing evidence of physical abuse of the minor by such parent.
(2) Compliance with a 96-hour waiting period after notice has been received by the parents.
(3) Compliance with any injunction granted under section 3 relating to the abortion.
(b) Fine for violation.—Whoever willfully violates subsection (a) shall be fined not more than $100,000 or imprisoned not more than one year, or both, for each violation.
(c) Exception.—Subsection (a) shall not apply with respect to an unemancipated minor for whom an abortion is sought if a physician (other than the physician with principal responsibility for making the decision to perform the abortion) makes a determination that—
(1) a medical emergency exists which, with reasonable medical certainty, so complicates the medical condition of the minor that the death of the minor would result from the failure to immediately treat her physical condition even though the treatment may result in the death of her unborn child;
(2) parental notification is not possible as a result of the medical emergency; and
(3) certifications regarding compliance with paragraphs (1) and (2) have been entered in the medical records of the minor, together with the reasons upon which the determinations are based, including a statement of relevant clinical findings.
(d) Parental notification requirements.—For purposes of this section, any parental notification provided to comply with the provisions of subsection (a) for a parent shall be—
(1) delivered personally to the parent; or
(2) provided through certified mail in accordance with all of the following procedures:
(A) The certified mail is addressed to the parent.
(B) The address used is the dwelling or usual place of abode of the parent.
(C) A return receipt is requested.
(D) The delivery is restricted to the parent.
(e) Parent defined To include legal guardian.—For purposes of this Act, the term “parent” includes, with respect to an unemancipated minor, any legal guardian of the minor.
SEC. 3. Parental intervention.
Any parent required to be notified pursuant to section 2 regarding an abortion of an unemancipated minor may bring an action in the Federal district court where the parent resides or where the unemancipated minor is located to enjoin the performance of the abortion. The court shall issue a temporary injunction barring the performance of the abortion until the issue has been adjudicated and the judgment is final. The court shall issue relief permanently enjoining the abortion unless the court determines that granting such relief would be unlawful.
SEC. 4. Preemption.
Nothing in this Act shall be construed to preempt any provision of State law to the extent that such State law establishes, implements, or continues in effect greater parental notification requirements or intervention rights regarding abortion than those provided under this Act.
SEC. 5. Effective date and severability.
(a) Effective date.—The provisions of this Act shall take effect upon its enactment.
(b) Severability.—The provisions of this Act shall be severable. If any provision of this Act, or any application thereof, is found unconstitutional, that finding shall not affect any provision or application of the Act not so adjudicated.
H.R.895 – To amend title 18, United States Code, to require the Attorney General to investigate alleged violations of the partial birth abortion ban.
H.R.1349 – To amend title XI of the Social Security Act to exclude providers of certain abortion services from participation in the Medicare program.
Voting
H. R. 7 No Taxpayer Funding for Abortion and Abortion Insurance Full Disclosure Act of 2025
Summary: This bill modifies provisions relating to federal funding for, and health insurance coverage of, abortions.
Specifically, the bill prohibits the use of federal funds for abortions or for health coverage that includes abortions. Additionally, abortions may not be provided in a federal health care facility or by a federal employee.
Historically, language has been included in annual appropriations bills for the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) that prohibits the use of federal funds for abortions—such language is commonly referred to as the Hyde Amendment. Similar language is also frequently included in appropriations bills for other federal agencies and the District of Columbia. The bill makes these restrictions permanent and extends the restrictions to all federal funds (rather than specific agencies).
The bill’s restrictions regarding the use of federal funds do not apply in cases of rape, incest, or where a physical disorder, injury, or illness endangers a woman’s life unless an abortion is performed. The Hyde Amendment provides the same exceptions.
The bill also prohibits qualified health plans from including coverage for abortions. Currently, qualified health plans may cover abortion, but the portion of the premium attributable to abortion coverage is not eligible for subsidies.
SECTION 1. table of contents.
(b) Table of contents.
Sec. 1. Short title; table of contents.
TITLE I—PROHIBITING FEDERALLY FUNDED ABORTIONS
Sec. 101. Prohibiting taxpayer funded abortions.
Sec. 102. Amendment to table of chapters.
TITLE II—APPLICATION UNDER THE AFFORDABLE CARE ACT
Sec. 201. Clarifying application of prohibition to premium credits and cost-sharing reductions under ACA.
Sec. 202. Revision of notice requirements regarding disclosure of extent of health plan coverage of abortion and abortion premium surcharges.
TITLE I—Prohibiting Federally Funded Abortions
SEC. 101. Prohibiting taxpayer funded abortions.
Title 1, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following new chapter:
“CHAPTER 4—PROHIBITING TAXPAYER FUNDED ABORTIONS
“301. Prohibition on funding for abortions.
“302. Prohibition on funding for health benefits plans that cover abortion.
“303. Limitation on Federal facilities and employees.
“304. Construction relating to separate coverage.
“305. Construction relating to the use of non-Federal funds for health coverage.
“306. Non-preemption of other Federal laws.
“307. Construction relating to complications arising from abortion.
“308. Treatment of abortions related to rape, incest, or preserving the life of the mother.
“309. Application to District of Columbia.
Ҥ 301. Prohibition on funding for abortions
“No funds authorized or appropriated by Federal law, and none of the funds in any trust fund to which funds are authorized or appropriated by Federal law, shall be expended for any abortion.
Ҥ 302. Prohibition on funding for health benefits plans that cover abortion
“None of the funds authorized or appropriated by Federal law, and none of the funds in any trust fund to which funds are authorized or appropriated by Federal law, shall be expended for health benefits coverage that includes coverage of abortion.
Ҥ 303. Limitation on Federal facilities and employees
“No health care service furnished—
“(1) by or in a health care facility owned or operated by the Federal Government; or
“(2) by any physician or other individual employed by the Federal Government to provide health care services within the scope of the physician’s or individual’s employment,
may include abortion.
Ҥ 304. Construction relating to separate coverage
“Nothing in this chapter shall be construed as prohibiting any individual, entity, or State or locality from purchasing separate abortion coverage or health benefits coverage that includes abortion so long as such coverage is paid for entirely using only funds not authorized or appropriated by Federal law and such coverage shall not be purchased using matching funds required for a federally subsidized program, including a State’s or locality’s contribution of Medicaid matching funds.
Ҥ 305. Construction relating to the use of non-Federal funds for health coverage
“Nothing in this chapter shall be construed as restricting the ability of any non-Federal health benefits coverage provider from offering abortion coverage, or the ability of a State or locality to contract separately with such a provider for such coverage, so long as only funds not authorized or appropriated by Federal law are used and such coverage shall not be purchased using matching funds required for a federally subsidized program, including a State’s or locality’s contribution of Medicaid matching funds.
Ҥ 306. Non-preemption of other Federal laws
“Nothing in this chapter shall repeal, amend, or have any effect on any other Federal law to the extent such law imposes any limitation on the use of funds for abortion or for health benefits coverage that includes coverage of abortion, beyond the limitations set forth in this chapter.
Ҥ 307. Construction relating to complications arising from abortion
“Nothing in this chapter shall be construed to apply to the treatment of any infection, injury, disease, or disorder that has been caused by or exacerbated by the performance of an abortion. This rule of construction shall be applicable without regard to whether the abortion was performed in accord with Federal or State law, and without regard to whether funding for the abortion is permissible under section 308.
Ҥ 308. Treatment of abortions related to rape, incest, or preserving the life of the mother
“The limitations established in sections 301, 302, and 303 shall not apply to an abortion—
“(1) if the pregnancy is the result of an act of rape or incest; or
“(2) in the case where a woman suffers from a physical disorder, physical injury, or physical illness that would, as certified by a physician, place the woman in danger of death unless an abortion is performed, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself.
Ҥ 309. Application to District of Columbia
“(1) Any reference to funds appropriated by Federal law shall be treated as including any amounts within the budget of the District of Columbia that have been approved by an Act of Congress pursuant to section 446 of the District of Columbia Home Rule Act (or any applicable successor Federal law).
“(2) The term ‘Federal Government’ includes the Government of the District of Columbia.”.
SEC. 102. Amendment to table of chapters.
The table of chapters for title 1, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following new item:
- “4. Prohibiting taxpayer funded abortions 301”.
TITLE II—Application under the Affordable Care Act
SEC. 201. Clarifying application of prohibition to premium credits and cost-sharing reductions under ACA.
(a) In general.—
(1) DISALLOWANCE OF REFUNDABLE CREDIT AND COST-SHARING REDUCTIONS FOR COVERAGE UNDER QUALIFIED HEALTH PLAN WHICH PROVIDES COVERAGE FOR ABORTION.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—Subparagraph (A) of section 36B(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by inserting before the period at the end the following: “or any health plan that includes coverage for abortions (other than any abortion or treatment described in section 307 or 308 of title 1, United States Code)”.
(B) OPTION TO PURCHASE OR OFFER SEPARATE COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Paragraph (3) of section 36B(c) of such Code is amended by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(C) SEPARATE ABORTION COVERAGE OR PLAN ALLOWED.—
“(i) OPTION TO PURCHASE SEPARATE COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall be construed as prohibiting any individual from purchasing separate coverage for abortions described in such subparagraph, or a health plan that includes such abortions, so long as no credit is allowed under this section with respect to the premiums for such coverage or plan.
“(ii) OPTION TO OFFER COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall restrict any non-Federal health insurance issuer offering a health plan from offering separate coverage for abortions described in such subparagraph, or a plan that includes such abortions, so long as premiums for such separate coverage or plan are not paid for with any amount attributable to the credit allowed under this section (or the amount of any advance payment of the credit under section 1412 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act).”.
(2) DISALLOWANCE OF SMALL EMPLOYER HEALTH INSURANCE EXPENSE CREDIT FOR PLAN WHICH INCLUDES COVERAGE FOR ABORTION.—Subsection (h) of section 45R of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended—
(A) by striking “Any term” and inserting the following:
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Any term”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(2) EXCLUSION OF HEALTH PLANS INCLUDING COVERAGE FOR ABORTION.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The term ‘qualified health plan’ does not include any health plan that includes coverage for abortions (other than any abortion or treatment described in section 307 or 308 of title 1, United States Code).
“(B) SEPARATE ABORTION COVERAGE OR PLAN ALLOWED.—
“(i) OPTION TO PURCHASE SEPARATE COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall be construed as prohibiting any employer from purchasing for its employees separate coverage for abortions described in such subparagraph, or a health plan that includes such abortions, so long as no credit is allowed under this section with respect to the employer contributions for such coverage or plan.
“(ii) OPTION TO OFFER COVERAGE OR PLAN.—Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall restrict any non-Federal health insurance issuer offering a health plan from offering separate coverage for abortions described in such subparagraph, or a plan that includes such abortions, so long as such separate coverage or plan is not paid for with any employer contribution eligible for the credit allowed under this section.”.
(3) CONFORMING ACA AMENDMENTS.—Section 1303(b) of Public Law 111–148 (42 U.S.C. 18023(b)) is amended—
(A) by striking paragraph (2);
(B) by striking paragraph (3), as amended by section 202(a); and
(C) by redesignating paragraph (4) as paragraph (2).
(b) Application to multi-State plans.—Paragraph (6) of section 1334(a) of Public Law 111–148 (42 U.S.C. 18054(a)) is amended to read as follows:
“(6) COVERAGE CONSISTENT WITH FEDERAL ABORTION POLICY.—In entering into contracts under this subsection, the Director shall ensure that no multi-State qualified health plan offered in an Exchange provides health benefits coverage for which the expenditure of Federal funds is prohibited under chapter 4 of title 1, United States Code.”.
(c) Effective date.—The amendments made by subsection (a) shall apply to taxable years ending after December 31, 2025, but only with respect to plan years beginning after such date, and the amendment made by subsection (b) shall apply to plan years beginning after such date.
SEC. 202. Revision of notice requirements regarding disclosure of extent of health plan coverage of abortion and abortion premium surcharges.
(a) In general.—Paragraph (3) of section 1303(b) of Public Law 111–148 (42 U.S.C. 18023(b)) is amended to read as follows:
“(3) RULES RELATING TO NOTICE.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The extent of coverage (if any) of services described in paragraph (1)(B)(i) or (1)(B)(ii) by a qualified health plan shall be disclosed to enrollees at the time of enrollment in the plan and shall be prominently displayed in any marketing or advertising materials, comparison tools, or summary of benefits and coverage explanation made available with respect to such plan by the issuer of the plan, by an Exchange, or by the Secretary, including information made available through an Internet portal or Exchange under sections 1311(c)(5) and 1311(d)(4)(C).
“(B) SEPARATE DISCLOSURE OF ABORTION SURCHARGES.—In the case of a qualified health plan that includes the services described in paragraph (1)(B)(i) and where the premium for the plan is disclosed, including in any marketing or advertising materials or any other information referred to in subparagraph (A), the surcharge described in paragraph (2)(B)(i)(II) that is attributable to such services shall also be disclosed and identified separately.”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by subsection (a) shall apply to materials, tools, or other information made available more than 30 days after the date of the enactment of this Act.
H.R.49 – No Pro-Abortion Task Force Act
SEC. 2. Prohibition against use of Federal funds for HHS Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force.
No Federal funds may be used for—
(1) the HHS Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force, announced by the Secretary of Health and Human Services on January 21, 2022; or
(2) any successor or substantially similar task force.
- R. 73 Abortion Is Not Health Care Act of 2025
Summary: This bill excludes amounts paid for an abortion from the itemized tax deduction for qualified medical and dental expenses.
Under current law, individuals who itemize their tax deductions may deduct qualified medical and dental expenses to the extent that such expenses exceed 7.5% of the individual’s adjusted gross income for the tax year. Further, under current law, the calculation of the itemized tax deduction for medical and dental expenses may include amounts paid for a legal abortion.
SEC. 2. Amounts paid for abortion not taken into account in determining deduction for medical expenses.
(a) In general.—Section 213 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(f) Amounts paid for abortion not taken into account.—An amount paid during the taxable year for an abortion shall not be taken into account under subsection (a).”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by this section shall apply to taxable years beginning after the date of the enactment of this Act.
H.R.78 – Pregnant Women Health and Safety Act of 2025
Summary: This bill establishes requirements for physicians who perform abortions and abortion clinics. Specifically, the bill requires a physician who performs an abortion (1) to have admitting privileges at a nearby hospital; and (2) at the time of the abortion, to notify the patient of the hospital location where the patient can receive follow-up care if complications arise.
A physician who fails to comply is subject to criminal penalties—a fine, a prison term of up to two years, or both. A woman who undergoes an abortion may not be prosecuted.
The bill also requires an abortion clinic, in order to receive federal funds or assistance, to (1) be licensed by the state in which it is located, and (2) be in compliance with federal standards for ambulatory surgical centers.
SEC. 2. Requirement for physicians relating to the performance of abortions.
(a) In general.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) in the chapter heading by striking “Partial-Birth”; and
(2) by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Prohibition on certain procedures
“(a) Definition.—In this section, the term ‘physician’ means a doctor of medicine or osteopathy legally authorized to practice medicine and surgery by the State in which the doctor performs such activity, or any other individual legally authorized by the State to perform abortions.
“(b) Requirements.—A physician who performs an abortion shall—
“(1) have admitting privileges at a hospital located within 15 miles from the principal medical office of the physician and the location in which the abortion is being performed; and
“(2) at the time of the abortion, notify the patient involved of the hospital location where the patient can receive follow-up care by the physician if complications resulting from the abortion arise.
“(c) Offense.—It shall be unlawful for a physician, in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce, to knowingly perform an abortion and, in doing so, fail to comply with subsection (b).
“(d) Penalty.—Any physician who violates subsection (c) shall be fined under this title, imprisoned not more than 2 years, or both.
“(e) Limitation.—A woman upon whom a procedure described in subsection (c) is performed may not be prosecuted under this section, for a conspiracy to violate this section, or for an offense under section 2, 3, or 4 of this title based on a violation of this section.”.
(b) Technical and conforming amendments.—
(1) CHAPTER 74.—The table of sections for such chapter is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 1531 the following:
“1532. Prohibition on certain procedures.”.
(2) PART I.—The table of chapters for part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking the item relating to chapter 74 and inserting the following:
- “74. Abortions 1531”
SEC. 3. Requirement of abortion clinics.
(a) In general.—Subject to subsection (b), as a condition for receiving any Federal funds or assistance, an abortion clinic shall—
(1) be licensed by the State in which it is located; and
(2) be in compliance with the requirements for ambulatory surgery centers under title XVIII of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395 et seq.), except for any requirement relating to a certificate of public need for State licensing purposes.
(b) Waiver.—For purposes of complying with subsection (a)(2) with respect to an abortion clinic, a State board of health may waive the application of certain structural requirements (as the Secretary of Health and Human Services determines appropriate).
(c) Definition.—In this section, the term “abortion clinic” means a facility, other than a hospital or ambulatory surgery center, in which first, second, or third trimester abortions are performed during any 12-month period.
H.R.599 – Protect Funding for Women’s Health Care Act
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds as follows:
(1) State and county health departments, community health centers, hospitals, physicians’ offices, and other entities currently provide, and will continue to provide, health services to women. Such health services include relevant diagnostic laboratory and radiology services, well-child care, prenatal and postpartum care, immunization, family planning services including contraception, sexually transmitted disease testing, cervical and breast cancer screenings, and referrals.
(2) Many such entities provide services to all persons, regardless of the person’s ability to pay, and provide services in medically underserved areas and to medically underserved populations.
(3) All funds no longer available to Planned Parenthood Federation of America will continue to be made available to other eligible entities to provide women’s health care services.
SEC. 3. Prohibition.
(a) In general.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, no Federal funds may be made available to Planned Parenthood Federation of America, or to any of its affiliates, subsidiaries, successors, or clinics.
(b) Rules of construction.—Nothing in this Act shall be construed to—
(1) affect any limitation contained in an appropriations Act relating to abortion; or
(2) reduce overall Federal funding available in support of women’s health.
H.R.629 – Ending Chemical Abortions Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) In 2000, the Food and Drug Administration approved chemical abortion drugs for use in the United States. The agency illegally categorized pregnancy as an illness and asserted chemical abortion drugs provide a meaningful therapeutic benefit.
(2) In 2016, the Food and Drug Administration reduced the number of doctor visits required for administration of chemical abortion drugs from 3 visits to 1 visit. The agency also removed the requirement for both the in-person administration of misoprostol and a subsequent follow-up appointment. At this time, the agency also expanded the availability of inducing a chemical abortion from 7 to 10 weeks.
(3) In 2021, the Food and Drug Administration eliminated the in-person dispensing requirement for chemical abortion drugs, purporting to allow these drugs to be dispensed by mail in violation of longstanding Federal law.
(4) When compared to surgical abortions, chemical abortions are consistently more likely to result in complications that are miscoded as a spontaneous abortion or “miscarriage”.
(5) According to the Guttmacher Institute, the Abortion Industry’s think tank, since 2000, the administration of mifepristone and misoprostol has grown to comprise over 50 percent of all induced abortions in the United States.
(6) There is a four times higher risk of experiencing complications due to a chemical abortion than a surgical abortion.
SEC. 3. Renaming chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code.
The table of chapters for part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking the item related to chapter 74 and inserting the following:
“74. Abortion crimes.”.
SEC. 4. Chemical abortions prohibited.
(a) In general.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Chemical abortions
“(a) Prohibition.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, whoever prescribes, dispenses, distributes, or sells, any drug, medication, or chemical for the purpose of procuring or performing an abortion on any woman, shall be imprisoned for not more than 25 years, fined under this title, or both.
“(b) Exceptions.—Subsection (a) shall not apply to any of the following:
“(1) The sale, use, prescription or administration of any contraceptive agent administered before conception or before pregnancy can be confirmed through conventional testing.
“(2) The treatment of a miscarriage according to medical guidelines as accepted as of the date of the miscarriage.
“(3) In the case where a woman suffers from a physical disorder, physical injury, or physical illness, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, that would, as certified by a physician, place the woman in danger of death.
“(c) Bar to prosecution.—A woman upon whom a chemical abortion is performed or attempted may not be criminally prosecuted under this section.
“(d) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) ABORTION.—The term ‘abortion’ means intentionally terminating the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(A) to produce a live birth;
“(B) to remove a dead unborn child caused by miscarriage; or
“(C) to treat an ectopic or molar pregnancy.
“(2) PREGNANT; PREGNANCY.—The term ‘pregnant’ or ‘pregnancy’ refers to the human female reproductive condition of having a living unborn child within her body throughout the entire embryonic and fetal stages from fertilization to full gestation and childbirth.
“(3) UNBORN CHILD.—The term ‘unborn child’ means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b) of title 1, United States Code.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 1531 the following:
“1532. Chemical abortions.”.
H.R.682 – Heartbeat Protection Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Abortions prohibited without a check for fetal heartbeat, or if a fetal heartbeat is detectable.
(a) Abortions prohibited without a check for fetal heartbeat, or if a fetal heartbeat is detectable.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) in the chapter heading, by striking “Partial-Birth”;
(2) by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Abortions prohibited without a check for fetal heartbeat, or if a fetal heartbeat is detectable
“(a) Offense.—Any physician who knowingly performs an abortion and thereby kills a human unborn child—
“(1) without determining, according to standard medical practice, whether the unborn child has a detectable heartbeat;
“(2) without informing the mother of the results of that determination; or
“(3) after determining, according to standard medical practice, that the unborn child has a detectable heartbeat,
shall be fined under this title or imprisoned not more than 5 years, or both. This subsection does not apply to an abortion that is necessary to save the life of a mother whose life is endangered by a physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, but not including psychological or emotional conditions.
“(b) Exceptions.—Subsection (a) shall not apply if—
“(1) in reasonable medical judgment, the abortion is necessary to save the life of a pregnant woman whose life is endangered by a physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, but not including psychological or emotional conditions;
“(2) the pregnancy is the result of rape against an adult woman, and at least 48 hours prior to the abortion—
“(A) she has obtained counseling for the rape; or
“(B) she has obtained medical treatment for the rape or an injury related to the rape; or
“(3) the pregnancy is a result of rape against a minor or incest against a minor, and the rape or incest has been reported at any time prior to the abortion to either—
“(A) a government agency legally authorized to act on reports of child abuse; or
“(B) a law enforcement agency.
“(c) Documentation requirements.—
“(1) DOCUMENTATION PERTAINING TO ADULTS.—A physician who performs or attempts to perform an abortion under an exception provided by subsection (b)(2) shall, prior to performing the abortion, place in the patient medical file documentation from a hospital licensed by the State or operated under authority of a Federal agency, a medical clinic licensed by the State or operated under authority of a Federal agency, from a personal physician licensed by the State, a counselor licensed by the State, or a victim’s rights advocate provided by a law enforcement agency that the adult woman seeking the abortion obtained medical treatment or counseling for the rape or an injury related to the rape.
“(2) DOCUMENTATION PERTAINING TO MINORS.—A physician who performs or attempts to perform an abortion under an exception provided by subsection (b)(3) shall, prior to performing the abortion, place in the patient medical file documentation from a government agency legally authorized to act on reports of child abuse that the rape or incest was reported prior to the abortion; or, as an alternative, documentation from a law enforcement agency that the rape or incest was reported prior to the abortion.
“(d) Requirement for data retention.—Paragraph (j)(2) of section 164.530 of title 45, Code of Federal Regulations, shall apply to documentation required to be placed in a patient’s medical file pursuant to paragraph (6) of such section and a consent form required to be retained in a patient’s medical file pursuant to paragraph (7) of such section in the same manner and to the same extent as such paragraph applies to documentation required by paragraph (j)(1) of such section.
“(e) Additional exceptions and requirements.—
“(1) EXCLUSION OF CERTAIN FACILITIES.—Notwithstanding the definitions set forth in subsection (j), the counseling described in subsection (b)(2)(A) and subsection (c)(1) or medical treatment may not be provided by a facility that performs abortions (unless that facility is a hospital).
“(2) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION IN CASES OF REPORTS TO LAW ENFORCEMENT.—The requirements of subsection (b)(2) do not apply if the rape has been reported at any time prior to the abortion to a law enforcement agency or Department of Defense victim assistance personnel.
“(f) Defendant may seek hearing.—A defendant indicted for an offense under this section may seek a hearing before the State Medical Board on whether the physician’s conduct was necessary to save the life of the mother whose life was endangered by a physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, but not including psychological or emotional conditions. The findings on that issue are admissible on that issue at the trial of the defendant. Upon a motion of the defendant, the court shall delay the beginning of the trial for not more than 30 days to permit such a hearing to take place.
“(g) No liability for the mother on whom abortion is performed.—A mother upon whom an abortion is performed may not be prosecuted under this section, for a conspiracy to violate this section, or for an offense under section 2, 3, or 4 of this title based on a violation of this section.
“(h) Requirement for data retention.—The physician shall include in the medical file of the mother documentation of the determination, according to standard medical practice, of whether the unborn child has a detectable heartbeat, the results of that determination, notification of the mother of those results, and any information entered into evidence in any proceedings under subsection (b). Paragraph (j)(2) of section 164.530 of title 45, Code of Federal Regulations, shall apply to such documentation.
“(i) Severability.—If any provision of this section or the application of such provision to any person or circumstance is held to be invalid, the remainder of this section and the application of the provisions of the remainder to any person or circumstance shall not be affected thereby.
“(j) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) The term ‘counseling’ means counseling provided by a counselor licensed by the State, or a victims rights advocate provided by a law enforcement agency.
“(2) The term ‘medical treatment’ means treatment provided at a hospital licensed by the State or operated under authority of a Federal agency, at a medical clinic licensed by the State or operated under authority of a Federal agency, or from a personal physician licensed by the State.
“(3) The term ‘abortion’ means the use or prescription of any instrument, medicine, drug, or any other substance or device—
“(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) after viability to produce a live birth and preserve the life and health of the child born alive; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
“(4) The term ‘attempt’, with respect to an abortion, means conduct that, under the circumstances as the actor believes them to be, constitutes a substantial step in a course of conduct planned to culminate in performing an abortion.
“(5) The term ‘facility’ means any medical or counseling group, center or clinic and includes the entire legal entity, including any entity that controls, is controlled by, or is under common control with such facility.
“(6) The term ‘perform’, with respect to an abortion, includes inducing an abortion through a medical or chemical intervention including writing a prescription for a drug or device intended to result in an abortion.
“(7) The term ‘physician’ means a person licensed to practice medicine and surgery or osteopathic medicine and surgery, or otherwise legally authorized to perform an abortion.
“(8) The term ‘reasonable medical judgment’ means a medical judgment that would be made by a reasonably prudent physician, knowledgeable about the case and the treatment possibilities with respect to the medical conditions involved.
“(9) The term ‘unborn child’ means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b) of title 1.
“(10) The term ‘woman’ means a female human being whether or not she has reached the age of majority.
“(k) Rules of construction.—
“(1) GREATER PROTECTIONS.—Nothing in this section may be construed to pre-empt or limit any Federal, State, or local law that provides greater protections for an unborn child than those provided in this section.
“(2) CREATION OF RECOGNITION OF RIGHT.—Nothing in this section may be construed to create or recognize a right to abortion or to make lawful an abortion that is unlawful on the effective date of this section.”; and
(3) in the table of sections, by inserting after the item pertaining to section 1841 the following:
“1532. Abortions prohibited without a check for fetal heartbeat, or if a fetal heartbeat is detectable.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of chapters for part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended, in the item relating to chapter 74, to read as follows:
- “74. Abortions 1531”.
H.R.685 – SAVE Moms and Babies Act of 2025
To amend the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act to prohibit the approval of new abortion drugs, to prohibit investigational use exemptions for abortion drugs, and to impose additional regulatory requirements with respect to previously approved abortion drugs, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Abortion drugs prohibited.
(a) In general.—Section 505 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355) (as amended by Public Law 117–328) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(aa) Abortion drugs.—
“(1) PROHIBITIONS.—The Secretary shall not approve—
“(A) any application submitted under subsection (b) or (j) for marketing an abortion drug; or
“(B) grant an investigational use exemption under subsection (i) for—
“(i) an abortion drug; or
“(ii) any investigation in which the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant is knowingly destroyed.
“(2) PREVIOUSLY APPROVED ABORTION DRUGS.—If an approval described in paragraph (1) is in effect for an abortion drug as of the date of enactment of the Support And Value Expectant Moms and Babies Act of 2025, the Secretary shall—
“(A) not approve any labeling change—
“(i) to approve the use of such abortion drug after 70 days gestation; or
“(ii) to approve the dispensing of such abortion drug by any means other than in-person administration by the prescribing health care practitioner;
“(B) treat such abortion drug as subject to section 503(b)(1); and
“(C) require such abortion drug to be subject to a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy under section 505–1 that at a minimum—
“(i) requires health care practitioners who prescribe such abortion drug—
“(I) to be certified in accordance with the strategy; and
“(II) to not be acting in their capacity as a pharmacist;
“(ii) as part of the certification process referred to in clause (i), requires such practitioners—
“(I) to have the ability to assess the duration of pregnancy accurately;
“(II) to have the ability to diagnose ectopic pregnancies;
“(III) to have the ability to provide surgical intervention in cases of incomplete abortion or severe bleeding;
“(IV) to have the ability to ensure patient access to medical facilities equipped to provide blood transfusions and resuscitation, if necessary; and
“(V) to report any deaths or other adverse events associated with the use of such abortion drug to the Food and Drug Administration and to the manufacturer of such abortion drug, identifying the patient by a non-identifiable reference and the serial number from each package of such abortion drug;
“(iii) limits the dispensing of such abortion drug to patients—
“(I) in a clinic, medical office, or hospital by means of in-person administration by the prescribing health care practitioner; and
“(II) not in pharmacies or any setting other than the health care settings described in subclause (I);
“(iv) requires the prescribing health care practitioner to give to the patient documentation on any risk of serious complications associated with use of such abortion drug and receive acknowledgment of such receipt from the patient;
“(v) requires all known adverse events associated with such abortion drug to be reported, excluding any individually identifiable patient information, to the Food and Drug Administration by the—
“(I) manufacturers of such abortion drug; and
“(II) prescribers of such abortion drug; and
“(vi) requires reporting of administration of the abortion drug as required by State law, or in the absence of a State law regarding such reporting, in the same manner as a surgical abortion.
“(3) REPORTING ON ADVERSE EVENTS BY OTHER HEALTH CARE PRACTITIONERS.—The Secretary shall require all other health care practitioners to report to the Food and Drug Administration any adverse events experienced by their patients that are connected to use of an abortion drug, excluding any individually identifiable patient information.
“(4) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to restrict the authority of the Federal Government, or of a State, to establish, implement, and enforce requirements and restrictions with respect to abortion drugs under provisions of law other than this section that are in addition to the requirements and restrictions under this section.
“(5) DEFINITIONS.—In this section:
“(A) The term ‘abortion drug’ means any drug, substance, or combination of drugs or substances that is intended for use or that is in fact used (irrespective of how the product is labeled) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant, or to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) to produce a live birth;
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child; or
“(iii) to treat an ectopic pregnancy.
“(B) The term ‘adverse event’ includes each of the following:
“(i) A fatality.
“(ii) An ectopic pregnancy.
“(iii) A hospitalization.
“(iv) A blood loss requiring a transfusion.
“(v) An infection, including endometritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and pelvic infections with sepsis.
“(vi) A severe infection.
“(C) The term ‘gestation’ means the period of days beginning on the first day of the last menstrual period.
“(D) The term ‘health care practitioner’ means any individual who is licensed, registered, or otherwise permitted, by the United States or the jurisdiction in which the individual practices, to prescribe drugs subject to section 503(b)(1).
“(E) The term ‘unborn child’ means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b) of title 1, United States Code.”.
(b) Ongoing investigational use.—In the case of any investigational use of a drug pursuant to an investigational use exemption under section 505(i) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355(i)) that was granted before the date of enactment of this Act, such exemption is deemed to be rescinded as of the day that is 3 years after the date of enactment of this Act if the Secretary would be prohibited by section 505(aa)(1)(B) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, as added by subsection (a), from granting such exemption as of such day.
H.R.722 – To implement equal protection under the 14th article of amendment to the Constitution for the right to life of each born and preborn human person.
Text not available
H.R.729 – Teleabortion Prevention Act of 2025
To prohibit chemical abortions performed without the presence of a healthcare provider, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Chemical abortions prohibited without a healthcare provider present.
(a) Chemical abortions prohibited without a physician present.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) in the chapter heading by striking “Partial-Birth”; and
(2) by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Chemical abortions prohibited without a healthcare provider physically present
“(a) Offense.—Any healthcare provider who, in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce, who knowingly provides or attempts to provide a chemical abortion—
“(1) without physically examining the patient;
“(2) without being physically present at the location of the chemical abortion; and
“(3) without scheduling a follow-up visit for the patient to occur not more than 14 days after the administration or use of the drug to assess the patient’s physical condition,
shall be fined not more than $1,000 or imprisoned not more than 2 years, or both. This subsection does not apply to a chemical abortion that is necessary to save the life of a mother whose life is endangered by a physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself.
“(b) No liability of the patient.—A patient upon whom an abortion is performed may not be prosecuted under this section or for a conspiracy to violate this section.
“(c) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) ABORTION DRUG.—The term ‘abortion drug’ means any medicine, drug or any other substance, or any combination of drugs, medicines or substances, when it is used—
“(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) to produce a live birth; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
“(2) ATTEMPTS TO PROVIDE.—In this section, the term ‘attempts to provide’, means conduct that, under the circumstances as the actor believes them to be, constitutes a substantial step in a course of conduct planned to culminate in a chemical abortion.
“(3) HEALTHCARE PROVIDER.—The term ‘healthcare provider’ means any person licensed to prescribe prescription drugs under applicable Federal and State laws.
“(4) PROVIDE.—In this section, the term ‘provide’, means to dispense or prescribe an abortion drug, or to otherwise make an abortion drug available to a patient.
“(5) CHEMICAL ABORTION.—The term ‘chemical abortion’ refers to the use of an abortion drug to—
“(A) intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) to produce a live birth; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
“(6) UNBORN CHILD.—The term ‘unborn child’ means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b).
“(d) Rule of construction regarding ectopic pregnancy.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to have any impact on the treatment of a verified ectopic pregnancy.
“(e) Severability.—If any provision of this section or the application of such provision to any person or circumstance is held to be invalid, the remainder of this section and the application of the provisions of the remainder to any person or circumstance shall not be affected thereby.”.
(b) Clerical amendments.—
(1) CHAPTER 74.—The table of sections for such chapter is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 1531 the following:
“1532. Chemical abortions prohibited without a healthcare provider physically present.”.
(2) PART I.—The table of chapters for part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking the item relating to chapter 74, and inserting the following:
- “74. Abortions 1531”.
H.R.796 – Second Chance for Moms Act
To amend the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act to require a warning label advising that the effects of mifepristone can be counteracted, to amend the Public Health Service Act to establish a hotline to provide information to women seeking to counteract the effects of mifepristone, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Mifepristone warning label and hotline.
(a) Warning label.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 502 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 352) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(hh) If it is the drug mifepristone, and its labeling does not bear the following statement printed in conspicuous text: ‘WARNING: Medical evidence suggests that the abortifacient effects of mifepristone can be counteracted by natural progesterone, which can increase the chance of fetal survival. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine has determined that natural progesterone is safe in the first trimester of pregnancy. For more information, call [___].’ (with the blank filled in to refer to the appropriate number for the hotline under section 1009 of the Public Health Service Act).”.
(2) EFFECTIVE DATE.—Section 502(hh) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (as added by paragraph (1)) applies beginning on the date that is 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act.
(b) Hotline.—Title X of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 300 et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 1009. Hotline for reversal of effects of mifepristone.
“(a) In general.—The Secretary shall establish or maintain, directly or by grant or contract, a toll-free hotline to provide support for 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, for women seeking to reverse the effects of the drug mifepristone.
“(b) Referrals to APR providers only.—A referral through the hotline described in subsection (a) may only be made to a health care provider that provides abortion pill reversal services.”.
H.R.797 – Ultrasounds Save Lives Act of 2025
To ensure that women seeking an abortion are notified, before giving informed consent to receive an abortion, of the medical risks associated with the abortion procedure and the major developmental characteristics of the unborn child.
SEC. 2. Requirement of informed consent.
(a) In general.—
(1) REQUIREMENT OF COMPLIANCE BY PROVIDERS.—Any abortion provider, acting in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce, who knowingly performs, or attempts to perform, any abortion shall comply with the requirements of this section.
(2) REVIEW OF MEDICAL RISKS AND UNBORN HEALTH STATUS.—Except in the case of a medical emergency, an abortion provider who intends to perform, or attempt to perform, an abortion may not perform any part of the abortion procedure without first—
(A) performing an ultrasound on the woman seeking the abortion, using whichever method the physician and patient agree is best under the circumstance, and sharing the results of such ultrasound with the woman; and
(B) obtaining a signed Informed Consent Authorization form in accordance with this subsection.
(3) INFORMED CONSENT AUTHORIZATION FORM.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—The Informed Consent Authorization form required under this subsection shall—
(i) be presented in person by the abortion provider 24 hours prior to performing, or attempting to perform, the abortion to the woman seeking the abortion; and
(ii) consist of—
(I) a statement by the abortion provider indicating—
(aa) the probable gestational age, in completed days, of the child;
(bb) all medical risks associated with abortion-inducing drugs or the specific abortion procedure; and
(cc) the major developmental characteristics of unborn children at such gestational age, including the presence of a heartbeat, the ability to react to painful stimuli, and the development of organs, appendages, and facial features;
(II) a statement by the abortion provider that an ultrasound has been performed, and the results of such ultrasound have been shared, as required by paragraph (2)(A);
(III) a statement that the requirements of this subsection are binding upon the abortion provider and all other medical personnel, that such abortion providers and medical personnel are subject to criminal and civil penalties for violations of these requirements, and that a woman on whom an abortion has been performed may take civil action if these requirements are not followed; and
(IV) an affirmation that each individual signing the Informed Consent Authorization form has filled out the form to the best of his or her knowledge and understands the information contained in the form.
(B) SIGNATORIES REQUIRED.—The Informed Consent Authorization form required under this subsection shall be signed in person by the woman seeking the abortion, the abortion provider performing or attempting to perform the abortion, and a witness.
(C) RETENTION OF CONSENT FORM.—The abortion provider performing or attempting to perform an abortion shall retain the signed Informed Consent Authorization form required under this subsection in the patient’s medical file.
(D) REQUIREMENT FOR DATA RETENTION.—Paragraph (j)(2) of section 164.530 of title 45, Code of Federal Regulations, shall apply to the Informed Consent Authorization form required to be placed in a patient’s medical file pursuant to subparagraph (C) in the same manner and to the same extent as such paragraph applies to documentation required by paragraph (j)(1) of such section.
(4) EXCEPTIONS.—The requirements of this subsection shall not apply if, in reasonable medical judgment, compliance with paragraph (2) would pose a greater risk of—
(A) the death of the pregnant woman; or
(B) the substantial and irreversible physical impairment of a major bodily function, not including psychological or emotional conditions, of the pregnant woman.
(b) Penalty for failure To comply.—
(1) CIVIL PENALTY.—
(A) ENFORCEMENT BY ATTORNEY GENERAL.—The Attorney General shall commence a civil action in an appropriate district court of the United States under this subsection against any abortion provider who knowingly commits a violation of subsection (a).
(B) PENALTY.—In a civil action under subparagraph (A), the court may, to vindicate the public interest, assess a civil penalty against the abortion provider in an amount—
(i) not less than $100,000 and not more than $150,000, for each such violation that is adjudicated in the first proceeding against such abortion provider under this subsection; or
(ii) not less than $150,001 and not more than $250,000, for each such violation that is adjudicated in a subsequent proceeding against such abortion provider under this subsection.
(C) NOTIFICATION.—Upon the assessment of a civil penalty under subparagraph (B), the Attorney General shall notify the appropriate State medical licensing authority.
(D) NO PENALTIES FOR PREGNANT WOMEN.—A pregnant woman shall not be subject to any penalty under this section.
(2) PRIVATE RIGHT OF ACTION.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—A woman or a parent of a minor upon whom an abortion has been performed in violation of subsection (a) may commence a civil action against the abortion provider for appropriate relief.
(B) APPROPRIATE RELIEF.—
(i) IN GENERAL.—Subject to clause (ii), appropriate relief in a civil action under this paragraph includes—
(I) objectively verifiable money damages for all injuries, psychological and physical, occasioned by the violation;
(II) statutory damages equal to 3 times the cost of the abortion; and
(III) punitive damages.
(ii) EXCEPTION.—No damages may be awarded to a plaintiff in a civil action under this paragraph if the pregnancy in relation to which an abortion was performed in violation of subsection (a) resulted from the plaintiff’s criminal conduct.
(C) ATTORNEY’S FEES FOR PLAINTIFF.—The court shall award a reasonable attorney’s fee as part of the costs to a prevailing plaintiff in a civil action under this paragraph.
(D) ATTORNEY’S FEES FOR DEFENDANT.—If a defendant in a civil action under this paragraph prevails and the court finds that the plaintiff’s suit was frivolous, the court shall award a reasonable attorney’s fee in favor of the defendant against the plaintiff.
(E) AWARDS AGAINST WOMAN.—In any civil action under this paragraph, no damages or other monetary relief, and no attorney’s fees except as provided under subparagraph (D), may be assessed against the woman upon whom the abortion was performed or attempted.
(c) Preemption.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to preempt any provision of State law to the extent that such State law establishes, implements, or continues in effect disclosure requirements regarding abortion or penalties for failure to comply with such requirements that are more extensive than those provided under this section.
(d) Rule of construction.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to prohibit an abortion provider from presenting the information required under subsection (a) to a pregnant woman at the same time as acquiring informed consent for an abortion from such woman in accordance with State law, provided that the presentation of such information occurs at least 24 hours before the abortion.
(e) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) ABORTION.—The term “abortion” means the use or prescription of any instrument, medicine, drug, or any other substance or device—
(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
(i) after viability to produce a live birth and preserve the life and health of the child born alive; or
(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
(2) ABORTION PROVIDER.—The term “abortion provider” means a person—
(A) licensed to practice medicine and surgery or osteopathic medicine and surgery; or
(B) otherwise legally authorized to perform an abortion.
(3) ATTEMPT.—The term “attempt”, with respect to an abortion, means conduct that, under the circumstances as the actor believes them to be, constitutes a substantial step in a course of conduct planned to culminate in performing an abortion.
(4) MINOR.—The term “minor” means an individual who has not attained the age of 18 years.
(5) PERFORM.—The term “perform”, with respect to an abortion, includes inducing an abortion through a medical or chemical intervention including writing a prescription for a drug or device intended to result in an abortion.
(6) REASONABLE MEDICAL JUDGMENT.—The term “reasonable medical judgment” means a medical judgment that would be made by a reasonably prudent abortion provider, knowledgeable about the case and the treatment possibilities with respect to the medical conditions involved.
(7) UNBORN CHILD.—The term “unborn child” means an individual organism of the species homo sapiens, beginning at fertilization, until the point of being born alive as defined in section 8(b) of title 1, United States Code.
(8) WOMAN.—The term “woman” means a female human being whether or not she has reached the age of majority.
H.R.798 – Dignity for Aborted Children Act
To protect the dignity of fetal remains, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Constitutional authority.
Congress enacts the following pursuant to Congress’ power under—
(1) the Interstate Commerce Clause of section 8 of article I of the Constitution;
(2) section 5 of the 14th Amendment to the Constitution of the United States, including the power to enforce the prohibition on government action denying equal protection of the laws; and
(3) section 8 of article I of the Constitution of the United States to make all laws necessary and proper for the carrying into execution of powers vested by the Constitution in the Government of the United States.
SEC. 3. Protection of fetal remains.
(a) In general.—Part H of title IV of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 289 et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 498F. Protection of fetal remains.
“(a) Consent requirement.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Any abortion provider, after performing an abortion, shall provide the patient with an informed consent form, offering the patient the following options for disposal of the human fetal tissue from the abortion:
“(A) The patient may take possession of the human fetal tissue and may choose to transfer the tissue to an entity providing interment or cremation services.
“(B) The patient may elect to release the human fetal tissue to the abortion provider, who shall be subject to the requirements of subsection (b).
“(2) CONSENT REQUIREMENTS.—An abortion provider described in paragraph (1) shall—
“(A) obtain a patient signature on each consent form required under paragraph (1); and
“(B) retain each such form in the patient’s file.
“(b) Provider disposal requirement.—It shall be unlawful for any abortion provider who, after performing an abortion in which the woman on whom the abortion was performed elects, pursuant to subsection (a)(1)(B), to release the human fetal tissue to the abortion provider, to fail to provide for the final disposition of the human fetal tissue through interment or cremation, consistent with State law regarding the disposal of human remains, not later than 7 days after the date on which the abortion procedure was performed. Such final disposition of human fetal tissue may be carried out through interment or cremation of tissue from more than one abortion procedure collectively.
“(c) Penalties.—
“(1) INFORMED CONSENT VIOLATIONS.—An abortion provider who fails to maintain the documentation required under subsection (a)(2)(B) shall be subject to civil monetary penalties in an amount not to exceed $50,000.
“(2) DISPOSAL VIOLATIONS.—Any abortion provider who violates subsection (b) shall be fined in accordance with title 18, United States Code, imprisoned not more than 5 years, or both.
“(3) BAR TO PROSECUTION.—A patient upon whom an abortion in violation of subsection (b) is performed or attempted may not be prosecuted under, or for a conspiracy to violate, paragraph (1), or for an offense under section 2, 3, or 4 of title 18, United States Code, based on such a violation.
“(d) Reporting.—Each abortion provider described in subsection (a)(1) shall submit annual reports to the Secretary indicating, with respect to the reporting period—
“(1) the aggregate number of abortion procedures performed by such abortion provider;
“(2) the gestational age at the time of each such procedure; and
“(3) for abortions carried out using an abortion method other than chemical abortion, the aggregate number of fetal remains transferred for interment or cremation and the number released to patients.
“(e) Annual reports by the Secretary.—The Secretary shall submit to Congress an annual report on the number of abortions by State, procedure type, and method of disposal of human fetal tissue.
“(f) Non-Preemption.—Nothing in this section shall preempt any State requirement that, at a minimum, requires interment or cremation in the same manner that other human remains are required to be treated in such State.
“(g) Definitions.—In this section—
“(1) the term ‘abortion’ means the use or prescription of any instrument, medicine, drug, or any other substance or device—
“(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) after viability to produce a live birth and preserve the life and health of the child born alive; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child;
“(2) the term ‘abortion provider’ means an individual or entity that performs abortions; and
“(3) the term ‘human fetal tissue’ has the meaning given the term in section 498A(g).”.
H.R.799 – Parental Notification and Intervention Act of 2025
To provide for parental notification and intervention in the case of an unemancipated minor seeking an abortion.
SEC. 2. Parental notification.
(a) In general.—It shall be unlawful for any person or organization in or affecting interstate or foreign commerce or who solicits or accepts Federal funds to perform any abortion on an unemancipated minor under the age of 18, to permit the facilities of the person or organization to be used to perform any abortion on such a minor, or to assist in the performance of any abortion on such a minor if the person or organization has failed to comply with all of the following requirements:
(1) The provision of written notification to the parents (as defined in subsection (e)) of the minor informing the parents that an abortion has been requested for the minor, except that such notification is not required for a parent if the physician is presented with documentation showing with a reasonable degree of certainty that a court of record in the minor’s State of residence has waived any parental notification. The court of record shall not waive any parental notification requirement unless there is clear and convincing evidence of physical abuse of the minor by such parent.
(2) Compliance with a 96-hour waiting period after notice has been received by the parents.
(3) Compliance with any injunction granted under section 3 relating to the abortion.
(b) Fine for violation.—Whoever willfully violates subsection (a) shall be fined not more than $100,000 or imprisoned not more than one year, or both, for each violation.
(c) Exception.—Subsection (a) shall not apply with respect to an unemancipated minor for whom an abortion is sought if a physician (other than the physician with principal responsibility for making the decision to perform the abortion) makes a determination that—
(1) a medical emergency exists which, with reasonable medical certainty, so complicates the medical condition of the minor that the death of the minor would result from the failure to immediately treat her physical condition even though the treatment may result in the death of her unborn child;
(2) parental notification is not possible as a result of the medical emergency; and
(3) certifications regarding compliance with paragraphs (1) and (2) have been entered in the medical records of the minor, together with the reasons upon which the determinations are based, including a statement of relevant clinical findings.
(d) Parental notification requirements.—For purposes of this section, any parental notification provided to comply with the provisions of subsection (a) for a parent shall be—
(1) delivered personally to the parent; or
(2) provided through certified mail in accordance with all of the following procedures:
(A) The certified mail is addressed to the parent.
(B) The address used is the dwelling or usual place of abode of the parent.
(C) A return receipt is requested.
(D) The delivery is restricted to the parent.
(e) Parent defined To include legal guardian.—For purposes of this Act, the term “parent” includes, with respect to an unemancipated minor, any legal guardian of the minor.
SEC. 3. Parental intervention.
Any parent required to be notified pursuant to section 2 regarding an abortion of an unemancipated minor may bring an action in the Federal district court where the parent resides or where the unemancipated minor is located to enjoin the performance of the abortion. The court shall issue a temporary injunction barring the performance of the abortion until the issue has been adjudicated and the judgment is final. The court shall issue relief permanently enjoining the abortion unless the court determines that granting such relief would be unlawful.
SEC. 4. Preemption.
Nothing in this Act shall be construed to preempt any provision of State law to the extent that such State law establishes, implements, or continues in effect greater parental notification requirements or intervention rights regarding abortion than those provided under this Act.
SEC. 5. Effective date and severability.
(a) Effective date.—The provisions of this Act shall take effect upon its enactment.
(b) Severability.—The provisions of this Act shall be severable. If any provision of this Act, or any application thereof, is found unconstitutional, that finding shall not affect any provision or application of the Act not so adjudicated.
H.R.895 – To amend title 18, United States Code, to require the Attorney General to investigate alleged violations of the partial birth abortion ban.
H.R.1349 – To amend title XI of the Social Security Act to exclude providers of certain abortion services from participation in the Medicare program.
Guns
H. R. 38 Constitutional Concealed Carry Reciprocity Act
To amend title 18, United States Code, to provide a means by which nonresidents of a State whose residents may carry concealed firearms may also do so in the State.
SEC. 2. Reciprocity for the carrying of certain concealed firearms.
(a) In general.—Chapter 44 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by inserting after section 926C the following:
Ҥ 926D. Reciprocity for the carrying of certain concealed firearms
“(a) Notwithstanding any provision of the law of any State or political subdivision thereof (except as provided in subsection (b)) and subject only to the requirements of this section, a person who is not prohibited by Federal law from possessing, transporting, shipping, or receiving a firearm, who is carrying a valid identification document containing a photograph of the person, and who is carrying a valid license or permit which is issued pursuant to the law of a State and which permits the person to carry a concealed firearm or is entitled to carry a concealed firearm in the State in which the person resides, may possess or carry a concealed handgun (other than a machine gun or destructive device) that has been shipped or transported in interstate or foreign commerce, in any State that—
“(1) has a statute under which residents of the State may apply for a license or permit to carry a concealed firearm; or
“(2) does not prohibit the carrying of concealed firearms by residents of the State for lawful purposes.
“(b) This section shall not be construed to supersede or limit the laws of any State that—
“(1) permit private persons or entities to prohibit or restrict the possession of concealed firearms on their property; or
“(2) prohibit or restrict the possession of firearms on any State or local government property, installation, building, or base.
“(c) (1) A person who carries or possesses a concealed handgun in accordance with subsections (a) and (b) may not be arrested or otherwise detained for violation of any law or any rule or regulation of a State or any political subdivision thereof related to the possession, transportation, or carrying of firearms unless there is probable cause to believe that the person is doing so in a manner not provided for by this section. Presentation of facially valid documents as specified in subsection (a) is prima facie evidence that the individual has a license or permit as required by this section.
“(2) When a person asserts this section as a defense in a criminal proceeding, the prosecution shall bear the burden of proving, beyond a reasonable doubt, that the conduct of the person did not satisfy the conditions set forth in subsections (a) and (b).
“(3) When a person successfully asserts this section as a defense in a criminal proceeding, the court shall award the prevailing defendant a reasonable attorney’s fee.
“(d) (1) A person who is deprived of any right, privilege, or immunity secured by this section, under color of any statute, ordinance, regulation, custom, or usage of any State or any political subdivision thereof, may bring an action in any appropriate court against any other person, including a State or political subdivision thereof, who causes the person to be subject to the deprivation, for damages or other appropriate relief.
“(2) The court shall award a plaintiff prevailing in an action brought under paragraph (1) damages and such other relief as the court deems appropriate, including a reasonable attorney’s fee.
“(e) In subsection (a):
“(1) The term ‘identification document’ means a document made or issued by or under the authority of the United States Government, a State, or a political subdivision of a State which, when completed with information concerning a particular individual, is of a type intended or commonly accepted for the purpose of identification of individuals.
“(2) The term ‘handgun’ includes any magazine for use in a handgun and any ammunition loaded into the handgun or its magazine.
“(f) (1) A person who possesses or carries a concealed handgun under subsection (a) shall not be subject to the prohibitions of section 922(q).
“(2) A person possessing or carrying a concealed handgun in a State under subsection (a) may do so in any of the following areas in the State that are open to the public:
“(A) A unit of the National Park System.
“(B) A unit of the National Wildlife Refuge System.
“(C) Public land under the jurisdiction of the Bureau of Land Management.
“(D) Land administered and managed by the Army Corps of Engineers.
“(E) Land administered and managed by the Bureau of Reclamation.
“(F) Land administered and managed by the Forest Service.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for such chapter is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 926C the following:
“926D. Reciprocity for the carrying of certain concealed firearms.”.
(c) Severability.—Notwithstanding any other provision of this Act, if any provision of this section, or any amendment made by this section, or the application of such provision or amendment to any person or circumstance is held to be unconstitutional, this section and amendments made by this section and the application of such provision or amendment to other persons or circumstances shall not be affected thereby.
(d) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall take effect 90 days after the date of the enactment of this Act.
- R. 45 “Firearm Industry Non-Discrimination Act” or the “FIND Act”.
To amend title 41, United States Code, to prohibit the Federal Government from entering into contracts with an entity that discriminates against the firearm and ammunition industry, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Prohibition on entering into contracts with entities discriminating against the firearm and ammunition industry.
(a) Prohibition.—Chapter 47 of title 41, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
Ҥ 4715. Prohibition on entering into contracts with entities discriminating against the firearm and ammunition industry.
“(a) Prohibition.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—The head of an executive agency shall include in each contract for the procurement of goods or services awarded by the executive agency, a clause requiring the prime contractor to certify that the contractor—
“(A) has no policy, practice, guidance, or directive that discriminates against a firearm entity or firearm trade association; and
“(B) will not adopt a policy, practice, guidance, or directive that discriminates against a firearm entity or firearm trade association during the term of the contract.
“(2) SUBCONTRACTS.—The head of an executive agency shall include in each contract for the procurement of goods or services awarded by the executive agency, a clause that prohibits the prime contractor on such contract from—
“(A) awarding a first-tier subcontract with a value greater than 10 percent of the total value of the prime contract to an entity that fails to certify in writing to the prime contractor that the entity—
“(i) has no policy, practice, guidance, or directive that discriminates against a firearm entity or firearm trade association; and
“(ii) will not adopt a policy, practice, guidance, or directive that discriminates against a firearm entity or firearm trade association during the term of the contract; and
“(B) structuring subcontract tiers in a manner designed to avoid violating subparagraph (A) by enabling a subcontractor to perform more than 10 percent of the total value of the prime contract as a lower-tier subcontractor.
“(3) PENALTIES.—The clause included in contracts pursuant to paragraph (1) or paragraph (2) shall provide that, in the event that the prime contractor violates the clause—
“(A) the prime contract shall be terminated for default; and
“(B) a suspension or debarment proceeding will be initiated for the contractor on the basis of the violation.
“(b) Exception.—Subsection (a) shall not apply to a contract for the procurement of goods or services that is a sole-source contract.
“(c) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) DISCRIMINATE.—The term ‘discriminate’ means to—
“(A) make a judgement about a policy, practice, guidance, or directive on the basis of—
“(i) partial criteria or a category-based assessment analysis, rather than—
“(I) on a case-by-case basis; or
“(II) using empirical data evaluated under quantifiable standards; or
“(ii) criteria other than criteria free from—
“(I) favoritism or prejudice against or dislike for the firearm entity or trade association or the products or services sold by the firearm entity or trade association; or
“(II) favoritism for market alternatives to the business of the firearm entity or the trade association;
“(B) refuse to provide services, or deny, cancel, or limit services, to the firearm entity or trade association on the basis of criteria other than—
“(i) criteria free from—
“(I) favoritism or prejudice against or dislike for the firearm entity or trade association or the products or services sold by the firearm entity or trade association; or
“(II) favoritism for market alternatives to the business of the firearm entity or the trade association;
“(ii) criteria related to credit history and financial risk specific to a customer or potential customer; or
“(iii) criteria related to noncompliance with Federal, State, or local law; or
“(C) limit the operations of the firearm entity or trade association in manner not required by—
“(i) Federal, State, or local law; or
“(ii) Federal, State, or local regulation.
“(2) FIREARM ENTITY.—The term ‘firearm entity’ means any—
“(A) person who is licensed under section 923 of title 18 to import, manufacture, or deal in firearms;
“(B) seller of ammunition, as defined in section 7903 of title 15;
“(C) manufacturer or importer of, or dealer in, a secure gun storage or safety device, as defined in section 921(a) of title 18; and
“(D) manufacturer or importer of, or dealer in, a component part or accessory of a firearm or ammunition.
“(3) FIREARM TRADE ASSOCIATION.—The term ‘firearm trade association’ has the meaning in section 7903 of title 15.
“(4) FIRST-TIER SUBCONTRACT.—The term ‘first-tier subcontract’ means a subcontract entered into by a subcontractor with the prime contractor for the purposes of carrying out the prime contract.
“(5) LOWER-TIER SUBCONTRACTOR.—The term ‘lower-tier subcontractor’ means any person entering into a contract with a subcontractor of a prime contractor for the purposes of carrying out the prime contract.
“(6) PRIME CONTRACT; PRIME CONTRACTOR.—The terms ‘prime contract’ and ‘prime contractor’ have the meaning given those terms in section 8701 of title 41.”.
(b) Application.—Section 4715 of title 41, United States Code, as added by subsection (a), shall apply with respect to contracts awarded on or after the date of the enactment of this Act.
(c) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for chapter 47 of title 41, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
“4715. Prohibition on entering into contracts with entities discriminating against the firearm and ammunition industry.”.
H. R. 221 Abolish the ATF Act
To abolish the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.
SEC. 2. Abolishment of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.
The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives is hereby abolished.
- R. 223 Preventing Unjust Red Flag Laws Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Prohibition on funding for implementation and enforcement of red flag laws or rules.
(a) Prohibition on funding.—None of the funds made available for any Federal department or agency may be used to—
(1) implement or enforce Federal red flag laws; or
(2) provide assistance to States, local, tribal, or territorial government departments or agencies for the implementation or enforcement of red flag laws.
(b) Red flag law defined.—In this section, the term “red flag law” means a risk-based, temporary, and preemptive protective order that authorizes the removal of a firearm without due process.
H.R.335 – Repeal the NFA Act
SEC. 2. Repeal of National Firearms Act.
Chapter 53 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, and the item relating to such chapter in the table of chapters for subtitle E, are hereby repealed.
H.R.404 – Hearing Protection Act
SEC. 2. Equal treatment of silencers and firearms.
(a) In general.—Section 5845(a) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking “(7) any silencer” and all that follows through “; and (8)” and inserting “and (7)”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by this section shall apply to calendar quarters beginning more than 90 days after the date of the enactment of this Act.
SEC. 3. Treatment of certain silencers.
Section 5841 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(f) Firearm silencers.—A person acquiring or possessing a firearm silencer in accordance with chapter 44 of title 18, United States Code, shall be treated as meeting any registration and licensing requirements of the National Firearms Act with respect to such silencer.”.
SEC. 4. Preemption of certain State laws in relation to firearm silencers.
H.R.624 – RIFLE Act of 2025 or “Reining In Federal Licensing Enforcement Act of 2025”
To reform the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives.
SEC. 2. Graduated penalties for civil violations by Federal firearms licensees.
Section 923 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking subsections (e) and (f) and inserting the following:
“(e) (1) (A) If the Attorney General determines that a licensee under this section has violated this chapter—
“(i) in the case of a violation that is not willful, the Attorney General shall notify the licensee of the violation and work with the licensee to rectify the violation within a commercially reasonable time frame; or
“(ii) in the case of a willful violation, if the Attorney General, after working with the licensee to rectify the violation within a commercially reasonable time frame, finds that a lesser action (such as a warning, warning letter, or warning conference) is not likely to lead to future compliance, and the Attorney General seeks revocation of the license in an administrative action, the Attorney General may—
“(I) if the licensee has no history of noncompliance with this chapter, suspend the license for not more than 30 days or such lesser period as would apply on compliance with such conditions as are specified by the Attorney General; or
“(II) in any other case, revoke the license.
“(B) In applying subparagraph (A), the Attorney General shall presume that the violation is not willful, absent clear and convincing evidence to the contrary.
“(C) For purposes of subparagraph (A):
“(i) A violation of this chapter with respect to 2 or more firearms during a single transaction shall be considered a single violation.
“(ii) A violation of this chapter with respect to any category of record keeping requirements, even if involving multiple instances, shall be considered a single violation.
“(D) The Attorney General may not commence an enforcement action under subparagraph (A) with respect to a violation, after the 3-year period that begins with—
“(i) the date the violation occurred; or
“(ii) if the licensee intentionally obstructed discovery of the violation, the date the violation is discovered.
“(E) The Attorney General may not commence an enforcement action under subparagraph (A) with respect to a violation without first notifying the licensee of the reasons for the contemplated action and affording the licensee an opportunity to demonstrate or achieve compliance with this chapter and to submit facts, arguments, or proposals of adjustment.
“(2) (A) (i) Not less than 60 days before the effective date of any penalty imposed on a licensee by reason of a determination made under paragraph (1), the Attorney General shall send the licensee a written notice by certified return receipt mail—
“(I) of the determination, and the grounds on which the determination was made;
“(II) that sets forth the facts on which the Attorney General relied as a basis for the determination, including the facts pertaining to any determination of willfulness;
“(III) of the nature of the penalty; and
“(IV) that the licensee may, within 60 days after receipt of the notice, request in writing a hearing to review the determination.
“(ii) Within 5 calendar days after serving the written notice on the licensee, the Attorney General, shall give written notice to the licensee of the date the written notice was so served and provide the licensee with proof of the service.
“(B) A hearing to review a determination made under paragraph (1) with respect to a licensee shall not be held unless the licensee or an agent of the licensee requests such a hearing within 60 days after receiving the written notice required by subparagraph (A), and if held, shall be open to the public
“(C) On timely receipt from the licensee of a request for such a review, the Attorney General shall stay the imposition of any penalty under paragraph (1), pending resolution of the hearing, unless, in the case of a license revocation, the Attorney General establishes, at a hearing before an administrative law judge, by clear and convincing evidence, that the licensee committed the violation willfully and that the continued operation by the licensee of the business involved poses an immediate and grave threat to public safety.
“(3) (A) Within not fewer than 60 days after timely receipt from a licensee or an agent of the licensee of a written request for a hearing to review a determination made under paragraph (1) (or at such later time as is agreed to by the Attorney General and the licensee), an administrative law judge shall hold an evidentiary hearing, at a location convenient to the licensee, to review the determination, except that, if the licensee moves for leave to take the deposition of any witness identified by the Attorney General or any officer or employee of the Department of Justice who was involved in the inspection or examination, or any prior inspection or examination on which the Attorney General relies, the administrative law judge shall grant the motion and adjust the hearing date accordingly.
“(B) Not less than 30 days before the hearing, the Attorney General shall deliver to the licensee—
“(i) a document identifying each person whom the Attorney General intends to call as a witness during the hearing and a summary of the proposed sworn testimony of the witness;
“(ii) a copy of each document, in unredacted form, that will be introduced by the Attorney General as evidence at the hearing;
“(iii) copies of all documents on which the determination is based;
“(iv) a complete copy of the file of the licensee maintained by the Attorney General; and
“(v) a sworn statement from the Attorney General as to whether or not there is a pending criminal investigation by the Attorney General of the licensee, which statement shall be supplemented or amended by the Attorney General if a criminal investigation is initiated before the conclusion of the hearing.
“(C) (i) Within 120 days after the hearing, the administrative law judge shall issue a written decision setting forth findings of fact and conclusions of law, and a decision as to whether to affirm, modify, or reverse the determination.
“(ii) The findings of fact and conclusions of law and decision of the administrative law judge shall be—
“(I) de novo and not predicated on a presumption that the determination of the Attorney General was correct; and
“(II) based on a clear and convincing standard of proof, which shall be borne by the Attorney General.
“(iii) The administrative law judge shall not make a determination to revoke a license unless the administrative law judge finds, by clear and convincing evidence, that—
“(I) the Attorney General notified the licensee in writing of all reasons for the contemplated action of the Attorney General;
“(II) the Attorney General afforded the licensee a commercially reasonable opportunity to demonstrate or achieve compliance with this chapter; and
“(III) the licensee has not complied, and is unlikely to be able to achieve compliance, with this chapter.
“(iv) The Attorney General shall provide to the licensee a complete copy of the hearing transcript, including exhibits, within 60 days after the date of the hearing.
“(D) On request of the licensee, the Attorney General shall stay the effective date of any penalty, suspension, or revocation until there is a final, unreviewable judgment with respect to the determination of the administrative law judge, unless, in the case of a license revocation, the Attorney General establishes, at a hearing before an administrative law judge, by clear and convincing evidence, that the licensee committed the violation willfully and that the continued operation by the licensee of the business involved poses an immediate and grave threat to public safety.
“(E) An action of an administrative law judge under this subsection shall be considered final agency action for all purposes, and may be reviewed only as provided in subsection (f).
“(4) This subsection shall not be interpreted to affect the authority of the Attorney General under section 922(t)(5), except that the provisions of section 922(t)(5) regarding notice and opportunity for a hearing shall be subject to the procedural and evidentiary requirements provided in this subsection.
“(f) (1) Within 60 days after a party receives a notice issued under subsection (d) of a decision to deny a license, or a notice issued under subsection (e)(3)(C) of a determination to suspend or revoke a license, the party may file a petition with the United States district court for the district in which the party resides or has a principal place of business for a de novo trial of the determination.
“(2) In a proceeding conducted under this subsection, the court shall, on application of a party, consider any evidence submitted by the parties to the proceeding whether or not the evidence was considered at the hearing held under subsection (d) or (e)(3).
“(3) (A) If the court decides that the determination was not authorized by law, the court shall order the Attorney General to take such action as may be necessary to comply with the judgment of the court.
“(B) The court shall not make a determination to revoke a license unless the court finds, by clear and convincing evidence, that—
“(i) the Attorney General notified the licensee in writing of all reasons for the contemplated action of the Attorney General;
“(ii) the Attorney General afforded the licensee a commercially reasonable opportunity to demonstrate or achieve compliance with this chapter; and
“(iii) the licensee has not complied, and is unlikely to be able to comply, with this chapter.
“(4) If criminal proceedings are instituted against an applicant for a license under this chapter or a licensee alleging a violation of this chapter, and the applicant or licensee, as the case may be, is acquitted of the charges, or the proceedings are terminated, other than on motion of the Government before trial on the charges, the Attorney General shall be absolutely barred from denying a license under this chapter, or suspending or revoking a license granted under this chapter, if the action would be based in whole or in part on the facts which form the basis of the criminal charges.
“(5) The Attorney General may not institute a proceeding to suspend or revoke a license granted under this chapter, more than 1 year after the filing of the indictment or information.
“(6) The Attorney General may not institute a proceeding to suspend or revoke a license granted under this chapter, based on a violation that is finally determined to have occurred with respect to a different license.”.
SEC. 3. Consideration of Federal firearms license applications.
Section 923(d) of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking paragraph (2) and inserting the following:
“(2) The Attorney General shall make a preliminary determination as to whether to approve or deny an application submitted under subsection (a) or (b). If the preliminary determination is to deny the application, the Attorney General shall notify the applicant in writing of the preliminary determination and the reasons for the preliminary determination, and shall afford the applicant an opportunity to supplement the application with additional information and to request a hearing on the application. If the applicant, in a timely manner, requests such a hearing, the Attorney General shall hold the hearing at a location convenient to the applicant, and shall notify the applicant in writing of the time and place of the hearing.
“(3) The Attorney General may not deny an application for a license based on—
“(A) any prior violation of this chapter by the applicant, if more than 5 years have elapsed since the date a license previously issued to the applicant under this chapter was terminated, unless the Attorney General finds that the applicant is a person described in section 922(g);
“(B) the applicant having been employed by, or a responsible party for, a licensee whose license under this chapter was revoked, unless there is clear and convincing evidence that the applicant willfully violated this chapter in that capacity; or
“(C) the applicant being a spouse, former spouse, or child of a licensee whose license under this chapter was revoked, unless there is clear and convincing evidence that the applicant willfully violated this chapter as a responsible party under the license.
“(4) The procedures provided for in subsection (e) shall apply with respect to any applicant for a license under this chapter and any application for such a license.”.
SEC. 4. Definition of “willfully”; certain evidence inadmissible to prove willfulness.
Section 923(e) of title 18, United States Code, as amended by section 2(a) of this Act, is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(5) For purposes of this subsection, the term ‘willfully’ means, with respect to conduct of an individual who holds a license or is designated in the records of the Attorney General as a responsible party under a specific license, that the person—
“(A) had actual knowledge of a clearly established legal duty;
“(B) understood the obligation imposed by the legal duty; and
“(C) engaged in the conduct knowingly and in deliberate disregard of the legal duty.
“(6) Evidence that a person has received a document or other communication containing information about a requirement imposed by or under this chapter and evidence that the person has signed an acknowledgment that the person understands the legal obligations of the person under this chapter shall not be admissible as part of the determination of the Attorney General, in an administrative law hearing or in a court of law, to prove actual knowledge and shall not be admissible as evidence to establish a willful violation of this chapter.
“(7) Evidence that a person has substantial experience as a licensee, or has in other instances successfully complied with this chapter, shall not be admissible as part of the determination of the Attorney General, in an administrative law hearing or in a court of law, to prove actual knowledge and shall not be admissible as evidence to established a willful violation of this chapter.
“(8) In determining under this subsection whether conduct of a licensee was willful, the entire historical administrative record of the licensee shall be considered.”.
SEC. 5. Reconsideration of denied applications from former firearm licensees, in light of new rules pertaining to willfullness; reversal of license revocations, suspensions and denials made while certain ATF orders are in effect.
(a) Reconsideration of applications.—The Attorney General shall reconsider each application for a license under chapter 44 of title 18, United States Code, that is submitted by a person formerly licensed under such chapter whose application for a license under such chapter was denied before the date of the enactment of this Act, and that was disposed of on or before such date of enactment, and, in doing so, the Attorney General shall apply the amendments made by section 4 of this Act.
(b) Reversal of revocations, suspension, and denials.—In the case of any person whose license under chapter 44 of title 18, United States Code, is revoked or suspended, or whose application for such a license is denied, while ATF Order 5370.1E, ATF Order 5370.1F, or ATF Order 5370.1G is in effect, the Attorney General shall, absent clear and convincing evidence that the continued operation by the licensee of the business subject to the license poses an immediate and grave threat to public safety—
(1) (A) in the case of such a revocation, reinstate the license;
(B) in the case of such a suspension, end the suspension; or
(C) in the case of such a denial, reconsider the application; and
(2) in each case, reimburse the person for all legal fees incurred by the person, while the Order is in effect, with respect to any proceeding involving the revocation, suspension, or application.
(c) Establishment of website for administration of relief.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Within 120 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Attorney General shall—
(A) establish a website, entitled “gunrightsrestored.gov”, through which a person described in subsection (a) or (b) may submit a claim for the reimbursement described in subsection (b)(2); and
(B) publish in the Federal Register all information about how such a person may so submit such a claim.
(2) NONDELEGATION.—The Attorney General may not delegate the implementation of paragraph (1) to any entity that is not in the Office of the Attorney General or the Office of the Deputy Attorney General.
(d) Reports.—Within 6 months after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Attorney General and the Inspector General of the Department of Justice shall prepare and submit to the Committee on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives and the Committee on the Judiciary of the Senate separate reports on the implementation of this section.
SEC. 6. Establishment of formal inspection, examination, and investigative standards.
(a) In general.—The Attorney General shall establish written standards for how the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives is to—
(1) conduct inspections, examinations, or investigations of a possible violation of chapter 40 or 44 of title 18, United States Code; and
(2) make license application denial, license suspension, license revocation or other adverse determinations regarding an applicant or licensee.
(b) Inclusion of mitigating factors.—The standards shall include mitigation factors that must be considered before the Attorney General initiates any adverse action against an applicant or licensee.
(c) Availability.—The written standards shall be made available to the public, and shall be provided by the Attorney General to applicants and licensees at the time of any license application and on demand.
SEC. 7. Limitations on use of firearms purchaser information.
Section 923(g)(1)(D) of title 18, United States Code, is amended in the last sentence by inserting “, except that information identifying a person who has purchased or received firearms or ammunition and who is not prohibited from doing so may not be so made available or so provided unless the agency involved has certified that the agency will not disclose the information to any entity other than a court, federal, State or local law enforcement agency, or prosecutor” before the period.
SEC. 8. Liquidation of inventory in Federal firearms license expiration, surrender, or revocation cases.
Section 923 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(m) (1) Except as provided in paragraph (2), an entity whose license issued under this chapter is expired, surrendered, or revoked shall be afforded 90 days from the effective date of the expiration, surrender, or revocation (not counting any period in which an appeal of such a revocation is pending) to liquidate the firearms business inventory of the entity, which time may be extended on a showing of reasonable cause. During the 90-day period (including any extension of the period), the license involved shall continue to be considered valid, notwithstanding the expiration, surrender, or revocation, and the Attorney General shall issue letters of authorization to the entity on which licensees under this chapter and commercial third parties may rely. At any time before the expiration of the disposition period, the entity may transfer any remaining firearms from the firearms business inventory of the entity to the entity or, if more than 1 person holds an interest in the entity, to the interest holders, at which point the firearms are deemed to be a personal collection of the entity or interest holders, as the case may be.
“(2) Paragraph (1) shall not apply with respect to a person if a United States district court for the judicial district in which the person resides or in which the principal place of business of the person subject to the license is located finds, by clear and convincing evidence, that the continued operation by the person of the firearms business involved poses an immediate and grave threat to public safety, in which case the person may transfer all firearms from the firearms business inventory of the person to the personal collection of the person or to another licensee for consignment or other liquidation at the direction of the person.”.
SEC. 9. Opportunity to cure violations after acquisition of firearms business.
Section 923 of title 18, United States Code, is further amended by adding at the end the following:
“(n) If the Attorney General is made aware that a business licensed under this chapter has been transferred to a surviving spouse or child of the licensee, to an executor, administrator, or other legal representative of a deceased or incompetent licensee, to a receiver or trustee in bankruptcy, to an assignee for benefit of creditors, or to an entity holding a security interest in an item as collateral pursuant to Article 9 of the Uniform Commercial Code (U.C.C. § 9–102(a)(73)), and, before the transfer, or on the first inspection or examination by the Attorney General of the records of the licensee after the transfer, the licensee is found to be operating the business in violation of this chapter, the Attorney General—
“(1) shall notify the transferee of the violation by the transferor; and
“(2) shall not presume that the transferee is committing the violation.”.
SEC. 10. Standards for criminal violations of recordkeeping requirements.
Section 922(m) of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by striking “any false entry” and inserting “a materially false entry”;
(2) by striking “appropriate entry” and inserting “a materially significant entry”; and
(3) by striking “properly maintain” and inserting “retain custody of”.
H.R.645 – National Constitutional Carry Act
To enforce the rights protected by the Second and Fourteenth Amendments against the States.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) Recognizing the preexisting right to self-defense, the Second Amendment to the Constitution of the United States guarantees individually to American citizens the right “to keep and bear arms”, including the right to bear arms in public.
(2) The Second Amendment decrees that these rights to keep and bear arms “shall not be infringed”, and was enumerated in order to preserve “the security of a free State”.
(3) In District of Columbia v. Heller (554 U.S. 570, 595 (2008)), the Supreme Court confirmed that “[t]here seems to us no doubt, on the basis of both text and history, that the Second Amendment conferred an individual right to keep and bear arms”.
(4) In McDonald v. City of Chicago (561 U.S. 742, 791 (2010)), the Supreme Court ruled that the Fourteenth Amendment makes the Second Amendment fully applicable to the States. Four Justices concluded that the rights protected by the Second Amendment are fundamental to the Nation’s scheme of ordered liberty and deeply rooted in this Nation’s “history and tradition”, and therefore incorporated to the States through the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. Justice Thomas agreed that the rights protected by the Second Amendment are both “fundamental” and “deeply rooted” and, as such, are enforceable against the States under the Fourteenth Amendment’s Privileges and Immunities Clause.
(5) Recently, the Supreme Court acknowledged in New York State Rifle & Pistol Ass’n v. Bruen (142 S. Ct. 2111, 2156 (2022)), that the Second and Fourteenth Amendments protect the individual right to carry arms outside the home for self-defense. Further, the Court reiterated that the Second Amendment’s otherwise “unqualified command” only accommodates laws that are “consistent with this Nation’s historical tradition of firearm regulation” (Id. at 2126).
(6) Certain States and localities have enacted gun control laws that are not consistent with the text of the Second Amendment or this Nation’s historical tradition of firearm regulation. The criminalization of peaceable, public firearms carry is repugnant to the original meaning of the Second Amendment.
(7) Any State or local restriction on the right of American citizens to keep and bear arms impairs the ability of the Second Amendment to achieve its textually specified purpose, “the security of a free State”.
SEC. 3. The right to keep and bear arms.
(a) In general.—Section 927 of title 18, United States Code, is amended to read as follows:
Ҥ 927. The right to keep and bear arms
“(a) No State or political subdivision of a State may impose a criminal or civil penalty on, or otherwise indirectly limit the carrying of firearms (including by imposing a financial or other barrier to entry) in public by residents or nonresidents of that State who are citizens of the United States and otherwise eligible to possess firearms under State and Federal law.
“(b) Any statute, ordinance, regulation, custom, or usage of a State or a political subdivision of a State that criminalizes, penalizes, or otherwise indirectly dissuades the carrying of firearms (including by imposing a financial or other barrier to entry) in public by any resident or nonresident who is a United States citizen and otherwise eligible to possess firearms under State and Federal law, shall have no force or effect.
“(c) The term ‘State’ as used in this section includes the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and the possessions of the United States (not including the Canal Zone).
“(d) The term ‘public’ as used in this section—
“(1) includes any place held open to the public, regardless of ownership, but in the case of a privately-owned location held open to the public, does not include a place where the owner communicates clearly and conspicuously a prohibition of firearms on the premises; and
“(2) does not include a place where screening for firearms is conducted under State law.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for such chapter is amended by striking the item relating to section 927 and inserting the following:
“927. The right to keep and bear arms.”.
H.R.1307 – To establish the Office of Gun Violence Prevention, and for other purposes.
National Security
H. R. 38 Constitutional Concealed Carry Reciprocity Act
To amend title 18, United States Code, to provide a means by which nonresidents of a State whose residents may carry concealed firearms may also do so in the State.
SEC. 2. Reciprocity for the carrying of certain concealed firearms.
(a) In general.—Chapter 44 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by inserting after section 926C the following:
Ҥ 926D. Reciprocity for the carrying of certain concealed firearms
“(a) Notwithstanding any provision of the law of any State or political subdivision thereof (except as provided in subsection (b)) and subject only to the requirements of this section, a person who is not prohibited by Federal law from possessing, transporting, shipping, or receiving a firearm, who is carrying a valid identification document containing a photograph of the person, and who is carrying a valid license or permit which is issued pursuant to the law of a State and which permits the person to carry a concealed firearm or is entitled to carry a concealed firearm in the State in which the person resides, may possess or carry a concealed handgun (other than a machine gun or destructive device) that has been shipped or transported in interstate or foreign commerce, in any State that—
“(1) has a statute under which residents of the State may apply for a license or permit to carry a concealed firearm; or
“(2) does not prohibit the carrying of concealed firearms by residents of the State for lawful purposes.
“(b) This section shall not be construed to supersede or limit the laws of any State that—
“(1) permit private persons or entities to prohibit or restrict the possession of concealed firearms on their property; or
“(2) prohibit or restrict the possession of firearms on any State or local government property, installation, building, or base.
“(c) (1) A person who carries or possesses a concealed handgun in accordance with subsections (a) and (b) may not be arrested or otherwise detained for violation of any law or any rule or regulation of a State or any political subdivision thereof related to the possession, transportation, or carrying of firearms unless there is probable cause to believe that the person is doing so in a manner not provided for by this section. Presentation of facially valid documents as specified in subsection (a) is prima facie evidence that the individual has a license or permit as required by this section.
“(2) When a person asserts this section as a defense in a criminal proceeding, the prosecution shall bear the burden of proving, beyond a reasonable doubt, that the conduct of the person did not satisfy the conditions set forth in subsections (a) and (b).
“(3) When a person successfully asserts this section as a defense in a criminal proceeding, the court shall award the prevailing defendant a reasonable attorney’s fee.
“(d) (1) A person who is deprived of any right, privilege, or immunity secured by this section, under color of any statute, ordinance, regulation, custom, or usage of any State or any political subdivision thereof, may bring an action in any appropriate court against any other person, including a State or political subdivision thereof, who causes the person to be subject to the deprivation, for damages or other appropriate relief.
“(2) The court shall award a plaintiff prevailing in an action brought under paragraph (1) damages and such other relief as the court deems appropriate, including a reasonable attorney’s fee.
“(e) In subsection (a):
“(1) The term ‘identification document’ means a document made or issued by or under the authority of the United States Government, a State, or a political subdivision of a State which, when completed with information concerning a particular individual, is of a type intended or commonly accepted for the purpose of identification of individuals.
“(2) The term ‘handgun’ includes any magazine for use in a handgun and any ammunition loaded into the handgun or its magazine.
“(f) (1) A person who possesses or carries a concealed handgun under subsection (a) shall not be subject to the prohibitions of section 922(q).
“(2) A person possessing or carrying a concealed handgun in a State under subsection (a) may do so in any of the following areas in the State that are open to the public:
“(A) A unit of the National Park System.
“(B) A unit of the National Wildlife Refuge System.
“(C) Public land under the jurisdiction of the Bureau of Land Management.
“(D) Land administered and managed by the Army Corps of Engineers.
“(E) Land administered and managed by the Bureau of Reclamation.
“(F) Land administered and managed by the Forest Service.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for such chapter is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 926C the following:
“926D. Reciprocity for the carrying of certain concealed firearms.”.
(c) Severability.—Notwithstanding any other provision of this Act, if any provision of this section, or any amendment made by this section, or the application of such provision or amendment to any person or circumstance is held to be unconstitutional, this section and amendments made by this section and the application of such provision or amendment to other persons or circumstances shall not be affected thereby.
(d) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall take effect 90 days after the date of the enactment of this Act.
- R. 45 “Firearm Industry Non-Discrimination Act” or the “FIND Act”.
To amend title 41, United States Code, to prohibit the Federal Government from entering into contracts with an entity that discriminates against the firearm and ammunition industry, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Prohibition on entering into contracts with entities discriminating against the firearm and ammunition industry.
(a) Prohibition.—Chapter 47 of title 41, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
Ҥ 4715. Prohibition on entering into contracts with entities discriminating against the firearm and ammunition industry.
“(a) Prohibition.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—The head of an executive agency shall include in each contract for the procurement of goods or services awarded by the executive agency, a clause requiring the prime contractor to certify that the contractor—
“(A) has no policy, practice, guidance, or directive that discriminates against a firearm entity or firearm trade association; and
“(B) will not adopt a policy, practice, guidance, or directive that discriminates against a firearm entity or firearm trade association during the term of the contract.
“(2) SUBCONTRACTS.—The head of an executive agency shall include in each contract for the procurement of goods or services awarded by the executive agency, a clause that prohibits the prime contractor on such contract from—
“(A) awarding a first-tier subcontract with a value greater than 10 percent of the total value of the prime contract to an entity that fails to certify in writing to the prime contractor that the entity—
“(i) has no policy, practice, guidance, or directive that discriminates against a firearm entity or firearm trade association; and
“(ii) will not adopt a policy, practice, guidance, or directive that discriminates against a firearm entity or firearm trade association during the term of the contract; and
“(B) structuring subcontract tiers in a manner designed to avoid violating subparagraph (A) by enabling a subcontractor to perform more than 10 percent of the total value of the prime contract as a lower-tier subcontractor.
“(3) PENALTIES.—The clause included in contracts pursuant to paragraph (1) or paragraph (2) shall provide that, in the event that the prime contractor violates the clause—
“(A) the prime contract shall be terminated for default; and
“(B) a suspension or debarment proceeding will be initiated for the contractor on the basis of the violation.
“(b) Exception.—Subsection (a) shall not apply to a contract for the procurement of goods or services that is a sole-source contract.
“(c) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) DISCRIMINATE.—The term ‘discriminate’ means to—
“(A) make a judgement about a policy, practice, guidance, or directive on the basis of—
“(i) partial criteria or a category-based assessment analysis, rather than—
“(I) on a case-by-case basis; or
“(II) using empirical data evaluated under quantifiable standards; or
“(ii) criteria other than criteria free from—
“(I) favoritism or prejudice against or dislike for the firearm entity or trade association or the products or services sold by the firearm entity or trade association; or
“(II) favoritism for market alternatives to the business of the firearm entity or the trade association;
“(B) refuse to provide services, or deny, cancel, or limit services, to the firearm entity or trade association on the basis of criteria other than—
“(i) criteria free from—
“(I) favoritism or prejudice against or dislike for the firearm entity or trade association or the products or services sold by the firearm entity or trade association; or
“(II) favoritism for market alternatives to the business of the firearm entity or the trade association;
“(ii) criteria related to credit history and financial risk specific to a customer or potential customer; or
“(iii) criteria related to noncompliance with Federal, State, or local law; or
“(C) limit the operations of the firearm entity or trade association in manner not required by—
“(i) Federal, State, or local law; or
“(ii) Federal, State, or local regulation.
“(2) FIREARM ENTITY.—The term ‘firearm entity’ means any—
“(A) person who is licensed under section 923 of title 18 to import, manufacture, or deal in firearms;
“(B) seller of ammunition, as defined in section 7903 of title 15;
“(C) manufacturer or importer of, or dealer in, a secure gun storage or safety device, as defined in section 921(a) of title 18; and
“(D) manufacturer or importer of, or dealer in, a component part or accessory of a firearm or ammunition.
“(3) FIREARM TRADE ASSOCIATION.—The term ‘firearm trade association’ has the meaning in section 7903 of title 15.
“(4) FIRST-TIER SUBCONTRACT.—The term ‘first-tier subcontract’ means a subcontract entered into by a subcontractor with the prime contractor for the purposes of carrying out the prime contract.
“(5) LOWER-TIER SUBCONTRACTOR.—The term ‘lower-tier subcontractor’ means any person entering into a contract with a subcontractor of a prime contractor for the purposes of carrying out the prime contract.
“(6) PRIME CONTRACT; PRIME CONTRACTOR.—The terms ‘prime contract’ and ‘prime contractor’ have the meaning given those terms in section 8701 of title 41.”.
(b) Application.—Section 4715 of title 41, United States Code, as added by subsection (a), shall apply with respect to contracts awarded on or after the date of the enactment of this Act.
(c) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for chapter 47 of title 41, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
“4715. Prohibition on entering into contracts with entities discriminating against the firearm and ammunition industry.”.
H. R. 221 Abolish the ATF Act
To abolish the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.
SEC. 2. Abolishment of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.
The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives is hereby abolished.
- R. 223 Preventing Unjust Red Flag Laws Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Prohibition on funding for implementation and enforcement of red flag laws or rules.
(a) Prohibition on funding.—None of the funds made available for any Federal department or agency may be used to—
(1) implement or enforce Federal red flag laws; or
(2) provide assistance to States, local, tribal, or territorial government departments or agencies for the implementation or enforcement of red flag laws.
(b) Red flag law defined.—In this section, the term “red flag law” means a risk-based, temporary, and preemptive protective order that authorizes the removal of a firearm without due process.
H.R.335 – Repeal the NFA Act
SEC. 2. Repeal of National Firearms Act.
Chapter 53 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, and the item relating to such chapter in the table of chapters for subtitle E, are hereby repealed.
H.R.404 – Hearing Protection Act
SEC. 2. Equal treatment of silencers and firearms.
(a) In general.—Section 5845(a) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking “(7) any silencer” and all that follows through “; and (8)” and inserting “and (7)”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by this section shall apply to calendar quarters beginning more than 90 days after the date of the enactment of this Act.
SEC. 3. Treatment of certain silencers.
Section 5841 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(f) Firearm silencers.—A person acquiring or possessing a firearm silencer in accordance with chapter 44 of title 18, United States Code, shall be treated as meeting any registration and licensing requirements of the National Firearms Act with respect to such silencer.”.
SEC. 4. Preemption of certain State laws in relation to firearm silencers.
H.R.624 – RIFLE Act of 2025 or “Reining In Federal Licensing Enforcement Act of 2025”
To reform the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives.
SEC. 2. Graduated penalties for civil violations by Federal firearms licensees.
Section 923 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking subsections (e) and (f) and inserting the following:
“(e) (1) (A) If the Attorney General determines that a licensee under this section has violated this chapter—
“(i) in the case of a violation that is not willful, the Attorney General shall notify the licensee of the violation and work with the licensee to rectify the violation within a commercially reasonable time frame; or
“(ii) in the case of a willful violation, if the Attorney General, after working with the licensee to rectify the violation within a commercially reasonable time frame, finds that a lesser action (such as a warning, warning letter, or warning conference) is not likely to lead to future compliance, and the Attorney General seeks revocation of the license in an administrative action, the Attorney General may—
“(I) if the licensee has no history of noncompliance with this chapter, suspend the license for not more than 30 days or such lesser period as would apply on compliance with such conditions as are specified by the Attorney General; or
“(II) in any other case, revoke the license.
“(B) In applying subparagraph (A), the Attorney General shall presume that the violation is not willful, absent clear and convincing evidence to the contrary.
“(C) For purposes of subparagraph (A):
“(i) A violation of this chapter with respect to 2 or more firearms during a single transaction shall be considered a single violation.
“(ii) A violation of this chapter with respect to any category of record keeping requirements, even if involving multiple instances, shall be considered a single violation.
“(D) The Attorney General may not commence an enforcement action under subparagraph (A) with respect to a violation, after the 3-year period that begins with—
“(i) the date the violation occurred; or
“(ii) if the licensee intentionally obstructed discovery of the violation, the date the violation is discovered.
“(E) The Attorney General may not commence an enforcement action under subparagraph (A) with respect to a violation without first notifying the licensee of the reasons for the contemplated action and affording the licensee an opportunity to demonstrate or achieve compliance with this chapter and to submit facts, arguments, or proposals of adjustment.
“(2) (A) (i) Not less than 60 days before the effective date of any penalty imposed on a licensee by reason of a determination made under paragraph (1), the Attorney General shall send the licensee a written notice by certified return receipt mail—
“(I) of the determination, and the grounds on which the determination was made;
“(II) that sets forth the facts on which the Attorney General relied as a basis for the determination, including the facts pertaining to any determination of willfulness;
“(III) of the nature of the penalty; and
“(IV) that the licensee may, within 60 days after receipt of the notice, request in writing a hearing to review the determination.
“(ii) Within 5 calendar days after serving the written notice on the licensee, the Attorney General, shall give written notice to the licensee of the date the written notice was so served and provide the licensee with proof of the service.
“(B) A hearing to review a determination made under paragraph (1) with respect to a licensee shall not be held unless the licensee or an agent of the licensee requests such a hearing within 60 days after receiving the written notice required by subparagraph (A), and if held, shall be open to the public
“(C) On timely receipt from the licensee of a request for such a review, the Attorney General shall stay the imposition of any penalty under paragraph (1), pending resolution of the hearing, unless, in the case of a license revocation, the Attorney General establishes, at a hearing before an administrative law judge, by clear and convincing evidence, that the licensee committed the violation willfully and that the continued operation by the licensee of the business involved poses an immediate and grave threat to public safety.
“(3) (A) Within not fewer than 60 days after timely receipt from a licensee or an agent of the licensee of a written request for a hearing to review a determination made under paragraph (1) (or at such later time as is agreed to by the Attorney General and the licensee), an administrative law judge shall hold an evidentiary hearing, at a location convenient to the licensee, to review the determination, except that, if the licensee moves for leave to take the deposition of any witness identified by the Attorney General or any officer or employee of the Department of Justice who was involved in the inspection or examination, or any prior inspection or examination on which the Attorney General relies, the administrative law judge shall grant the motion and adjust the hearing date accordingly.
“(B) Not less than 30 days before the hearing, the Attorney General shall deliver to the licensee—
“(i) a document identifying each person whom the Attorney General intends to call as a witness during the hearing and a summary of the proposed sworn testimony of the witness;
“(ii) a copy of each document, in unredacted form, that will be introduced by the Attorney General as evidence at the hearing;
“(iii) copies of all documents on which the determination is based;
“(iv) a complete copy of the file of the licensee maintained by the Attorney General; and
“(v) a sworn statement from the Attorney General as to whether or not there is a pending criminal investigation by the Attorney General of the licensee, which statement shall be supplemented or amended by the Attorney General if a criminal investigation is initiated before the conclusion of the hearing.
“(C) (i) Within 120 days after the hearing, the administrative law judge shall issue a written decision setting forth findings of fact and conclusions of law, and a decision as to whether to affirm, modify, or reverse the determination.
“(ii) The findings of fact and conclusions of law and decision of the administrative law judge shall be—
“(I) de novo and not predicated on a presumption that the determination of the Attorney General was correct; and
“(II) based on a clear and convincing standard of proof, which shall be borne by the Attorney General.
“(iii) The administrative law judge shall not make a determination to revoke a license unless the administrative law judge finds, by clear and convincing evidence, that—
“(I) the Attorney General notified the licensee in writing of all reasons for the contemplated action of the Attorney General;
“(II) the Attorney General afforded the licensee a commercially reasonable opportunity to demonstrate or achieve compliance with this chapter; and
“(III) the licensee has not complied, and is unlikely to be able to achieve compliance, with this chapter.
“(iv) The Attorney General shall provide to the licensee a complete copy of the hearing transcript, including exhibits, within 60 days after the date of the hearing.
“(D) On request of the licensee, the Attorney General shall stay the effective date of any penalty, suspension, or revocation until there is a final, unreviewable judgment with respect to the determination of the administrative law judge, unless, in the case of a license revocation, the Attorney General establishes, at a hearing before an administrative law judge, by clear and convincing evidence, that the licensee committed the violation willfully and that the continued operation by the licensee of the business involved poses an immediate and grave threat to public safety.
“(E) An action of an administrative law judge under this subsection shall be considered final agency action for all purposes, and may be reviewed only as provided in subsection (f).
“(4) This subsection shall not be interpreted to affect the authority of the Attorney General under section 922(t)(5), except that the provisions of section 922(t)(5) regarding notice and opportunity for a hearing shall be subject to the procedural and evidentiary requirements provided in this subsection.
“(f) (1) Within 60 days after a party receives a notice issued under subsection (d) of a decision to deny a license, or a notice issued under subsection (e)(3)(C) of a determination to suspend or revoke a license, the party may file a petition with the United States district court for the district in which the party resides or has a principal place of business for a de novo trial of the determination.
“(2) In a proceeding conducted under this subsection, the court shall, on application of a party, consider any evidence submitted by the parties to the proceeding whether or not the evidence was considered at the hearing held under subsection (d) or (e)(3).
“(3) (A) If the court decides that the determination was not authorized by law, the court shall order the Attorney General to take such action as may be necessary to comply with the judgment of the court.
“(B) The court shall not make a determination to revoke a license unless the court finds, by clear and convincing evidence, that—
“(i) the Attorney General notified the licensee in writing of all reasons for the contemplated action of the Attorney General;
“(ii) the Attorney General afforded the licensee a commercially reasonable opportunity to demonstrate or achieve compliance with this chapter; and
“(iii) the licensee has not complied, and is unlikely to be able to comply, with this chapter.
“(4) If criminal proceedings are instituted against an applicant for a license under this chapter or a licensee alleging a violation of this chapter, and the applicant or licensee, as the case may be, is acquitted of the charges, or the proceedings are terminated, other than on motion of the Government before trial on the charges, the Attorney General shall be absolutely barred from denying a license under this chapter, or suspending or revoking a license granted under this chapter, if the action would be based in whole or in part on the facts which form the basis of the criminal charges.
“(5) The Attorney General may not institute a proceeding to suspend or revoke a license granted under this chapter, more than 1 year after the filing of the indictment or information.
“(6) The Attorney General may not institute a proceeding to suspend or revoke a license granted under this chapter, based on a violation that is finally determined to have occurred with respect to a different license.”.
SEC. 3. Consideration of Federal firearms license applications.
Section 923(d) of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking paragraph (2) and inserting the following:
“(2) The Attorney General shall make a preliminary determination as to whether to approve or deny an application submitted under subsection (a) or (b). If the preliminary determination is to deny the application, the Attorney General shall notify the applicant in writing of the preliminary determination and the reasons for the preliminary determination, and shall afford the applicant an opportunity to supplement the application with additional information and to request a hearing on the application. If the applicant, in a timely manner, requests such a hearing, the Attorney General shall hold the hearing at a location convenient to the applicant, and shall notify the applicant in writing of the time and place of the hearing.
“(3) The Attorney General may not deny an application for a license based on—
“(A) any prior violation of this chapter by the applicant, if more than 5 years have elapsed since the date a license previously issued to the applicant under this chapter was terminated, unless the Attorney General finds that the applicant is a person described in section 922(g);
“(B) the applicant having been employed by, or a responsible party for, a licensee whose license under this chapter was revoked, unless there is clear and convincing evidence that the applicant willfully violated this chapter in that capacity; or
“(C) the applicant being a spouse, former spouse, or child of a licensee whose license under this chapter was revoked, unless there is clear and convincing evidence that the applicant willfully violated this chapter as a responsible party under the license.
“(4) The procedures provided for in subsection (e) shall apply with respect to any applicant for a license under this chapter and any application for such a license.”.
SEC. 4. Definition of “willfully”; certain evidence inadmissible to prove willfulness.
Section 923(e) of title 18, United States Code, as amended by section 2(a) of this Act, is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(5) For purposes of this subsection, the term ‘willfully’ means, with respect to conduct of an individual who holds a license or is designated in the records of the Attorney General as a responsible party under a specific license, that the person—
“(A) had actual knowledge of a clearly established legal duty;
“(B) understood the obligation imposed by the legal duty; and
“(C) engaged in the conduct knowingly and in deliberate disregard of the legal duty.
“(6) Evidence that a person has received a document or other communication containing information about a requirement imposed by or under this chapter and evidence that the person has signed an acknowledgment that the person understands the legal obligations of the person under this chapter shall not be admissible as part of the determination of the Attorney General, in an administrative law hearing or in a court of law, to prove actual knowledge and shall not be admissible as evidence to establish a willful violation of this chapter.
“(7) Evidence that a person has substantial experience as a licensee, or has in other instances successfully complied with this chapter, shall not be admissible as part of the determination of the Attorney General, in an administrative law hearing or in a court of law, to prove actual knowledge and shall not be admissible as evidence to established a willful violation of this chapter.
“(8) In determining under this subsection whether conduct of a licensee was willful, the entire historical administrative record of the licensee shall be considered.”.
SEC. 5. Reconsideration of denied applications from former firearm licensees, in light of new rules pertaining to willfullness; reversal of license revocations, suspensions and denials made while certain ATF orders are in effect.
(a) Reconsideration of applications.—The Attorney General shall reconsider each application for a license under chapter 44 of title 18, United States Code, that is submitted by a person formerly licensed under such chapter whose application for a license under such chapter was denied before the date of the enactment of this Act, and that was disposed of on or before such date of enactment, and, in doing so, the Attorney General shall apply the amendments made by section 4 of this Act.
(b) Reversal of revocations, suspension, and denials.—In the case of any person whose license under chapter 44 of title 18, United States Code, is revoked or suspended, or whose application for such a license is denied, while ATF Order 5370.1E, ATF Order 5370.1F, or ATF Order 5370.1G is in effect, the Attorney General shall, absent clear and convincing evidence that the continued operation by the licensee of the business subject to the license poses an immediate and grave threat to public safety—
(1) (A) in the case of such a revocation, reinstate the license;
(B) in the case of such a suspension, end the suspension; or
(C) in the case of such a denial, reconsider the application; and
(2) in each case, reimburse the person for all legal fees incurred by the person, while the Order is in effect, with respect to any proceeding involving the revocation, suspension, or application.
(c) Establishment of website for administration of relief.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Within 120 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Attorney General shall—
(A) establish a website, entitled “gunrightsrestored.gov”, through which a person described in subsection (a) or (b) may submit a claim for the reimbursement described in subsection (b)(2); and
(B) publish in the Federal Register all information about how such a person may so submit such a claim.
(2) NONDELEGATION.—The Attorney General may not delegate the implementation of paragraph (1) to any entity that is not in the Office of the Attorney General or the Office of the Deputy Attorney General.
(d) Reports.—Within 6 months after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Attorney General and the Inspector General of the Department of Justice shall prepare and submit to the Committee on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives and the Committee on the Judiciary of the Senate separate reports on the implementation of this section.
SEC. 6. Establishment of formal inspection, examination, and investigative standards.
(a) In general.—The Attorney General shall establish written standards for how the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives is to—
(1) conduct inspections, examinations, or investigations of a possible violation of chapter 40 or 44 of title 18, United States Code; and
(2) make license application denial, license suspension, license revocation or other adverse determinations regarding an applicant or licensee.
(b) Inclusion of mitigating factors.—The standards shall include mitigation factors that must be considered before the Attorney General initiates any adverse action against an applicant or licensee.
(c) Availability.—The written standards shall be made available to the public, and shall be provided by the Attorney General to applicants and licensees at the time of any license application and on demand.
SEC. 7. Limitations on use of firearms purchaser information.
Section 923(g)(1)(D) of title 18, United States Code, is amended in the last sentence by inserting “, except that information identifying a person who has purchased or received firearms or ammunition and who is not prohibited from doing so may not be so made available or so provided unless the agency involved has certified that the agency will not disclose the information to any entity other than a court, federal, State or local law enforcement agency, or prosecutor” before the period.
SEC. 8. Liquidation of inventory in Federal firearms license expiration, surrender, or revocation cases.
Section 923 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(m) (1) Except as provided in paragraph (2), an entity whose license issued under this chapter is expired, surrendered, or revoked shall be afforded 90 days from the effective date of the expiration, surrender, or revocation (not counting any period in which an appeal of such a revocation is pending) to liquidate the firearms business inventory of the entity, which time may be extended on a showing of reasonable cause. During the 90-day period (including any extension of the period), the license involved shall continue to be considered valid, notwithstanding the expiration, surrender, or revocation, and the Attorney General shall issue letters of authorization to the entity on which licensees under this chapter and commercial third parties may rely. At any time before the expiration of the disposition period, the entity may transfer any remaining firearms from the firearms business inventory of the entity to the entity or, if more than 1 person holds an interest in the entity, to the interest holders, at which point the firearms are deemed to be a personal collection of the entity or interest holders, as the case may be.
“(2) Paragraph (1) shall not apply with respect to a person if a United States district court for the judicial district in which the person resides or in which the principal place of business of the person subject to the license is located finds, by clear and convincing evidence, that the continued operation by the person of the firearms business involved poses an immediate and grave threat to public safety, in which case the person may transfer all firearms from the firearms business inventory of the person to the personal collection of the person or to another licensee for consignment or other liquidation at the direction of the person.”.
SEC. 9. Opportunity to cure violations after acquisition of firearms business.
Section 923 of title 18, United States Code, is further amended by adding at the end the following:
“(n) If the Attorney General is made aware that a business licensed under this chapter has been transferred to a surviving spouse or child of the licensee, to an executor, administrator, or other legal representative of a deceased or incompetent licensee, to a receiver or trustee in bankruptcy, to an assignee for benefit of creditors, or to an entity holding a security interest in an item as collateral pursuant to Article 9 of the Uniform Commercial Code (U.C.C. § 9–102(a)(73)), and, before the transfer, or on the first inspection or examination by the Attorney General of the records of the licensee after the transfer, the licensee is found to be operating the business in violation of this chapter, the Attorney General—
“(1) shall notify the transferee of the violation by the transferor; and
“(2) shall not presume that the transferee is committing the violation.”.
SEC. 10. Standards for criminal violations of recordkeeping requirements.
Section 922(m) of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by striking “any false entry” and inserting “a materially false entry”;
(2) by striking “appropriate entry” and inserting “a materially significant entry”; and
(3) by striking “properly maintain” and inserting “retain custody of”.
H.R.645 – National Constitutional Carry Act
To enforce the rights protected by the Second and Fourteenth Amendments against the States.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) Recognizing the preexisting right to self-defense, the Second Amendment to the Constitution of the United States guarantees individually to American citizens the right “to keep and bear arms”, including the right to bear arms in public.
(2) The Second Amendment decrees that these rights to keep and bear arms “shall not be infringed”, and was enumerated in order to preserve “the security of a free State”.
(3) In District of Columbia v. Heller (554 U.S. 570, 595 (2008)), the Supreme Court confirmed that “[t]here seems to us no doubt, on the basis of both text and history, that the Second Amendment conferred an individual right to keep and bear arms”.
(4) In McDonald v. City of Chicago (561 U.S. 742, 791 (2010)), the Supreme Court ruled that the Fourteenth Amendment makes the Second Amendment fully applicable to the States. Four Justices concluded that the rights protected by the Second Amendment are fundamental to the Nation’s scheme of ordered liberty and deeply rooted in this Nation’s “history and tradition”, and therefore incorporated to the States through the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. Justice Thomas agreed that the rights protected by the Second Amendment are both “fundamental” and “deeply rooted” and, as such, are enforceable against the States under the Fourteenth Amendment’s Privileges and Immunities Clause.
(5) Recently, the Supreme Court acknowledged in New York State Rifle & Pistol Ass’n v. Bruen (142 S. Ct. 2111, 2156 (2022)), that the Second and Fourteenth Amendments protect the individual right to carry arms outside the home for self-defense. Further, the Court reiterated that the Second Amendment’s otherwise “unqualified command” only accommodates laws that are “consistent with this Nation’s historical tradition of firearm regulation” (Id. at 2126).
(6) Certain States and localities have enacted gun control laws that are not consistent with the text of the Second Amendment or this Nation’s historical tradition of firearm regulation. The criminalization of peaceable, public firearms carry is repugnant to the original meaning of the Second Amendment.
(7) Any State or local restriction on the right of American citizens to keep and bear arms impairs the ability of the Second Amendment to achieve its textually specified purpose, “the security of a free State”.
SEC. 3. The right to keep and bear arms.
(a) In general.—Section 927 of title 18, United States Code, is amended to read as follows:
Ҥ 927. The right to keep and bear arms
“(a) No State or political subdivision of a State may impose a criminal or civil penalty on, or otherwise indirectly limit the carrying of firearms (including by imposing a financial or other barrier to entry) in public by residents or nonresidents of that State who are citizens of the United States and otherwise eligible to possess firearms under State and Federal law.
“(b) Any statute, ordinance, regulation, custom, or usage of a State or a political subdivision of a State that criminalizes, penalizes, or otherwise indirectly dissuades the carrying of firearms (including by imposing a financial or other barrier to entry) in public by any resident or nonresident who is a United States citizen and otherwise eligible to possess firearms under State and Federal law, shall have no force or effect.
“(c) The term ‘State’ as used in this section includes the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and the possessions of the United States (not including the Canal Zone).
“(d) The term ‘public’ as used in this section—
“(1) includes any place held open to the public, regardless of ownership, but in the case of a privately-owned location held open to the public, does not include a place where the owner communicates clearly and conspicuously a prohibition of firearms on the premises; and
“(2) does not include a place where screening for firearms is conducted under State law.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for such chapter is amended by striking the item relating to section 927 and inserting the following:
“927. The right to keep and bear arms.”.
H.R.1307 – To establish the Office of Gun Violence Prevention, and for other purposes.
Citizenship
H.R.50 – KAMALA Act or Keeping Aid for Municipalities And Localities Accountable Act
Summary: This bill prohibits the use of Community Development Block Grant (CDBG) funding to assist non-U.S. nationals (aliens under federal law) who are not lawfully admitted permanent residents. The CDBG program is administered by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) and provides states, local governments, and Indian tribes with funds for economic and community development.
The bill also specifically prohibits HUD from making a CDBG grant to any state, local government, or Indian tribe that carries out a housing or community development program that assists such individuals.
To prohibit grants provided under section 106 of the Housing and Community Development Act of 1974 from being used to assist persons who are neither a national of the United States nor lawfully admitted for permanent residence, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Prohibition on assistance for persons not lawfully present.
(a) In general.—Section 105 of the Housing and Community Development Act of 1974 (42 U.S.C. 5305) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(i) Prohibition on use of assistance for persons not lawfully present.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, no amount from a grant under section 106 made in fiscal year 2024 or any succeeding fiscal year may be used to assist persons who are neither a national of the United States nor lawfully admitted for permanent residence under section 101(a)(20) of the Immigration and Nationality Act.”.
SEC. 3. Prohibition on grants to entities that provide assistance to persons not lawfully present.
Section 103 of the Housing and Community Development Act of 1974 (42 U.S.C. 5303) is amended—
(1) by striking “The Secretary is authorized to” and inserting:
“(a) In general.—The Secretary is authorized to”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following:
“(b) Limitation.—The Secretary may not make a grant to any State, unit of general local government, or Indian tribe to carry out activities in accordance with the provisions of this title if such State, unit of general local government, or Indian tribe carries out any housing or community development related program that provides assistance to persons who are neither a national of the United States nor lawfully admitted for permanent residence under section 101(a)(20) of the Immigration and Nationality Act.”.
H.R.151 – Equal Representation Act
To require a citizenship question on the decennial census, to require reporting on certain census statistics, and to modify apportionment of Representatives to be based on United States citizens instead of all persons.
SEC. 2. Citizenship status on decennial census.
(a) In general.—Section 141 of title 13, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by redesignating subsection (g) as subsection (h); and
(2) by inserting after subsection (f) the following:
“(g) (1) In conducting the 2030 decennial census and each decennial census thereafter, the Secretary shall include in any questionnaire distributed or otherwise used for the purpose of determining the total population by States a checkbox or other similar option for the respondent to indicate, for the respondent and for each of the members of the household of the respondent, whether that individual is—
“(A) a citizen of the United States;
“(B) a national of the United States but not a citizen of the United States;
“(C) an alien lawfully residing in the United States; or
“(D) an alien unlawfully residing in the United States.
“(2) Not later than 120 days after completion of a decennial census of the population under subsection (a), the Secretary shall make publicly available the number of persons per State, disaggregated by each of the 4 categories described in subparagraphs (A) through (D) of paragraph (1), as tabulated in accordance with this section.”.
SEC. 3. Exclusion of noncitizens from number of persons used to determine apportionment of representatives and number of electoral votes.
(a) Exclusion.—Section 22(a) of the Act entitled “An Act to provide for the fifteenth and subsequent decennial censuses and to provide for an apportionment of Representatives in Congress”, approved June 18, 1929 (2 U.S.C. 2a(a)), is amended by inserting after “not taxed” the following: “and individuals who are not citizens of the United States”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by subsection (a) shall apply with respect to the apportionment of Representatives carried out pursuant to the decennial census conducted during 2030 and any succeeding decennial census.
SEC. 4. Severability clause.
If any provision of this Act or amendment made by this Act, or the application thereof to any person or circumstance, is held to be unconstitutional, the remainder of the provisions of this Act and amendments made by this Act, and the application of the provision or amendment to any other person or circumstance, shall not be affected.
H.R.551 – Make the Migrant Protection Protocols Mandatory Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Mandatory implementation of the Migrant Protection Protocols.
Section 235(b)(2)(C) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1225(b)(2)(C)) is amended by striking “may” and inserting “shall”.
H.R.569 – Birthright Citizenship Act of 2025
To amend section 301 of the Immigration and Nationality Act to clarify those classes of individuals born in the United States who are nationals and citizens of the United States at birth.
SEC. 2. Citizenship at birth for certain persons born in the United States.
(a) In general.—Section 301 of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1401) is amended—
(1) by inserting “(a) In general.—” before “The following”;
(2) by redesignating subsections (a) through (h) as paragraphs (1) through (8), respectively; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(b) Definition.—Acknowledging the right of birthright citizenship established by section 1 of the 14th amendment to the Constitution, a person born in the United States shall be considered ‘subject to the jurisdiction’ of the United States for purposes of subsection (a)(1) if the person is born in the United States of parents, one of whom is—
“(1) a citizen or national of the United States;
“(2) an alien lawfully admitted for permanent residence in the United States whose residence is in the United States; or
“(3) an alien with lawful status under the immigration laws performing active service in the armed forces (as defined in section 101 of title 10, United States Code).”.
- Applicability.—The amendment made by subsection (a)(3) shall not be construed to affect the citizenship or nationality status of any person born before the date of the enactment of this Act.
Discrimination
H.R.711 – FAIR Act of 2025 “Fairness, Anti-discrimination and Individual Rights Act of 2025”
SEC. 2. Prohibition against discrimination and preferential treatment.
Notwithstanding any other provision of law, neither the Federal Government nor any officer, employee, or agent of the Federal Government shall—
(1) intentionally discriminate against, or grant a preference to, any person or group based in whole or in part on race, color, or national origin, in connection with—
(A) a Federal contract or subcontract;
(B) Federal employment; or
(C) any other federally conducted program or activity; or
(2) require or encourage a Federal contractor or subcontractor, or the recipient of a license or financial assistance, to discriminate intentionally against, or grant a preference to, any person or group based in whole or in part on race, color, or national origin, in connection with any Federal contract or subcontract or Federal license or financial assistance.
SEC. 3. Prohibition relating to recipients of Federal aid.
A State or private entity that receives Federal financial assistance may not discriminate against, or grant a preference to, any person or group based in whole or in part on race, color, or national origin, in connection with—
(1) any contract or subcontract;
(2) employment; or
(3) admission to any educational institution.
SEC. 4. Construction.
This Act does not affect any law governing immigration or nationality, or the administration of any such law.
SEC. 5. Compliance review of policies and regulations.
Not later than 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act, the head of each department or agency of the Federal Government, in consultation with the Attorney General, shall review all existing policies and regulations that such department or agency head is charged with administering, modify such policies and regulations to conform to the requirements of this Act, and report to the Committee on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives and the Committee on the Judiciary of the Senate the results of the review and any modifications to the policies and regulations.
SEC. 6. Remedies.
(a) In general.—Any person aggrieved by a violation of section 2 or 3 may, in a civil action against the violator (including a violator that is a governmental entity), obtain appropriate relief (which may include back pay). A prevailing plaintiff in a civil action under this section shall be awarded a reasonable attorney’s fee as part of the costs.
(b) Construction.—This section does not affect any remedy available under any other law.
SEC. 7. Effect on pending matters.
(a) Pending cases.—This Act does not affect any case pending on the date of enactment of this Act.
(b) Pending contracts and subcontracts.—This Act does not affect any contract or subcontract in effect on the date of enactment of this Act, including any option exercised under such contract or subcontract before or after such date of enactment.
SEC. 8. Definitions.
In this Act, the following definitions apply:
(1) FEDERAL GOVERNMENT.—The term “Federal Government” means executive and legislative branches of the Government of the United States.
(2) PREFERENCE.—The term “preference” means an advantage of any kind, and includes a quota, set-aside, numerical goal, timetable, or other numerical objective.
H.R.925 – To ensure equal protection of the law, to prevent racism in the Federal Government, and for other purposes.
H.R.1007 – To provide for the consideration of a definition of antisemitism set forth by the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance for the enforcement of Federal antidiscrimination laws concerning education programs or activities, and for other purposes.
Sexuality
H.R.1015 – To amend title 18, United States Code, to provide for certain rules for housing or transportation based on gender and to provide for a limitation on gender-related medical treatment.
H.R.1016 – To prohibit individuals from accessing or using single-sex facilities on Federal property other than those corresponding to their biological sex, and for other purposes.
Veterans
H.R.71 – Veterans Health Care Freedom Act
To direct the Secretary of Veterans Affairs to carry out a pilot program to improve the ability of veterans to access medical care in medical facilities of the Department of Veterans Affairs and in the community by providing the veterans the ability to choose health care providers.
SEC. 2. Pilot program on ability of veterans to choose health care providers.
(a) Pilot program.—
(1) REQUIREMENT.—The Secretary of Veterans Affairs, acting through the Center for Innovation for Care and Payment, shall carry out a pilot program to improve the ability of eligible veterans to access hospital care, medical services, and extended care services through the covered care system by providing the eligible veterans the ability to choose health care providers.
(2) LOCATIONS.—The Secretary shall select a minimum of four Veterans Integrated Service Networks in which to carry out the pilot program under paragraph (1). In making such selection, the Secretary shall ensure that the pilot program is carried out in varied geographic areas that include both rural and urban locations.
(b) Removal of certain requirements To access care.—In carrying out the pilot program under subsection (a), the Secretary shall furnish hospital care, medical services, and extended care services to eligible veterans through the covered care system as follows:
(1) At medical facilities of the Department of Veterans Affairs, regardless of whether the facility is in the same Veterans Integrated Service Network as the Network in which the veteran resides.
(2) At non-Department facilities pursuant to, as appropriate—
(A) section 1703 of title 38, United States Code, without regard to the requirements specified in subsection (d) of such section; or
(B) section 1703A of such title, without regard to the requirements specified in subsection (a)(1)(C) of such section.
(c) Election of veteran.—In accordance with subsections (d) and (e), an eligible veteran participating in the pilot program may elect to receive hospital care, medical services, and extended care services at any provider in the covered care system.
(d) Coordination of care.—
(1) SELECTION.—Each eligible veteran participating in the pilot program shall select a primary care provider in the covered care system. The primary care provider shall—
(A) coordinate with the Secretary and other health care providers the hospital care, medical services, and extended care services furnished to the veteran under the pilot program; and
(B) refer the veteran to specialty care providers in the covered care system, as clinically necessary.
(2) SYSTEMS.—The Secretary shall establish systems as the Secretary determines appropriate to ensure that a primary care provider can effectively coordinate the hospital care, medical services, and extended care services furnished to a veteran under the pilot program.
(e) Specialty care.—
(1) ACCESS.—Subject to subsection (d)(1)(B), an eligible veteran participating in the pilot program may select any specialty care provider in the covered care system from which to receive specialty care.
(2) DESIGNATION.—The Secretary may designate a specialty care provider as a primary care provider of an eligible veteran participating in the pilot program if the Secretary determines that such designation is in the health interests of the veteran (such as an endocrinologist with respect to a veteran diagnosed with diabetes, a neurologist with respect to a veteran diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, or an obstetrician-gynecologist with respect to a female veteran).
(f) Mental health care.—An eligible veteran participating in the pilot program may select a mental health care provider in the covered care system from which to receive mental health care.
(g) Information.—In carrying out the pilot program, the Secretary shall furnish to eligible veterans the information on eligibility, cost sharing, treatments, and providers required for veterans to make informed decisions with respect to—
(1) selecting primary care providers and specialty care providers; and
(2) treatments available to the veteran.
(h) Duration.—
(1) PHASE IN.—The Secretary shall carry out the pilot program during the three-year period beginning on the date that is one year after the date of the enactment of this Act.
(2) PERMANENT REQUIREMENT.—
(A) VETERANS COMMUNITY CARE PROGRAM.—Section 1703(d) of title 38, United States Code, is amended—
(i) in paragraph (1), by striking “The Secretary shall” and inserting “Except as provided by paragraph (5), the Secretary shall”; and
(ii) by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(5) Beginning on the date that is four years after the date of the enactment of the Veterans Health Care Freedom Act—
“(A) the requirements under paragraphs (1), (2), and (3) shall not apply with respect to furnishing hospital care, medical services, and extended care services to a covered veteran under this section; and
“(B) the Secretary shall furnish hospital care, medical services, and extended care services to a covered veteran under this section with the same conditions on the ability of the veteran to choose health care providers as specified in the pilot program described in section 2 of such Act.”.
(B) VETERANS CARE AGREEMENTS.—Section 1703A(a)(1) of such title is amended—
(i) in subparagraph (C), by striking “For purposes” and inserting “Except as provided by subparagraph (E), for purposes”; and
(ii) by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(E) Beginning on the date that is four years after the date of the enactment of the Veterans Health Care Freedom Act—
“(i) the requirements under subparagraph (C) shall not apply with respect to furnishing hospital care, medical services, and extended care services to a covered veteran under this section; and
“(ii) the Secretary shall furnish hospital care, medical services, and extended care services to a covered veteran under this section with the same conditions on the ability of the veteran to choose health care providers as specified in the pilot program described in section 2 of such Act.”.
(C) VISNS.—Beginning on the date that is four years after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary shall furnish hospital care, medical services, and extended care services to veterans under chapter 17 of title 38, United States Code, at medical facilities of the Department of Veterans Affairs, regardless of whether the facility is in the same Veterans Integrated Service Network as the Network in which the veteran resides.
(i) Reports.—
(1) IMPLEMENTATION.—On a quarterly basis during the two-year period beginning on the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary shall submit to the Committees on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives and the Senate a report on the implementation of the pilot program. One such report shall contain a description of the final design of the pilot program.
(2) ANNUAL.—On an annual basis during the period beginning on the date that is one year after the date of the submission of the final report under paragraph (1) and ending on the date of the conclusion of the pilot program, the Secretary shall submit to the Committees on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives and the Senate a report on the results of the pilot program.
(j) Regulations.—The Secretary, in consultation with the Committees on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives and the Senate, may prescribe regulations to carry out this section.
(k) No additional appropriations.—No additional funds are authorized to be appropriated to carry out this section, and this section shall be carried out using amounts otherwise made available to the Veterans Health Administration.
(l) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) The term “covered care system” means each—
(A) medical facility of the Department;
(B) health care provider specified in subsection 1703(c) of title 38, United States Code; and
(C) eligible entity or provider that has entered into a Veterans Care Agreement under section 1703A of such title.
(2) The term “eligible veteran” means a veteran who is enrolled in the patient enrollment system of the Department of Veterans Affairs under section 1705 of title 38, United States Code.
(3) The term “non-Department facility” has the meaning given that term in section 1701 of title 38, United States Code.
H.R.72 – TBI and PTSD Treatment Act
To amend title 38, United States Code, to direct the Secretary of Veterans Affairs to furnish hyperbaric oxygen therapy to veterans with traumatic brain injury or post-traumatic stress disorder.
SEC. 2. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for veterans with traumatic brain injury or post-traumatic stress disorder.
(a) In general.—Chapter 17 of title 38, United States Code, is amended by inserting after section 1710E the following new section:
Ҥ 1710F. Traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic stress disorder: hyperbaric oxygen therapy
“(a) Authority.—The Secretary shall furnish hyperbaric oxygen therapy to a veteran who has a condition specified in subsection (b) through a health care provider described in section 1703(c)(5) of this title.
“(b) Covered conditions.—The conditions specified in this subsection are the following:
“(1) Traumatic brain injury.
“(2) Post-traumatic stress disorder.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections at the beginning of such chapter is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 1710E the following new item:
“1710F. Traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic stress disorder: hyperbaric oxygen therapy.”.
H.R.109 – TEAM Veteran Caregivers Act
Summary: Transparency and Effective Accountability Measures for Veteran Caregivers Act or the TEAM Veteran Caregivers Act
The bill revises the administration of Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) caregiver programs. Specifically, the bill requires the VA to formally recognize caregivers of veterans by identifying any caregiver in the health record of the veteran. Such caregivers covered by the bill include those participating in the Program of Comprehensive Assistance for Family Caregivers and those participating in the Program of General Caregiver Support Services.
The bill requires the VA to notify veterans and their caregivers regarding any clinical determinations made relating to claims, tier reduction, or termination of assistance under, or eligibility for, the specified caregiver programs. The notifications must be standardized and contain specified details regarding the decisions.
The bill also requires the VA to temporarily extend benefits under the Program of Comprehensive Assistance for Family Caregivers for at least 90 days after the receipt of notice that a veteran is no longer clinically eligible for the program. Such an extension shall not apply to the termination of caregiver benefits (1) if the VA determines the caregiver committed fraud or abused or neglected the veteran, (2) if another primary provider or individual caregiver is designated within 90 days after the termination, (3) if the terminated individual moves out or abandons their relationship with the veteran, or (4) upon request of the caregiver or veteran.
H.R.211 – Equal Access to Contraception for Veterans Act
To amend title 38, United States Code, to provide for limitations on copayments for contraception furnished by the Department of Veterans Affairs, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Limitation on copayments for contraception.
Section 1722A(a)(2) of title 38, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by striking “to pay” and all that follows through the period and inserting “to pay—”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following new subparagraphs:
“(A) an amount in excess of the cost to the Secretary for medication described in paragraph (1); or
“(B) an amount for any contraceptive item for which coverage under health insurance coverage is required without the imposition of any cost-sharing requirement pursuant to section 2713(a)(4) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 300gg–13(a)(4)).”.
H.R.224 – Disabled Veterans Housing Support Act
To amend section 102(a)(20) of the Housing and Community Development Act of 1974 to require the exclusion of service-connected disability compensation when determining whether a person is a person of low and moderate income, a person of low income, or a person of moderate income, and for other purposes.
Summary: This bill excludes compensation received for a military service-connected disability from a veteran’s income when determining eligibility for assistance under the Community Development Block Grant (CDBG) program.
The CDBG program provides grants to urban communities for development activities focused on revitalizing neighborhoods, economic development, and providing improved community facilities and services.
Additionally, the Government Accountability Office must report on how service-connected disability compensation is treated when determining eligibility for all programs administered by the Department of Housing and Urban Development. This includes identifying instances where the treatment of such compensation is inconsistent with the requirement under this bill.
SEC. 2. Service connected disability compensation.
Section 102(a)(20) of the Housing and Community Development Act of 1974 (42 U.S.C. 5302(a)(20)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(C) SERVICE-CONNECTED DISABILITY COMPENSATION.—When determining whether a person is a person of low and moderate income, a person of low income, or a person of moderate income under this paragraph, a State, unit of general local government, or Indian tribe shall exclude any service-connected disability compensation received by such person from the Department of Veterans Affairs.”.
SEC. 3. Report.
The Comptroller General of the United States shall, not later than 1 year after the date of the enactment of this Act, submit to the Congress a report that—
(1) examines how service-connected disability compensation is treated for the purposes of determining eligibility for all programs administered by the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development;
(2) identifies any instances where service-connected disability compensation is treated in a manner inconsistent with the amendment made by section 2; and
(3) with respect to each program administered by the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development in which service-connected disability compensation is treated inconsistently, provides legislative recommendations relating to how such program could better serve veteran populations, and under-served communities.
Passed the House of Representatives February 10, 2025.
H.R.965 – Housing Unhoused Disabled Veterans Act
To amend section 3(b)(4) of the United States Housing Act of 1937 to exclude certain disability benefits from income for the purposes of determining eligibility for the supported housing program under section 8(o)(19), and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Exclusion of certain disability benefits.
Section 3(b)(4)(B) of the United States Housing Act of 1937 (42 U.S.C. 1437a(b)(4)(B)) is amended—
(1) by redesignating clauses (iv) and (v) as clauses (vi) and (vii), respectively; and
(2) by inserting after clause (iii) the following:
“(iv) with respect to the supported housing program under section 8(o)(19), any disability benefits received under chapter 11 or chapter 15 of title 38, United States Code, received by a veteran, except that this exclusion may not apply to the definition of adjusted income;
“(v) with respect to any household receiving rental assistance under the supported housing program under section 8(o)(19) as it relates to eligibility for other types of housing assistance, any disability benefits received under chapter 11 or chapter 15 of title 38, United States Code, received by a veteran, except that this exclusion may not apply to the definition of adjusted income;”.
SEC. 3. Treatment of certain disability benefits.
(a) In general.—When determining the eligibility of a veteran to rent a residential dwelling unit constructed on Department property on or after the date of the enactment of this Act, for which assistance is provided as part of a housing assistance program administered by the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development and not yet in existence at the time of the enactment of this section, the Secretary shall exclude from income any disability benefits received under chapter 11 or chapter 15 of title 38, United States Code by such person.
(b) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) SECRETARY.—The term “Secretary” means the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development.
(2) DEPARTMENT PROPERTY.—The term “Department property” has the meaning given the term in section 901 of title 38, United States Code.
Passed the House of Representatives February 10, 2025.
H.R.1248 – To amend title 38, United States Code, to require the consideration of continuity of health care in determining best medical interest under the Veterans Community Care Program, and for other purposes.
Border
H.R.76 – Fund and Complete the Border Wall Act
Summary: This bill establishes funding for a U.S.-Mexico border barrier and revises how border patrol agents are compensated for overtime.
The Department of the Treasury shall set up an account for funding the design, construction, and maintenance of the barrier. The funds in the account are appropriated only for that purpose and for vehicles and equipment for border patrol agents.
For each fiscal year, financial assistance to a country shall be reduced by $2,000 for each citizen or national of that country apprehended for illegally entering the United States through its southern border. The reduced amount shall be transferred to the border barrier account. The Department of State may opt not to reduce amounts appropriated to Mexico for various military and law enforcement-related activities.
This bill establishes a 5% fee on foreign remittance transfers and increases the fee for the arrival/departure I-94 form for various aliens entering the United States, with part of the fees going to the border barrier account.
By December 31, 2025, the Department of Homeland Security shall (1) take all actions necessary, including constructing barriers, to prevent illegal crossings along the U.S.-Mexico barrier; and (2) achieve operational control over all U.S. international borders.
The bill changes how border patrol agents receive overtime pay when working up to 100 hours in a two-week period. For hours worked above 80, an agent shall receive at least 150% of the agent’s regular hourly rate.
SEC. 2. Border wall trust fund.
(a) Establishment of fund.—At the end of subchapter III of chapter 33 of title 31, United States Code, insert the following:
Ҥ 3344. Secure the Southern Border Fund
“(a) In general.—Not later than 60 days after the date of enactment of this section, the Secretary of the Treasury shall establish an account in the Treasury of the United States, to be known as the ‘Secure the Southern Border Fund’, into which funds shall be deposited in accordance with the Fund and Complete the Border Wall Act and the amendments made by that Act.
“(b) Appropriation.—Funds deposited in the Secure the Southern Border Fund shall be available until expended. Such funds are authorized to be appropriated, and are appropriated, to the Secretary of Homeland Security only—
“(1) to plan, design, construct, or maintain a barrier along the international border between the United States and Mexico; and
“(2) to purchase and maintain necessary vehicles and equipment for U.S. Border Patrol agents.
“(c) Limitation.—Not more than 5 percent of the funds deposited in the Secure the Southern Border Fund may be used for the purpose described in subsection (b)(2).”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of contents for chapter 33 of title 31, United States Code, is amended by inserting at the end the following:
“3344. Secure the Southern Border Fund.”.
SEC. 3. Border crossing accountability and security.
(a) Estimation of annual illegal border crossings.—Beginning with the first fiscal year that begins after the date of the enactment of this Act, not later than 30 days after the end of each fiscal year, the Secretary of Homeland Security shall determine and report to the Secretary of State and the Committees on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives and of the Senate—
(1) the number of apprehensions that occurred during such fiscal year of aliens who entered the United States by illegally crossing the international land border between the United States and Mexico; and
(2) the nationality of aliens described in paragraph (1).
(b) Reduction of foreign assistance.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Except as provided under paragraph (2), the Secretary of State shall proportionately reduce the amount of Federal financial assistance provided to a foreign state for the fiscal year in which a report under subsection (a) is made by a total of $2,000 for each alien described in such report who is a citizen or national of that country.
(2) EXCEPTION.—Notwithstanding paragraph (1), the Secretary of State may opt not to reduce the amounts appropriated for the Government of Mexico from the International Military Education and Training Fund, the International Narcotics Control and Law Enforcement Fund, and the fund to carry out nonproliferation, anti-terrorism, demining, and related programs and activities.
(c) Transfer of funds To Secure the Southern Border Fund.—The Secretary of State, in consultation with the Secretary of Homeland Security and the Secretary of the Treasury, shall transfer funds described in subsection (b) into the Secure the Southern Border Fund established by the amendment made by section 2 of this Act.
SEC. 4. Fees for certain remittance transfers.
Section 920 of the Electronic Fund Transfer Act (relating to remittance transfers) (15 U.S.C. 1693o–1) is amended—
(1) by redesignating subsection (g) as subsection (h); and
(2) by inserting after subsection (f) the following:
“(g) Secure the Southern Border Fund fee.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—If the designated recipient of a remittance transfer is located outside of the United States, a remittance transfer provider shall collect from the sender of such remittance transfer a remittance fee equal to 5 percent of the United States dollar amount to be transferred.
“(2) TRANSFER OF FUNDS.—Not later than 90 days after the date of enactment of this subsection, the Secretary of the Treasury, in consultation with the Bureau and remittance transfer providers, shall develop and make available a system for remittance transfer providers to submit the remittance fees collected in accordance with paragraph (1) to the Secure the Southern Border Fund established under section 3344 of title 31, United States Code.
“(3) PENALTIES.—
“(A) Whoever, with the intent to evade a remittance fee to be collected in accordance with this subsection, and who has knowledge that, at the time of a remittance transfer, the value of the funds involved in the transfer will be further transferred to a recipient located outside of the United States, requests or facilitates such remittance transfer to a recipient located outside of the United States shall be subject to a penalty of not more than $500,000 or twice the value of the funds involved in the remittance transfer, whichever is greater, or imprisonment for not more than 20 years, or both.
“(B) Any foreign country that, in the joint determination of the Secretary of Homeland Security, the Secretary of the Treasury, and the Secretary of State, aids or harbors an individual conspiring to avoid the fee collected in accordance with this subsection shall be ineligible to receive foreign assistance and to participate in the visa waiver program or any other programs, at the discretion of the Secretaries described in this subparagraph.”.
SEC. 5. Fees for Form I–94.
(a) Fee Increase.—The Secretary of Homeland Security shall increase the fee collected for services performed in processing U.S. Customs and Border Protection Form I–94, Arrival/Departure Record, from $6 to $25.
(b) Disposition of fees collected.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, including section 286(q) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1356(q)), all fees collected for services performed in processing U.S. Customs and Border Protection Form I–94 shall be allocated as follows:
(1) $6 shall be deposited in the Land Border Inspection Fee Account and used in accordance with such section 286(q).
(2) To the extent provided in advance in appropriations Acts, $10 shall be used for salaries for U.S. Border Patrol agents.
(3) $9 shall be deposited in the Secure the Southern Border Fund established by the amendment made by section 2 of this Act.
SEC. 6. Construction of border wall.
(a) Improvement of barriers at border.—Section 102 of the Illegal Immigration Reform and Immigrant Responsibility Act of 1996 (division C of Public Law 104–208; 8 U.S.C. 1103 note) is amended—
(1) by amending subsection (a) to read as follows:
“(a) In general.—Not later than December 31, 2025, the Secretary of Homeland Security shall take such actions as may be necessary (including the removal of obstacles to detection of illegal entrants) to design, test, construct, and install physical barriers, roads, and technology along the international land border between the United States and Mexico to prevent illegal crossings in all areas.”;
(2) in subsection (b)—
(A) in paragraph (1)—
(i) in the paragraph heading, by striking “Additional fencing” and inserting “Fencing”;
(ii) by striking subparagraph (A) and inserting the following:
“(A) PHYSICAL BARRIERS.—In carrying out subsection (a), the Secretary of Homeland Security shall construct physical barriers, including secondary barriers in locations where there is already a fence, along the international land border between the United States and Mexico that will prevent illegal entry and will assist in gaining operational control of the border (as defined in section 2(b) of the Secure Fence Act of 2006 (8 U.S.C. 1701 note; Public Law 109–367)).”;
(iii) by striking subparagraph (B) and redesignating subparagraphs (C) and (D) as subparagraphs (B) and (C), respectively;
(iv) in subparagraph (B), as so redesignated—
(I) by striking clause (i) and inserting the following:
“(i) IN GENERAL.—In carrying out this section, the Secretary of Homeland Security shall, before constructing physical barriers in a specific area or region, consult with the Secretary of the Interior, the Secretary of Agriculture, appropriate Federal, State, local, and Tribal governments, and appropriate private property owners in the United States to minimize the impact on the environment, culture, commerce, and quality of life for the communities and residents located near the sites at which such physical barriers are to be constructed. Nothing in this paragraph should be construed to limit the Secretary of Homeland Security’s authority to move forward with construction after consultation.”;
(II) by redesignating clause (ii) as clause (iii); and
(III) by inserting after clause (i), as amended, the following new clause:
“(ii) NOTIFICATION.—Not later than 60 days after the consultation required under clause (i), the Secretary of Homeland Security shall notify the Committees on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives and of the Senate, the Committee on Homeland Security of the House of Representatives, and the Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs of the Senate of the type of physical barriers, tactical infrastructure, or technology the Secretary has determined is most practical and effective to achieve situational awareness and operational control in a specific area or region and the other alternatives the Secretary considered before making such a determination.”; and
(v) by striking subparagraph (C), as so redesignated, and inserting the following:
“(C) LIMITATION ON REQUIREMENTS.—Notwithstanding subparagraph (A), nothing in this paragraph shall require the Secretary of Homeland Security to install fencing, physical barriers, or roads in a particular location along the international border between the United States and Mexico, if the Secretary determines there is a pre-existing geographical barrier or pre-constructed, impenetrable wall. The Secretary shall notify the Committees on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives and the Senate, the Committee on Homeland Security of the House of Representatives, and the Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs of the Senate of any decision not to install fencing in accordance with this provision within 30 days of such a determination being made.”;
(B) in paragraph (2)—
(i) by striking “Attorney General” and inserting “Secretary of Homeland Security”; and
(ii) by striking “fences” and inserting “physical barriers and roads”; and
(C) in paragraph (3)—
(i) by striking “Attorney General” and inserting “Secretary of Homeland Security”; and
(ii) by striking “additional fencing” and inserting “physical barriers and roads”; and
(3) in subsection (c), by amending paragraph (1) to read as follows:
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Secretary of Homeland Security shall have the authority to waive all legal requirements the Secretary, in the Secretary’s sole discretion, determines necessary to ensure the expeditious design, testing, construction, installation, deployment, operation, and maintenance of physical barriers, roads, and technology under this section. Any such decision by the Secretary shall be effective upon publication in the Federal Register.”.
(b) Achieving operational control on the border.—Subsection (a) of section 2 of the Secure Fence Act of 2006 (8 U.S.C. 1701 note) is amended, in the matter preceding paragraph (1), by striking “18 months after the date of the enactment of this Act” and inserting “December 31, 2025”.
SEC. 7. Fair Labor Standards Act for U.S. Border Patrol.
(a) In general.—Section 7 of the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 (29 U.S.C. 207) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(r) Employment as a Border Patrol agent.—No public agency shall be deemed to have violated subsection (a) with respect to the employment of any Border Patrol agent (as defined in section 5550 of title 5, United States Code) if, during a work period of 14 consecutive days, the Border Patrol agent receives compensation at a rate that is not less than 150 percent of the regular rate at which the agent is employed for all hours of work from 80 hours to 100 hours. Payments required under this section shall be in addition to any payments made under such section, and shall be made notwithstanding any pay limitations set forth in such title.”.
(b) Technical and conforming amendments.—Section 13(a) of the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 (29 U.S.C. 213(a)) is amended by striking paragraph (18) and redesignating paragraph (19) as paragraph (18).
SEC. 8. Severability.
If any provision of this Act, or an amendment made by this Act, or the application of such provision or amendment to any person or circumstance, is held to be invalid, the remainder of this Act, or an amendment made by this Act, or the application of such provision to other persons or circumstances, shall not be affected.
H.R.116 – Stopping Border Surges Act
To close loopholes in the immigration laws that serve as incentives to aliens to attempt to enter the United States unlawfully, and for other purposes.
(b) Table of contents.—The table of contents for this Act is as follows:
Sec. 1. Short title; table of contents.
TITLE I—UNACCOMPANIED ALIEN CHILDREN
Sec. 101. Repatriation of unaccompanied alien children.
Sec. 102. Clarification of standards for family detention.
Sec. 103. Special immigrant juvenile status for immigrants unable to reunite with either parent.
Sec. 201. Credible fear interviews.
Sec. 202. Jurisdiction of asylum applications.
Sec. 203. Recording expedited removal and credible fear interviews.
Sec. 204. Safe third country.
Sec. 205. Renunciation of asylum status pursuant to return to home country.
Sec. 206. Notice concerning frivolous asylum applications.
Sec. 207. Anti-fraud investigative work product.
Sec. 208. Clarification of asylum eligibility.
Sec. 209. Application timing.
Sec. 210. Clarification of burden of proof.
Sec. 211. Additional exception.
Sec. 212. Clarification regarding employment eligibility.
Sec. 213. Penalties for asylum fraud.
Sec. 214. Statute of limitations for asylum fraud.
Sec. 215. Technical amendments.
H.R.285 – Advanced Border Coordination Act of 2025
To establish Joint Operations Centers along the southern border of the United States, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Establishment of Joint Operations Centers.
(a) In general.—Not later than 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act, the Department shall establish not fewer than 2 Joint Operations Centers along the southern border of the United States to provide unified coordination centers, where law enforcement from multiple Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies can collaborate in accordance with the purposes described in subsection (b).
(b) Matters covered.—The Centers shall provide centralized operations hubs for matters related to the following:
(1) Implementing coordination and communication for field operations between participating Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies, as needed.
(2) Coordinating operations across participating Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies, as needed, including ground, air, and sea or amphibious operations.
(3) Coordinating and supporting border operations, including deterring and detecting criminal activity related to—
(A) transnational criminal organizations;
(B) illegal border crossings;
(C) the seizure of weapons;
(D) the seizure of drugs;
(E) the seizure of high valued property;
(F) terrorism;
(G) human trafficking;
(H) drug trafficking; and
(I) such additional matters as the Secretary considers appropriate.
(c) Information sharing.—To ensure effective transmission of information between participating Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies, for purposes of subsection (b), coordination and communication shall include—
(1) Federal agencies sharing pertinent information with participating State, local, and Tribal agencies through the Centers; and
(2) Federal agencies notifying participating State, local, and Tribal agencies of operations occurring within the jurisdictions of those agencies.
(d) Workforce capabilities.—The Centers shall—
(1) track and coordinate deployment of participating personnel; and
(2) coordinate training, as needed.
(e) Report.—Not later than one year after the date of the enactment of this Act and annually thereafter, the Secretary shall consult with participating Federal agencies, and shall seek feedback from participating State, local, and Tribal agencies, to report to Congress—
(1) a description of the efforts undertaken to establish the Centers;
(2) an identification of the resources used for the operations of the Centers;
(3) a description of the key operations coordinated and supported by each Center;
(4) a description of any significant interoperability and communication gaps identified between participating Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies within each Center;
(5) recommendations for improved coordination and communication between participating Federal agencies in developing and operating current and future Centers; and
(6) other data as the Secretary determines appropriate.
(f) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) CENTERS.—The term “Centers” means the Joint Operations Centers established under section 3(a).
(2) DEPARTMENT.—The term “Department” means the Department of Homeland Security.
(3) PARTICIPATING FEDERAL AGENCY.—The term “participating Federal agency” means—
(A) the Department;
(B) the Department of Defense;
(C) the Department of Justice; and
(D) any other Federal agency as the Secretary determines appropriate.
(4) SECRETARY.—The term “Secretary” means the Secretary of Homeland Security.
(5) STATE.—The term “State” means each State of the United States, the District of Columbia, and any territory or possession of the United States.
H.R.318 – Border Safety and Security Act of 2025
To authorize the Secretary of Homeland Security to suspend the entry of aliens, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Suspension of entry of aliens.
(a) Authority To suspend entry of aliens at borders of the United States.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, if the Secretary of Homeland Security determines, in his discretion, that the suspension of the entry of covered aliens at an international land or maritime border of the United States is necessary in order to achieve operational control over such border, the Secretary may prohibit, in whole or in part, the entry of covered aliens at such border for such period of time as the Secretary determines is necessary for such purpose.
(b) Required suspension of entry of aliens.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Secretary of Homeland Security shall prohibit the entry of covered aliens for any period during which the Secretary cannot—
(1) detain such covered aliens as required under section 235(b)(1)(B) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1225(b)(1)(B)); or
(2) place such covered aliens in a program consistent with section 235(b)(2)(C) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1225(b)(2)(C)).
(c) Enforcement by State Attorneys General.—The attorney general of a State, or other authorized State officer, alleging a violation of a subsection (b) that affects such State or its residents, may bring an action against the Secretary of Homeland Security on behalf of the residents of the State in an appropriate United States district court to obtain appropriate injunctive relief.
(d) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) Except as otherwise provided, the terms have the meanings given such terms in section 101 of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1101).
(2) The term “covered alien” means an alien seeking entry to the United States who is inadmissible under section 212(a)(7) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1182(a)(7)).
(3) The term “operational control” has the meaning given such term in section 2 of the Secure Fence Act of 2006 (8 U.S.C. 1701 note).
H.R.326 – Border Wall Waste Accountability Act
To require the GAO to conduct a study detailing the total cost of unused construction materials that were obtained for the construction of a border wall along the United States-Mexico border.
SEC. 2. GAO study on cost of unused construction materials for border wall.
Not later than 90 days after the date of the enactment of this section, the Comptroller General of the United States shall submit to Congress a study detailing the total cost of unused construction materials that were obtained for the construction of a border wall along the United States-Mexico border from January 20, 2021, to January 20, 2025.
H.R.495 – Subterranean Border Defense Act
To require annual reports on counter illicit cross-border tunnel operations, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Annual reports on counter illicit cross-border tunnel operations.
Paragraph (2) of section 7134(a) of the James M. Inhofe National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2023 (Public Law 117–263; 6 U.S.C. 257 note) is amended by inserting “and annually thereafter” after “development of the strategic plan”.
H.R.520 – Empowering Law Enforcement To Fight Sex Trafficking Demand Act of 2025
To amend the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 to include an additional permissible use of amounts provided as grants under the Byrne JAG program, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Additional authorized use of Byrne JAG funds.
Section 501(a)(1) of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10152(a)(1)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(I) Programs to combat human trafficking (including programs to reduce the demand for trafficked persons).”.
Healthcare
H.R.59 – Mens Rea Reform Act of 2025
Summary: This bill establishes a default mens rea standard (i.e., state of mind requirement) for federal criminal offenses—statutory and regulatory—that lack an explicit standard.
The government must generally prove that a defendant acted knowingly with respect to each element of an offense for which the text does not specify a state of mind.
SEC. 2. State of mind element for criminal offenses.
(a) In general.—Chapter 1 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
Ҥ 28. State of mind when not otherwise specifically provided
“(a) Definitions.—In this section—
“(1) the term ‘covered offense’—
“(A) means an offense—
“(i) specified in—
“(I) this title or any other Act of Congress;
“(II) any regulation; or
“(III) any law (including regulations) of any State or foreign government incorporated by reference into this title or any other Act of Congress; and
“(ii) that is punishable by imprisonment, a maximum criminal fine of at least $2,500, or both; and
“(B) does not include—
“(i) any offense set forth in chapter 47 or chapter 47A of title 10; or
“(ii) any offense incorporated by section 13(a) of this title;
“(2) the term ‘knowingly’, as related to an element of an offense, means—
“(A) if the element involves the nature of the conduct of a person or the attendant circumstances, that the person is aware that the conduct of the person is of that nature or that such circumstances exist; and
“(B) if the element involves a result of the conduct of a person, that the person is aware that it is practically certain that the conduct of the person will cause such a result;
“(3) the term ‘state of mind’ means willfully, intentionally, maliciously, knowingly, recklessly, wantonly, negligently, with reason to believe, or any other word or phrase that is synonymous with or substantially similar to any such term; and
“(4) the term ‘willfully’, as related to an element of an offense, means—
“(A) that the person acted with knowledge that the person’s conduct was unlawful; and
“(B) if the element involves the nature, attendant circumstances, object, or result of the conduct of a person, that—
“(i) the person had knowledge of the nature, attendant circumstances, object, or result of the conduct of the person; and
“(ii) it was the conscious object of the person to engage in conduct—
“(I) of that nature;
“(II) with that attendant circumstance;
“(III) with that object; or
“(IV) to cause such a result.
“(b) Default requirement.—Except as provided in subsections (c) and (d), a covered offense shall be construed to require the Government to prove beyond a reasonable doubt that the defendant acted—
“(1) with the state of mind specified in the text of the covered offense for each element of the offense for which the text specifies a state of mind; and
“(2) knowingly, with respect to any element of the offense for which the text of the covered offense does not specify a state of mind.
“(c) Failure To distinguish among elements.—Except as provided in subsection (d), if the text of a covered offense specifies the state of mind required for commission of the covered offense without specifying the elements of the covered offense to which the state of mind applies, the state of mind specified shall apply to all elements of the covered offense, unless a contrary purpose plainly appears.
“(d) Exceptions.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Subsections (b)(2) and (c) shall not apply with respect to—
“(A) any element for which the text of the covered offense makes clear that Congress affirmatively intended not to require the Government to prove any state of mind with respect to such element;
“(B) any element of a covered offense, to the extent that the element establishes—
“(i) subject matter jurisdiction over the covered offense; or
“(ii) venue with respect to trial of the covered offense; or
“(C) any element of a covered offense, to the extent that applying subsections (b)(2) and (c) to such element would lessen the degree of mental culpability that the Government is required to prove with respect to that element under—
“(i) precedent of the Supreme Court of the United States; or
“(ii) any other provision of this title, any other Act of Congress, or any regulation.
“(2) MERE ABSENCE INSUFFICIENT.—For purposes of paragraph (1)(A), the mere absence of a specified state of mind for an element of a covered offense in the text of the covered offense shall not be construed to mean that Congress affirmatively intended not to require the Government to prove any state of mind with respect to that element.
“(e) Applicability.—This section shall apply with respect to a covered offense—
“(1) without regard to whether the provision or provisions specifying the covered offense are enacted, promulgated, or finalized before, on, or after the date of enactment of this section; and
“(2) that was committed—
“(A) on or after the date of enactment of this section; or
“(B) before the date of enactment of this section, unless—
“(i) applying this section to such covered offense would—
“(I) punish as a crime conduct that was innocent when done;
“(II) increase the punishment for the covered offense; or
“(III) deprive a person charged with the covered offense of any defense available according to law at the time the covered offense occurred;
“(ii) a jury has been empaneled and sworn in a prosecution for the covered offense before the date of enactment of this section;
“(iii) the first witness has been sworn in a prosecution for the covered offense tried without a jury before the date of enactment of this section; or
“(iv) a sentence has been imposed following a plea of guilty or nolo contendere in a prosecution for the covered offense before the date of enactment of this section.
“(f) Subsequently enacted laws.—No provision of law enacted after the date of enactment of this section shall be construed to repeal, modify the text or effect of, or supersede in whole or in part this section, unless such law specifically refers to this section and explicitly repeals, modifies the text or effect of, or supersedes in whole or in part this section.”.
(b) Technical and conforming amendment.—The table of sections for chapter 1 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by adding at the end the following:
“28. State of mind when not otherwise specifically provided.”.
H.R.74 – Freedom for Families Act
SEC. 2. Distributions from health savings accounts during periods of qualified caregiving.
(a) In general.—Paragraphs (1) and (2) of section 223(f) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 are amended to read as follows:
“(1) EXCLUSION OF AMOUNTS USED FOR QUALIFIED MEDICAL EXPENSES OR DISTRIBUTED DURING PERIODS OF QUALIFIED CAREGIVING.—Any amount paid or distributed out of a health savings account shall not be includible in gross income if it is—
“(A) used exclusively to pay qualified medical expenses of any account beneficiary, or
“(B) paid or distributed during a period of qualified caregiving.
“(2) INCLUSION OF AMOUNTS NEITHER USED FOR QUALIFIED MEDICAL EXPENSES NOR DISTRIBUTED DURING PERIODS OF QUALIFIED CAREGIVING.—Any amount paid or distributed out of a health savings account shall be included in the gross income of the account beneficiary if it is not described in paragraph (1).”.
(b) Definition of period of qualified caregiving.—Section 223(f) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(9) Period of qualified caregiving.—For purposes of this section, the term ‘period of qualified caregiving’ means any period during which an individual is on leave or not employed by reason of a situation described in subparagraphs (A) through (E) of section 102(a)(1) of the Family and Medical Leave Act of 1993.”.
(c) Conforming amendments.—
(1) Section 223(d)(1) of such Code is amended by inserting “or the expenses incurred during a period of qualified caregiving of the account beneficiary” after “paying the qualified medical expenses of the account beneficiary”.
(2) Section 223(f)(4) of such Code is amended in the heading by striking “distributions not used for qualified medical expenses” and inserting “certain distributions”.
(d) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply with respect to taxable years beginning after the date of the enactment of this Act.
SEC. 3. No high deductible health plan required for health savings accounts.
(a) In general.—Section 223(a) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking “who is an eligible individual for any month during the taxable year”.
(b) Conforming amendments.—
(1) Section 223(b) of such Code is amended by striking paragraphs (7) and (8).
(2) Section 223 of such Code is amended by striking subsection (c).
(c) Increase in contribution limit for health savings accounts.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 223(b)(1) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking “the sum of the monthly” and all that follows through “eligible individual” and inserting “$9,000 (twice such amount in the case of a joint return)”.
(2) CONFORMING AMENDMENTS.—
(A) Section 223(b) of such Code is amended by striking paragraphs (2), (3), and (5) and by redesignating paragraphs (4) and (6) as paragraphs (2) and (3), respectively.
(B) Section 223(b)(2) of such Code (as redesignated by subparagraph (A)) is amended by striking the last sentence.
(C) Section 223(d)(1)(A)(ii) is amended by striking “the sum of” and all that follows through the period at the end and inserting “the dollar amount in effect under subsection (b)(1).”.
(D) Section 223(g)(1) of such Code is amended—
(i) by striking “Each dollar amount in subsections (b)(2) and (c)(2)(A)” and inserting “The dollar amount in subsection (b)(1)”;
(ii) by striking “thereof” and all that follows through “ ‘calendar year 2003’.” and inserting “ ‘calendar year 1997’.”; and
(iii) by striking “under subsections (b)(2) and (c)(2)(A)” and inserting “under subsection (b)(1)”.
(d) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply with respect to months in taxable years beginning after the date of the enactment of this Act.
H.R.79 – Freedom from Mandates Act
Summary: This bill nullifies certain executive orders regarding COVID-19 safety and prohibits the Departments of Labor and Health and Human Services (HHS) from taking specified actions with respect to vaccination against COVID-19.
Specifically, the bill nullifies Executive Order 14042 (relating to ensuring adequate COVID-19 safety protocols for federal contractors) and Executive Order 14043 (requiring COVID-19 vaccination for federal employees).
Labor may not issue any rule requiring employers to mandate vaccination of employees against COVID-19 or requiring testing of employees who are unvaccinated.
HHS may not (1) require a health care provider, as a condition of participation in the Medicare or Medicaid program, to mandate vaccination of employees against COVID-19 or require testing of employees who are unvaccinated; or (2) otherwise penalize such a provider for failure to mandate such vaccination or require such testing.
SEC. 2. Nullification of certain Executive orders.
(a) Safety protocols for Federal Contractors.—Executive Order 14042 (86 Fed. Reg. 50985, relating to ensuring adequate COVID–19 safety protocols for Federal contractors) shall have no force or effect.
(b) COVID–19 vaccine requirement.—Executive Order 14043 (86 Fed. Reg. 50989, relating to requiring COVID–19 vaccination for Federal employees) shall have no force or effect.
SEC. 3. Prohibition of rules mandating vaccination.
The Secretary of Labor may not issue any rule requiring employers to mandate vaccination of employees against COVID–19 or requiring testing of employees who are unvaccinated against COVID–19.
SEC. 4. Prohibition on Medicare and Medicaid COVID–19 vaccination mandates.
Notwithstanding any provision of title XI, XVIII, or XIX of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1301 et seq., 1395 et seq., 1396 et seq.), the Secretary of Health and Human Services may not require a health care provider, as a condition of participation in the Medicare or Medicaid program, to mandate vaccination of employees against COVID–19 or require testing of employees who are unvaccinated against COVID–19, and may not otherwise penalize such a provider for such provider’s failure to so mandate such vaccination or so require such testing.
H.R.86 – NOSHA Act
To abolish the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. In general.
The Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 is repealed. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration is abolished.
H.R.87 – Protecting Our Children from the CDC Act
To amend the Public Health Service Act to prohibit the Secretary of Health and Human Services from placing any vaccine for COVID–19 on the child and adolescent immunization schedule unless the Secretary has posted on the public website of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention all clinical data in the possession of the Department of Health and Human Services relating to the safety and efficacy of such vaccine, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Posting of all clinical data for COVID–19 vaccines before placement on child and adolescent schedule.
Part C of subtitle 2 of title XXI of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 300aa–25 et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 2129. Posting of all clinical data for COVID–19 vaccines before placement on child and adolescent schedule.
“(a) No inclusion of COVID vaccines.—The Secretary, and any official, agency, or office of the Department of Health and Human Services (including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Advisory Committee of Immunization Practices), shall not include any vaccine for COVID–19 on the child and adolescent immunization schedule unless the Secretary has posted on the public website of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention all clinical data in the possession of the Department of Health and Human Services (including the Advisory Committee of Immunization Practices) relating to the safety and efficacy (including any adverse effects) of such vaccine. All such data posted under this subsection shall be deidentified to protect all individually identifiable health information, and information with respect to the agency and sponsor personnel of the data involved.
“(b) Vaccines already on schedule as of enactment.—
“(1) REMOVAL.—Any vaccine for COVID–19 that is included on the child and adolescent immunization schedule as of the date of enactment of this section is hereby deemed to be removed from such schedule.
“(2) ADMINISTRATIVE ACTION.—The Secretary shall take such actions as may be necessary to effectuate the removal of a vaccine from the child and adolescent immunization schedule by operation of paragraph (1).
“(3) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION.—The removal of a vaccine from the child and adolescent immunization schedule by operation of paragraph (1) shall not be construed to affect the authority of the Secretary (or other officials, agencies, or offices) to place such vaccine back on such schedule so long as such placement is in accordance with subsection (a) and other applicable provisions of law.
“(c) Definition.—In this section, the term ‘child and adolescent immunization schedule’ means the child and adolescent immunization schedule of the Advisory Committee of Immunization Practices (or any successor schedule).”.
H.R.88 – Medical Innovation Acceleration Act of 2025
To amend the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act to exempt from regulation as devices non-invasive diagnostic devices, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Exempting non-invasive diagnostic devices from regulation as devices.
Section 201(h) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 321(h)) is amended—
(1) by striking “section 520(o)” and inserting the following: “section 520(o) or any non-invasive diagnostic device”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following: “For purposes of the preceding sentence, the term ‘non-invasive’ means, with respect to a diagnostic device, that the device does not penetrate the skin or any other membrane of the body, is not inserted or implanted into the body, causes no more than ephemeral compression or temperature changes to in situ bodily tissues, and does not subject bodily tissues to ionizing radiation.”.
H.R.89 – Prescription Freedom Act of 2025
To repeal the authority of the Food and Drug Administration to require that drugs be dispensed only upon prescription, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Repeal of FDA authority to require prescriptions.
(a) Repeal.—Effective as of the date that is 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act, subsection (b) of section 503 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 353) is repealed.
(b) References.—Beginning on the effective date described in subsection (a), any reference in a Federal statute, regulation, or guidance—
(1) to prescribing, a prescription, a prescription drug, or a drug subject to section 503(b) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act is deemed to be a reference to prescribing, a prescription, or a prescription drug, respectively, under applicable State law; and
(2) to any requirement or provision of section 503(b) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act is deemed to be a reference to the corresponding requirement or provision, if any, in applicable State law, as determined by the Federal official or officials responsible for administering the respective Federal statute, regulation, or guidance.
(c) Exception.—Notwithstanding subsections (a) and (b), the Secretary of Health and Human Services may continue to exercise the authority vested by subsection (b) of section 503 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 353), as in effect on the day before the effective date described in subsection (a), with respect to any drug that is intended for use in terminating a pregnancy.
H.R.90 – Health Coverage Choice Act
To amend title XXVII of the Public Health Service Act to provide for a definition of short-term limited duration insurance, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Definition of short-term limited duration insurance.
Section 2791(b) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 300gg–91(b)) is amended by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(6) SHORT-TERM LIMITED DURATION INSURANCE.—The term ‘short-term limited duration insurance’ means health insurance coverage provided under a contract with a health insurance issuer that—
“(A) has an expiration date specified in the contract that is less than 12 months after the original effective date of the contract; and
“(B) has a duration of not more than 3 years (taking into account renewals or extensions) after the original effective date of the contract.”.
H.R.114 – Responsible Path to Full Obamacare Repeal Act
To repeal the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010.
SEC. 2. Repeal of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010.
(a) Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.—Effective October 1, 2025, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (Public Law 111–148) is repealed, and the provisions of law amended or repealed by such Act are restored or revived as if such Act had not been enacted.
(b) Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010.—Effective October 1, 2025, the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (Public Law 111–152) is repealed, and the provisions of law amended or repealed by such Act are restored or revived as if such Act had not been enacted.
H.R.119 – To prohibit any entity that receives Federal funds from the COVID relief packages from mandating employees receive a COVID19 vaccine, and for other purposes.
SECTION 1. COVID relief package funding restriction.
(a) Funding restriction.—Any entity that receives Federal funds from a COVID relief package may not mandate that any employee of such entity receives a COVID–19 vaccine.
(b) Return of funds.—Any entity that is in violation of subsection (a) shall return any funds received from the COVID relief package to the Federal Government.
(c) COVID relief package defined.—In this section, the term “COVID relief package” means any of the following:
(1) CARES Act (Public Law 116–136).
(2) Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriations Act, 2020 (Public Law 116–123).
(3) Families First Coronavirus Response Act (Public Law 116–127).
(4) Paycheck Protection Program and Health Care Enhancement Act (Public Law 116–139).
(5) Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 (Public Law 116–260).
(6) American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 (Public Law 117–2).
H.R.120 – No Mandates Act
SEC. 2. Prohibition on agencies issuing vaccine mandates.
(a) In general.—No agency may issue any rule, regulations, or guidance requiring any individual to receive a vaccination for COVID–19.
(b) Agency defined.—In this section, the term “agency” has the meaning given that term in section 551 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 3. Prohibition on requiring proof of COVID–19 vaccination for Federal access.
A vaccination for COVID–19 shall not be required for access to Federal property or Federal services, or for access to congressional grounds or services.
SEC. 4. Federal funding restrictions.
(a) Funding restriction.—No entity that received Federal funds under a COVID–19 relief package or that receives any other Federal funds after the date of the enactment of this Act may require any individual to have received a vaccination for COVID–19 as a condition of such entity providing any service to such individual.
(b) Return of funds.—Any entity that does not comply with subsection (a) shall be required to pay to the Government an amount equal to the sum of all funds such entity received.
(c) COVID–19 relief package defined.—In this section, the term “COVID–19 relief package” means any of the following:
(1) CARES Act (15 U.S.C. 9001 et seq.; Public Law 116–136; 134 Stat. 281).
(2) Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriations Act, 2020 (Public Law 116–123; 134 Stat. 146).
(3) Families First Coronavirus Response Act (Public Law 116–127; 134 Stat. 178).
(4) Paycheck Protection Program and Health Care Enhancement Act (Public Law 116–139; 134 Stat. 620).
(5) Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 (Public Law 116–260; 134 Stat. 1182).
(6) American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 (Public Law 117–2; 135 Stat. 41).
H.R.121 – No Vaccine Passports Act
To prohibit agencies from issuing vaccine passports, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Prohibition on agencies issuing vaccine passports.
(a) In general.—An agency may not issue a vaccine passport, vaccine pass, or other standardized documentation for the purpose of certifying the COVID–19 vaccination status of a citizen of the United States to a third party, or otherwise publish or share any COVID–19 vaccination record of a citizen of the United States, or similar health information.
(b) Agency defined.—In this section, the term “agency” has the meaning given that term in section 551 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 3. Prohibition on requiring proof of COVID–19 vaccination for Federal access.
Proof of COVID–19 vaccination shall not be deemed a requirement for access to Federal property or Federal services, or for access to congressional grounds or services.
H.R.127 – Protection from Obamacare Mandates and Congressional Equity Act
To amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to provide an exemption to the individual mandate to maintain health coverage for individuals residing in counties with fewer than 2 health insurance issuers offering plans on an Exchange; to require Members of Congress and congressional staff to abide by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act with respect to health insurance coverage; and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Modifications to exemption from requirement to maintain health coverage.
(a) Exemption for individuals in areas with fewer than 2 issuers offering plans on an exchange.—Section 5000A(e) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(6) INDIVIDUALS IN AREAS WITH FEWER THAN 2 ISSUERS OFFERING PLANS ON AN EXCHANGE.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Any applicable individual for any period during a calendar year if there are fewer than 2 health insurance issuers offering qualified health plans on an Exchange for such period in the county in which the applicable individual resides.
“(B) AGGREGATION RULES.—For purposes of subparagraph (A), all health insurance issuers treated as a single employer under subsection (a) or (b) of section 52, or subsection (m) or (o) of section 414, shall be treated as a single health insurance issuer.”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply to months beginning after the date of the enactment of this Act.
SEC. 3. Health insurance coverage for certain congressional staff and members of the executive branch.
Section 1312(d)(3)(D) of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (42 U.S.C. 18032(d)(3)(D)) is amended—
(1) by striking the subparagraph heading and inserting the following:
“(D) MEMBERS OF CONGRESS, CONGRESSIONAL STAFF, AND POLITICAL APPOINTEES IN THE EXCHANGE.—”;
(2) in clause (i), in the matter preceding subclause (I)—
(A) by striking “and congressional staff with” and inserting “, congressional staff, the President, the Vice President, and political appointees with”; and
(B) by striking “or congressional staff shall” and inserting “, congressional staff, the President, the Vice President, or a political appointee shall”;
(3) in clause (ii)—
(A) in subclause (II), by inserting after “Congress,” the following: “of a committee of Congress, or of a leadership office of Congress,”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following:
“(III) POLITICAL APPOINTEE.—The term ‘political appointee’ means any individual who—
“(aa) is employed in a position described under sections 5312 through 5316 of title 5, United States Code (relating to the Executive Schedule);
“(bb) is a limited term appointee, limited emergency appointee, or noncareer appointee in the Senior Executive Service, as defined under paragraphs (5), (6), and (7), respectively, of section 3132(a) of title 5, United States Code; or
“(cc) is employed in a position in the executive branch of the Government of a confidential or policy-determining character under schedule C of subpart C of part 213 of title 5 of the Code of Federal Regulations.”; and
(4) by adding at the end the following:
“(iii) GOVERNMENT CONTRIBUTION.—No Government contribution under section 8906 of title 5, United States Code, shall be provided on behalf of an individual who is a Member of Congress, a congressional staff member, the President, the Vice President, or a political appointee for coverage under this paragraph.
“(iv) LIMITATION ON AMOUNT OF TAX CREDIT OR COST SHARING.—An individual enrolling in health insurance coverage pursuant to this paragraph shall not be eligible to receive a tax credit under section 36B of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 or reduced cost sharing under section 1402 of this Act in an amount that exceeds the total amount for which a similarly situated individual (who is not so enrolled) would be entitled to receive under such sections.
“(v) LIMITATION ON DISCRETION FOR DESIGNATION OF STAFF.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, a Member of Congress shall not have discretion in determinations with respect to which employees employed by the office of such Member are eligible to enroll for coverage through an Exchange.
“(vi) CLARIFICATION.—The terms ‘small employer’ (as defined under section 1304(b)(2)) and ‘qualified employers’ (as defined under subsection (f)) do not include the Congress, with respect to enrollments in an Exchange and a SHOP Exchange.”.
H.R.238 – Healthy Technology Act of 2025
Summary: This bill establishes that artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning technology may be eligible to prescribe drugs.
Currently, certain drugs may be dispensed only upon a prescription provided by a practitioner licensed by law to administer the drug. Under this bill, an AI or machine learning technology may qualify as such a prescribing practitioner if the technology is (1) authorized by state law to prescribe the drug involved; and (2) approved, cleared, or authorized under certain federal provisions pertaining to medical devices and products.
To amend the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act to clarify that artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies can qualify as a practitioner eligible to prescribe drugs if authorized by the State involved and approved, cleared, or authorized by the Food and Drug Administration, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Prescription of drugs by artificial intelligence or machine learning technologies.
Section 503(b) of Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 353(b)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(6) In this subsection, the term ‘practitioner licensed by law to administer such drug’ includes artificial intelligence and machine learning technology that are—
“(A) authorized pursuant to a statute of the State involved to prescribe the drug involved; and
“(B) approved, cleared, or authorized under section 510(k), 513, 515, or 564.”.
H.R.247 – Health Care Affordability Act of 2025
To amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to expand eligibility for the refundable credit for coverage under a qualified health plan.
SEC. 2. Increase in eligibility for credit.
(a) In general.—Subparagraph (A) of section 36B(c)(1) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking “but does not exceed 400 percent” .
(b) Applicable percentages.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Subparagraph (A) of section 36B(b)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to read as follows:
“(A) APPLICABLE PERCENTAGE.—The applicable percentage for any taxable year shall be the percentage such that the applicable percentage for any taxpayer whose household income is within an income tier specified in the following table shall increase, on a sliding scale in a linear manner, from the initial premium percentage to the final premium percentage specified in such table for such income tier:
| “In the case of household income (expressed as a percent of poverty line) within the following income tier: | The initial premium percentage is— | The final premium percentage is— |
| Up to 150 percent | 0 | 0 |
| 150 percent up to 200 percent | 0 | 2.0 |
| 200 percent up to 250 percent | 2.0 | 4.0 |
| 250 percent up to 300 percent | 4.0 | 6.0 |
| 300 percent up to 400 percent | 6.0 | 8.5 |
| 400 percent and higher | 8.5 | 8.5.”. |
(2) CONFORMING AMENDMENTS RELATING TO AFFORDABILITY OF COVERAGE.—
(A) Paragraph (1) of section 36B(c) of such Code is amended by striking subparagraph (E).
(B) Subparagraph (C) of section 36B(c)(2) of such Code is amended by striking clause (iv).
(C) Paragraph (4) of section 36B(c) of such Code is amended by striking subparagraph (F).
(c) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply to taxable years beginning after December 31, 2025.
H.R.307 – ARC Act of 2025
Summary: This bill provides for coverage of peripheral artery disease screening tests without cost-sharing under Medicare and Medicaid for certain at-risk individuals. It also requires the development of certain educational programs, a payment model, and Medicare quality measures to reduce amputations relating to such disease.
To amend titles XVIII and XIX of the Social Security Act to provide for coverage of peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries under the Medicare and Medicaid programs without the imposition of cost-sharing requirements, and for other purposes.
SECTION 1. Short title; findings.
(a) Short title.—This Act may be cited as the “Amputation Reduction and Compassion Act of 2025” or the “ARC Act of 2025”.
(b) Findings.—Congress makes the following findings:
(1) Atherosclerosis occurs when blood flow is reduced because arteries become narrowed or blocked with fatty deposits.
(2) Atherosclerosis is responsible for more deaths in the United States than any other condition, and heart attacks, resulting from clogged coronary arteries, are the leading cause of death in America.
(3) Atherosclerosis also occurs in the legs and is known as peripheral artery disease (in this subsection referred to as “PAD”) and having PAD significantly increases the risk for heart attack, stroke, amputation, and death.
(4) While most Americans are aware of atherosclerosis in the heart, many Americans have never heard of PAD and Americans with PAD are often unaware of the serious risks of the disease.
(5) An estimated 21 million Americans have PAD, and about 200,000 of them—disproportionately minorities—suffer avoidable amputations every year as a result of such disease.
(6) According to the Dartmouth Atlas, amputation risks for African Americans living with diabetes are as much as four times higher than the national average.
(7) Data analyses have similarly found that Native Americans are more than twice as likely to be subjected to amputation and Hispanics are up to 75 percent more likely to have an amputation.
(8) Fifty-two percent of patients with an above-the-knee amputation and 33 percent of patients with a below-the-knee amputation will die within two years of their amputation.
(9) Screening and arterial testing for PAD is cost-effective and should be part of routine medical care.
(10) Once PAD is detected, amputations and deaths can be reduced through the use of national, evidence-based PAD care guidelines.
(11) Americans with a PAD diagnosis are associated with a 67-percent increase in the risk of cardiac death compared to people without a PAD diagnosis. Consequently, screening for PAD enables health care professionals to identify cardiac risk factors earlier and take proactive measures to reduce the risk of cardiac death.
SEC. 2. Peripheral artery disease education program.
Part P of title III of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 280g et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following new section:
“SEC. 399V–8. Peripheral artery disease education program.
“(a) Establishment.—The Secretary, acting through the Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in collaboration with the Administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, the Administrator of the Health Resources and Services Administration, leading clinical and patient advocacy organizations, and other interested stakeholders shall establish and coordinate a peripheral artery disease education program to support, develop, and implement educational initiatives and outreach strategies that inform health care professionals and the public about the existence of peripheral artery disease and methods to reduce amputations related to such disease, particularly with respect to at-risk populations.
“(b) Best practices.—The Secretary shall, as appropriate, identify and disseminate to health care professionals best practices with respect to peripheral artery disease.
“(c) Authorization of appropriations.—There is authorized to be appropriated to carry out this section $6,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2026 through 2030.”.
SEC. 3. Medicare coverage of peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries without imposition of cost-sharing requirements.
(a) In general.—Section 1861 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x) is amended—
(1) in subsection (s)(2)—
(A) in subparagraph (JJ), by striking the semicolon at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(KK) peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in subsection (nnn)).”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(nnn) Peripheral artery disease screening test; At-Risk beneficiary.— (1) The term ‘peripheral artery disease screening test’ means—
“(A) noninvasive physiologic studies of extremity arteries (commonly referred to as ankle-brachial index testing);
“(B) arterial duplex scans of lower extremity arteries vascular; and
“(C) such other items and services as the Secretary determines, in consultation with relevant stakeholders, to be appropriate for screening for peripheral artery disease for at-risk beneficiaries.
“(2) The term ‘at-risk beneficiary’ means an individual entitled to, or enrolled for, benefits under part A and enrolled for benefits under part B—
“(A) who is 65 years of age or older;
“(B) who is at least 50 years of age but not older than 64 years of age with risk factors for atherosclerosis (such as diabetes mellitus, a history of smoking, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension) or a family history of peripheral artery disease;
“(C) who is younger than 50 years of age with diabetes mellitus and one additional risk factor for atherosclerosis; or
“(D) with a known atherosclerotic disease in another vascular bed such as coronary, carotid, subclavian, renal, or mesenteric artery stenosis, or abdominal aortic aneurysm.
“(3) The Secretary shall, in consultation with appropriate organizations, establish standards regarding the frequency for peripheral artery disease screening tests described in subsection (s)(2)(KK) for purposes of coverage under this title.”.
(b) Inclusion of peripheral artery disease screening tests in initial preventive physical examination.—Section 1861(ww)(2) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(ww)(2)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (N), by moving the margins of such subparagraph 2 ems to the left;
(2) by redesignating subparagraph (O) as subparagraph (P); and
(3) by inserting after subparagraph (N) the following new subparagraph:
“(O) Peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at risk-beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in subsection (nnn)).”.
(c) Payment.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 1833(a) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395l(a)) is amended—
(A) in paragraph (1)—
(i) in subparagraph (N), by inserting “and other than peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in section 1861(nnn))” after “other than personalized prevention plan services (as defined in section 1861(hhh)(1))”;
(ii) by striking “and” before “(HH)”; and
(iii) by adding at the end the following: “and (II) with respect to peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in section 1861(nnn)), the amount paid shall be 100 percent of the lesser of the actual charge for the services or the amount determined under the payment basis determined under section 1848;”; and
(B) in paragraph (2)—
(i) in subparagraph (G), by striking “and” at the end;
(ii) in subparagraph (H), by striking the semicolon at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(iii) by inserting after subparagraph (H) the following new subparagraph:
“(I) with respect to peripheral artery disease screening tests (as defined in paragraph (1) of section 1861(nnn)) furnished by an outpatient department of a hospital to at-risk beneficiaries (as defined in paragraph (2) of such section), the amount determined under paragraph (1)(II);”.
(2) NO DEDUCTIBLE.—Section 1833(b) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395l(b)) is amended, in the first sentence—
(A) by striking “, and” before “(13)”; and
(B) by inserting before the period at the end the following: “, and (14) such deductible shall not apply with respect to peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in section 1861(nnn))”.
(3) EXCLUSION FROM PROSPECTIVE PAYMENT SYSTEM FOR HOSPITAL OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENT SERVICES.—Section 1833(t)(1)(B)(iv) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395l(t)(1)(B)(iv)) is amended—
(A) by striking “, or personalized” and inserting “, personalized”; and
(B) by inserting “, or peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in section 1861(nnn))” after “personalized prevention plan services (as defined in section 1861(hhh)(1))”.
(4) CONFORMING AMENDMENT.—Section 1848(j)(3) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–4(j)(3)) is amended by striking “(2)(FF) (including administration of the health risk assessment),” and inserting “(2)(FF) (including administration of the health risk assessment), (2)(KK),”.
(d) Exclusion from coverage and Medicare as secondary payer for tests performed more frequently than allowed.—Section 1862(a)(1) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395y(a)(1)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (O), by striking “and” at the end;
(2) in subparagraph (P), by striking the semicolon at the end and inserting “, and”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(Q) in the case of peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in section 1861(nnn)), which are performed more frequently than is covered under such section;”.
(e) Authority To modify or eliminate coverage of certain preventive services.—Section 1834(n) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395m(n)) is amended—
(1) by redesignating subparagraphs (A) and (B) of paragraph (1) as clauses (i) and (ii), respectively, and moving the margins of such clauses, as so redesignated, 2 ems to the right;
(2) by redesignating paragraphs (1) and (2) as subparagraphs (A) and (B), respectively, and moving the margins of such subparagraphs, as so redesignated, 2 ems to the right;
(3) by striking “Certain Preventive Services” and all that follows through “any other provision of this title” and inserting: “Certain Preventive Services.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Notwithstanding any other provision of this title”; and
(4) by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(2) INAPPLICABILITY.—The Secretarial authority described in paragraph (1) shall not apply with respect to preventive services described in section 1861(ww)(2)(O).”.
(f) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply with respect to items and services furnished on or after January 1, 2026.
SEC. 4. Medicaid coverage of peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries without imposition of cost-sharing requirements.
(a) In general.—Section 1905 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396d) is amended—
(1) in subsection (a)—
(A) in paragraph (31), by striking “and” at the end;
(B) by redesignating paragraph (32) as paragraph (33); and
(C) by inserting after paragraph (31) the following new paragraph:
“(32) peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in subsection (kk)); and”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(kk) Peripheral artery disease screening test; At-Risk beneficiary.—
“(1) PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASE SCREENING TEST.—The term ‘peripheral artery disease screening test’ means—
“(A) noninvasive physiologic studies of extremity arteries (commonly referred to as ankle-brachial index testing);
“(B) arterial duplex scans of lower extremity arteries vascular; and
“(C) such other items and services as the Secretary determines, in consultation with relevant stakeholders, to be appropriate for screening for peripheral artery disease for at-risk beneficiaries.
“(2) AT-RISK BENEFICIARY.—The term ‘at-risk beneficiary’ means an individual enrolled under a State plan (or a waiver of such plan)—
“(A) who is 65 years of age or older;
“(B) who is at least 50 years of age but not older than 64 years of age with risk factors for atherosclerosis (such as diabetes mellitus, a history of smoking, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension) or a family history of peripheral artery disease;
“(C) who is younger than 50 years of age with diabetes mellitus and one additional risk factor for atherosclerosis; or
“(D) with a known atherosclerotic disease in another vascular bed such as coronary, carotid, subclavian, renal, or mesenteric artery stenosis, or abdominal aortic aneurysm.
“(3) FREQUENCY.—The Secretary shall, in consultation with appropriate organizations, establish standards regarding the frequency for peripheral artery disease screening tests described in subsection (a)(31) for purposes of coverage under a State plan under this title.”.
(b) No cost sharing.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Subsections (a)(2) and (b)(2) of section 1916 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396o) are each amended—
(A) in subparagraph (I), by striking “or” at the end;
(B) in subparagraph (J), by striking “; and” and inserting “, or”; and
(C) by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(K) peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in section 1905(kk)); and”.
(2) APPLICATION TO ALTERNATIVE COST SHARING.—Section 1916A(b)(3)(B) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396o–1(b)(3)(B)) is amended by adding at the end the following new clause:
“(xv) Peripheral artery disease screening tests furnished to at-risk beneficiaries (as such terms are defined in section 1905(kk)).”.
(c) Conforming amendments.—
(1) Section 1902(nn)(3) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396a(nn)(3)) is amended by striking “following paragraph (31)” and inserting “following paragraph (32)”.
(2) Section 1905(a) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396d(a)) is amended by striking “following paragraph (31)” and inserting “following paragraph (32)”.
SEC. 5. Development and implementation of quality measures.
(a) Development.—The Secretary of Health and Human Services (referred to in this section as the “Secretary”) shall, in consultation with relevant stakeholders, develop quality measures for nontraumatic, lower-limb, major amputation that utilize appropriate diagnostic screening (including peripheral artery disease screening) in order to encourage alternative treatments (including revascularization) in lieu of such an amputation.
(b) Implementation.—Not later than 18 months after the date of enactment of this Act, the Secretary shall complete appropriate testing and validation of the measures developed under subsection (a) and shall incorporate such measures in quality reporting programs for appropriate providers of services and suppliers under the Medicare program under title XVIII of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395 et seq.), including for purposes of—
(1) the merit-based incentive payment system under section 1848(q) of such Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–4(q));
(2) incentive payments for participation in eligible alternative payment models under section 1833(z) of such Act (42 U.S.C. 1395l(z));
(3) the shared savings program under section 1899 of such Act (42 U.S.C. 1395jjj);
(4) models under section 1115A of such Act (42 U.S.C. 1315a); and
(5) such other payment systems or models as the Secretary may specify.
SEC. 6. Amputation prevention pilot program.
(a) In general.—Section 1115A(b)(2)(B) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1315a(b)(2)(B)) is amended by adding at the end the following new clause:
“(xxviii) Promoting voluntary, nontraumatic lower-limb major amputation prevention programs at hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, and office-based centers that will increase access to amputation prevention services, reduce amputation rates, and reduce costs to such hospitals, surgical centers, and office-based centers, through—
“(I) patient risk modification and management;
“(II) early screening and detection and surveillance;
“(III) testing and treatment for peripheral artery disease; and
“(IV) improved care coordination for individuals at high risk for amputation.”.
(b) Testing of model.—Not later than 18 months after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Deputy Administrator and Director of the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation shall test the model described under subsection (a).
H.R.317 – Healthcare Freedom Act of 2025
To amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to create health freedom accounts available to all individuals.
SEC. 2. Health freedom accounts.
(a) In general.—Section 223 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking “health savings account” and “health savings accounts” each place such terms appear and inserting “health freedom account” and “health freedom accounts”, respectively.
(b) All individuals allowed deductions for contributions.—Section 223(a) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking “who is an eligible individual for any month during the taxable year”.
(c) No limitation on purchasing health coverage from health freedom accounts.—Section 223(d)(2) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking subparagraphs (B) and (C) and the last sentence of subparagraph (A) and by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(B) ADDITIONAL EXPENSES.—The term ‘qualified medical expenses’ includes costs associated with direct primary care, health care sharing ministries, and medical cost sharing organizations.”.
(d) Transfers allowed to other health freedom accounts.—Section 223(f)(5) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to read as follows:
“(5) ROLLOVER CONTRIBUTION.—An amount paid or distributed from a health freedom account is a rollover contribution to the extent the amount received is paid into any other health freedom account not later than the 60th day after the date of such payment or distribution.”.
(e) Increase in contribution limits.—Section 223(b)(1) of such Code is amended by striking “the sum of the monthly” and all that follows through “eligible individual” and inserting “$12,000 (twice such amount in the case of a joint return)”.
(f) Conforming amendments.—
(1) Section 223(b) of such Code is amended by striking paragraphs (2), (5), (7), and (8) and by redesignating paragraphs (3), (4), and (6) as paragraphs (2), (3), and (4), respectively.
(2) Section 223(b)(2) of such Code (as redesignated by paragraph (2)) is amended to read as follows:
“(2) ADDITIONAL CONTRIBUTIONS FOR INDIVIDUALS 55 OR OLDER.—In the case of an individual who has attained age 55 before the close of the taxable year, the limitation under paragraph (1) shall be increased by $5,000.”.
(3) Section 223(b)(3) of such Code (as redesignated by subparagraph (A)) is amended by striking the last sentence.
(4) Section 223 of such Code is amended by striking subsection (c).
(5) Section 223(d)(1)(A) of such Code is amended by striking “will be accepted” and all that follows through the period at the end and inserting “will be accepted unless it is in cash.”.
(6) Section 223(f) of such Code is amended by striking paragraphs (7) and (8).
(7) Section 223(g)(1) of such Code is amended—
(A) by striking “Each dollar amount in subsections (b)(2) and (c)(2)(A)” and inserting “The dollar amount in subsection (b)(1)”;
(B) by striking “thereof” and all that follows in subparagraph (B) through “ ‘calendar year 2003’.” and inserting “ ‘calendar year 1997’.”; and
(C) by striking “under subsections (b)(2) and (c)(2)(A)” and inserting “under subsection (b)(1)”.
(8) The table of sections for part VII of subchapter B of chapter 1 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended in the item relating to section 223 by striking “savings” and inserting “freedom”.
(g) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply with respect to months in taxable years beginning after the date of the enactment of this Act.
SEC. 3. Exclusion for employer contributions to health freedom accounts.
(a) Employer exclusion.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by inserting after section 106 the following new section:
“SEC. 106A. Contributions by employers to health freedom accounts.
“In the case of any employee hired by an employer on or after the date that is 5 years after the date of the enactment of this section, gross income of such employee does not include amounts contributed by such employer to a health freedom account of such employee.”.
(2) EXCLUSION FOR CONTRIBUTIONS BY EMPLOYER TO ACCIDENT AND HEALTH PLANS.—Section 106 of such Code is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(h) Termination.—In the case of any employee hired by an employer on or after the date that is 5 years after the date of the enactment of this section, this section shall not apply to coverage provided by such employer with respect to such employee.”.
(3) CONFORMING AMENDMENT.—The table of sections for part III of subchapter B of chapter 1 of such Code is amended by striking the item relating to section 106 and inserting the following:
“Sec. 106A. Contributions by employers to health freedom accounts.”.
(4) EFFECTIVE DATE.—The amendments made by this subsection shall apply with respect to employees hired on or after the date that is 5 years after the date of the enactment of this Act.
(b) Transition rule.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 106(d)(1) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to read as follows:
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Amounts contributed by an employee’s employer to any health freedom account (as defined in section 223(d)) of such employee shall be treated as employer-provided coverage for medical expenses under an accident or health plan.”.
(2) IN GENERAL.—The amendment made by this subsection shall apply with respect to taxable years beginning after the date of the enactment of this Act.
H.R.479 – Healthy SNAP Act of 2025
Summary: This bill amends the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) to redefine the foods eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits.
Under the bill, SNAP benefits may not be used for soft drinks, candy, ice cream, or prepared desserts, such as cakes, pies, cookies, or similar products.
Further, the Department of Agriculture (USDA) must designate by regulation foods and food products to include in the SNAP definition of the term food. USDA must consider food and products that (1) based on nutrition research, contain nutrients lacking in the diets of people in the United States; and (2) promote the health of the population served by SNAP, based on relevant nutrition science, public health concerns, and cultural eating patterns. USDA must also, to the maximum extent practicable, ensure that the fat, sugar, and salt content of the food and food products are appropriate. At least every five years, USDA must review and amend the list.
In addition, prepared meals purchased with SNAP benefits must have nutritional values consistent with standards developed by USDA for the list of food and food products.
A state agency may substitute different foods for food USDA designated under this bill, with USDA approval, so long as the foods are nutritionally equivalent; this is permitted to allow for different cultural eating patterns.
To amend the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 to require the Secretary to designate food and food products to be made available under the supplemental nutrition assistance program, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Food under supplemental nutrition assistance program.
(a) Definition of food.—Section 3(k)(1) of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 2012(k)(1)) is amended—
(1) by striking “except alcoholic beverages, tobacco” and inserting the following “designated by the Secretary under section 4(d), except any alcoholic beverages, tobacco, soft drinks, candy, ice cream, prepared desserts such as cakes, pies, cookies, or similar products”; and
(2) by striking “clauses” and inserting “paragraphs”.
(b) Designated food.—Section 4 of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 2013) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(d) Designated food.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this subsection, the Secretary shall designate by regulation the foods and food products that shall be included in the definition of the term ‘food’ under section 3(k)(1).
“(2) CONSIDERATIONS.—In carrying out paragraph (1), the Secretary shall—
“(A) take into consideration food and food products that—
“(i) based on nutrition research, contain nutrients lacking in the diets of people in the United States; and
“(ii) promote the health of the population served by the supplemental nutrition assistance program, based on relevant nutrition science, public health concerns, and cultural eating patterns; and
“(B) to the maximum extent practicable, ensure that the fat, sugar, and salt content of the food and food products is appropriate.
“(3) REVIEW OF AVAILABLE FOODS.—As frequently as determined by the Secretary to be necessary to reflect the most recent scientific knowledge, but not less frequently than once every 5 years, the Secretary shall—
“(A) conduct a scientific review of the food and food products designated under paragraph (1); and
“(B) amend those foods and food products, as necessary, to reflect nutrition science, public health concerns, and cultural eating patterns.
“(4) PREPARED MEALS.—Prepared meals described in section 3(k) shall have nutritional values consistent with regulations developed by the Secretary under this subsection.
“(5) CULTURAL CUISINES.—To allow for different cultural eating patterns, State agencies may, with the approval of the Secretary, substitute different food for food designated under paragraph (1) subject to the condition that the different food is nutritionally equivalent to the substituted food.”.
H.R.530 – ACES Act
To provide for a study by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine on the prevalence and mortality of cancer among individuals who served as active duty aircrew in the Armed Forces, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. National Academies study on prevalence and mortality of cancer among individuals who served as active duty aircrew in the Armed Forces.
(a) In general.—The Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall enter into an agreement with the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (in this section referred to as the “National Academies”), under which the National Academies shall conduct a study on the prevalence and mortality of cancers among covered individuals.
(b) Study.—The study required under subsection (a) shall—
(1) identify exposures associated with military occupations of covered individuals, including relating to chemicals, compounds, agents, and other phenomena;
(2) review the literature to determine associations between exposures referred to in paragraph (1) and the incidence or prevalence of overall cancer morbidity, overall cancer mortality, and increased incidence or prevalence of—
(A) brain cancer;
(B) colon and rectal cancers;
(C) kidney cancer;
(D) lung cancer;
(E) melanoma skin cancer;
(F) non-Hodgkin lymphoma;
(G) pancreatic cancer;
(H) prostate cancer;
(I) testiscular cancer;
(J) thyroid cancer;
(K) urinary bladder cancer; and
(L) other cancers as determined appropriate by the Secretary of Veterans Affairs, in consultation with the National Academies; and
(3) determine, to the extent possible, the prevalence of and mortality from the cancers specified in paragraph (2) among covered individuals by using available sources of data, which may include—
(A) health care and other administrative databases of the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Department of Defense, and the individual Services, respectively;
(B) the national death index maintained by the National Center for Health Statistics of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; and
(C) the study conducted under section 750 of the William M. (Mac) Thornberry National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2021 (Public Law 116–283; 134 Stat. 3716).
(c) Report.—At the conclusion of the study required under subsection (a), the National Academies shall submit to the Secretary and to the Committees on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives and the Senate a report containing the results of the study described in subsection (b).
(d) Covered individual defined.—In this section, the term “covered individual” means an individual who served on active duty in the Army, Navy, Air Force, or Marine Corps as an aircrew member of a fixed-wing aircraft, including as a pilot, navigator, weapons systems operator, aircraft system operator, or any other crew member who regularly flew in a fixed-wing aircraft.
H.R.539 – Chiropractic Medicare Coverage Modernization Act of 2025
To amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to provide Medicare coverage for all physicians’ services furnished by doctors of chiropractic within the scope of their license, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Findings; Statement of purpose.
(a) Findings.—Congress finds the following:
(1) In 1972, coverage was established under the Medicare program for beneficiaries to receive chiropractic care.
(2) Unfortunately, the antiquated statute restricts beneficiaries to one service in a chiropractic clinic and Medicare chiropractic coverage has not kept up with private sector coverage and other Federal health delivery systems.
(3) Today, due to positive evidence-based outcomes and cost effectiveness of the services provided by doctors of chiropractic, private coverage for chiropractic services has evolved and State licensure for chiropractors has advanced to meet patient needs and health outcomes.
(4) This Act would bring Medicare chiropractic coverage more in line with that provided with the Department of Veterans Affairs, Department of Defense, the Federal Employee Health Benefits Program, and private health insurance coverage.
(b) Purpose.—It is the purpose of this Act to expand recognition and coverage of a doctor of chiropractic as a “physician” under the Medicare program in connection with the performance of any function or action, including current service of “manual manipulation of the spine to correct a subluxation”, as is legally authorized by the State in which such doctor performs such function or action.
SEC. 3. Providing Medicare coverage for all physicians’ services furnished by doctors of chiropractic within the scope of their license.
(a) In general.—Section 1861(r)(5) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(r)(5)) is amended by striking “a chiropractor who is licensed as such by the State (or in a State which does not license chiropractors as such, is legally authorized to perform the services of a chiropractor in the jurisdiction in which he performs such services), and who meets uniform minimum standards promulgated by the Secretary, but only for the purpose of sections 1861(s)(1) and 1861(s)(2)(A) and only with respect to treatment by means of manual manipulation of the spine (to correct a subluxation) which he is legally authorized to perform by the State or jurisdiction in which such treatment is provided” and inserting “a doctor of chiropractic who is licensed as a doctor of chiropractic or a chiropractor by the State in which the function or action is performed and whose license provides legal authorization to perform such function or action in such State or in the jurisdiction in which the function or action is performed”.
(b) Certain coverage limits.—Section 1833 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395l) is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(ee) Limitation on payment of services provided by certain doctors of chiropractic.—Notwithstanding any other provision of this part, in the case of services of a doctor of chiropractic described in section 1861(r)(5), payment may only be made under this part for such services if—
“(1) such services are furnished by a doctor of chiropractic who is verified once, by a process designed by the Secretary, as attending an educational documentation webinar, or other similar electronic product, designed by the Secretary or an updated modified version of such webinar, as designed by the Secretary; or
“(2) such services are treatment by means of manual manipulation of the spine to correct a subluxation.”.
H.R.609 – Assuring Medicare’s Promise Act of 2025
To amend the Social Security Act and the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to include net investment income tax imposed in the Federal Hospital Insurance Trust Fund and to modify the net investment income tax.
SEC. 2. Inclusion of net investment income tax in Hospital Insurance Trust Fund.
(a) In general.—Section 1817(a) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395i(a)) is amended—
(1) by striking “and” at the end of paragraph (1);
(2) by striking the period at the end of paragraph (2) and inserting “; and”; and
(3) by inserting after paragraph (2) the following new paragraph:
“(3) the taxes imposed by section 1411 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 reported to the Secretary of the Treasury or the Secretary’s delegate on tax returns under subtitle F of such Code.”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply with respect to taxes imposed for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2025.
SEC. 3. Application of net investment income tax to trade or business income of certain high income individuals.
(a) In general.—Section 1411 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(f) Application to certain high income individuals.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—In the case of any individual whose modified adjusted gross income for the taxable year exceeds the high income threshold amount, subsection (a)(1) shall be applied by substituting ‘the greater of specified net income or net investment income’ for ‘net investment income’ in subparagraph (A) thereof.
“(2) PHASE-IN OF INCREASE.—The increase in the tax imposed under subsection (a)(1) by reason of the application of paragraph (1) of this subsection shall not exceed the amount which bears the same ratio to the amount of such increase (determined without regard to this paragraph) as—
“(A) the excess described in paragraph (1), bears to
“(B) $100,000 (½ such amount in the case of a married taxpayer (as defined in section 7703) filing a separate return).
“(3) HIGH INCOME THRESHOLD AMOUNT.—For purposes of this subsection, the term ‘high income threshold amount’ means—
“(A) except as provided in subparagraph (B) or (C), $400,000,
“(B) in the case of a taxpayer making a joint return under section 6013 or a surviving spouse (as defined in section 2(a)), $500,000, and
“(C) in the case of a married taxpayer (as defined in section 7703) filing a separate return, ½ of the dollar amount determined under subparagraph (B).
“(4) SPECIFIED NET INCOME.—For purposes of this section, the term ‘specified net income’ means net investment income determined—
“(A) without regard to the phrase ‘other than such income which is derived in the ordinary course of a trade or business not described in paragraph (2),’ in subsection (c)(1)(A)(i),
“(B) without regard to the phrase ‘described in paragraph (2)’ in subsection (c)(1)(A)(ii),
“(C) without regard to the phrase ‘other than property held in a trade or business not described in paragraph (2)’ in subsection (c)(1)(A)(iii),
“(D) without regard to paragraphs (2), (3), and (4) of subsection (c), and
“(E) by treating paragraphs (5) and (6) of section 469(c) (determined without regard to the phrase ‘To the extent provided in regulations,’ in such paragraph (6)) as applying for purposes of subsection (c) of this section.”.
(b) Application to trusts and estates.—Section 1411(a)(2)(A) of such Code is amended by striking “undistributed net investment income” and inserting “the greater of undistributed specified net income or undistributed net investment income”.
(c) Clarifications with respect to determination of net investment income.—
(1) CERTAIN EXCEPTIONS.—Section 1411(c)(6) of such Code is amended to read as follows:
“(6) SPECIAL RULES.—Net investment income shall not include—
“(A) any item taken into account in determining self-employment income for such taxable year on which a tax is imposed by section 1401(b),
“(B) wages received with respect to employment on which a tax is imposed under section 3101(b) or 3201(a) (including amounts taken into account under section 3121(v)(2)), and
“(C) wages received from the performance of services earned outside the United States for a foreign employer.”.
(2) NET OPERATING LOSSES NOT TAKEN INTO ACCOUNT.—Section 1411(c)(1)(B) of such Code is amended by inserting “(other than section 172)” after “this subtitle”.
(3) INCLUSION OF CERTAIN FOREIGN INCOME.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—Section 1411(c)(1)(A) of such Code is amended by striking “and” at the end of clause (ii), by striking “over” at the end of clause (iii) and inserting “and”, and by adding at the end the following new clause:
“(iv) any amount includible in gross income under section 951, 951A, 1293, or 1296, over”.
(B) PROPER TREATMENT OF CERTAIN PREVIOUSLY TAXED INCOME.—Section 1411(c) of such Code is amended by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(7) CERTAIN PREVIOUSLY TAXED INCOME.—The Secretary shall issue regulations or other guidance providing for the treatment of—
“(A) distributions of amounts previously included in gross income for purposes of chapter 1 but not previously subject to tax under this section, and
“(B) distributions described in section 962(d).”.
(d) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply to taxable years beginning after December 31, 2025.
(e) Transition rule.—The regulations or other guidance issued by the Secretary under section 1411(c)(7) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (as added by this section) shall include provisions which provide for the proper coordination and application of clauses (i) and (iv) of section 1411(c)(1)(A) with respect to—
(1) taxable years beginning on or before December 31, 2025, and
(2) taxable years beginning after such date.
H.R.610 – Close the Medigap Act of 2025
To amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to provide for certain reforms with respect to medicare supplemental health insurance policies.
SEC. 2. Guaranteed issue.
(a) In general.—Section 1882(s) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395ss(s)) is amended to read as follows:
“(s) (1) Subject to paragraph (2), the issuer of a medicare supplemental policy may not, in the case of an individual entitled to benefits under part A and enrolled under part B—
“(A) deny or condition the issuance or effectiveness of a medicare supplemental policy, or discriminate in the pricing of the policy, because of health status, claims experience, receipt of health care, or medical condition;
“(B) exclude benefits based on a preexisting condition;
“(C) provide any time period applicable to preexisting conditions, waiting periods, elimination periods, and probationary periods for any benefit;
“(D) deny or condition the issuance or effectiveness of the policy (including the imposition of any exclusion of benefits under the policy based on a preexisting condition) or discriminate in the pricing of the policy (including the adjustment of premium rates) of an individual on the basis of the genetic information with respect to such individual;
“(E) deny or condition the issuance or effectiveness of a medicare supplemental policy that is offered and is available for issuance to new enrollees by such issuer; or
“(F) establish any period limiting enrollment under a medicare supplemental policy to such period for any individual.
“(2) Paragraph (1) shall not apply to an individual entitled to benefits under part A solely by reason of section 226A.
“(3) Nothing in this subsection or in subparagraph (A) or (B) of subsection (x)(2) shall be construed to limit the ability of an issuer of a medicare supplemental policy from, to the extent otherwise permitted under this title—
“(A) denying or conditioning the issuance or effectiveness of the policy or increasing the premium for an employer based on the manifestation of a disease or disorder of an individual who is covered under the policy; or
“(B) increasing the premium for any policy issued to an individual based on the manifestation of a disease or disorder of an individual who is covered under the policy (in such case, the manifestation of a disease or disorder in one individual cannot also be used as genetic information about other group members.”.
(b) Outreach plan.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary of Health and Human Services shall develop an outreach plan to notify individuals entitled to benefits under part A or enrolled under part B of title XVIII of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395 et seq.) of the effects of the amendment made by subsection (a).
(2) CONSULTATION.—In implementing the outreach plan developed under paragraph (1), the Secretary shall consult with consumer advocates, brokers, insurers, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners, and State Health Insurance Assistance Programs.
(c) Effective date; phase-In authority.—
(1) EFFECTIVE DATE.—Subject to paragraph (2), the amendment made by subsection (a) shall apply to medicare supplemental policies effective on or after January 1, 2026.
(2) PHASE-IN AUTHORITY.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—Subject to subparagraph (B), the Secretary of Health and Human Services may phase in the implementation of the amendment made under subsection (a) (with such phase-in beginning on or after January 1, 2026) in such manner as the Secretary determines appropriate in order to minimize any adverse impact on individuals enrolled under a medicare supplemental policy.
(B) PHASE-IN PERIOD MAY NOT EXCEED 5 YEARS.—The Secretary of Health and Human Services shall ensure that the amendment made by subsection (a) is fully implemented by not later than January 1, 2031.
SEC. 3. Medical loss ratio.
Section 1882(r)(1)(A) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395ss(r)(1)(A)) is amended—
(1) by inserting “and periodically reviewed” after “developed”; and
(2) by striking “policy, at least 75 percent of the aggregate amount of premiums collected in the case of group policies and at least 65 percent in the case of individual policies; and” and inserting the following: “policy—
“(i) with respect to periods beginning before January 1, 2026, at least 75 percent of the aggregate amount of premiums collected in the case of group policies and at least 65 percent in the case of individual policies; and
“(ii) with respect to periods beginning on or after January 1, 2026, a percent of the aggregate amount of premiums collected that, in the case of group policies or individual policies, as applicable, is equal to or greater than both—
“(I) the applicable percent specified in clause (i) with respect to such policies; and
“(II) such percent as the National Association of Insurance Commissioners may recommend to the Secretary with respect to such policies for purposes of this paragraph; and”.
SEC. 4. Limitations on pricing discrimination.
(a) In general.—Section 1882 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395ss), as amended by section 6, is further amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(aa) Development of new standards relating to pricing discrimination.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary shall request the National Association of Insurance Commissioners to review and revise the standards for all benefit packages under subsection (p)(1), including the core benefit package, in order to provide coverage consistent with paragraph (2). Such revisions shall be made consistent with the rules applicable under subsection (p)(1)(E) (with the reference to the ‘1991 NAIC Model Regulation’ deemed a reference to the NAIC Model Regulation as most recently updated by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners to reflect previous changes in law and the reference to ‘date of enactment of this subsection’ deemed a reference to the date of enactment of this subsection).
“(2) CHANGES IN COST-SHARING DESCRIBED.—Under the revised standards, coverage shall not be available under a Medicare supplemental insurance policy unless the issuer of the policy, in addition to conforming to the other applicable requirements of this section—
“(A) does not discriminate in the pricing of the policy because of the age of the individual to whom the policy is issued;
“(B) does not, to an extent that jeopardizes the access to such policy for individuals who are eligible to participate in the program under this title because the individuals are individuals described in paragraph (2) or (3) of section 1811, discriminate in the pricing of the policy because the individual to whom the policy is issued is so eligible to participate in such program because the individual is an individual so described in such a paragraph; and
“(C) does not establish premiums applicable under such policy on a basis that would apply to a portion of, but not the entirety of, a county or equivalent area specified by the Secretary.
“(3) APPLICATION DATE.—The revised standards shall apply to benefit packages sold, issued, or renewed under this section to individuals who first become entitled to benefits under part A or first enrolls in part B on or after January 1, 2026.”.
(b) Conforming amendment.—Section 1882(o)(1) of such Act (42 U.S.C. 1395ss(o)(1)) is amended by striking “, and (y)” and inserting “(y), and (aa)”.
SEC. 5. Clarifying beneficiary options on the Medicare plan finder website.
Section 1804 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395b–2) is amended by adding at the end the following new subsections:
“(d) In the case that the Secretary provides for a Medicare plan finder internet website of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (or a successor website), the Secretary shall, with respect to such website and in accordance with subsection (f)—
“(1) make available on such website—
“(A) access to provider networks in order to provide to individuals entitled to benefits under part A or enrolled under part B information to assist such individuals in understanding the restrictions on providers and potential costs entailed by their decisions regarding enrollment under parts A and B, under part C, and in medicare supplemental policies under section 1882;
“(B) a review of out-of-pocket expenditures, including deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, monthly premiums, and estimated annual out-of-pocket costs, displayed overall and by components, based on the best available information as determined by the Secretary; and
“(C) during the period prior to January 1, 2026, information regarding the rules that, in each State, pertain to guaranteed issue of medicare supplemental health insurance policies prior to implementation of the provisions of the Close the Medigap Act of 2025 and, in the case that a State has no such rules pertaining to guaranteed issue of such policies, clear language explaining the implications of such lack of rules for individuals with pre-existing conditions;
“(2) not later than January 1, 2026, and periodically thereafter, perform a review of such website in order to ensure that such website makes available to individuals entitled to benefits under part A or enrolled under part B the information that the Secretary determines is necessary for such individuals to make informed choices regarding their options under the program under this title; and
“(3) not later than 12 months after the last day of each period for the request for information under subsection (e), update such website, taking into consideration the information collected pursuant to such subsection, to clarify the presentation of consumer options for medicare supplemental health insurance policy options, including by presenting such information in a manner calculated to be understood by the average consumer and in a manner that—
“(A) improves consumer access to information regarding the applicable premiums under such policy options as of the date on which such website is so updated;
“(B) facilitates consumers’ ability to compare and sort policy options and premium information across plan offerings in a given location;
“(C) clarifies and explains differences in policy value;
“(D) rates and explains the financial stability of issuers of such policies;
“(E) provides data on the inflation rate of different policies;
“(F) provides information regarding the guaranteed issue requirements that apply to medicare supplemental health insurance policies under section 1882(s)(3); and
“(G) includes such general information as is determined by the Secretary to be necessary for individuals entitled to benefits under part A or enrolled under part B to understand costs under MA plans available pursuant to part C and prescription drug plans available pursuant to part D.
“(e) Not later than 6 months after the date of the enactment of this subsection and beginning on December 7 of each year thereafter, the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall provide an opportunity for public comment during which the Secretary requests information, including recommendations, from stakeholders regarding potential improvements to the presentation of medicare supplemental health insurance policy options under section 1882 on the Medicare plan finder internet website of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (or a successor website).
“(f) With respect to any information that the Secretary makes available on the Medicare plan finder internet website of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (or a successor website) pursuant to subsection (d), the Secretary shall, prior to making such information available—
“(1) provide, in consultation with the National Association of Insurance Commissioners, an opportunity for consumer testing of such information;
“(2) share the results of such consumer testing of such information with interested stakeholders; and
“(3) provide a 60-day public comment period with respect to such information.”.
SEC. 6. Restoring access to first-dollar Medigap coverage.
Section 1882 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395ss) is amended by striking subsection (z).
SEC. 7. Broker transparency.
Section 1128G of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1320a–7h) is amended—
(1) in subsection (c)(1)(A), by striking “2011,” and inserting “2011 (or, with respect to information required to be submitted under subsection (f)(1), not later than six months after the date of the enactment of such subsection),”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(f) Application to Medigap insurance brokers.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Beginning not later than 12 months after the date of enactment of this subsection, each issuer of a medicare supplemental health insurance policy shall annually submit to the Secretary a report regarding payments or other transfers of value made during the previous year to agents, brokers, and other third parties representing such policy. Each such report shall include the following information, with respect to such a payment or other transfer of value:
“(A) The name of the recipient of the payment or other transfer of value.
“(B) The business address of the recipient.
“(C) The amount of the payment or other transfer of value.
“(D) The dates on which the payment or transfer of value was provided.
“(E) A description of the form of the payment or transfer of value.
“(F) Any other categories of information the Secretary determines appropriate.
“(2) APPLICATION OF TRANSPARENCY SYSTEM.—The provisions of subsections (b) through (d) shall apply to an issuer described in paragraph (1), information required to be reported under such paragraph, and agents, brokers, and other third parties described in such paragraph in the same manner and to the same extent as such provisions apply to an applicable manufacturer, information required to be reported under subsection (a), and a covered recipient.”.
H.R.612 – Health Care Providers Safety Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Grants to health care providers to enhance security.
Part P of title III of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 280g et seq.) (as amended by Public Law 117–328) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 399V–8. Grants to health care providers to enhance security.
“(a) In general.—The Secretary may award grants to health care providers to pay for security services and otherwise enhance the physical and cyber security of their facilities, personnel, and patients to ensure safe access.
“(b) Use of funds.—A health care provider receiving a grant under this section may use the grant to pay the costs of necessary security services and enhancements to physical access and cyber security, including video surveillance camera systems, data privacy enhancements, and structural improvements.”.
H.R.649 – Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act of 2025
Summary:
This bill revises requirements for milk provided by the National School Lunch Program of the Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Currently, schools participating in the program must provide milk that is consistent with the most recent Dietary Guidelines for Americans; USDA regulations require milk to be fat-free or low-fat and allow milk to be flavored or unflavored. The bill modifies these restrictions and instead permits schools to offer students whole, reduced-fat, low-fat, and fat-free flavored and unflavored milk. The milk that is offered may be organic or nonorganic. Further, USDA may not prohibit a participating school from offering students any of these milk choices.
Further, schools currently must provide a substitute for fluid milk, on receipt of a written statement from a licensed physician, for students whose disability restricts their diet. Under the bill, a parent or legal guardian may also provide the written statement.
In addition, schools currently participating in the program must provide meals that meet certain nutrition requirements; USDA regulations require that the average saturated fat content of the meals offered must be less than 10% of the total calories. Under the bill, fluid milk is excluded from the saturated fat content calculation; milk fat included in any fluid milk provided by the program must not be considered saturated fat for the purposes of measuring compliance with USDA regulations.
Finally, the bill prohibits schools participating in the program from purchasing or offering milk produced by Chinese state-owned enterprises.
H.R.999 – To protect an individuals ability to access contraceptives and to engage in contraception and to protect a health care providers ability to provide contraceptives, contraception, and information related to contraception.
Other Bills
H.J.Res.12 – Proposing an amendment to the Constitution of the United States to limit the number of terms that a Member of Congress may serve.
This joint resolution proposes an amendment to the Constitution establishing term limits for individuals serving in the Senate and the House of Representatives.
The proposed amendment makes an individual who has served two terms in the Senate ineligible for appointment or election to the Senate and an individual who has served three terms as a Member of the House of Representatives ineligible for election to the House of Representatives.
The joint resolution provides that the amendment shall be valid when ratified by the legislatures of three-fourths of the states within seven years after the date of its submission for ratification.
Under Article V of the Constitution, both chambers of Congress may propose an amendment by a vote of two-thirds of all Members present for such vote. A proposed amendment must be ratified by the states as prescribed in Article V and as specified by Congress.
JOINT RESOLUTION
Proposing an amendment to the Constitution of the United States to limit the number of terms that a Member of Congress may serve.
Resolved by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America in Congress assembled (two-thirds of each House concurring therein), That the following article is proposed as an amendment to the Constitution of the United States, which shall be valid to all intents and purposes as part of the Constitution when ratified by the legislatures of three-fourths of the several States within seven years after the date of its submission for ratification:
“article —
“ section 1. No person who has served 3 terms as a Representative shall be eligible for election to the House of Representatives. For purposes of this section, the election of a person to fill a vacancy in the House of Representatives shall be included as 1 term in determining the number of terms that such person has served as a Representative if the person fills the vacancy for more than 1 year.
“ section 2. No person who has served 2 terms as a Senator shall be eligible for election or appointment to the Senate. For purposes of this section, the election or appointment of a person to fill a vacancy in the Senate shall be included as 1 term in determining the number of terms that such person has served as a Senator if the person fills the vacancy for more than 3 years.
“ section 3. No term beginning before the date of the ratification of this article shall be taken into account in determining eligibility for election or appointment under this article.”.
H.R.98 – End Endless Criminal Statutes Act
To repeal certain unnecessary criminal offenses, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds that actions which may unnecessarily carry criminal penalties under Federal statues include the following:
(1) Writing a check for less than $1.
(2) Selling or possessing colored oleomargarine or colored margarine unless they are packaged and labeled or served in a triangular shape.
(3) Discarding produce without sufficient cause or making a false report concerning that produce.
(4) Removing a stamp from any mail matter.
(5) Making metal coins of original design or attempting to use such coins.
(6) Wearing the uniform of letter carriers of the Postal Service.
(7) Detaining a seaman’s clothing.
(8) Boarding any vessel about to arrive at her destination before such arrival is complete.
(9) Placing mailable matter in a mailbox without postage attached to it.
(10) Sledding on the Capitol grounds when the Capitol Police are directed to prevent any portion of the Capitol grounds from being used as a playground.
SEC. 3. Repeal of Federal provisions.
(a) Section 336 of title 18, United States Code, is repealed.
(b) Subsections (b), (c), and (d) of section 407 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 347) are repealed.
(c) Section 1 of the Act of March 3, 1927 (7 U.S.C. 491; 44 Stat. 1355) is repealed.
(d) Section 1720 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking “Whoever unlawfully and willfully removes from any mail matter any stamp attached thereto in payment of postage; or”.
(e) Section 486 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking “or of original design.”.
(f) Section 11110 of title 46, United States Code, is amended by striking the second sentence.
(g) Section 2279 of title 18, United States Code, is repealed.
(h) Section 1725 of title 18, United States Code, is repealed.
(i) The Act entitled “An Act to protect the public property, turf, and grass of the Capitol Grounds from injury.” (2 U.S.C. 1963) is repealed.
SEC. 4. Intent requirement for offense related to uniforms of letter carrier.
Section 1730 of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by inserting after “to be worn by letter carriers” the following: “with the intent to commit an offense under this chapter”; and
(2) by striking the second undesignated paragraph.
H.R.142 – Regulations from the Executive in Need of Scrutiny Act of 2025
SEC. 2. Purpose.
The purpose of this Act is to increase accountability for and transparency in the Federal regulatory process. Section 1 of article I of the United States Constitution grants all legislative powers to Congress. Over time, Congress has excessively delegated its constitutional charge while failing to conduct appropriate oversight and retain accountability for the content of the laws it passes. By requiring a vote in Congress, the REINS Act will result in more carefully drafted and detailed legislation, an improved regulatory process, and a legislative branch that is truly accountable to the American people for the laws imposed upon them.
Long bill
H.R.274 – Sunset Chevron Act
To provide for the sunset of rules upheld based on Chevron deference.
SEC. 2. Definitions.
In this Act:
(1) The term “Chevron deference” means the legal doctrine of judicial deference pursuant to Chevron U.S.A., Inc. v. Natural Resources Defense Council, Inc. (467 U.S. 837 (1984)).
(2) The term “sunset date” means the date on which a rule will cease to have force or effect.
(3) The term “rule” has the meaning given such term in section 551 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 3. GAO Review of Rules Upheld by Chevron Deference.
(a) In general.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this Act, the Comptroller General of the United States shall compile and publish a list of each decision issued by a Federal court that—
(1) upheld a rule based on Chevron deference;
(2) was not subsequently overturned; and
(3) pertains to a rule that is in effect on the date of enactment of this Act.
(b) Organization of list.—Such list shall—
(1) be organized by the agency that made the rule, and for each such agency, the list shall be in reverse chronological order of the date on which the agency made the relevant rule; and
(2) provide a sunset date for each rule.
(c) Sunset date calculation.—The Comptroller General shall calculate the sunset date for each rule identified in the list compiled under subsection (a) as follows:
(1) The sunset date for the most recent rule made by each agency and identified in the list under subsection (a) shall be on the date that is 30 days after the list under subsection (a) is published.
(2) The sunset date for each prior rule made by such agency and identified in the list under subsection (a) shall be 30 days after the sunset date of the rule made by such agency and identified in such list that precedes such prior rule.
SEC. 4. Exception to the CRA to the 6-Legislative-Day Window for Certain Rules.
Chapter 8 of title 5, United States Code, shall apply to each rule identified under section 3, except that the 60-day period for filing a joint resolution under section 802(a) of that title shall not apply.
H.R.425 – Repealing Big Brother Overreach Act
To repeal the Corporate Transparency Act.
SEC. 2. Repeal.
- In general.—The Corporate Transparency Act (title LXIV of division F of the William M. (Mac) Thornberry National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2021 (Public Law 116–283; 134 Stat. 4604)) and the amendments made by that Act are repealed.
H.R.1078 – To amend the CARES Act to remove a requirement on lessors to provide notice to vacate, and for other purposes.
H.R.1106 – To amend the America COMPETES Act to establish certain scientific integrity policies for Federal agencies that fund, conduct, or oversee scientific research, and for other purposes.
H.R.1201 – To amend the Immigration and Nationality Act to increase the number of physicians who may be provided Conrad 30 waivers.
H.R.1232 – To preserve and protect the free choice of individual employees to form, join, or assist labor organizations, or to refrain from such activities.
Controlled Substances
H.R.27 – HALT Fentanyl Act or Halt All Lethal Trafficking of Fentanyl Act
This bill permanently places fentanyl-related substances as a class into schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act. A schedule I controlled substance is a drug, substance, or chemical that has a high potential for abuse; has no currently accepted medical value; and is subject to regulatory controls and administrative, civil, and criminal penalties under the Controlled Substances Act.
Under the bill, offenses involving fentanyl-related substances are triggered by the same quantity thresholds and subject to the same penalties as offenses involving fentanyl analogues (e.g., offenses involving 100 grams or more trigger a 10-year mandatory minimum prison term).
Additionally, the bill establishes a new, alternative registration process for certain schedule I research.
The bill also makes several other changes to registration requirements for conducting research with controlled substances, including
- permitting a single registration for related research sites in certain circumstances,
- waiving the requirement for a new inspection in certain situations, and
- allowing a registered researcher to perform certain manufacturing activities with small quantities of a substance without obtaining a manufacturing registration.
Finally, the bill expresses the sense that Congress agrees with the interpretation of Controlled Substances Act in United States v. McCray, a 2018 case decided by the U.S. District Court for the Western District of New York. In that case, the court held that butyryl fentanyl, a controlled substance, can be considered an analogue of fentanyl even though, under the Controlled Substances Act, the term controlled substance analogue specifically excludes a controlled substance.
To amend the Controlled Substances Act with respect to the scheduling of fentanyl-related substances, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Class scheduling of fentanyl-related substances.
Section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812(c)) is amended by adding at the end of schedule I the following:
“(e) (1) Unless specifically exempted or unless listed in another schedule, any material, compound, mixture, or preparation which contains any quantity of a fentanyl-related substance, or which contains the salts, isomers, and salts of isomers of a fentanyl-related substance whenever the existence of such salts, isomers, and salts of isomers is possible within the specific chemical designation.
“(2) For purposes of paragraph (1), except as provided in paragraph (3), the term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ means any substance that is structurally related to fentanyl by 1 or more of the following modifications:
“(A) By replacement of the phenyl portion of the phenethyl group by any monocycle, whether or not further substituted in or on the monocycle.
“(B) By substitution in or on the phenethyl group with alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyl, hydroxyl, halo, haloalkyl, amino, or nitro groups.
“(C) By substitution in or on the piperidine ring with alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyl, ester, ether, hydroxyl, halo, haloalkyl, amino, or nitro groups.
“(D) By replacement of the aniline ring with any aromatic monocycle whether or not further substituted in or on the aromatic monocycle.
“(E) By replacement of the N–propionyl group with another acyl group.
“(3) A substance that satisfies the definition of the term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ in paragraph (2) shall nonetheless not be treated as a fentanyl-related substance subject to this schedule if the substance—
“(A) is controlled by action of the Attorney General under section 201; or
“(B) is otherwise expressly listed in a schedule other than this schedule.
“(4) (A) The Attorney General may by order publish in the Federal Register a list of substances that satisfy the definition of the term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ in paragraph (2).
“(B) The absence of a substance from a list published under subparagraph (A) does not negate the control status of the substance under this schedule if the substance satisfies the definition of the term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ in paragraph (2).”.
SEC. 3. Registration requirements related to research.
(a) Alternative registration process for schedule I research.—Section 303 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 823) is amended—
(1) by redesignating the second subsection (l) (relating to required training for prescribers) as subsection (m); and
(2) by adding at the end the following:
“(n) Special provisions for practitioners conducting certain research with schedule i controlled substances.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Notwithstanding subsection (g), a practitioner may conduct research described in paragraph (2) of this subsection with 1 or more schedule I substances in accordance with subparagraph (A) or (B) of paragraph (3) of this subsection.
“(2) RESEARCH SUBJECT TO EXPEDITED PROCEDURES.—Research described in this paragraph is research that—
“(A) is with respect to a drug that is the subject of an investigational use exemption under section 505(i) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act; or
“(B) is—
“(i) conducted by the Department of Health and Human Services, the Department of Defense, or the Department of Veterans Affairs; or
“(ii) funded partly or entirely by a grant, contract, cooperative agreement, or other transaction from the Department of Health and Human Services, the Department of Defense, or the Department of Veterans Affairs.
“(3) EXPEDITED PROCEDURES.—
“(A) RESEARCHER WITH A CURRENT SCHEDULE I OR II RESEARCH REGISTRATION.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—If a practitioner is registered to conduct research with a controlled substance in schedule I or II, the practitioner may conduct research under this subsection on and after the date that is 30 days after the date on which the practitioner sends a notice to the Attorney General containing the following information, with respect to each substance with which the practitioner will conduct the research:
“(I) The chemical name of the substance.
“(II) The quantity of the substance to be used in the research.
“(III) Demonstration that the research is in the category described in paragraph (2), which demonstration may be satisfied—
“(aa) in the case of a grant, contract, cooperative agreement, or other transaction, or intramural research project, by identifying the sponsoring agency and supplying the number of the grant, contract, cooperative agreement, other transaction, or project; or
“(bb) in the case of an application under section 505(i) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, by supplying the application number and the sponsor of record on the application.
“(IV) Demonstration that the researcher is authorized to conduct research with respect to the substance under the laws of the State in which the research will take place.
“(ii) VERIFICATION OF INFORMATION BY HHS OR VA.—Upon request from the Attorney General, the Secretary of Health and Human Services, the Department of Defense, or the Secretary of Veterans Affairs, as appropriate, shall verify information submitted by an applicant under clause (i)(III).
“(B) RESEARCHER WITHOUT A CURRENT SCHEDULE I OR II RESEARCH REGISTRATION.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—If a practitioner is not registered to conduct research with a controlled substance in schedule I or II, the practitioner may send a notice to the Attorney General containing the information listed in subparagraph (A)(i), with respect to each substance with which the practitioner will conduct the research.
“(ii) ATTORNEY GENERAL ACTION.—The Attorney General shall—
“(I) treat notice received under clause (i) as a sufficient application for a research registration; and
“(II) not later than 45 days of receiving such a notice that contains all information required under subparagraph (A)(i)—
“(aa) register the applicant; or
“(bb) serve an order to show cause upon the applicant in accordance with section 304(c).
“(4) ELECTRONIC SUBMISSIONS.—The Attorney General shall provide a means to permit a practitioner to submit a notification under paragraph (3) electronically.
“(5) LIMITATION ON AMOUNTS.—A practitioner conducting research with a schedule I substance under this subsection may only possess the amounts of schedule I substance identified in—
“(A) the notification to the Attorney General under paragraph (3); or
“(B) a supplemental notification that the practitioner may send if the practitioner needs additional amounts for the research, which supplemental notification shall include—
“(i) the name of the practitioner;
“(ii) the additional quantity needed of the substance; and
“(iii) an attestation that the research to be conducted with the substance is consistent with the scope of the research that was the subject of the notification under paragraph (3).
“(6) IMPORTATION AND EXPORTATION REQUIREMENTS NOT AFFECTED.—Nothing in this subsection alters the requirements of part A of title III, regarding the importation and exportation of controlled substances.
“(7) INSPECTOR GENERAL REPORT.—Not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of this Act, the Inspector General of the Department of Justice shall complete a study, and submit a report thereon, about research described in paragraph (2) of this subsection with fentanyl.”.
(b) Separate registrations not required for additional researcher in same institution.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 302(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822(c)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(4) An agent or employee of a research institution that is conducting research with a controlled substance if—
“(A) the agent or employee is acting within the scope of the professional practice of the agent or employee;
“(B) another agent or employee of the institution is registered to conduct research with a controlled substance in the same schedule;
“(C) the researcher who is so registered—
“(i) informs the Attorney General of the name, position title, and employing institution of the agent or employee who is not separately registered;
“(ii) authorizes that agent or employee to perform research under the registration of the registered researcher; and
“(iii) affirms that any act taken by that agent or employee involving a controlled substance shall be attributable to the registered researcher, as if the researcher had directly committed the act, for purposes of any proceeding under section 304(a) to suspend or revoke the registration of the registered researcher; and
“(D) the Attorney General does not, within 30 days of receiving the information, authorization, and affirmation described in subparagraph (C), refuse, for a reason listed in section 304(a), to allow the agent or employee to possess the substance without a separate registration.”.
(2) TECHNICAL CORRECTION.—Section 302(c)(3) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822(c)(3)) is amended by striking “(25)” and inserting “(27)”.
(c) Single registration for related research sites.—Section 302(e) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822(e)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(4) (A) Notwithstanding paragraph (1), a person registered to conduct research with a controlled substance under section 303(g) may conduct the research under a single registration if—
“(i) the research occurs exclusively on sites all of which are—
“(I) within the same city or county; and
“(II) under the control of the same institution, organization, or agency; and
“(ii) before commencing the research, the researcher notifies the Attorney General of each site where—
“(I) the research will be conducted; or
“(II) the controlled substance will be stored or administered.
“(B) A site described in subparagraph (A) shall be included in a registration described in that subparagraph only if the researcher has notified the Attorney General of the site—
“(i) in the application for the registration; or
“(ii) before the research is conducted, or before the controlled substance is stored or administered, at the site.
“(C) The Attorney General may, in consultation with the Secretary, issue regulations addressing, with respect to research sites described in subparagraph (A)—
“(i) the manner in which controlled substances may be delivered to the research sites;
“(ii) the storage and security of controlled substances at the research sites;
“(iii) the maintenance of records for the research sites; and
“(iv) any other matters necessary to ensure effective controls against diversion at the research sites.”.
(d) New inspection not required in certain situations.—Section 302(f) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822(f)) is amended—
(1) by striking “(f) The” and inserting “(f)(1) The”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following:
“(2) (A) If a person is registered to conduct research with a controlled substance and applies for a registration, or for a modification of a registration, to conduct research with a second controlled substance that is in the same schedule as the first controlled substance, or is in a schedule with a higher numerical designation than the schedule of the first controlled substance, a new inspection by the Attorney General of the registered location is not required.
“(B) Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall prohibit the Attorney General from conducting an inspection that the Attorney General determines necessary to ensure that a registrant maintains effective controls against diversion.”.
(e) Continuation of research on substances newly added to schedule I.—Section 302 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(h) Continuation of research on substances newly added to schedule I.—If a person is conducting research on a substance when the substance is added to schedule I, and the person is already registered to conduct research with a controlled substance in schedule I—
“(1) not later than 90 days after the scheduling of the newly scheduled substance, the person shall submit a completed application for registration or modification of existing registration, to conduct research on the substance, in accordance with regulations issued by the Attorney General for purposes of this paragraph;
“(2) the person may, notwithstanding subsections (a) and (b), continue to conduct the research on the substance until—
“(A) the person withdraws the application described in paragraph (1) of this subsection; or
“(B) the Attorney General serves on the person an order to show cause proposing the denial of the application under section 304(c);
“(3) if the Attorney General serves an order to show cause as described in paragraph (2)(B) and the person requests a hearing, the hearing shall be held on an expedited basis and not later than 45 days after the request is made, except that the hearing may be held at a later time if so requested by the person; and
“(4) if the person sends a copy of the application described in paragraph (1) to a manufacturer or distributor of the substance, receipt of the copy by the manufacturer or distributor shall constitute sufficient evidence that the person is authorized to receive the substance.”.
(f) Treatment of certain manufacturing activities as coincident to research.—Section 302 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822), as amended by subsection (e), is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(i) Treatment of certain manufacturing activities as coincident to research.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Except as provided in paragraph (3), a person who is registered to perform research on a controlled substance may perform manufacturing activities with small quantities of that substance, including activities described in paragraph (2), without being required to obtain a manufacturing registration, if—
“(A) the activities are performed for the purpose of the research; and
“(B) the activities and the quantities of the substance involved in the activities are stated in—
“(i) a notification submitted to the Attorney General under section 303(n);
“(ii) a research protocol filed with an application for registration approval under section 303(g); or
“(iii) a notification to the Attorney General that includes—
“(I) the name of the registrant; and
“(II) an attestation that the research to be conducted with the small quantities of manufactured substance is consistent with the scope of the research that is the basis for the registration.
“(2) ACTIVITIES INCLUDED.—Activities permitted under paragraph (1) include—
“(A) processing the substance to create extracts, tinctures, oils, solutions, derivatives, or other forms of the substance consistent with—
“(i) the information provided as part of a notification submitted to the Attorney General under section 303(n); or
“(ii) a research protocol filed with an application for registration approval under section 303(g); and
“(B) dosage form development studies performed for the purpose of requesting an investigational new drug exemption under section 505(i) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355(i)).
“(3) EXCEPTION REGARDING MARIHUANA.—The authority under paragraph (1) to manufacture substances does not include the authority to grow marihuana.”.
(g) Transparency regarding special procedures.—Section 303 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 823), as amended by subsection (a), is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(o) Transparency regarding special procedures.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—If the Attorney General determines, with respect to a controlled substance, that an application by a practitioner to conduct research with the substance should be considered under a process, or subject to criteria, different from the process or criteria applicable to applications to conduct research with other controlled substances in the same schedule, the Attorney General shall make public, including by posting on the website of the Drug Enforcement Administration—
“(A) the identities of all substances for which such determinations have been made;
“(B) the process and criteria that shall be applied to applications to conduct research with those substances; and
“(C) how the process and criteria described in subparagraph (B) differ from the process and criteria applicable to applications to conduct research with other controlled substances in the same schedule.
“(2) TIMING OF POSTING.—The Attorney General shall make information described in paragraph (1) public upon making a determination described in that paragraph, regardless of whether a practitioner has submitted such an application at that time.”.
SEC. 4. Technical correction on controlled substances dispensing.
Effective as if included in the enactment of Public Law 117–328—
(1) section 1252(a) of division FF of Public Law 117–328 (136 Stat. 5681) is amended, in the matter being inserted into section 302(e) of the Controlled Substances Act, by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”;
(2) section 1262 of division FF of Public Law 117–328 (136 Stat. 5681) is amended—
(A) in subsection (a)—
(i) in the matter preceding paragraph (1), by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”;
(ii) in the matter being stricken by subsection (a)(2), by striking “(g)(1)” and inserting “(h)(1)”; and
(iii) in the matter being inserted by subsection (a)(2), by striking “(g) Practitioners” and inserting “(h) Practitioners”; and
(B) in subsection (b)—
(i) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (1), by striking “303(g)(1)” and inserting “303(h)(1)”;
(ii) in the matter being inserted by paragraph (1), by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”;
(iii) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (2)(A), by striking “303(g)(2)” and inserting “303(h)(2)”;
(iv) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (3), by striking “303(g)(2)(B)” and inserting “303(h)(2)(B)”;
(v) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (5), by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”; and
(vi) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (6), by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”; and
(3) section 1263(b) of division FF of Public Law 117–328 (136 Stat. 5685) is amended—
(A) by striking “303(g)(2)” and inserting “303(h)(2)”; and
(B) by striking “(21 U.S.C. 823(g)(2))” and inserting “(21 U.S.C. 823(h)(2))”.
SEC. 5. Rulemaking.
(a) Interim final rules.—The Attorney General—
(1) shall, not later than 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act, issue rules to implement this Act and the amendments made by this Act; and
(2) may issue the rules under paragraph (1) as interim final rules.
(b) Procedure for final rule.—
(1) EFFECTIVENESS OF INTERIM FINAL RULES.—A rule issued by the Attorney General as an interim final rule under subsection (a) shall become immediately effective as an interim final rule without requiring the Attorney General to demonstrate good cause therefor, notwithstanding subparagraph (B) of section 553(b) of title 5, United States Code.
(2) OPPORTUNITY FOR COMMENT AND HEARING.—An interim final rule issued under subsection (a) shall give interested persons the opportunity to comment and to request a hearing.
(3) FINAL RULE.—After the conclusion of such proceedings, the Attorney General shall issue a final rule to implement this Act and the amendments made by this Act in accordance with section 553 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 6. Penalties.
(a) In general.—Section 401(b)(1) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 841(b)(1)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (A)(vi), by inserting “or a fentanyl-related substance” after “any analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide”; and
(2) in subparagraph (B)(vi), by inserting “or a fentanyl-related substance” after “any analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide”.
(b) Importation and exportation.—Section 1010(b) of the Controlled Substances Import and Export Act (21 U.S.C. 960(b)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1)(F), by inserting “or a fentanyl-related substance” after “any analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide”; and
(2) in paragraph (2)(F), by inserting “or a fentanyl-related substance” after “any analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide”.
(c) Definition of fentanyl-related substance.—Section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 802) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(60) The term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ has the meaning given the term in subsection (e)(2) of schedule I of section 202(c).”.
SEC. 7. Applicability; other matters.
(a) In general.—Irrespective of the date on which the rules required by section 5 are finalized, the amendments made by this Act apply beginning as of the enactment of this Act.
(b) Rule of construction.—Nothing in the amendments made by this Act may be construed as evidence that, in applying sections 401(b)(1) and 1010(b) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 841(b)(1) and 960(b)) with respect to conduct occurring before the date of the enactment of this Act, a fentanyl-related substance (as defined by such amendments) is not an analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide.
(c) Sense of congress.—The Congress agrees with the interpretation of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 801 et seq.) in United States v. McCray, 346 F. Supp. 3d 363 (2018).
Passed the House of Representatives February 6, 2025.
- R. 128 “Fentanyl is a WMD Act”.
WMD = Weapon of Mass Destruction
SEC. 2. Treatment of illicit fentanyl as a weapon of mass destruction.
The Assistant Secretary for the Countering Weapons of Mass Destruction Office of the Department of Homeland Security shall treat illicit fentanyl as a weapon of mass destruction for purposes of title XIX of the Homeland Security Act of 2002 (6 U.S.C. 590 et seq.).
H.R.830 – To amend the Controlled Substances Act with respect to fentanyl-related substances, and for other purposes.
H.R.1046 – To require the Director of the Bureau of Prisons to develop and implement a strategy to interdict fentanyl and other synthetic drugs in the mail at Federal correctional facilities.
H.R.1100 – To amend the Controlled Substances Act to provide for the regulation of critical parts of tableting machines and encapsulating machines, and for other purposes.
H.R.1142 – To amend the Public Health Service Act to direct the Secretary of Health and Human Services to establish drug adherence guidelines, and for other purposes.
H.R.1231 – To reauthorize and expand the pilot program to help individuals in recovery from a substance use disorder become stably housed, and for other purposes.
H.R.1266 – To prohibit certain uses of xylazine, and for other purposes.
Aliens
H.R.134 – Protecting our Communities from Sexual Predators Act
To amend the Immigration and Nationality Act to provide for the detention, inadmissibility, and removal of aliens who commit sexual assault.
SEC. 2. Detention of certain aliens who commit sexual assault.
Section 236(c)(1) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1226(c)(1)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (C), by striking “, or” and inserting a comma;
(2) in subparagraph (D), by adding “or” at the end; and
(3) by inserting after subparagraph (D) the following:
“(E) (i) is inadmissible under section 212(a)(6)(A) or (C) or under section 212(a)(7); and
“(ii) is charged with, arrested for, convicted of, admits having committed, or admits committing acts which constitute the essential elements of, any offense involving sexual assault (as such term is defined in section 214(d)(3)(A)),”.
SEC. 3. Inadmissilibity and deportability related to sexual assault.
(a) Inadmissibility.— Section 212(a)(2) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1182(a)(2)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(J) SEXUAL ASSAULT.—Any alien who has been convicted of, who admits having committed, or who admits committing acts which constitute the essential elements of, any offense involving sexual assault (as such term is defined in section 214(d)(3)(A)), is inadmissible.”.
(b) Deportability.—Section 237(a)(2) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1227(a)(2)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(G) SEXUAL ASSAULT.—Any alien who has been convicted of, who admits having committed, or who admits committing acts which constitute the essential elements of, any offense involving sexual assault (as such term is defined in section 214(d)(3)(A)), is deportable.”.
H. R. 175 Deport Alien Gang Members Act
This bill makes non-U.S. nationals (aliens under federal law) associated with criminal gangs inadmissible for entry into the United States and deportable. The bill also establishes procedures to designate groups as criminal gangs.
An individual shall be inadmissible if certain officers or agencies know or have reason to believe that the individual is or was a criminal gang member or has participated or aided such a group’s illegal activities. An individual who is or was a member of such a gang, has participated or aided such a group’s illegal activities, or seeks to enter or has entered the United States in furtherance of such activity shall be deportable.
Such individuals must be subject to mandatory detention. Furthermore, such individuals shall not be eligible for (1) asylum; (2) temporary protected status; (3) special immigrant juvenile visas; or (4) parole, unless they are assisting the government in a law enforcement matter.
The bill defines a criminal gang as a group of five or more persons (1) where one of its primary purposes is committing specified criminal offenses and its members have engaged in a continuing series of such offenses within the past five years, or (2) that has been designated as a criminal gang by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS).
The bill also establishes procedures for DHS to designate a group as a criminal gang, including notifying Congress, publishing a notice in the Federal Register, and providing an opportunity for the group to petition for review of the designation.
To amend the Immigration and Nationality Act with respect to aliens associated with criminal gangs, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Grounds of inadmissibility and deportability for alien gang members.
(a) Definition of gang member.—Section 101(a) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1101(a)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(53) The term ‘criminal gang’ means an ongoing group, club, organization, or association of 5 or more persons that has as 1 of its primary purposes the commission of 1 or more of the offenses described in this paragraph and the members of which engage, or have engaged within the past 5 years, in a continuing series of such offenses, or that has been designated as a criminal gang by the Secretary of Homeland Security, in consultation with the Attorney General, as meeting these criteria. The offenses described, whether committed, in whole or in part, within or outside of the United States and regardless of whether the offenses occurred before, on, or after the date of the enactment of this paragraph, are the following:
“(A) A Federal, State, local, or Tribal offense that is punishable by imprisonment for more than 1 year and relates to a controlled substance (as so classified under the relevant Federal, State, local, or Tribal law), regardless of whether the substance is classified as a controlled substance under section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 802).
“(B) A foreign offense that is punishable by imprisonment for more than 1 year and relates to a controlled substance as defined under section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 802).
“(C) An offense that is punishable by imprisonment for more than 1 year and involves firearms or explosives (as defined under the relevant Federal, State, local, Tribal, or foreign law) or in violation of section 931 of title 18, United States Code (relating to purchase, ownership, or possession of body armor by violent felons).
“(D) An offense under section 274 (relating to bringing in and harboring certain aliens), section 277 (relating to aiding or assisting certain aliens to enter the United States), or section 278 (relating to importation of alien for immoral purpose).
“(E) A crime of violence (as defined in section 16(a) of title 18, United States Code).
“(F) A crime involving obstruction of justice, tampering with or retaliating against a witness, victim, or informant, or burglary (as such terms are defined under the relevant Federal, State, local, Tribal, or foreign law).
“(G) Any conduct punishable under sections 1028, 1028A, and 1029 of title 18, United States Code (relating to fraud, aggravated identity theft or fraud and related activity in connection with identification documents or access devices), sections 1581 through 1594 of such title (relating to peonage, slavery, and trafficking in persons), section 1951 of such title (relating to interference with commerce by threats or violence), section 1952 of such title (relating to interstate and foreign travel or transportation in aid of racketeering enterprises), section 1956 of such title (relating to the laundering of monetary instruments), section 1957 of such title (relating to engaging in monetary transactions in property derived from specified unlawful activity), or sections 2312 through 2315 of such title (relating to interstate transportation of stolen motor vehicles or stolen property).
“(H) A conspiracy to commit an offense described in subparagraphs (A) through (G).”.
(b) Inadmissibility.—Section 212(a)(2) of such Act (8 U.S.C. 1182(a)(2)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(J) ALIENS ASSOCIATED WITH CRIMINAL GANGS.—Any alien is inadmissible who a consular officer, an immigration officer, the Secretary of Homeland Security, or the Attorney General knows, or has reason to believe—
“(i) is, or has been, a member of a criminal gang;
“(ii) has promoted, conspired with, aided, or participated in the activities of a criminal gang, whether within or outside of the United States; or
“(iii) seeks to enter the United States, or has entered the United States, in furtherance of the activities of a criminal gang, whether those activities take place within or outside of the United States.”.
(c) Deportability.—Section 237(a)(2) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1227(a)(2)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(G) ALIENS ASSOCIATED WITH CRIMINAL GANGS.—Any alien is deportable who—
“(i) is or has been a member of a criminal gang; or
“(ii) has promoted, conspired with, aided, or participated in the activities of a criminal gang, whether within or outside of the United States.”.
(d) Designation.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Chapter 2 of title II of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1182) is amended by inserting after section 219 the following:
“Sec. 220. Designation of criminal gang.
(2) CLERICAL AMENDMENT.—The table of contents for such Act is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 219 the following:
“Sec. 220. Designation.”.
(e) Mandatory detention of criminal gang members.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 236(c)(1) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1226(c)(1)) is amended—
(A) in subparagraph (C), by striking “or” at the end;
(B) in subparagraph (D), by inserting “or” at the end; and
(C) by inserting after subparagraph (D) the following:
“(E) is inadmissible under section 212(a)(2)(J) or deportable under section 217(a)(2)(G),”.
(2) ANNUAL REPORT.—Not later than March 1 of each year (beginning 1 year after the date of the enactment of this Act), the Secretary of Homeland Security, after consultation with the appropriate Federal agencies, shall submit a report to the Committees on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives and of the Senate on the number of aliens detained under the amendments made by paragraph (1).
(f) Claims based on gang affiliation.—
(1) INAPPLICABILITY OF RESTRICTION ON REMOVAL TO CERTAIN COUNTRIES.—Section 241(b)(3)(B) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1251(b)(3)(B)) is amended, in the matter preceding clause (i), by inserting “who is described in section 212(a)(2)(J)(i) or section 237(a)(2)(G)(i) or who is” after “to an alien”.
(2) INELIGIBILITY FOR ASYLUM.—Section 208(b)(2)(A) of such Act (8 U.S.C. 1158(b)(2)(A)) (as amended by section 201 of this Act) is further amended—
(A) in clause (v), by striking “or” at the end;
(B) by redesignating clause (vi) as clause (vii); and
(C) by inserting after clause (v) the following:
“(vi) the alien is described in section 212(a)(2)(J)(i) or section 237(a)(2)(G)(i); or”.
(g) Temporary protected status.—Section 244 of such Act (8 U.S.C. 1254a) is amended—
(1) by striking “Attorney General” each place it appears and inserting “Secretary of Homeland Security”;
(2) in subparagraph (c)(2)(B)—
(A) in clause (i), by striking “or” at the end;
(B) in clause (ii), by striking the period and inserting “; or”; and
(C) by adding at the end the following:
“(iii) the alien is, or at any time has been, described in section 212(a)(2)(J) or section 237(a)(2)(G).”; and
(3) in subsection (d)—
(A) by striking paragraph (3); and
(B) in paragraph (4), by adding at the end the following: “The Secretary of Homeland Security may detain an alien provided temporary protected status under this section whenever appropriate under any other provision of law.”.
(h) Special immigrant juvenile visas.—Section 101(a)(27)(J)(iii) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1101(a)(27)(J)(iii)) is amended—
(1) in subclause (I), by striking “and”;
(2) in subclause (II), by adding “and” at the end; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(III) no alien who is, or at any time has been, described in section 212(a)(2)(J) or section 237(a)(2)(G) shall be eligible for any immigration benefit under this subparagraph;”.
(i) Parole.—An alien described in section 212(a)(2)(J) of the Immigration and Nationality Act, as added by subsection (b), shall not be eligible for parole under section 212(d)(5)(A) of such Act unless—
(1) the alien is assisting or has assisted the United States Government in a law enforcement matter, including a criminal investigation; and
(2) the alien’s presence in the United States is required by the Government with respect to such assistance.
(j) Ineligibility for other relief.—An alien described in section 212(a)(2)(J) or 237(a)(2)(G) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1182(a)(2)(J) or 1227(a)(2)(G)) shall be ineligible for any other relief under the immigration laws, including under section 2242 of the Omnibus Consolidated and Emergency Supplemental Appropriations Act, 1999 (and any regulations issued pursuant to such section).
(k) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall take effect on the date of the enactment of this Act and shall apply to acts that occur before, on, or after the date of the enactment of this Act.
H. R. 190 SEND THEM BACK Act of 2025
Sending Evading Non-Documented Threats Home Especially Migrants Biden Accepted Carelessly and Knowingly Act of 2025 or the SEND THEM BACK Act of 2025
This bill subjects non-U.S. nationals (aliens under federal law) who illegally entered the United States on or after January 20, 2021, to expedited removal (i.e., removal without further hearing or review). This applies even if such an individual indicated an intention to apply for asylum or expressed a fear of persecution. The bill does not apply to an individual serving in the Armed Forces as of January 1, 2025.
To provide for expedited removal of certain illegal aliens.
SEC. 2. Expedited removal of certain illegal aliens.
(a) In general.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, an alien who entered the United States illegally on or since January 20, 2021, shall be subject to expedited removal, even if such alien indicated an intention to apply for asylum or a fear of persecution.
(b) Exception.—Subsection (a) shall not apply to any alien who is currently a member of the Armed Forces of the United States as of January 1, 2025.
H.R.218 – State Immigration Enforcement Act
To authorize State enforcement of immigration laws, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. State enforcement of immigration laws.
States, or political subdivisions of States, may enact, implement and enforce criminal penalties that penalize the same conduct that is prohibited in the criminal provisions of immigration laws (as defined in section 101(a)(17) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1101(a)(17))), as long as the criminal penalties do not exceed the relevant Federal criminal penalties (without regard to ancillary issues such as the availability of probation or pardon). States, or political subdivisions of States, may enact, implement and enforce civil penalties that penalize the same conduct that is prohibited in the civil provisions of immigration laws (as defined in such section 101(a)(17)), as long as the civil penalties do not exceed the relevant Federal civil penalties.
SEC. 3. Conforming amendment.
Section 274A(h) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1324a(h)) is amended by striking paragraph (2).
- R. 273 REMAIN in Mexico Act of 2025
This Act may be cited as the “Return Excessive Migrants and Asylees to International Neighbors in Mexico Act of 2025” or the “REMAIN in Mexico Act of 2025”.
SEC. 2. Migrant Protection Protocols.
Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Secretary of Homeland Security shall implement the Migrant Protection Protocols in accordance with the memorandum of Secretary of Homeland Security Nielsen entitled “Policy Guidance for Implementation of the Migrant Protection Protocols”, dated January 25, 2019.
H.R.275 – Special Interest Alien Reporting Act of 2024
To require the Secretary of Homeland Security to publish on a monthly basis the number of special interest aliens encountered attempting to unlawfully enter the United States, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Publication by the Department of Homeland Security of the number of special interest aliens encountered attempting to unlawfully enter the United States.
(a) In general.—Not later than the seventh day of each month, the Secretary of Homeland Security shall publish on a publicly available webpage of the Department of Homeland Security and submit to the Committee on Homeland Security of the House of Representatives and the Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs of the Senate a report on the total number, and an identification of the nationalities or countries of last habitual residence, of special interest aliens encountered by the Department attempting to unlawfully enter the United States during the immediately preceding month. Each such report shall also include the following:
(1) Such number disaggregated by geographic regions of such encounters.
(2) Specifications relating to whether such encounters were made at land, air, or sea ports of entry, between ports of entry, or in the interior of the United States.
(3) Identification of any such nationalities or countries of last habitual residence that are covered nations.
(b) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) ALIEN.—The term “alien” has the meaning given such term in section 101 of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1101).
(2) COVERED NATION.—The term “covered nation” has the meaning given such term in section 4872(d)(2) of title 10, United States Code.
(3) SPECIAL INTEREST ALIEN.—The term “special interest alien” means an alien who, based on an analysis of travel patterns, potentially poses a national security risk to the United States or its interests.
H.R.355 – Justice for Jocelyn Act
To remove aliens who fail to comply with a release order, to enroll all aliens on the nondetained docket of an immigration court in the Alternatives to Detention program with continuous GPS monitoring, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Limitation on participation in alternatives to detention.
No alien may be released as part of any program under the Alternatives to Detention program unless—
(1) all detention beds available to the Secretary have been filled;
(2) there exists no available option to hold aliens in detention; and
(3) the Secretary exercised and exhausted all reasonable efforts to hold aliens in detention.
SEC. 3. Gps tracking and curfew requirements for certain aliens.
Each alien on the Immigration and Customs Enforcement’s nondetained docket shall be enrolled in the Alternatives to Detention program and—
(1) shall be continuously subject to GPS monitoring—
(A) for the duration of all applicable immigration proceedings, including any appeal; and
(B) in the case of an alien who is ordered removed from the United States, until removal; and
(2) shall be required to stay in their Alternatives to Detention-compliant home address between the hours of 10 p.m. to 5 a.m.
SEC. 4. Removal of aliens who fail to comply with release order.
Section 240(b)(5) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1229a(b)(5)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(F) FAILURE TO COMPLY WITH RELEASE ORDER.—In the case that an immigration officer submits an affidavit to an immigration judge stating that an alien failed to comply with a condition of release under section 236(a), such alien shall be ordered removed in absentia.”.
SEC. 5. Severability.
If any provision of this Act or the application of such provision to any person or circumstance is held by a Federal court to be unconstitutional, the remainder of this Act and the application of such provisions to any other person or circumstance shall not be affected.
H.R.630 – Neighbors Not Enemies Act
To repeal the Alien Enemies Act, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Repeal of Alien Enemies Act.
Sections 4067 through 4070 of the Revised Statutes of the United States (50 U.S.C. 21–24) are repealed.
H.R.875 – To amend the Immigration and Nationality Act to provide that aliens who have been convicted of or who have committed an offense for driving while intoxicated or impaired are inadmissible and deportable.
H.R.924 – To transfer and limit Executive Branch authority to suspend or restrict the entry of a class of aliens.
H.R.1061 – To amend section 287 of the Immigration and Nationality Act to limit immigration enforcement actions at sensitive locations, to clarify the powers of immigration officers at sensitive locations, and for other purposes.
H.R.1088 – To provide for the use of funds for deportation purposes.
H.R.1168 – To direct the Director of the Office of Management and Budget to require the disclosure of violations of Federal law with respect to human trafficking or alien smuggling, and for other purposes.
Anti-Trump
H.J.Res.54 – Proposing an amendment to the Constitution of the United States providing that the rights protected and extended by the Constitution are the rights of natural persons only.
“ section 1. The rights and privileges protected and extended by the Constitution of the United States are the rights and privileges of natural persons only. An artificial entity, such as a corporation, limited liability company, or other entity, established by the laws of any State, the United States, or any foreign state shall have no rights under the Constitution and are subject to regulation by the People, through Federal, State, or local law. The privileges of an artificial entity shall be determined by the People, through Federal, State, or local law, and shall not be construed to be inherent or inalienable.
“ section 2. Federal, State, and local government shall regulate, limit, or prohibit contributions and expenditures, including a candidate’s own contributions and expenditures, to ensure that all citizens, regardless of their economic status, have access to the political process, and that no person gains, as a result of that person’s money, substantially more access or ability to influence in any way the election of any candidate for public office or any ballot measure. Federal, State, and local governments shall require that any permissible contributions and expenditures be publicly disclosed. The judiciary shall not construe the spending of money to influence elections to be speech under the First Amendment.
“ section 3. This amendment shall not be construed to abridge the right secured by the Constitution of the United States of the freedom of the press.”.
H.Res.68 – Expressing strong disapproval of the President’s announcement to withdraw the United States from the Paris Agreement.
Expressing strong disapproval of the President’s announcement to withdraw the United States from the Paris Agreement.
Whereas 2024 was the hottest year on record;
Whereas the previous 10 years were the 10 hottest years recorded since 1850;
Whereas global climate change is a threat to all Americans’ health, prosperity, and security;
Whereas global climate change is a threat to the United States public health, national economy, national security, and the legacy we will leave to our children;
Whereas, according to the 2023 Fifth National Climate Assessment, “harmful impacts from more frequent and severe extremes are increasing across the country—including increases in heat-related illnesses and death, costlier storm damages, longer droughts that reduce agricultural productivity and strain water systems, and larger, more severe wildfires that threaten homes and degrade air quality”;
Whereas, according to the 2023 Fifth National Climate Assessment, “Extreme events cost the US close to $150 billion each year—a conservative estimate that does not account for loss of life, healthcare-related costs, or damages to ecosystem services”;
Whereas. according to the 2023 Fifth National Climate Assessment, “Billion-dollar weather and climate disasters are events where damages/costs reach or exceed $1 billion, including adjustments for inflation. Between 2018 and 2022, 89 such events affected the US, including 4 droughts, 6 floods, 52 severe storms, 18 tropical cyclones, 5 wildfires, and 4 winter storm events”;
Whereas the most vulnerable among us, including children, the elderly, low-income individuals, and those with underlying health conditions, face even greater health risks as a result of climate change;
Whereas the National Intelligence Council’s 2021 report on climate change stated that “Risks to US national security interests through 2040 will increase as countries respond to the intensifying physical effects of climate change. Global temperatures most likely will surpass the Paris Agreement goal of 1.5°C by around 2030, and the physical effects are projected to continue intensifying”;
Whereas, on May 27, 2021, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff General Mark Milley, in a statement to the House Appropriations Defense Subcommittee for the Fiscal Year 2022 defense budget request, stated that “Climate change presents a growing threat to U.S. national security interests and defense objectives. The adverse impacts of climate change are already being felt across the Joint Force in terms of increased operational demands, adverse impacts on our installations and new requirements for equipment and formations able to operate in a world defined by climate change and as a contributing factor to regional instability”;
Whereas the Paris Agreement is an international accord that aims to limit the increase in global temperatures to less than two degrees Celsius and urges efforts to limit the increase to one and a half degrees Celsius by 2100 in order to avoid the most disastrous impacts of climate change;
Whereas the Paris Agreement was adopted on December 12, 2015, opened for signature on April 22, 2016, and entered into force on November 4, 2016;
Whereas 195 parties, including the largest emitters of carbon pollution—China, India, and the European Union—have signed the Paris Agreement;
Whereas, on January 20, 2025, President Trump announced his intention to withdraw the United States from the Paris Agreement;
Whereas, during his first term in office on June 1, 2017, President Trump withdrew the United States from the Paris Agreement, and on November 4, 2020, the United States formally withdrew from the Paris Agreement;
Whereas United States withdrawal from the Paris Agreement reneges on our commitment to the global community to fulfill our responsibility as a party to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and as a major emitter of carbon pollution to reduce our emissions;
Whereas the United States exit from the Paris Agreement will cede leadership on clean energy technologies, and the jobs they create, to China and other nations;
Whereas if the United States again withdraws from the Paris Agreement, it will join Iran, Libya, and Yemen as the only nationstates not participating in the agreement;
Whereas President Biden brought the United States back into the Paris Agreement on February 19, 2021;
Whereas, since rejoining the Paris Agreement, the United States passed consequential climate legislation including the Inflation Reduction Act, Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, and CHIPS and Science Act, which put together have created 406,000 new jobs and $422 billion in private investments as of January 2025 and put the United States on track to achieve approximately 40 percent CO2 emissions reductions, bringing the United States closer to fulfilling its commitment under the Paris Agreement achieving of 50-percent reductions by 2030;
Whereas the United States is rapidly onshoring critical supply chains and encouraging a resurgence of investments in domestic manufacturing for innovative technologies, resulting in the manufacturing sector contribution to United States gross domestic product reaching an all-time high;
Whereas the United States can continue to lead the world in innovation and manufacturing clean energy technologies, creating good-paying jobs, modernizing the energy grid, and growing new companies that will be the titans of a new clean energy economy;
Whereas, according to research published on April 2024 in the European Economic Review, it is estimated that, “Non-participation of the US would eliminate more than a third of the world emissions reduction (31.8% direct effect and 6.4% leakage effect), while a potential non-participation of China lowers the world emission reduction by 24.1% (11.9% direct effect and 12.2% leakage effect). In terms of welfare, the overwhelming majority of countries gain from the implementation of the Paris Agreement and most countries have only very little to gain from unilaterally deciding not to participate”;
Whereas leaders of the world’s religious communities recognize the grave threat to humanity posed by climate change and our moral obligation to protect the Earth and its people publicly have called upon politicians, business leaders, and the faithful to take action to address climate change;
Whereas, on October 10, 2024, the Alliance of CEO Climate Leaders, representing $4 trillion in revenues and 12 million employees, wrote an open letter reiterating the need to enhance collaboration to deliver on the Paris Agreement goals;
Whereas a group of 22 States, including Arizona, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, Washington, Wisconsin, and the territories of Puerto Rico and Guam, have all joined the United States Climate Alliance, a bipartisan group of States committed to upholding the goals of the Paris Agreement;
Whereas, according to data from the 2023 Chicago Council Survey, conducted in September 2023, found that the American public broadly supports United States participation in international agreements, with 68 percent of Americans supporting the Paris Agreement; and
Whereas millions of Americans have made their voices heard in support of the Paris Agreement, and the United States upholding its commitments to the international community to reduce carbon pollution for the benefit of good-paying jobs, families, and the environment now and in future generations: Now, therefore, be it
Resolved, That the House of Representatives—
(1) strongly disapproves of the President’s announcement to withdraw the United States from the Paris Agreement;
(2) commends the group of States, cities, colleges and universities, businesses, investors, and individuals who have publicly expressed their support for the Paris Agreement;
(3) urges the President to reverse his decision and maintain United States participation in the Paris Agreement; and
(4) urges Congress to prioritize the United States global leadership on addressing climate change.
H.Res.94 – Expressing support for the Nation’s local public K-12 schools and condemning any actions that would defund public education or weaken or dismantle the Department of Education.
RESOLUTION
Expressing support for the Nation’s local public K–12 schools and condemning any actions that would defund public education or weaken or dismantle the Department of Education.
Whereas the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 (20 U.S.C. 6301 et seq.) defines free public education as education that is “provided at public expense, under public supervision and direction, and without tuition charge” and “provided as elementary or secondary education in the applicable State or to preschool children”;
Whereas publicly funded local K–12 schools serve millions of students and families and provide economic opportunity for all, including in rural and geographically isolated areas;
Whereas, approximately 90 percent of students in the United States in prekindergarten through 12th grade and about 95 percent of students with disabilities attend a public school;
Whereas State and local funding for public K–12 schools varies significantly within States and across the United States, creating additional need among schools in under-resourced communities;
Whereas the role of the Federal Government in public education has historically been to level the playing field by creating equity of opportunity for all students, regardless of their background, ability, or ZIP Code in which they are educated;
Whereas Federal funding plays a critical role in narrowing funding gaps for disadvantaged students, providing integrated and wraparound supports for students and families, helping students meet challenging State academic standards, and increasing the chances of success in education and the workforce;
Whereas 2025 marks the 60th anniversary of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 (ESEA) and the 50th anniversary of the Education for All Handicapped Children Act, now known as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) (20 U.S.C. 1400 et seq.);
Whereas the Department of Education Organization Act (20 U.S.C. 3401 et seq.), enacted in 1979, declares “that the establishment of a Department of Education is in the public interest, will promote the general welfare of the United States, will help ensure that education issues receive proper treatment at the Federal level, and will enable the Federal Government to coordinate its education activities more effectively”;
Whereas the Department of Education serves approximately 100,000 public K–12 schools across the country, which collectively educate more than 49,000,000 students;
Whereas reading and mathematics scores and college degree attainment have substantially increased since the Department of Education was established;
Whereas the Department of Education is also a civil rights agency responsible for protecting students from discrimination and advancing educational equity and its Office for Civil Rights enforces Federal laws prohibiting discrimination and harassment, including investigating record numbers of incidents of discrimination and hate in recent years despite employing only about half of the staff the Office had when it was originally established;
Whereas the Department of Education administers IDEA grants to help public schools serve more than 7,500,000 students with disabilities, a substantial financial commitment that cannot reasonably be assumed by State or local governments, and provides monitoring and oversight to hold States accountable for providing a free appropriate public education for students with disabilities;
Whereas the Department of Education provides supplementary funding through ESEA title I–A grants to more than 51,000 public schools serving concentrated populations of students from low-income families in rural, suburban, and urban communities;
Whereas the Department of Education provides funding through ESEA title IV–F to support full-service community schools, which partner with local stakeholders, parents, and families to provide common sense, locally driven solutions to the challenges students and families face;
Whereas the Department of Education provides vital support to thousands of rural school districts through the Rural Education Achievement program under ESEA title V–B, which funds both the Small, Rural School Achievement grant program and the Rural and Low-Income School grant program;
Whereas the Department of Education directly invests in the quality and effectiveness of nearly 90 percent of teachers and approximately 20 percent of school leaders nationwide through ESEA title II–A professional development grants, ultimately improving retention rates, addressing the nationwide educator shortage, and improving student achievement;
Whereas the Department of Education provides supplementary funding to help more than 5,000,000 English-language learners achieve language proficiency and meet State academic standards through ESEA title III–A grants;
Whereas the Department of Education provides supplementary funding to help tens of thousands of public schools provide well-rounded education, technology support, and school safety measures through ESEA title IV–A, IV–B, and IV–F grants;
Whereas the Department of Education provides grants under ESEA title IV–E to support the work of Statewide Family Engagement Centers, which provide parent education initiatives, family engagement programs, and family-school partnerships;
Whereas the Department of Education supports the education of Indian, Native Hawaiian, and Alaska Native children, consistent with the historic trust responsibility, through ESEA title VI grants;
Whereas the Department of Education provides funds to strengthen and support career and technical education programs for more than 8,200,000 secondary students across the country through title I of the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act (20 U.S.C. 2321 et seq.);
Whereas the Department of Education provides necessary oversight so students have access to targeted interventions and services;
Whereas the Department of Education protects students, families, and staff from discrimination based on race, color, or national origin under title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 (42 U.S.C. 2000d et seq.), based on sex under title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972 (20 U.S.C. 1681 et seq.), and based on disability under section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (29 U.S.C. 794) and the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (42 U.S.C. 12101 et seq.) so all individuals can access equal educational and employment opportunities;
Whereas the Department of Education invests in research to understand and disseminate information about the interventions and practices that are most effective at providing excellent educational opportunities for all students;
Whereas the Department of Education employs the smallest staff of any Department, with the lowest overall staff-to-budget ratio of all 15 Departments;
Whereas dismantling or relocating any major offices within the Department of Education may substantially disrupt program administration and create a delay or loss of vitally important supports for students and funding for public schools across the Nation; and
Whereas, without Federal investment, State and local educational agencies would be forced to enact drastic funding cuts that would disproportionately affect students from rural areas, low-income families, students of color, and students with disabilities, as well as harm American competition in the global economy: Now, therefore, be it
Resolved, That the House of Representatives—
(1) strongly supports Federal investment in public K–12 schools and the students and families served by these schools;
(2) affirms that the Department of Education plays a vital role in the Nation’s system of public education;
(3) affirms that the Federal Government’s investment is important to the success of students in public schools, and investment in public education should not be diverted, including through the use of vouchers, to privately run K–12 schools; and
(4) rejects any claim that the executive branch has the legal authority to, or would serve the Nation by—
(A) dismantling or relocating major offices within the Department of Education;
(B) dismantling or relocating the Department of Education; or
(C) reducing Federal funding for public education, blocking the granting of major Federal grant programs for education, or transferring funding burdens for education to State and local governments.
H.Res.116 – Condemning the pardons for individuals who were found guilty of assaulting Capitol Police Officers.
Condemning the pardons for individuals who were found guilty of assaulting Capitol Police Officers.
Resolved, That the House of Representatives disapproves of any pardons for individuals who were found guilty of assaulting Capitol Police officers.
H.R.407 – Prevent Tariff Abuse Act
SEC. 2. Prohibition on the imposition of import duties and quotas from presidential authorities under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act.
Section 203 of the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (50 U.S.C. 1702) is amended—
(1) by redesignating subsection (c) as subsection (d); and
(2) by inserting after subsection (b) the following:
“(c) The authority granted to the President by this section does not include the authority to impose duties, tariff-rate quotas, or other quotas on articles entering the United States.”.
H.R.433 – Department of Education Protection Act
To prohibit funds made available to the Department of Education by previous Appropriations Acts from being used for any activity relating to implementing a reorganization of the Department, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) Congress has a fundamental role in shaping and reshaping the Federal agency landscape, including by—
(A) providing oversight;
(B) creating, structuring, and locating offices;
(C) delegating specific or general missions, powers, duties, and functions to offices and officers;
(D) defining the parameters of personnel systems;
(E) confirming the leadership of an agency;
(F) providing funding; and
(G) evaluating whether or not an agency shall continue in existence.
(2) The current organization of the Department of Education is designed to promote student achievement and equal access to education, including through the following offices and institutes of the Department:
(A) Federal Student Aid.
(B) The Institute of Education Sciences.
(C) The Office of the Chief Information Officer.
(D) The Office of Communications and Outreach.
(E) The Office for Civil Rights.
(F) The Office of Career, Technical, and Adult Education.
(G) The Office of the Deputy Secretary.
(H) The Office of English Language Acquisition.
(I) The Office of Elementary and Secondary Education.
(J) The Office of Finance and Operations.
(K) The Office of the General Counsel.
(L) The Office of Inspector General.
(M) The Office of Legislation and Congressional Affairs.
(N) The Office of Postsecondary Education.
(O) The Office of Planning, Evaluation and Policy Development.
(P) The Office of the Secretary.
(Q) The Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services.
(R) The Office of the Under Secretary.
SEC. 3. Prohibiting use of appropriated funds to reorganize Department of Education.
Notwithstanding any other provision of law, none of the funds made available by previous Appropriations Acts to the Department of Education for obligation or expenditure in the current fiscal year may be used for any activity relating to implementing a reorganization of the Department that decentralizes, reduces the staffing level of, or alters the responsibilities, structure, authority, or functionality of the Department, relative to the organization and operation of the Department on January 1, 2025.
H.R.521 – Ending Presidential Overreach on Public Lands Act
To reserve to Congress the authority to establish or extend a national monument.
SEC. 2. National monuments.
Section 320301 of title 54, United States Code (commonly referred to as the “Antiquities Act”), is amended to read as follows:
Ҥ 320301. National monuments
“The establishment or extension of a national monument may be undertaken only by express authorization of Congress.”.
H.R.738 – Universal Right To Vote by Mail Act of 2025
To amend the Help America Vote Act of 2002 to allow all eligible voters to vote by mail in Federal elections.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) An inequity of voting rights exists in the United States because voters in some States have the universal right to vote by mail while voters in other States do not.
(2) Many voters often have work, family, or other commitments that make getting to polls on the date of an election difficult or impossible. Under current State laws, many of these voters are not permitted to vote by mail.
(3) 36 States and the District of Columbia currently allow universal absentee voting (also known as “no-excuse” absentee voting), which permits any voter to request a mail-in ballot without providing a reason for the request, and no State which has implemented no-excuse absentee voting has switched back.
(4) Voting by mail gives voters more time to consider their choices, which is especially important as many ballots contain greater numbers of questions about complex issues than in the past due to the expanded use of the initiative and referendum process in many States.
(5) Allowing all voters the option to vote by mail can lead to increased voter participation.
(6) Allowing all voters the option to vote by mail can reduce waiting times for those voters who choose to vote at the polls.
(7) Voting by mail is preferable to many voters as an alternative to going to the polls. Voting by mail has become increasingly popular with voters who want to be certain that they are able to vote no matter what comes up on Election Day.
(8) No evidence exists suggesting the potential for fraud in absentee balloting is greater than the potential for fraud by any other method of voting.
(9) Many of the reasons which voters in many States are required to provide in order to vote by mail require the revelation of personal information about health, travel plans, or religious activities, which violate voters’ privacy while doing nothing to prevent voter fraud.
(10) State laws which require voters to obtain a notary signature to vote by mail only add cost and inconvenience to voters without increasing security.
SEC. 3. Promoting ability of voters to vote by mail in Federal elections.
(a) In general.—Subtitle A of title III of the Help America Vote Act of 2002 (52 U.S.C. 21081 et seq.) is amended by inserting after section 303 the following new section:
“SEC. 303A. Promoting ability of voters to vote by mail.
“(a) In General.—If an individual in a State is eligible to cast a vote in an election for Federal office, the State may not impose any additional conditions or requirements on the eligibility of the individual to cast the vote in such election by mail, except to the extent that the State imposes a deadline for requesting the ballot and related voting materials from the appropriate State or local election official and for returning the ballot to the appropriate State or local election official.
“(b) Notice and opportunity To cure discrepancy or defect.—
“(1) NOTICE AND OPPORTUNITY TO CURE DISCREPANCY IN SIGNATURES.—If an individual submits a mail-in ballot or an absentee ballot and the appropriate State or local election official determines that a discrepancy exists between the signature on such ballot and the signature of such individual on the official list of registered voters in the State or other official record or document used by the State to verify the signatures of voters, such election official, prior to making a final determination as to the validity of such ballot, shall—
“(A) as soon as practical, but not later than the next business day after such determination is made, make a good faith effort to notify the individual by mail, telephone, and (if available) text message and electronic mail that—
“(i) a discrepancy exists between the signature on such ballot and the signature of the individual on the official list of registered voters in the State or other official record or document used by the State to verify the signatures of voters; and
“(ii) if such discrepancy is not cured prior to the expiration of the third day following the State’s deadline for receiving mail-in ballots or absentee ballots, such ballot will not be counted; and
“(B) cure such discrepancy and count the ballot if, prior to the expiration of the third day following the State’s deadline for receiving mail-in ballots or absentee ballots, the individual provides the official with information to cure such discrepancy, either in person, by telephone, or by electronic methods.
“(2) NOTICE AND OPPORTUNITY TO CURE MISSING SIGNATURE OR OTHER DEFECT.—If an individual submits a mail-in ballot or an absentee ballot without a signature or submits a mail-in ballot or an absentee ballot with another defect which, if left uncured, would cause the ballot to not be counted, the appropriate State or local election official, prior to making a final determination as to the validity of the ballot, shall—
“(A) as soon as practical, but not later than the next business day after such determination is made, make a good faith effort to notify the individual by mail, telephone, and (if available) text message and electronic mail that—
“(i) the ballot did not include a signature or has some other defect; and
“(ii) if the individual does not provide the missing signature or cure the other defect prior to the expiration of the third day following the State’s deadline for receiving mail-in ballots or absentee ballots, such ballot will not be counted; and
“(B) count the ballot if, prior to the expiration of the third day following the State’s deadline for receiving mail-in ballots or absentee ballots, the individual provides the official with the missing signature on a form proscribed by the State or cures the other defect.
This paragraph does not apply with respect to a defect consisting of the failure of a ballot to meet the applicable deadline for the acceptance of the ballot under State law.
“(c) Rule of Construction.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to affect the authority of States to conduct elections for Federal office through the use of polling places at which individuals cast ballots on the date of the election.
“(d) Effective Date.—A State shall be required to comply with the requirements of this section with respect to elections for Federal office held in years beginning with 2026.”.
(b) Conforming amendment relating to enforcement.—Section 401 of such Act (52 U.S.C. 21111) is amended by striking “and 304” and inserting “303A, and 304”.
(c) Clerical amendment.—The table of contents for such Act is amended by inserting after the item relating to section 303 the following new item:
“Sec. 303A. Promoting ability of voters to vote by mail.”.
H.R.1101 – To prohibit unlawful access to the payment system of the Bureau of the Fiscal Service within the Department of the Treasury, and for other purposes.
Senate Bills:
Citizenship
A bill to amend section 301 of the Immigration and Nationality Act to clarify those classes of individuals born in the United States who are nationals and citizens of the United States at birth.
SEC. 2. Citizenship at birth for certain persons born in the United States.
(a) In general.—Section 301 of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1401) is amended—
(1) by inserting “(a) In general.—” before “The following”;
(2) by redesignating subsections (a) through (h) as paragraphs (1) through (8), respectively; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(b) Definition.—Acknowledging the right of birthright citizenship established by section 1 of the 14th amendment to the Constitution, a person born in the United States shall be considered ‘subject to the jurisdiction’ of the United States for purposes of subsection (a)(1) if the person is born in the United States of parents, one of whom is—
“(1) a citizen or national of the United States;
“(2) an alien lawfully admitted for permanent residence in the United States whose residence is in the United States; or
“(3) an alien in lawful status performing active service in the armed forces (as defined in section 101 of title 10, United States Code).”.
(b) Applicability.—The amendment made by subsection (a)(3) shall not be construed to affect the citizenship or nationality status of any person born before the date of the enactment of this Act.
Aliens
S.628 – Alan T. Shao II Fentanyl Public Health Emergency and Overdose Prevention Act
A bill to suspend the entry of covered aliens in response to the fentanyl public health crisis.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) More than 100,000 Americans died from drug overdoses during 2023, with the majority of such deaths caused by fentanyl.
(2) Fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid drug that is 50 times more potent than heroin and 100 times more potent than morphine.
(3) Fentanyl is involved in more deaths of Americans younger than 50 years of age than any other cause of death, including heart disease, cancer, homicide, suicide, and other accidents.
(4) In 2023, the United States Drug Enforcement Agency seized more than 80,000,000 fentanyl-laced pills and approximately 12,000 pounds of fentanyl powder, which is enough fentanyl to kill every American.
(5) Just 2 milligrams of fentanyl is considered a lethal dose.
(6) The smuggling of fentanyl into the United States constitutes a major public health crisis.
SEC. 3. Definitions.
In this Act:
(1) COVERED ALIEN.—The term “covered alien” means any person who—
(A) is attempting to unlawfully enter the United States from Canada or from Mexico;
(B) does not possess the required travel documents to be admitted to the United States; and
(C) is being held at a point of entry or a Border Patrol station to facilitate immigration processing.
(2) SECRETARY.—The term “Secretary” means the Secretary of Homeland Security.
SEC. 4. Suspending the introduction of covered aliens into the United States due to the fentanyl public health crisis.
(a) In general.—Beginning on the date of the enactment of this Act, the admittance of covered aliens into the United States is suspended to protect the public health.
(b) Relocation.—Covered aliens who attempt to enter the United States, either through a point of entry or between points of entry, while the suspension described in subsection (a) remains in place shall be returned to their country of origin or to the country from which they entered the United States as rapidly as possible to lower the risk of such aliens introducing, selling, trafficking, or otherwise illicitly disseminating or promoting the dissemination of deadly fentanyl into the United States.
(c) Repatriation flights.—The Secretary is authorized to transport covered aliens being relocated pursuant to subsection (b) on scheduled repatriation flights, on a space available basis.
Border
S.41 – Advanced Border Coordination Act of 2025
A bill to establish Joint Operations Centers along the southern border of the United States, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Definitions.
In this Act:
(1) CENTERS.—The term “Centers” means the Joint Operations Centers established under section 3(a).
(2) DEPARTMENT.—The term “Department” means the Department of Homeland Security.
(3) PARTICIPATING FEDERAL AGENCY.—The term “participating Federal agency” means—
(A) the Department;
(B) the Department of Defense;
(C) the Department of Justice; and
(D) any other Federal agency as the Secretary determines appropriate.
(4) SECRETARY.—The term “Secretary” means the Secretary of Homeland Security.
(5) STATE.—The term “State” means each State of the United States, the District of Columbia, and any territory or possession of the United States.
SEC. 3. Establishment of Joint Operations Centers.
(a) In general.—Not later than 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act, the Department shall establish not less than 2 Joint Operations Centers along the southern border of the United States to provide unified coordination centers, where law enforcement from multiple Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies can collaborate in accordance with the purposes described in subsection (b).
(b) Matters covered.—The Centers shall provide centralized operations hubs for matters related to the following:
(1) Implementing coordination and communication for field operations between participating Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies, as needed.
(2) Coordinating operations across participating Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies, as needed, including ground, air, and sea or amphibious operations.
(3) Coordinating and supporting border operations, including deterring and detecting criminal activity related to—
(A) transnational criminal organizations;
(B) illegal border crossings;
(C) the seizure of weapons;
(D) the seizure of drugs;
(E) the seizure of high valued property;
(F) terrorism;
(G) human trafficking;
(H) drug trafficking; and
(I) such additional matters as the Secretary considers appropriate.
(c) Information sharing.—To ensure effective transmission of information between participating Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies, for purposes of subsection (b), coordination and communication shall include—
(1) Federal agencies sharing pertinent information with participating State, local, and Tribal agencies through the Centers; and
(2) Federal agencies notifying participating State, local, and Tribal agencies of operations occurring within the jurisdictions of those agencies.
(d) Workforce capabilities.—The Centers shall—
(1) track and coordinate deployment of participating personnel; and
(2) coordinate training, as needed.
SEC. 4. Report.
Not later than 1 year after enactment of this Act, and annually thereafter, the Secretary shall consult with participating Federal agencies, and shall seek feedback from participating State, local, and Tribal agencies, to report to Congress—
(1) a description of the efforts undertaken to establish the Centers;
(2) an identification of the resources used for the operations of the Centers;
(3) a description of the key operations coordinated and supported by each Center;
(4) a description of any significant interoperability and communication gaps identified between participating Federal, State, local, and Tribal agencies within each Center;
(5) recommendations for improved coordination and communication between participating Federal agencies in developing and operating current and future Centers; and
(6) other data as the Secretary determines appropriate.
S. 42 – Build the Wall Act of 2025
A bill to establish the Southern Border Wall Construction Fund and to transfer unobligated amounts from the Coronavirus State and local fiscal recovery funds to such Fund to construct and maintain physicl barriers along the southern border.
SEC. 2. Southern Border Wall Construction Fund.
(a) Establishment.—There is established in the general fund of the Treasury a separate account, which shall be known as the “Southern Border Wall Construction Fund” (referred to in this section as the “Fund”).
(b) Deposits.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, there shall be immediately deposited into the Fund all of the unobligated amounts in the Coronavirus State and local fiscal recovery funds established under sections 602 and 603 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 802 and 803).
(c) Use of funds.—Amounts in the Fund shall be used by the Secretary of Homeland Security to construct and maintain physical barriers along the southern international border of the United States.
S. 481 – Securing our Border Act
A bill to reprogram all remaining unobligated funds from the IRS enforcement account
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) United States border security is paramount to the general welfare of our Nation and ensures the efficient and meaningful flow of goods and individuals through legal means.
(2) During 2023, an estimated 105,007 drug overdose deaths occurred in the United States.
(3) Only 2 percent of passenger vehicles and 20 percent of commercial vehicles crossing the southern border are scanned by nonintrusive inspection technology through a radiation portal monitor.
(4) During fiscal year 2023, U.S. Customs and Border Protection agents processed more than 1,081,030 passengers and pedestrians.
(5) Limiting the amount of deadly illicit narcotics, including fentanyl, from entering the United States would reduce the number of Americans who die annually from the use of such narcotics.
(6) Because of the failure to update nonintrusive inspection technologies at land ports of entry along the southern border of the United States, there has been an increase in the amount of illicit narcotics, such as fentanyl, being trafficked across the southern border.
(7) The amount of illicit drugs seized by U.S. Customs and Border Protection along the southwest border was approximately—
(A) 241,000 pounds during fiscal year 2023; and
(B) 275,000 pounds during fiscal year 2024.
(8) U.S. Customs and Border Protection agents had 2,135,005 encounters along the southern border during fiscal year 2024, including—
(A) 1,218,880 single adults;
(B) 804,456 family units; and
(C) 109,998 unaccompanied minors.
(9) According to the Department of Homeland Security, 750 migrants died attempting to cross the southern border during fiscal year 2022, which is—
(A) more migrant deaths than occurred in any previous fiscal year; and
(B) more than 200 more migrant deaths than the number of such deaths during fiscal year 2021.
(10) As of September 30, 2024, the immigration court backlog was 3,558,995 cases.
(11) Since the end of fiscal year 2019, U.S. Customs and Border Protection has reported 2,371 encounters with potential terrorists at ports of entry along the southern and northern borders.
(12) According to U.S. Customs and Border Protection onboard staffing data, approximately 2,700 additional U.S. Customs and Border Protection officers need to be stationed at United States ports of entry to fully staff such ports.
(13) Due to shifting priorities, construction delays, a lack of available technology solutions, and funding constraints, most southern U.S. Border Patrol sectors still rely on obsolete systems or technologies.
SEC. 3. Funding for nonintrusive border inspections.
One-third of the unobligated balances (as of the date of the enactment of this Act) from amounts made available under section 10301(1)(A)(ii) of Public Law 117–169 shall be transferred to U.S. Customs and Border Protection during the period beginning on the date of the enactment of this Act and ending on February 6, 2034, for nonintrusive inspection systems to achieve a 100 percent nonintrusive inspection scanning rate at all northern border and southwest border land ports of entry by February 6, 2034.
SEC. 4. Funding for border wall construction.
(a) In general.—Two-thirds of the unobligated balances (as of the date of the enactment of this Act) from amounts made available under section 10301(1)(A)(ii) of Public Law 117–169 shall be transferred to the Department of Homeland Security during the period beginning on the date of the enactment of this Act and ending on February 6, 2034, for activities related to the construction of a border wall system along the southwest international border of the United States.
(b) Quarterly reports.—The Secretary of Homeland Security shall submit quarterly reports to the Committee on Appropriations of the Senate, the Committee on Finance of the Senate, the Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs of the Senate, the Committee on Appropriations of the House of Representatives, the Committee on Ways and Means of the House of Representatives, and the Committee on Homeland Security of the House of Representatives that contains—
(1) an implementation plan with benchmarks related to stemming illegal immigration; and
(2) cost estimates associated with border wall system construction.
SEC. 5. Authorization to provide bonuses to U.S. Customs and Border Protection agents.
(a) Recruitment bonuses.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Subject to the approval of the Secretary of Homeland Security, the Commissioner of U.S. Customs and Border Protection may pay a recruitment bonus, not to exceed $15,000, to each newly hired U.S. Customs and Border Protection agent after—
(A) the agent completes initial basic training; and
(B) the execution of a written agreement described in paragraph (2).
(2) WRITTEN AGREEMENT.—A written agreement described in this paragraph is a legally binding agreement between a newly hired agent and U.S. Customs and Border Protection that—
(A) specifies the amount of the bonus payment to be paid to such agent, including the timing of such payment;
(B) the length of the period of service required to be completed before such agent is entitled to retain such payment; and
(C) any other terms and conditions to which such payment is subject.
(b) Retention bonuses.—Subject to the approval of the Secretary of Homeland Security, the Commissioner of U.S. Customs and Border Protection may pay annual retention bonuses, not to exceed 15 percent of the agent’s basic pay, to U.S. Border Patrol agents after the completion of each year of satisfactory service, as determined by the Commissioner.
(c) Relocation bonus.—Subject to the approval of the Secretary of Homeland Security, the Commissioner of U.S. Customs and Border Protection may pay a relocation bonus, not to exceed 15 percent of the agent’s annual basic pay, to a U.S. Customs and Border Protection agent who agrees to be transferred and to serve for not less than 3 years at the new duty station.
(d) Limitation.—None of the bonuses paid to a U.S. Customs and Border Protection agent pursuant to subsections (a) through (c) may be considered part of the basic pay of such agent for any purpose, including for retirement or in computing a lump-sum payment to the agent for accumulated and accrued annual leave under section 5551 or 5552 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 6. Treatment of aliens arriving from contiguous territory.
Section 235(b)(2)(C) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1225(b)(2)(C)) is amended by striking “may return” and all that follows and inserting the following:
““shall—
“(i) return the alien to such territory, or to a safe third country (as described in section 208), pending the completion of a proceeding under section 240; or
“(ii) detain the alien for further consideration of an application for asylum, which shall include a determination of credible fear of persecution.”.
S. 703 – CATCH Fentanyl Act or the Contraband Awareness Technology Catches Harmful Fentanyl Act
A bill to establish a pilot program to assess the use of technology to speed up and enhance the cargo inspection process at land ports of entry along the border.
SEC. 2. Definitions.
In this Act:
(1) APPROPRIATE CONGRESSIONAL COMMITTEES.—The term “appropriate congressional committees” means—
(A) the Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs of the Senate; and
(B) the Committee on Homeland Security of the House of Representatives.
(2) ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE; AI.—The terms “artificial intelligence” and “AI” have the meaning given the term “artificial intelligence” in section 238(g) of the John S. McCain National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2019 (Public Law 115–232; 10 U.S.C. 4061 note).
(3) CBP INNOVATION TEAM.—The term “CBP Innovation Team” means the U.S. Customs and Border Protection Innovation Team within the Office of the Commissioner.
(4) NONINTRUSIVE INSPECTION TECHNOLOGY; NII TECHNOLOGY.—The terms “nonintrusive inspection technology” and “NII technology” means technical equipment and machines, such as X-ray or gamma-ray imaging equipment, that allow cargo inspections without the need to open the means of transport and unload the cargo.
(5) PILOT PROJECTS.—The term “pilot projects” means the projects required under section 3(a) for testing and assessing the use of technologies to improve the inspection process at land ports of entry.
(6) SECRETARY.—The term “Secretary” means the Secretary of Homeland Security.
SEC. 3. Pilot projects allowing additional technology providers to participate in inspecting cars, trucks, and cargo containers at certain ports of entry.
(a) Establishment.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 1 year after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary, acting through CBP Innovation Team, and in coordination with the Office of Field Operations and the Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Directorate, shall begin the implementation of pilot projects for testing and assessing the use of technologies or technology enhancements to improve the process for inspecting, including by increasing efficiencies of such inspections, any conveyance or mode of transportation at land ports of entry along the borders of the United States. The technologies or technology enhancements tested and assessed under the pilot projects shall be for the purpose of assisting U.S. Customs and Border Protection personnel to detect contraband, illegal drugs, illegal weapons, human smuggling, and threats on inbound and outbound traffic, in conjunction with the use of imaging equipment, radiation portal monitors, and chemical detectors.
(2) REQUIREMENTS.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—In implementing the pilot projects at ports of entry, the CBP Innovation Team, in coordination with the Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Directorate, shall test and collect data regarding not fewer than 5 types of nonintrusive inspection technology enhancements that can be deployed at land ports of entry. The CBP Innovation Team shall test technology enhancements from at least 1 of the following categories:
(i) Artificial intelligence.
(ii) Machine learning.
(iii) High-performance computing.
(iv) Quantum information sciences, including quantum sensing.
(v) Other emerging technologies.
(B) IDENTIFICATION OF EFFECTIVE ENHANCEMENTS.—The pilot projects shall identify the most effective types of technology enhancements to improve the capabilities of nonintrusive inspection systems and other inspection systems used at land ports of entry based on—
(i) the technology enhancement’s ability to assist U.S. Customs and Border Protection accurately detect contraband, illegal drugs, illegal weapons, human smuggling, or threats in inbound and outbound traffic;
(ii) the technology enhancement’s ability to increase efficiencies of inspections to assist U.S. Customs and Border Protection address long wait times;
(iii) the technology enhancement’s ability to improve capabilities of aging detection equipment and infrastructure at land ports of entry;
(iv) the technology enhancement’s safety relative to As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) standard practices;
(v) the ability to integrate the new technology into the existing workflow and infrastructure;
(vi) the technology enhancement’s ability to incorporate automatic threat recognition technology using standard formats and open architecture;
(vii) the mobility of technology enhancements; and
(viii) other performance measures identified by the CBP Innovation Team.
(C) PRIVATE SECTOR INVOLVEMENT.—The CBP Innovation Team may solicit input from representatives of the private sector regarding commercially viable technologies.
(D) COST EFFECTIVENESS REQUIREMENT.—In identifying the most effective types of technology enhancements under subparagraph (B), the pilot projects shall prioritize solutions that demonstrate the highest cost-effectiveness in achievement the objectives described in clauses (i) through (ix) of subparagraph (B). Cost effectiveness shall account for improved detection capabilities, increased inspection efficiencies, reduced wait times, and total cost of implementation (including infrastructure upgrades and maintenance expenses).
(3) NONINTRUSIVE INSPECTION SYSTEMS PROGRAM.—The CBP Innovation Team shall work with existing nonintrusive inspection systems programs within U.S. Customs and Border Protection when planning and developing the pilot projects required under paragraph (1).
(4) DATA PRIVACY PROTECTIONS.—In implementing the pilot projects and utilizing new technologies, the Secretary shall safeguard the privacy and security of personal data collected during inspections through appropriate measures, including—
(A) adherence to relevant privacy laws and regulations;
(B) implementation of data anonymization techniques, if applicable; and
(C) regular audits to assess compliance with data privacy standards.
(5) SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DIRECTORATE.—The CBP Innovation Team shall work with the Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Directorate to align existing nonintrusive inspection research and development efforts within the Science and Technology Directorate when planning and developing pilot projects required under paragraph (1).
(b) Termination.—The pilot projects shall terminate on the date that is 5 years after the date of the enactment of this Act.
(c) Reports required.—Not later than 3 years after the date of the enactment of this Act, and 180 days after the termination of the pilot projects pursuant to subsection (b), the Secretary shall submit a report to the appropriate congressional committees that contains—
(1) an analysis of the effectiveness of technology enhancements tested based on the requirements described in subsection (a)(2);
(2) any recommendations from the testing and analysis concerning the ability to utilize such technologies at all land ports of entry;
(3) a plan to utilize new technologies that meet the performance goals of the pilot projects across all U.S. Customs and Border Protection land ports of entry at the border, including total costs and a breakdown of the costs of such plan, including any infrastructure improvements that may be required to accommodate recommended technology enhancements;
(4) a comprehensive list of existing technologies owned and utilized by U.S. Customs and Border protection for cargo and vehicle inspection, including—
(A) details on the implementation status of such technologies, such as whether the technologies have been fully installed and utilized, or whether there are challenges with the installation and utilization of the technology;
(B) an evaluation of the compatibility, interoperability, and scalability of existing cargo and vehicle inspection technologies within U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s physical and information technology infrastructure; and
(C) identification of any obstacles to the effective deployment and integration of such technologies; and
(5) the analysis described in subsection (d).
(d) Areas of analysis.—The report required under subsection (c) shall include an analysis containing—
(1) quantitative measurements of performance based on the requirements described in subsection (a)(2) of each technology tested compared with the status quo to reveal a broad picture of the performance of technologies and technology enhancements, such as—
(A) the probability of detection, false alarm rate, and throughput; and
(B) an analysis determining whether such observed performance represents a significant increase, decrease, or no change compared with current systems;
(2) an assessment of the relative merits of each such technology;
(3) any descriptive trends and patterns observed; and
(4) performance measures for—
(A) the technology enhancement’s ability to assist with the detection of contraband on inbound and outbound traffic through automated (primary) inspection by measuring and reporting the probability of detection and false alarm rate for each NII system under operational conditions;
(B) the throughput of cargo through each NII system with a technology enhancement, including a breakdown of the time needed for U.S. Customs and Border Protection—
(i) to complete the image review process and clear low-risk shipments; and
(ii) to complete additional inspections of high-risk items;
(C) changes in U.S. Customs and Border Protection officer time commitments and personnel needs to sustain high volume NII scanning operations when technology enhancements are utilized; and
(D) operational costs, including—
(i) estimated implementation costs for each NII system with technology enhancements; and
(ii) estimated cost savings due to improved efficiency due to technology enhancements, if applicable.
(e) Privacy and civil liberties reports.—The Secretary, in consultation with the CBP Innovation Team and other appropriate offices—
(1) prior to the implementation of the technologies referred to in this section, shall submit—
(A) a report or reports to the appropriate congressional committees regarding the potential privacy, civil liberties, and civil rights impacts of technologies being tested under the pilot projects pursuant to this section, including an analysis of the impacts of the technology enhancements on individuals crossing the United States border; and
(B) recommendations for mitigation measures to address any identified impacts; and
(2) not later than 180 days after the termination of the pilot projects pursuant to subsection (b), shall submit a report to the appropriate congressional committees containing—
(A) findings on the impacts to privacy, civil rights, and civil liberties resulting from the pilot projects;
(B) recommendations for mitigating these impacts in implementation of approved technologies; and
(C) any additional recommendations based on the lessons learned from the pilot projects.
SEC. 4. Prohibition on new appropriations.
No additional funds are authorized to be appropriated to carry out this Act.
S. 1138 – A bill to require the Secretary of Homeland Security to enhance capabilities for outbound inspections at the southern land border, and for other purposes.
Medicine
S.709 – Conrad State 30 and Physician Access Reauthorization Act
A bill to provide incentives to physicians to practice in rural and medically underserved communities, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Conrad State 30 program.
(a) Extension.—Section 220(c) of the Immigration and Nationality Technical Corrections Act of 1994 (Public Law 103–416; 8 U.S.C. 1182 note) is amended by striking “September 30, 2015” and inserting “on the date that is 3 years after the date of the enactment of the Conrad State 30 and Physician Access Reauthorization Act”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by subsection (a) shall take effect as if enacted on September 30, 2018.
SEC. 3. Retaining physicians who have practiced in medically underserved communities.
Section 201(b)(1) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1151(b)(1)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(F) (i) Alien physicians who have completed service requirements of a waiver requested under section 203(b)(2)(B)(ii), including—
“(I) alien physicians who completed such service before the date of the enactment of the Conrad State 30 and Physician Access Act; and
“(II) the spouse or children of an alien physician described in subclause (I).
“(ii) Nothing in this subparagraph may be construed—
“(I) to prevent the filing of a petition with the Secretary of Homeland Security for classification under section 204(a) or the filing of an application for adjustment of status under section 245 by an alien physician described in this subparagraph before the date by which such alien physician has completed the service described in section 214(l) or worked full-time as a physician for an aggregate of 5 years at the location identified in the section 214(l) waiver or in an area or areas designated by the Secretary of Health and Human Services as having a shortage of health care professionals; or
“(II) to permit the Secretary of Homeland Security to grant a petition or application described in subclause (I) until the alien has satisfied all of the requirements of the waiver received under section 214(l).”.
SEC. 4. Employment protections for physicians.
(a) Exceptions to 2-Year foreign residency requirement.—Section 214(l)(1) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1184(l)(1)) is amended—
(1) in the matter preceding subparagraph (A), by striking “Attorney General” and inserting “Secretary of Homeland Security”;
(2) in subparagraph (A), by striking “Director of the United States Information Agency” and inserting “Secretary of State”;
(3) in subparagraph (B), by inserting “, except as provided in paragraphs (7) and (8)” before the semicolon at the end;
(4) in subparagraph (C), by striking clauses (i) and (ii) and inserting the following:
“(i) the alien demonstrates a bona fide offer of full-time employment at a health facility or health care organization, which employment has been determined by the Secretary of Homeland Security to be in the public interest; and
“(ii) the alien—
“(I) has accepted employment with the health facility or health care organization in a geographic area or areas which are designated by the Secretary of Health and Human Services as having a shortage of health care professionals;
“(II) begins employment by the later of the date that is—
“(aa) 120 days after receiving such waiver;
“(bb) 120 days after completing graduate medical education or training under a program approved pursuant to section 212(j)(1); or
“(cc) 120 days after receiving nonimmigrant status or employment authorization, if the alien or the alien’s employer petitions for such nonimmigrant status or employment authorization not later than 120 days after the date on which the alien completes his or her graduate medical education or training under a program approved pursuant to section 212(j)(1); and
“(III) agrees to continue to work for a total of not less than 3 years in the status authorized for such employment under this subsection, except as provided in paragraph (8).”; and
(5) in subparagraph (D), in the matter preceding clause (i), by inserting “(except as provided in paragraph (8))” after “3 years”.
(b) Allowable visa status for physicians fulfilling waiver requirements in medically underserved areas.—Section 214(l)(2)(A) of such Act (8 U.S.C. 1184(l)(2)(A)) is amended to read as follows:
“(A) Upon the request of an interested Federal agency or an interested State agency for recommendation of a waiver under this section by a physician who is maintaining valid nonimmigrant status under section 101(a)(15)(J) and a favorable recommendation by the Secretary of State, the Secretary of Homeland Security may change the status of such physician to any status authorized for employment under this Act. The numerical limitations contained in subsection (g)(1)(A) shall not apply to any alien whose status is changed under this subparagraph.”.
(c) Violation of agreements.—Section 214(l)(3)(A) of such Act (8 U.S.C. 1184(l)(3)(A)) is amended by inserting “substantial requirement of an” before “agreement entered into”.
(d) Physician employment in underserved areas.—Section 214(l) of such Act, as amended by this section, is further amended by adding at the end the following:
“(4) (A) If an interested State agency denies an application for a waiver under paragraph (1)(B) from a physician pursuing graduate medical education or training pursuant to section 101(a)(15)(J) because the State has requested the maximum number of waivers permitted for that fiscal year, the physician’s nonimmigrant status shall be extended for up to 6 months if the physician agrees to seek a waiver under this subsection (except for paragraph (1)(D)(ii)) to work for an employer described in paragraph (1)(C) in a State that has not yet requested the maximum number of waivers.
“(B) Such physician shall be authorized to work only for the employer referred to in subparagraph (A) during the period beginning on the date on which a new waiver application is filed with such State and ending on the earlier of—
“(i) the date on which the Secretary of Homeland Security denies such waiver; or
“(ii) the date on which the Secretary approves an application for change of status under paragraph (2)(A) pursuant to the approval of such waiver.”.
(e) Contract requirements.—Section 214(l) of such Act, as amended by this section, is further amended by adding at the end the following:
“(5) An alien granted a waiver under paragraph (1)(C) shall enter into an employment agreement with the contracting health facility or health care organization that—
“(A) specifies the maximum number of on-call hours per week (which may be a monthly average) that the alien will be expected to be available and the compensation the alien will receive for on-call time;
“(B) specifies—
“(i) whether the contracting facility or organization—
“(I) has secured medical malpractice liability protection for the alien under section 224(g) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 233(g)); or
“(II) will pay the alien’s malpractice insurance premiums;
“(ii) whether the employer will provide malpractice insurance for the alien; and
“(iii) the amount of such liability protection that will be provided;
“(C) describes all of the work locations that the alien will work and includes a statement that the contracting facility or organization will not add additional work locations without the approval of the Federal agency or State agency that requested the waiver; and
“(D) does not include a non-compete provision.
“(6) An alien granted a waiver under this subsection whose employment relationship with a health facility or health care organization terminates under paragraph (1)(C)(ii) during the 3-year service period required under paragraph (1) shall be considered to be maintaining lawful status in an authorized period of stay during the 120-day period referred to in items (aa) and (bb) of subclause (III) of paragraph (1)(C)(ii) or the 45-day period referred to in subclause (III)(cc) of such paragraph.”.
(f) Recapturing waiver slots lost to other States.—Section 214(l) of such Act, as amended by this section, is further amended by adding at the end the following:
“(7) If a recipient of a waiver under this subsection terminates the recipient’s employment with a health facility or health care organization pursuant to paragraph (1)(C)(ii), including termination of employment because of circumstances described in paragraph (1)(C)(ii)(III), and accepts new employment with such a facility or organization in a different State, the State from which the alien is departing may be accorded an additional waiver by the Secretary of State for use in the fiscal year in which the alien’s employment was terminated.”.
(g) Exception to 3-Year work requirement.—Section 214(l) of such Act, as amended by this section, is further amended by adding at the end the following:
“(8) The 3-year work requirement set forth in subparagraphs (C) and (D) of paragraph (1) shall not apply if—
“(A) (i) the Secretary of Homeland Security determines that extenuating circumstances, including violations by the employer of the employment agreement with the alien or of labor and employment laws, exist that justify a lesser period of employment at such facility or organization; and
“(ii) the alien demonstrates, not later than 120 days after the employment termination date (unless the Secretary determines that extenuating circumstances would justify an extension), another bona fide offer of employment at a health facility or health care organization in a geographic area or areas which are designated by the Secretary of Health and Human Services as having a shortage of health care professionals, for the remainder of such 3-year period;
“(B) (i) the interested State agency that requested the waiver attests that extenuating circumstances, including violations by the employer of the employment agreement with the alien or of labor and employment laws, exist that justify a lesser period of employment at such facility or organization; and
“(ii) the alien demonstrates, not later than 120 days after the employment termination date (unless the Secretary determines that extenuating circumstances would justify an extension), another bona fide offer of employment at a health facility or health care organization in a geographic area or areas which are designated by the Secretary of Health and Human Services as having a shortage of health care professionals, for the remainder of such 3-year period; or
“(C) the alien—
“(i) elects not to pursue a determination of extenuating circumstances pursuant to subclause (A) or (B);
“(ii) terminates the alien’s employment relationship with the health facility or health care organization at which the alien was employed;
“(iii) demonstrates, not later than 45 days after the employment termination date, another bona fide offer of employment at a health facility or health care organization in a geographic area or areas, in the State that requested the alien’s waiver, which are designated by the Secretary of Health and Human Services as having a shortage of health care professionals; and
“(iv) agrees to be employed for the remainder of such 3-year period, and 1 additional year for each termination under clause (ii).”.
SEC. 5. Allotment of Conrad 30 waivers.
(a) In general.—Section 214(l) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1184(l)), as amended by section 4, is further amended by adding at the end the following:
“(9) (A) (i) All States shall be allotted a total of 35 waivers under paragraph (1)(B) for a fiscal year if 90 percent of the waivers available to the States receiving at least 5 waivers were used in the previous fiscal year.
“(ii) When an allotment occurs under clause (i), all States shall be allotted an additional 5 waivers under paragraph (1)(B) for each subsequent fiscal year if 90 percent of the waivers available to the States receiving at least 5 waivers were used in the previous fiscal year. If the States are allotted 45 or more waivers for a fiscal year, the States will only receive an additional increase of 5 waivers the following fiscal year if 95 percent of the waivers available to the States receiving at least 1 waiver were used in the previous fiscal year.
“(B) Any increase in allotments under subparagraph (A) shall be maintained indefinitely, unless in a fiscal year, the total number of such waivers granted is 5 percent lower than in the last year in which there was an increase in the number of waivers allotted pursuant to this paragraph, in which case—
“(i) the number of waivers allotted shall be decreased by 5 for all States beginning in the next fiscal year; and
“(ii) each additional 5 percent decrease in such waivers granted from the last year in which there was an increase in the allotment, shall result in an additional decrease of 5 waivers allotted for all States, provided that the number of waivers allotted for all States shall not drop below 30.”.
(b) Academic medical centers.—Section 214(l)(1)(D) of such Act (8 U.S.C. 1184(l)(1)(D)), as amended by section 4(a)(5), is further amended—
(1) in clause (ii), by striking “and” at the end;
(2) in clause (iii), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(iv) in the case of a request by an interested State agency—
“(I) the head of such agency determines that the alien is to practice medicine in, or be on the faculty of a residency program at, an academic medical center (as that term is defined in section 411.355(e)(2) of title 42, Code of Federal Regulations, or similar successor regulation), without regard to whether such facility is located within an area designated by the Secretary of Health and Human Services as having a shortage of health care professionals; and
“(II) the head of such agency determines that—
“(aa) the alien physician’s work is in the public interest; and
“(bb) the grant of such waiver would not cause the number of the waivers granted on behalf of aliens for such State for a fiscal year (within the limitation in subparagraph (B) and subject to paragraph (6)) in accordance with the conditions of this clause to exceed 3.”.
SEC. 6. Amendments to the procedures, definitions, and other provisions related to physician immigration.
(a) Dual intent for physicians seeking graduate medical training.—Section 214(b) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1184(b)) is amended by striking “(other than a nonimmigrant described in subparagraph (L) or (V) of section 101(a)(15), and other than a nonimmigrant described in any provision of section 101(a)(15)(H)(i) except subclause (b1) of such section)” and inserting “(other than a nonimmigrant described in subparagraph (L) or (V) of section 101(a)(15), a nonimmigrant described in any provision of section 101(a)(15)(H)(i) (except subclause (b1) of such section), and an alien coming to the United States to receive graduate medical education or training described in section 212(j) or to take examinations required to receive graduate medical education or training described in section 212(j))”.
(b) Physician national interest waiver clarifications.—
(1) PRACTICE AND GEOGRAPHIC AREA.—Section 203(b)(2)(B)(ii)(I) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1153(b)(2)(B)(ii)(I)) is amended by striking items (aa) and (bb) and inserting the following:
“(aa) the alien physician agrees to work on a full-time basis practicing primary care, specialty medicine, or a combination thereof, in an area or areas designated by the Secretary of Health and Human Services as having a shortage of health care professionals, or at a health care facility under the jurisdiction of the Secretary of Veterans Affairs; or
“(bb) the alien physician is pursuing such waiver based upon service at a facility or facilities that serve patients who reside in a geographic area or areas designated by the Secretary of Health and Human Services as having a shortage of health care professionals (without regard to whether such facility or facilities are located within such an area) and a Federal agency, or a local, county, regional, or State department of public health determines the alien physician’s work was or will be in the public interest.”.
(2) FIVE-YEAR SERVICE REQUIREMENT.—Section 203(b)(2)(B)(ii) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1153(B)(ii)) is amended—
(A) by moving subclauses (II), (III), and (IV) 4 ems to the left; and
(B) in subclause (II)—
(i) by inserting “(aa)” after “(II)”; and
(ii) by adding at the end the following:
“(bb) The 5-year service requirement under item (aa) shall begin on the date on which the alien physician begins work in the shortage area in any legal status and not on the date on which an immigrant visa petition is filed or approved. Such service shall be aggregated without regard to when such service began and without regard to whether such service began during or in conjunction with a course of graduate medical education.
“(cc) An alien physician shall not be required to submit an employment contract with a term exceeding the balance of the 5-year commitment yet to be served or an employment contract dated within a minimum time period before filing a visa petition under this subsection.
“(dd) An alien physician shall not be required to file additional immigrant visa petitions upon a change of work location from the location approved in the original national interest immigrant petition.”.
(c) Technical clarification regarding advanced degree for physicians.—Section 203(b)(2)(A) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1153(b)(2)(A)) is amended by adding at the end the following: “An alien physician holding a foreign medical degree that has been deemed sufficient for acceptance by an accredited United States medical residency or fellowship program is a member of the professions holding an advanced degree or its equivalent.”.
(d) Short-Term work authorization for physicians completing their residencies.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—A physician completing graduate medical education or training described in section 212(j) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1182(j)) as a nonimmigrant described in section 101(a)(15)(H)(i) of such Act (8 U.S.C. 1101(a)(15)(H)(i))—
(A) shall have such nonimmigrant status automatically extended until October 1 of the fiscal year for which a petition for a continuation of such nonimmigrant status has been submitted in a timely manner and the employment start date for the beneficiary of such petition is October 1 of that fiscal year; and
(B) shall be authorized to be employed incident to status during the period between the filing of such petition and October 1 of such fiscal year.
(2) TERMINATION.—The physician’s status and employment authorization shall terminate on the date that is 30 days after the date on which a petition described in paragraph (1)(A) is rejected, denied or revoked.
(3) AUTOMATIC EXTENSION.—A physician’s status and employment authorization will automatically extend to October 1 of the next fiscal year if all of the visas described in section 101(a)(15)(H)(i) of such Act that were authorized to be issued for the fiscal year have been issued.
(e) Applicability of section 212(e) to spouses and children of J–1 exchange visitors.—A spouse or child of an exchange visitor described in section 101(a)(15)(J) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1101(a)(15)(J)) shall not be subject to the requirements under section 212(e) of such Act (8 U.S.C. 1182(e)).
SEC. 7. Annual Conrad State 30 J–1 Visa Waiver Program statistical report.
The Director of U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services shall submit an annual report to Congress and to the Department of Health and Human Services that identifies the number of aliens admitted during the most recently concluded fiscal year as a result of the Conrad State 30 J–1 Visa Waiver Program established under sections 212(e) and 214(l) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (8 U.S.C. 1182(e) and 1184(l)), disaggregated by State.
S.942 – REDI Act or Resident Education Deferred Interest Act
A bill to amend the Higher Education Act of 1965 to provide for interest-free deferment on student loans for borrowers serving in a medical or dental internship or residency program.
SEC. 2. Deferment during a medical or dental internship or residency program.
Section 455(f) of the Higher Education Act of 1965 (20 U.S.C. 1087e(f)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1), in the matter preceding subparagraph (A), by striking “A borrower” and inserting “Except as provided in paragraph (6), a borrower”;
(2) in paragraph (2)(A)—
(A) in clause (i), by striking “or” after the semicolon;
(B) by striking the matter following clause (ii);
(C) in clause (ii), by striking the comma at the end and inserting “; or”; and
(D) by adding at the end the following:
“(iii) is serving in a medical or dental internship or residency program;”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(6) SPECIAL RULE FOR CERTAIN IN SCHOOL DEFERMENT.—Notwithstanding any other provision of this Act, a borrower described in paragraph (2)(A)(iii) shall be eligible for a deferment, during which periodic installments of principal need not be paid and interest shall not accrue on any loan made to the borrower under this part.”.
S.946 – MATE Improvement Act or the Medication Access and Training Expansion Improvement Act
A bill to clarify training requirements for prescribers of controlled substances.
SEC. 2. Required training for prescribers of controlled substances.
(a) In general.—Section 303 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 823) is amended—
(1) by redesignating the second subsection designated as subsection (l) as subsection (m); and
(2) in subsection (m)(1), as so redesignated—
(A) in subparagraph (A)—
(i) in clause (iv)—
(I) in subclause (I)—
(aa) by inserting “the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Podiatric Medical Association, the Academy of General Dentistry, the American Optometric Association,” before “or any other organization”;
(bb) by striking “or the Commission” and inserting “, the Commission”; and
(cc) by inserting “, or the Council on Podiatric Medical Education” before the semicolon at the end; and
(II) in subclause (III), by inserting “or the American Academy of Family Physicians” after “Association”; and
(ii) in clause (v), in the matter preceding subclause (I)—
(I) by striking “osteopathic medicine, dental surgery” and inserting “osteopathic medicine, podiatric medicine, dental surgery”; and
(II) by striking “or dental medicine curriculum” and inserting “or dental or podiatric medicine curriculum”; and
(B) in subparagraph (B)—
(i) in clause (i)—
(I) by inserting “the American Pharmacists Association, the Accreditation Council on Pharmacy Education, the American Psychiatric Nurses Association, the American Academy of Nursing, the American Academy of Family Physicians,” before “or any other organization”; and
(II) by inserting “, the American Academy of Family Physicians,” before “or the Accreditation Council”; and
(ii) in clause (ii)—
(I) by striking “or accredited school” and inserting “, an accredited school”; and
(II) by inserting “, or an accredited school of pharmacy” before “in the United States”.
(b) Effective Date.—The amendments made by subsection (a) shall take effect as if enacted on December 29, 2022.
S.975 – Expanding Medical Education Act
A bill to establish a grant program to support schools of medicine and schools of osteopathic medicine in underserved areas.
SEC. 2. Grants for schools of medicine and schools of osteopathic medicine in underserved areas.
Subpart II of part C of title VII of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 293m et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 749C. Grants for schools of medicine and schools of osteopathic medicine in underserved areas.
“(a) In general.—The Secretary may award grants to institutions of higher education (including consortiums of such institutions) for the establishment, improvement, or expansion of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, or a branch campus of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine.
“(b) Priority.—In selecting grant recipients under this section, the Secretary shall give priority to any institution of higher education (or consortium of such institutions) that—
“(1) proposes to use the grant for the establishment of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, or a branch campus of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, in an area—
“(A) in which—
“(i) no other such school is based; or
“(ii) in the case in which the school of medicine or osteopathic medicine proposed to be established would be a minority-serving institution, no other minority-serving institution that includes a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine is based; and
“(B) that is a medically underserved community or a health professional shortage area; or
“(2) is a minority-serving institution described in section 371(a) of the Higher Education Act of 1965 or an institution or program described in section 326(e) of such Act.
“(c) Considerations.—In awarding grants under this section, the Secretary, to the extent practicable, may ensure equitable distribution of awards among the geographical regions of the United States.
“(d) Use of funds.—An institution of higher education (or a consortium of such institutions)—
“(1) shall use grant amounts received under this section to—
“(A) recruit, enroll, and retain medical students who are pursuing a degree of doctor of medicine or doctor of osteopathy, including individuals who are from disadvantaged backgrounds (including racial and ethnic groups underrepresented among medical students and health professions), individuals from rural and underserved areas, low-income individuals, and first generation college students, at a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine or branch campus of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine; and
“(B) develop, implement, and expand curriculum that emphasizes care for rural and underserved populations, including accessible and culturally and linguistically appropriate care and services, at such school or branch campus; and
“(2) may use grant amounts received under this section to—
“(A) plan and construct—
“(i) a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, or a branch campus of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, in an area in which no other such school is based; or
“(ii) a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, or a branch campus of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, that will be a minority-serving institution, in an area in which no other such school that is a minority-serving institution is based;
“(B) plan, develop, and meet criteria for accreditation for a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine or branch campus of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine;
“(C) hire faculty, including faculty from racial and ethnic groups who are underrepresented among the medical and other health professions, and other staff to serve at such a school or branch campus;
“(D) support educational programs at such a school or branch campus;
“(E) modernize and expand infrastructure at such a school or branch campus; and
“(F) support other activities that the Secretary determines further the establishment, improvement, or expansion of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine or branch campus of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine.
“(e) Application.—To be eligible to receive a grant under subsection (a), an institution of higher education (or a consortium of such institutions), shall submit an application to the Secretary at such time, in such manner, and containing such information as the Secretary may require, including a description of the institution’s or consortium’s planned activities described in subsection (d).
“(f) Reporting.—
“(1) REPORTS FROM ENTITIES.—Each institution of higher education, or consortium of such institutions, awarded a grant under this section shall submit an annual report to the Secretary on the activities conducted under such grant, and other information as the Secretary may require.
“(2) REPORT TO CONGRESS.—Not later than 5 years after the date of enactment of this section and every 5 years thereafter, the Secretary shall submit to the Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions of the Senate and the Committee on Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives a report that provides a summary of the activities and outcomes associated with grants made under this section. Such reports shall include—
“(A) a list of awardees, including their primary geographic location, and location of any school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, or a branch campus of school of medicine or osteopathic medicine that was established, improved, or expanded under this program;
“(B) the total number of students (including the number of students from racial and ethnic groups underrepresented among medical students and health professions, low-income students, and first generation college students) who—
“(i) are enrolled at or who have graduated from any school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, or a branch campus of school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, that was established, improved, or expanded under this program, deidentified and disaggregated by race, ethnicity, age, sex, geographic region, disability status, and other relevant factors, to the extent such information is available; and
“(ii) who subsequently participate in an accredited internship or medical residency program upon graduation from any school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, or a branch campus of a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, that was established, improved, or expanded under this program, deidentified and disaggregated by race, ethnicity, age, sex, geographic region, disability status, medical specialty pursued, and other relevant factors, to the extent such information is available;
“(C) the effects of such program on the health care provider workforce, including any impact on demographic representation disaggregated by race, ethnicity, and sex, and the fields or specialties pursued by students who have graduated from any school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, or a branch campus of school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, that was established, improved, or expanded under this program;
“(D) the effects of such program on health care access in underserved areas, including medically underserved communities and health professional shortage areas; and
“(E) recommendations for improving the program described in this section, and any other considerations as the Secretary determines appropriate.
“(3) PUBLIC AVAILABILITY.—The Secretary shall make reports submitted under paragraph (2) publicly available on the website of the Department of Health and Human Services.
“(g) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) BRANCH CAMPUS.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The term ‘branch campus’, with respect to a school of medicine or osteopathic medicine, means an additional location of such school that is geographically apart and independent of the main campus, at which the school offers at least 50 percent of the program leading to a degree of doctor of medicine or doctor of osteopathy that is offered at the main campus.
“(B) INDEPENDENCE FROM MAIN CAMPUS.—For purposes of subparagraph (A), the location of a school described in such subparagraph shall be considered to be independent of the main campus described in such subparagraph if the location—
“(i) is permanent in nature;
“(ii) offers courses in educational programs leading to a degree, certificate, or other recognized educational credential;
“(iii) has its own faculty and administrative or supervisory organization; and
“(iv) has its own budgetary and hiring authority.
“(2) FIRST GENERATION COLLEGE STUDENT.—The term ‘first generation college student’ has the meaning given such term in section 402A(h)(3) of the Higher Education Act of 1965.
“(3) HEALTH PROFESSIONAL SHORTAGE AREA.—The term ‘health professional shortage area’ has the meaning given such term in section 332(a).
“(4) INSTITUTION OF HIGHER EDUCATION.—The term ‘institution of higher education’ has the meaning given such term in section 101 of the Higher Education Act of 1965.
“(5) MEDICALLY UNDERSERVED COMMUNITY.—The term ‘medically underserved community’ has the meaning given such term in section 799B(6).
“(h) Authorization of appropriations.—There is authorized to be appropriated such sums as may be necessary to carry out this section.”.
S.922 – A bill to amend the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act to define the term evidence-based.
SECTION 1. Evidence-based definition.
(a) In general.—Section 3 of the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (29 U.S.C. 3102) is amended by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(72) EVIDENCE-BASED.—The term ‘evidence-based’, when used with respect to an activity, service, strategy, or intervention, or content of materials, means an activity, service, strategy, or intervention, or content of materials that—
“(A) demonstrates a statistically significant effect on improving participant outcomes or other relevant outcomes based on—
“(i) strong evidence from at least 1 well-designed and well-implemented experimental study;
“(ii) moderate evidence from at least 1 well-designed and well-implemented quasi-experimental study; or
“(iii) promising evidence from at least 1 well-designed and well-implemented correlational study with statistical controls for selection bias; or
“(B) (i) demonstrates a rationale based on high-quality research findings or positive evaluation that such activity, service, strategy, intervention, or content is likely to improve student outcomes or other relevant outcomes; and
“(ii) includes ongoing efforts to examine the effects of such activity, service, strategy, intervention, or content.”.
(b) Description of evidence-Based programs.—Section 102(b)(1) of the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (29 U.S.C. 3112(b)(1)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (C), by inserting “the extent to which such activities are evidence-based,” after “of such activities,”;
(2) in subparagraph (D), by striking “and” at the end;
(3) in subparagraph (E), by striking the period and inserting “; and”; and
(4) by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(F) a description of any strategies the State will use to prioritize the funding of evidence-based programs through the funds reserved as described in section 128(a) and available for statewide workforce development activities.”.
What bill: A bill to amend the Public Health Service Act to authorize fellowships under the Minority Fellowship Program to be awarded for training for professionals in the addiction medicine field.
S.1044 – Physicians for Underserved Areas Act
A bill to amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to make improvements to the redistribution of residency slots under the Medicare program after a hospital closes.
SEC. 2. Improvements to the redistribution of residency slots under the Medicare program after a hospital closes.
(a) In general.—Section 1886(h)(4)(H)(vi) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395ww(h)(4)(H)(vi)) is amended—
(1) in subclause (II)—
(A) by striking item (cc) and redesignating item (dd) as item (cc); and
(B) in item (cc), as redesignated under subparagraph (A)—
(i) by striking “Fourth” and inserting “Third”; and
(ii) by striking “item (cc)” and inserting “item (bb)”; and
(2) in subclause (III), by striking “likelihood of filling” and all that follows and inserting the following: “likelihood of—
“(aa) starting to utilize the positions made available under this clause within 2 years; and
“(bb) filling the positions made available under this clause within 5 years.”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendments made by subsection (a) shall apply to the redistribution of residency slots with respect to hospitals that close on or after the date of enactment of this Act.
S.1062 – Suicide Prevention Act
A bill to authorize a pilot program to expand and intensify surveillance of self-harm in partnership with State and local public health departments, to establish a grant program to provide self-harm and suicide prevention services in hospital emergency departments, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Syndromic surveillance of self-harm behaviors program.
Title III of the Public Health Service Act is amended by inserting after section 317V of such Act (42 U.S.C. 247b–24) the following:
“SEC. 317W. Syndromic surveillance of self-harm behaviors program.
“(a) In general.—The Secretary shall award grants to State, local, Tribal, and territorial public health departments for the expansion of surveillance of self-harm.
“(b) Data sharing by grantees.—As a condition of receipt of such grant under subsection (a), each grantee shall agree to share with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in real time, to the extent feasible and as specified in the grant agreement, data on suicides and self-harm for purposes of—
“(1) tracking and monitoring self-harm to inform response activities to suicide clusters;
“(2) informing prevention programming for identified at-risk populations; and
“(3) conducting or supporting research.
“(c) Disaggregation of data.—The Secretary shall provide for the data collected through surveillance of self-harm under subsection (b) to be disaggregated by the following categories:
“(1) Nonfatal self-harm data of any intent.
Healthcare
S.36 – Protect Our Seniors Act
To protect the seniors of the United States, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Point of order for reductions in Medicare and Social Security benefits.
Section 301 of the Congressional Budget Act of 1974 (2 U.S.C. 632) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(j) Medicare and Social Security point of order.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—It shall not be in order in the Senate to consider any bill or resolution (or amendment, motion, or conference report on that bill or resolution) that would reduce benefits under the Medicare program under title XVIII of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395 et seq.) or benefits payable under title II of that Act (42 U.S.C. 401 et seq.).
“(2) WAIVER.—Paragraph (1) may be waived or suspended in the Senate only by the affirmative vote of two-thirds of the Members, duly chosen and sworn.”.
SEC. 3. Medicare point of order.
Section 301 of the Congressional Budget Act of 1974 (2 U.S.C. 632), as amended by section 3, is further amended by adding at the end the following:
“(k) Medicare point of order.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—It shall not be in order in the Senate to consider any bill or resolution (or amendment, motion, or conference report on that bill or resolution) for which the total budgetary effects of the measure, as determined by the Congressional Budget Office, use a decrease in outlays, or an increase in revenue, under the health insurance programs under title XVIII of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395 et seq.) to offset a cost of a provision of the measure that is not for the purpose of carrying out those programs.
“(2) WAIVER.—Paragraph (1) may be waived or suspended in the Senate only by the affirmative vote of two-thirds of the Members, duly chosen and sworn. An affirmative vote of two-thirds of the Members of the Senate, duly chosen and sworn, shall be required to sustain an appeal of the ruling of the Chair on a point of order raised under paragraph (1).”.
S. 106 – Chiropractic Medicare Coverage Modernization Act of 2025
To amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to provide Medicare coverage for all physicians’ services furnished by doctors of chiropractic within the scope of their license, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Findings; Statement of purpose.
(a) Findings.—Congress finds the following:
(1) In 1972, coverage was established under the Medicare program for beneficiaries to receive chiropractic care.
(2) Unfortunately, the antiquated statute restricts beneficiaries to one service in a chiropractic clinic and Medicare chiropractic coverage has not kept up with private sector coverage and other Federal health delivery systems.
(3) Today, due to positive evidence-based outcomes and cost effectiveness of the services provided by doctors of chiropractic, private coverage for chiropractic services has evolved and State licensure for chiropractors has advanced to meet patient needs and health outcomes.
(4) This Act would bring Medicare chiropractic coverage more in line with that provided with the Department of Veterans Affairs, Department of Defense, the Federal Employee Health Benefits Program, and private health insurance coverage.
(b) Purpose.—It is the purpose of this Act to expand recognition and coverage of a doctor of chiropractic as a “physician” under the Medicare program in connection with the performance of any function or action, including current service of “manual manipulation of the spine to correct a subluxation”, as is legally authorized by the State in which such doctor performs such function or action.
SEC. 3. Providing Medicare coverage for all physicians’ services furnished by doctors of chiropractic within the scope of their license.
(a) In general.—Section 1861(r)(5) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(r)(5)) is amended by striking “a chiropractor who is licensed as such by the State (or in a State which does not license chiropractors as such, is legally authorized to perform the services of a chiropractor in the jurisdiction in which he performs such services), and who meets uniform minimum standards promulgated by the Secretary, but only for the purpose of sections 1861(s)(1) and 1861(s)(2)(A) and only with respect to treatment by means of manual manipulation of the spine (to correct a subluxation) which he is legally authorized to perform by the State or jurisdiction in which such treatment is provided” and inserting “a doctor of chiropractic who is licensed as a doctor of chiropractic or a chiropractor by the State in which the function or action is performed and whose license provides legal authorization to perform such function or action in such State or in the jurisdiction in which the function or action is performed”.
(b) Certain coverage limits.—Section 1833 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395l) is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(ee) Limitation on payment of services provided by certain doctors of chiropractic.—Notwithstanding any other provision of this part, in the case of services of a doctor of chiropractic described in section 1861(r)(5), payment may only be made under this part for such services if—
“(1) such services are furnished by a doctor of chiropractic who is verified once, by a process designed by the Secretary, as attending an educational documentation webinar, or other similar electronic product, designed by the Secretary or an updated modified version of such webinar, as designed by the Secretary; or
“(2) such services are treatment by means of manual manipulation of the spine to correct a subluxation.”.
S. 208 – A bill to amend the Public Health Service Act to reauthorize the Stop, Observe, Ask, and Respond to Health and Wellness Training Program.
SECTION 1. Reauthorization of the SOAR to Health and Wellness Training Program.
(a) In general.—Section 1254(h) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 300d–54(h)) is amended by striking “fiscal years 2020 through 2024” and inserting “fiscal years 2025 through 2029”.
(b) Rescission of funds.—Of the unobligated balances in the Nonrecurring Expenses Fund (009–90–0125) of the Department of Health and Human Services, there is rescinded $20,000,000.
S. 763 – Telehealth Expansion Act of 2025
A bill to amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to permanently extend the exemption for telehealth services from certain high deductivle health plan rules.
SEC. 2. Exemption for telehealth services.
(a) In general.—Subparagraph (E) of section 223(c)(2) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to read as follows:
“(E) SAFE HARBOR FOR ABSENCE OF DEDUCTIBLE FOR TELEHEALTH.—A plan shall not fail to be treated as a high deductible health plan by reason of failing to have a deductible for telehealth and other remote care services.”.
(b) Certain coverage disregarded.—Clause (ii) of section 223(c)(1)(B) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by striking “(in the case of months or plan years to which paragraph (2)(E) applies)”.
(c) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply to plan years beginning after December 31, 2024.
S. 786 – Public Health Funding Restoration Act
A bill to fully fund the Prevention and Public Health Fund and reaffirm the importance of prevention in the United States healthcare system.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) The Prevention and Public Health Fund (section 4002 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (42 U.S.C. 300u–11) was designed “to provide for expanded and sustained national investment in prevention and public health programs to improve health and help restrain the rate of growth in private and public health care costs”.
(2) Funding under such section is essential to core efforts at the Department of Health and Human Services and in State, local, Tribal, and territorial health departments to prevent and control the spread of infectious disease and prevent injuries and the development of chronic conditions.
(3) Prevention and Public Health Fund dollars support evidenced-based investments in tobacco use prevention and cessation, nutrition, mental health, childhood lead poisoning prevention, elder care initiatives, and immunizations, among other prevention initiatives. Funding gives States and communities the flexibility to respond to public health threats that may be unique to their communities and bolsters the State, local, Tribal, and territorial response to global public health threats.
(4) Such prevention efforts have shown to be effective. Funding increases for community-based public health programs reduce infant deaths and preventable deaths caused by cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Every dollar spent on prevention saves nearly $6 in health spending and every dollar spent on childhood vaccines saves $16.50 in future health care costs.
(5) Investments in prevention reduce the cost of health care in the United States. $2,900,000,000 in investments in community-based disease prevention is estimated to save $16,500,000,000 annually within 5 years.
(6) Cuts to the Prevention and Public Health Fund and other public health prevention efforts undermine efforts to create an affordable and accessible health care system, and a better quality of life for Americans.
(7) Cuts to the Prevention and Public Health Fund endanger the ability of States and localities to distribute vaccinations and public health information successfully. The Prevention and Public Health Fund is critical to the growth of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s section 317 Immunization Program and to the Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity program.
(8) Restoring Prevention and Public Health Fund funding to $2,000,000,000 annually will allow the Fund to invest in more innovative, evidence-based public health programs and maintain and expand investments in programs with demonstrated success.
(9) Restoring Prevention and Public Health Fund funding to $2,000,000,000 will give the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and State, local, Tribal, and territorial health departments funding that they need to invest in prevention efforts that will help the country avoid future pandemics and epidemics.
SEC. 3. Prevention and public health fund.
Section 4002(b) of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (42 U.S.C. 300u–11(b)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (4), by adding at the end “and”; and
(2) by striking paragraphs (5) through (10) and inserting the following:
“(5) for fiscal year 2026 and each fiscal year thereafter, $2,000,000,000.”.
S. 891 – Bipartisan Health Care Act.
- Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness and Response Act
- SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Reauthorization Act of 2025
A bill to extend expiring health provisions and improve health care delivery.
SECTION 1. Short title; table of contents.
(a) Short title.—This Act may be cited as the “Bipartisan Health Care Act”.
(b) Table of contents.—The table of contents for this Act is as follows:
Sec. 1. Short title; table of contents.
Sec. 101. Streamlined enrollment process for eligible out-of-state providers under Medicaid and CHIP.
Sec. 102. Making certain adjustments to coverage of home or community-based services under Medicaid.
Sec. 103. Removing certain age restrictions on Medicaid eligibility for working adults with disabilities.
Sec. 104. Medicaid State plan requirement for determining residency and coverage for military families.
Sec. 105. Ensuring the reliability of address information provided under the Medicaid program.
Sec. 106. Codifying certain Medicaid provider screening requirements related to deceased providers.
Sec. 107. Modifying certain State requirements for ensuring deceased individuals do not remain enrolled.
Sec. 108. One-year delay of Medicaid and CHIP requirements for health screenings, referrals, and case management services for eligible juveniles in public institutions; State interim work plans.
Sec. 109. State studies and HHS report on costs of providing maternity, labor, and delivery services.
Sec. 110. Modifying certain disproportionate share hospital allotments.
Sec. 111. Modifying certain limitations on disproportionate share hospital payment adjustments under the Medicaid program.
Sec. 112. Ensuring accurate payments to pharmacies under Medicaid.
Sec. 113. Preventing the use of abusive spread pricing in Medicaid.
Sec. 201. Extension of increased inpatient hospital payment adjustment for certain low-volume hospitals.
Sec. 202. Extension of the Medicare-dependent hospital (MDH) program.
Sec. 203. Extension of add-on payments for ambulance services.
Sec. 204. Extending incentive payments for participation in eligible alternative payment models.
Sec. 205. Temporary payment increase under the Medicare physician fee schedule to account for exceptional circumstances.
Sec. 206. Extension of funding for quality measure endorsement, input, and selection.
Sec. 207. Extension of funding outreach and assistance for low-income programs.
Sec. 208. Extension of the work geographic index floor.
Sec. 209. Extension of certain telehealth flexibilities.
Sec. 210. Requiring modifier for use of telehealth to conduct face-to-face encounter prior to recertification of eligibility for hospice care.
Sec. 211. Extending acute hospital care at home waiver flexibilities.
Sec. 212. Enhancing certain program integrity requirements for DME under Medicare.
Sec. 213. Guidance on furnishing services via telehealth to individuals with limited English proficiency.
Sec. 214. In-home cardiopulmonary rehabilitation flexibilities.
Sec. 215. Inclusion of virtual diabetes prevention program suppliers in MDPP Expanded Model.
Sec. 216. Medication-induced movement disorder outreach and education.
Sec. 217. Report on wearable medical devices.
Sec. 218. Extension of temporary inclusion of authorized oral antiviral drugs as covered part D drugs.
Sec. 219. Extension of adjustment to calculation of hospice cap amount.
Sec. 220. Multiyear contracting authority for MedPAC and MACPAC.
Sec. 221. Contracting parity for MedPAC and MACPAC.
Sec. 222. Adjustments to Medicare part D cost-sharing reductions for low-income individuals.
Sec. 223. Requiring Enhanced and Accurate Lists of (REAL) Health Providers Act.
Sec. 224. Medicare coverage of multi-cancer early detection screening tests.
Sec. 225. Medicare coverage of external infusion pumps and non-self-administrable home infusion drugs.
Sec. 226. Assuring pharmacy access and choice for Medicare beneficiaries.
Sec. 227. Modernizing and Ensuring PBM Accountability.
Sec. 228. Requiring a separate identification number and an attestation for each off-campus outpatient department of a provider.
Sec. 229. Medicare sequestration.
Sec. 230. Medicare improvement fund.
Sec. 301. Sexual risk avoidance education extension.
Sec. 302. Personal responsibility education extension.
Sec. 303. Extension of funding for family-to-family health information centers.
TITLE IV—PUBLIC HEALTH EXTENDERS
Sec. 401. Extension for community health centers, National Health Service Corps, and teaching health centers that operate GME programs.
Sec. 402. Extension of special diabetes programs.
Subtitle B—World Trade Center Health Program
Sec. 411. 9/11 responder and survivor health funding corrections.
TITLE V—SUPPORT ACT REAUTHORIZATION
Sec. 511. Prenatal and postnatal health.
Sec. 512. Monitoring and education regarding infections associated with illicit drug use and other risk factors.
Sec. 513. Preventing overdoses of controlled substances.
Sec. 514. Support for individuals and families impacted by fetal alcohol spectrum disorder.
Sec. 515. Promoting State choice in PDMP systems.
Sec. 516. First responder training program.
Sec. 517. Donald J. Cohen National Child Traumatic Stress Initiative.
Sec. 518. Protecting suicide prevention lifeline from cybersecurity incidents.
Sec. 519. Bruce’s law.
Sec. 520. Guidance on at-home drug disposal systems.
Sec. 521. Assessment of opioid drugs and actions.
Sec. 522. Grant program for State and Tribal response to opioid use disorders.
Sec. 531. Residential treatment program for pregnant and postpartum women.
Sec. 532. Improving access to addiction medicine providers.
Sec. 533. Mental and behavioral health education and training grants.
Sec. 534. Loan repayment program for substance use disorder treatment workforce.
Sec. 535. Development and dissemination of model training programs for substance use disorder patient records.
Sec. 536. Task force on best practices for trauma-informed identification, referral, and support.
Sec. 537. Grants to enhance access to substance use disorder treatment.
Sec. 538. State guidance related to individuals with serious mental illness and children with serious emotional disturbance.
Sec. 539. Reviewing the scheduling of approved products containing a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone.
Sec. 541. Building communities of recovery.
Sec. 542. Peer support technical assistance center.
Sec. 543. Comprehensive opioid recovery centers.
Sec. 544. Youth prevention and recovery.
Sec. 545. CAREER Act.
Sec. 546. Addressing economic and workforce impacts of the opioid crisis.
Subtitle D—Miscellaneous matters
Sec. 551. Delivery of a controlled substance by a pharmacy to a prescribing practitioner.
Sec. 552. Technical correction on controlled substances dispensing.
Sec. 553. Required training for prescribers of controlled substances.
Sec. 554. Extension of temporary order for fentanyl-related substances.
TITLE VI—PANDEMIC AND ALL-HAZARDS PREPAREDNESS AND RESPONSE
Subtitle A—State and local readiness and response
Sec. 611. Temporary reassignment of State and local personnel during a public health emergency.
Sec. 612. Public Health Emergency Preparedness program.
Sec. 613. Hospital Preparedness Program.
Sec. 614. Facilities and capacities of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to combat public health security threats.
Sec. 615. Pilot program to support State medical stockpiles.
Sec. 616. Enhancing domestic wastewater surveillance for pathogen detection.
Sec. 617. Reauthorization of Mosquito Abatement for Safety and Health program.
Subtitle B—Federal planning and coordination
Sec. 621. All-Hazards Emergency Preparedness and Response.
Sec. 622. National Health Security Strategy.
Sec. 623. Improving development and distribution of diagnostic tests.
Sec. 624. Combating antimicrobial resistance.
Sec. 625. Strategic National Stockpile and material threats.
Sec. 626. Medical countermeasures for viral threats with pandemic potential.
Sec. 627. Public Health Emergency Medical Countermeasures Enterprise.
Sec. 628. Fellowship and training programs.
Sec. 629. Regional biocontainment research laboratories.
Sec. 629A. Limitation related to countries of concern conducting certain research.
Subtitle C—Addressing the needs of all individuals
Sec. 631. Improving access to certain programs.
Sec. 632. Supporting at-risk individuals during emergency responses.
Sec. 633. National advisory committees.
Sec. 634. National Academies study on prizes.
Subtitle D—Additional reauthorizations
Sec. 641. Medical countermeasure priority review voucher.
Sec. 642. Epidemic Intelligence Service.
Sec. 643. Monitoring and distribution of certain medical countermeasures.
Sec. 644. Regional health care emergency preparedness and response systems.
Sec. 645. Emergency system for advance registration of volunteer health professionals.
Sec. 646. Ensuring collaboration and coordination in medical countermeasure development.
Sec. 647. Military and civilian partnership for trauma readiness.
Sec. 648. National Disaster Medical System.
Sec. 649. Volunteer Medical Reserve Corps.
Sec. 649A. Epidemiology-laboratory capacity.
TITLE VII—PUBLIC HEALTH PROGRAMS
Sec. 701. Action for dental health.
Sec. 702. PREEMIE.
Sec. 703. Preventing maternal deaths.
Sec. 704. Sickle cell disease prevention and treatment.
Sec. 705. Traumatic brain injuries.
Sec. 706. Lifespan respite care.
Sec. 707. Dr. Lorna Breen health care provider protection.
Sec. 708. SCREENS for Cancer.
Sec. 709. DeOndra Dixon INCLUDE Project.
Sec. 710. IMPROVE Initiative.
Sec. 711. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network.
Sec. 712. Honor Our Living Donors.
Sec. 713. Program for pediatric studies of drugs.
TITLE VIII—FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION
Sec. 801. Research into pediatric uses of drugs; additional authorities of Food and Drug Administration regarding molecularly targeted cancer drugs.
Sec. 802. Ensuring completion of pediatric study requirements.
Sec. 803. FDA report on PREA enforcement.
Sec. 804. Extension of authority to issue priority review vouchers to encourage treatments for rare pediatric diseases.
Sec. 805. Limitations on exclusive approval or licensure of orphan drugs.
Subtitle B—United States-Abraham Accords Cooperation and Security
Sec. 811. Establishment of Abraham Accords Office within Food and Drug Administration.
TITLE IX—LOWERING PRESCRIPTION DRUG COSTS
Sec. 901. Oversight of pharmacy benefit management services.
Sec. 902. Full rebate pass through to plan; exception for innocent plan fiduciaries.
Sec. 903. Increasing transparency in generic drug applications.
Sec. 904. Title 35 amendments.
Sec. 1001. Extension of safe harbor for absence of deductible for telehealth.
The full bill is at https://www.congress.gov/bill/119th-congress/senate-bill/891/text?s=4&r=1
S. 976 – Insurance Fraud Accountability Act
A bill to amend the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act to reduce fraudulent enrollments in qualified health plans, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Reduction of fraudulent enrollment in qualified health plans.
(a) Penalties for agents and brokers.—Section 1411(h)(1) of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (42 U.S.C. 18081(h)(1)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (A)—
(A) by redesignating clause (ii) as clause (iv);
(B) in clause (i)—
(i) in the matter preceding subclause (I), by striking “If—” and all that follows through the “such person” in the matter following subclause (II) and inserting the following: “If any person (other than an agent or broker) fails to provide correct information under subsection (b) and such failure is attributable to negligence or disregard of any rules or regulations of the Secretary, such person”; and
(ii) in the second sentence, by striking “For purposes” and inserting the following:
“(iii) DEFINITIONS OF NEGLIGENCE, DISREGARD.—For purposes”;
(C) by inserting after clause (i) the following:
“(ii) CIVIL PENALTIES FOR CERTAIN VIOLATIONS BY AGENTS OR BROKERS.—If any agent or broker fails to provide correct information under subsection (b) or section 1311(c)(8) or other information, as specified by the Secretary, and such failure is attributable to negligence or disregard of any rules or regulations of the Secretary, such agent or broker shall be subject, in addition to any other penalties that may be prescribed by law, including subparagraph (C), to a civil penalty of not less than $10,000 and not more than $50,000 with respect to each individual who is the subject of an application for which such incorrect information is provided.”; and
(D) in clause (iv) (as so redesignated), by inserting “or (ii)” after “clause (i)”;
(2) in subparagraph (B)—
(A) by inserting “including subparagraph (C),” after “law,”;
(B) by striking “Any person” and inserting the following:
“(i) IN GENERAL.—Any person”; and
(C) by adding at the end the following:
“(ii) CIVIL PENALTIES FOR KNOWING VIOLATIONS BY AGENTS OR BROKERS.—
“(I) IN GENERAL.—Any agent or broker who knowingly provides false or fraudulent information under subsection (b) or section 1311(c)(8), or other false or fraudulent information as part of an application for enrollment in a qualified health plan offered through an Exchange, as specified by the Secretary, shall be subject, in addition to any other penalties that may be prescribed by law, including subparagraph (C), to a civil penalty of not more than $200,000 with respect to each individual who is the subject of an application for which such false or fraudulent information is provided.
“(II) PROCEDURE.—The provisions of section 1128A of the Social Security Act (other than subsections (a) and (b) of such section) shall apply to a civil monetary penalty under subclause (I) in the same manner as such provisions apply to a penalty or proceeding under section 1128A of the Social Security Act.”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(C) CRIMINAL PENALTIES.—Any agent or broker who knowingly and willfully provides false or fraudulent information under subsection (b) or section 1311(c)(8), or other false or fraudulent information as part of an application for enrollment in a qualified health plan offered through an Exchange, as specified by the Secretary, shall be fined under title 18, United States Code, imprisoned for not more than 10 years, or both.”.
(b) Consumer protections.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 1311(c) of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (42 U.S.C. 18031(c)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(8) AGENT- OR BROKER-ASSISTED ENROLLMENT IN QUALIFIED HEALTH PLANS IN CERTAIN EXCHANGES.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—For plan years beginning on or after such date specified by the Secretary, but not later than January 1, 2029, in the case of an Exchange that the Secretary operates pursuant to section 1321(c)(1), the Secretary shall establish a verification process for new enrollments of individuals in, and changes in coverage for individuals under, a qualified health plan offered through such Exchange, which are submitted by an agent or broker in accordance with section 1312(e) and for which the agent or broker is eligible to receive a commission.
“(B) REQUIREMENTS.—The enrollment verification process under subparagraph (A) shall include—
“(i) a requirement that the agent or broker provide with the new enrollment or coverage change such documentation or evidence (such as a standardized consent form) or other sources as the Secretary determines necessary to establish that the agent or broker has the consent of the individual for the new enrollment or coverage change;
“(ii) a requirement that any commissions due to a broker or agent for such new enrollment or coverage change are paid after the enrollee has resolved all inconsistencies in accordance with paragraphs (3) and (4) of section 1411(e);
“(iii) a requirement that the information required under clause (i) and, as applicable, the date on which inconsistencies are resolved as described in clause (ii), is accessible to the applicable qualified health plan through a database or other resource, as determined by the Secretary, so that any commissions due to a broker or agent for such enrollment can be effectuated at the appropriate time;
“(iv) a requirement that individuals are notified of any changes to enrollment, coverage, the agent of record, or premium tax credits in a timely manner and that such notice provides plain language instructions on how individuals can cancel unauthorized activity;
“(v) a requirement that individuals be able to access their account information on a website or other technology platform, as defined by the Secretary, when used to submit an enrollment or plan change, in lieu of the Exchange website described in subsection (d)(4)(C), including information on the agent of record, the qualified health plan, and when any changes are made to the agent of record or the qualified health plan, on a consumer-facing website or through a toll-free telephone hotline; and
“(vi) a requirement that the agent or broker report to the Secretary any third-party marketing organization or field marketing organization (as such terms are defined in section 1312(e)) involved in the chain of enrollment (as so defined) with respect to such new enrollment or coverage change.
“(C) CONSUMER PROTECTION.—The Secretary shall ensure that the enrollment verification process under subparagraph (A) prioritizes continuity of coverage and care for individuals, including by not disenrolling individuals from a qualified health plan without the consent of the individual, regardless of whether the broker, agent, or qualified health plan is in violation of any requirement under this paragraph.”.
(2) REQUIRED REPORTING.—Section 1311(c)(1) of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (42 U.S.C. 18031(c)(1)) is amended—
(A) in subparagraph (H), by striking “and” at the end;
(B) in subparagraph (I), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(C) by adding at the end the following:
“(J) report to the Secretary the termination (as defined in section 1312(e)(4)(C)) of an issuer.”.
(c) Authority To regulate field marketing organizations and third-Party marketing organizations.—Section 1312(e) of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (42 U.S.C. 18032(e)) is amended—
(1) by redesignating paragraphs (1) and (2) as subclauses (I) and (II), respectively, and adjusting the margins accordingly;
(2) in subclause (II) (as so redesignated), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”;
(3) by striking the subsection designation and heading and all that follows through “brokers—” and inserting the following:
“(e) Regulation of agents, brokers, and certain marketing organizations.—
“(1) AGENTS, BROKERS, AND CERTAIN MARKETING ORGANIZATIONS.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary shall establish procedures under which a State may allow—
“(i) agents or brokers—”; and
(4) by adding at the end the following:
“(ii) field marketing organizations and third-party marketing organizations to participate in the chain of enrollment for an individual with respect to qualified health plans offered through an Exchange.
“(B) CRITERIA.—For plan years beginning on or after such date specified by the Secretary, but not later than January 1, 2029, the Secretary, by regulation, shall establish criteria for States to use in determining whether to allow agents and brokers to enroll individuals and employers in qualified health plans as described in subclause (I) of subparagraph (A)(i) and to assist individuals as described in subclause (II) of such subparagraph and field marketing organizations and third-party marketing organizations to participate in the chain of enrollment as described in subparagraph (A)(ii). Such criteria shall, at a minimum, require that—
“(i) an agent or broker act in accordance with a standard of conduct that includes a duty of such agent or broker to act in the best interests of the enrollee;
“(ii) a field marketing organization or third-party marketing organization agree to report the termination of an agent or broker to the applicable State and the Secretary, including the reason for termination; and
“(iii) an agent, broker, field marketing organization, or third-party marketing organization—
“(I) meet such marketing requirements as are required by the Secretary;
“(II) meet marketing requirements in accordance with other applicable Federal or State law;
“(III) does not employ practices that are confusing or misleading, as determined by the Secretary;
“(IV) submit all marketing materials to the Secretary for, as determined appropriate by the Secretary, review and approval;
“(V) is a licensed agent or broker or meets other licensure requirements, as required by the State;
“(VI) register with the Secretary; and
“(VII) does not compensate any individual or organization for referrals or any other service relating to the sale of, marketing for, or enrollment in qualified health plans unless such individual or organization meets the criteria described in subclauses (I) through (VI).
“(C) DEFINITIONS.—In this paragraph:
“(i) CHAIN OF ENROLLMENT.—The term ‘chain of enrollment’, with respect to enrollment of an individual in a qualified health plan offered through an Exchange, means any steps taken from marketing to such individual, to such individual making an enrollment decision with respect to such a plan.
“(ii) FIELD MARKETING ORGANIZATION.—The term ‘field marketing organization’ means an organization or individual that directly employs or contracts with agents and brokers, or contracts with carriers, to provide functions relating to enrollment of individuals in qualified health plans offered through an Exchange as part of the chain of enrollment.
“(iii) MARKETING.—The term ‘marketing’ means the use of marketing materials to provide information to current and prospective enrollees in a qualified health plan offered through an Exchange.
“(iv) MARKETING MATERIALS.—The term ‘marketing materials’ means materials relating to a qualified health plan offered through an Exchange or benefits offered through an Exchange that—
“(I) are intended—
“(aa) to draw an individual’s attention to such plan or the premium tax credits or cost-sharing reductions for such plan or plans offered through an Exchange;
“(bb) to influence an individual’s decision-making process when selecting a qualified health plan in which to enroll; or
“(cc) to influence an enrollee’s decision to stay enrolled in such plan; and
“(II) include or address content regarding the benefits, benefit structure, premiums, or cost sharing of such plan.
“(v) TERMINATION.—The term ‘termination’, with respect to a contract or business arrangement between an agent or broker and a field marketing organization, third-party marketing organization, or health insurance issuer, means—
“(I) the ending of such contract or business arrangement, either unilaterally by one of the parties or on mutual agreement; or
“(II) the expiration of such contract or business arrangement that is not replaced by a substantially similar agreement.
“(vi) THIRD-PARTY MARKETING ORGANIZATION.—The term ‘third-party marketing organization’ means an organization or individual that is compensated to perform lead generation, marketing, or sales relating to enrollment of individuals in qualified health plans offered through an Exchange as part of the chain of enrollment.”.
(d) Transparency.—Section 1312(e) of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (42 U.S.C. 18032(e)) (as amended by subsection (c)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(2) AUDITS.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—For plan years beginning on or after such date specified by the Secretary, but not later than January 1, 2029, the Secretary, in coordination with the States and in consultation with the National Association of Insurance Commissioners, shall implement a process for the oversight and enforcement of agent and broker compliance with this section and other applicable Federal and State law (including regulations) that shall include—
“(i) periodic audits of agents and brokers based on—
“(I) complaints filed with the Secretary by individuals enrolled by such an agent or broker in a qualified health plan offered through an Exchange;
“(II) an incident or enrollment pattern that suggests fraud; and
“(III) other factors determined by the Secretary; and
“(ii) a process under which the Secretary shall share audit results and refer potential cases of fraud to the relevant State department of insurance.
“(B) EFFECT.—Nothing in this paragraph limits or restricts any referrals made under section 1311(i)(3) or any enforcement actions under section 1411(h).
“(3) LIST.—The Secretary shall develop a process to regularly provide to qualified health plans, Exchanges, and States a list of suspended and terminated agents and brokers.”.
S. 999 – Public Health Improvement Act
A bill to reform the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, limit the scope of public health authorities, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Terms of CDC and NIH directors.
(a) Term of CDC director.—Section 305(a) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 242c(a)) is amended by adding at the end the following: “No individual may serve as Director for a total period of more than 12 years.”.
(b) Term of NIH director.—Section 402(a) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 282(a)) is amended by adding at the end the following: “No individual may serve as Director of NIH for a total period of more than 12 years.”.
SEC. 3. Limiting the CDC strategic plan.
Section 305(c)(2)(A) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 242c(c)(2)(A)) is amended—
(1) in clause (i), by striking “and noncommunicable diseases or conditions, and addressing injuries, and occupational and environmental hazards” and inserting “diseases”;
(2) in clause (ii), by striking “or conditions”;
(3) in clause (iii), by adding “and” at the end;
(4) in clause (iv), by striking “; and” and inserting a semicolon; and
(5) by striking clause (v).
SEC. 4. Advisory committee to the CDC Director.
Section 305A(c) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 242c–1(c)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1), by striking “by the Secretary under” and inserting “as described in”; and
(2) in paragraph (3), by striking subparagraphs (A) and (B) and inserting the following:
“(A) Three members shall be appointed by the Secretary of Health and Human Services—
“(i) 1 of whom shall be appointed to represent the Department of Health and Human Services; and
“(ii) 1 of whom shall be a public health official.
“(B) Two members shall be appointed by the majority leader of the Senate.
“(C) Two members shall be appointed by the minority leader of the Senate.
“(D) Two members shall be appointed by the Speaker of the House of Representatives.
“(E) Two members shall be appointed by the minority leader of the House of Representatives.
“(F) Four members shall be appointed by the Comptroller General of the United States.”.
SEC. 5. Limiting the scope of regulations of the Department of Health and Human Services to control communicable diseases.
Section 361(a) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 264(a)) is amended to read as follows:
“(a) To prevent the introduction, transmission, or spread of communicable diseases from foreign countries into the States or possessions, or from one State or possession into any other State or possession, the Secretary may make and enforce regulations for the inspection, fumigation, disinfection, sanitation, pest extermination, or destruction of animals or articles found to be so infected or contaminated as to be sources of dangerous infection to human beings.”.
SEC. 6. Congressional approval for public health emergencies.
Section 319(a) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 247d(a)) is amended by striking the third and fourth sentences and inserting the following: “Determinations that terminate under the preceding sentence may be renewed by a majority vote in both chambers of Congress, and such a renewal period terminates upon the Secretary declaring that the emergency no longer exists or the expiration of the 90-day period beginning on the date on which both chambers of Congress have voted in favor of such renewal, whichever occurs first. Not later than 48 hours after making a determination under this subsection of a public health emergency, the Secretary shall submit to the Congress written notification of the determination.”.
SEC. 7. Transfer of offices to NIH.
(a) In general.—Effective on the date that is 2 years after the date of enactment of this Act, notwithstanding any other provision of law, the authorities, functions, personnel, and assets of the offices described in subsection (b) shall be transferred from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to the National Institutes of Health.
(b) Offices described.—The offices described in this subsection are the following:
(1) The National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities.
(2) The National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
(3) The National Center for Environmental Health.
(4) The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
(5) The National Center for Health Statistics.
(6) The National Center for HIV, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and Tuberculosis Prevention.
(7) The National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
(8) The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
SEC. 8. Regulations.
Not later than 90 days after the date of enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall issue such new or revised regulations as are necessary to carry out this Act (including the amendments made by this Act).
SEC. 9. Preemption.
The provisions of this Act (including the amendments made by this Act) shall supersede any provision of Federal, State, Tribal, territorial, or local law, declaration, guidance, or directive to the extent that such law, declaration, guidance, or directive is inconsistent with this Act (including such amendments).
S. 1056 – Home-Based Telemental Health Care Act of 2025
A bill to establish a home-based telemental health care grant program for purposes of increasing mental health and substance use services in rural medically underserved populations and for individuals in farming, fishing, and forestry occupations
SEC. 2. Mental health and substance use services delivered to rural underserved populations via telemental health care.
Title III of the Public Health Service Act is amended by inserting after section 330K (42 U.S.C. 254c–16) the following:
“SEC. 330K–1. Mental health and substance use services delivered to rural underserved populations via telemental health care.
“(a) Definitions.—In this section—
“(1) the term ‘covered populations’ means—
“(A) health professional shortage areas (as defined in section 332(a)(1)) in rural areas; or
“(B) populations engaged in a farming, fishing, or forestry industry;
“(2) the term ‘eligible entity’ means a public or nonprofit private telemental health provider network that offers services that include mental health and substance use services provided by professionals trained in mental health and substance use;
“(3) the term ‘farming, fishing, or forestry industry’ means an occupation defined as a farming, fishing, or forestry occupation by the Department of Labor in accordance with the Standard Occupational Classification System;
“(4) the term ‘home-based telemental’ means the use of telemental health services where the patient is in his or her own home or other place of comfort;
“(5) the term ‘professional trained in mental health’ means a psychiatrist, a qualified mental health professional (as defined in section 330K), or another mental health professional acting under the direction of a psychiatrist;
“(6) the term ‘rural’ has the meaning given such term by the Office of Rural Health Policy of the Health Resources and Services Administration; and
“(7) the term ‘telemental health’ means the use of electronic information and telecommunications technologies to support long distance clinical health care, patient and professional health-related education, public health, and health administration.
“(b) Program authorized.—The Secretary, in consultation with the Rural Health Liaison of the Department of Agriculture, shall award grants to eligible entities to expand and enhance access to mental health and substance use services for covered populations in their homes or other places of comfort, as delivered remotely by professionals trained in mental health and substance use using telemental health care.
“(c) Use of funds.—Recipients of a grant under this section shall use the grant funds to—
“(1) deliver home-based telemental health services to covered populations;
“(2) develop comprehensive metrics to measure the quality and impact of home-based telemental health services compared to traditional in-person mental health and substance use care; and
“(3) support infrastructure that enhances the capacity of health care providers to deliver telemental health services in patients’ homes or other places of comfort, including by—
“(A) expanding broadband access;
“(B) providing devices for patients to access telemental health services; and
“(C) offsetting costs of technology necessary for health care providers to deliver high quality care.
“(d) Report.—The Secretary, in consultation with the Secretary of Agriculture, not later than 3 years after the date on which the program under this section commences, and 2 years thereafter, shall submit to the appropriate congressional committees reports on the impact and quality of care of home-based telemental health care services for covered populations.
“(e) Authorized use of funds.—Out of any amounts made available to the Secretary, up to $10,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2025 through 2029 may be allocated to carrying out the program under this section.”.
S. 1140 – A bill to amend title XI of the Social Security Act to lower barriers to increase patient access to health care.
S. 1144 – A bill to amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to treat certain amounts paid for physical activity, fitness, and exercise as amounts paid for medical care.
S. 1147 – A bill to establish clear and consistent biological definitions of male and female.
Nurse Practitioners
S.575 – I CAN Act or the Improving Care and Access to Nurses Act
A bill to amend titles XVIII and XIX of the Social Security Act to increase access to services provided by advanced practice registered nurses under the Medicare and Medicaid programs, and for other purposes.
Summary: This bill allows other health care providers besides physicians (e.g., nurses) to provide certain services under Medicare and Medicaid.
Among other changes, the bill (1) allows a nurse practitioner or physician assistant to fulfill documentation requirements for Medicare coverage of special shoes for diabetic individuals; (2) expedites the ability of physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and clinical nurse specialists to supervise Medicare cardiac, intensive cardiac, and pulmonary rehabilitation programs; and (3) allows nurse practitioners to certify the need for inpatient hospital services under Medicare and Medicaid.
(b) Table of contents.—The table of contents of this Act is as follows:
Sec. 1. Short title; table of contents.
TITLE I—REMOVAL OF BARRIERS TO PRACTICE ON NURSE PRACTITIONERS
Sec. 101. Expanding access to cardiac rehabilitation programs and pulmonary rehabilitation programs under Medicare program.
Sec. 102. Permitting nurse practitioners and physician assistants to satisfy Medicare documentation requirement for coverage of certain shoes for individuals with diabetes.
Sec. 103. Improvements to the assignment of beneficiaries under the Medicare shared savings program.
Sec. 104. Expanding the availability of medical nutrition therapy service Medicare program.
Sec. 105. Preserving access to home infusion therapy.
Sec. 106. Increasing access to hospice care services.
Sec. 107. Streamlining care delivery in skilled nursing facilities and nursing facilities; authorizing Medicare and Medicaid inpatient hospital patients to be under the care of a nurse practitioner.
Sec. 108. Improving access to Medicaid clinic services.
TITLE II—REMOVAL OF BARRIERS TO PRACTICE ON CERTIFIED REGISTERED NURSE ANESTHETISTS
Sec. 201. Clarifying that certified registered nurse anesthetists can be reimbursed by Medicare for evaluation and management services.
Sec. 202. Revision of conditions of payment relating to services ordered and referred by certified registered nurse anesthetists.
Sec. 203. Special payment rule for teaching student registered nurse anesthetists.
Sec. 204. Removing unnecessary and costly supervision of certified registered nurse anesthetists.
Sec. 205. CRNA services as a Medicaid-required benefit.
TITLE III—REMOVAL OF BARRIERS TO PRACTICE ON CERTIFIED NURSE-MIDWIVES
Sec. 301. Improving access to training in maternity care.
Sec. 302. Improving Medicare patient access to home health services provided by certified nurse-midwives.
Sec. 303. Improving access to DMEPOS for Medicare beneficiaries.
Sec. 304. Technical changes to qualifications and conditions with respect to the services of certified nurse-midwives.
TITLE IV—IMPROVING FEDERAL HEALTH PROGRAMS FOR ALL ADVANCED PRACTICE REGISTERED NURSES
Sec. 401. Revising the local coverage determination process under the Medicare program.
Sec. 402. Locum tenens.
TITLE I—Removal of Barriers to Practice on Nurse Practitioners
SEC. 101. Expanding access to cardiac rehabilitation programs and pulmonary rehabilitation programs under Medicare program.
(a) Cardiac rehabilitation programs.—Section 1861(eee) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(eee)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (2)—
(A) in subparagraph (A)(i), by striking “a physician’s office” and inserting “the office setting”; and
(B) in subparagraph (C), by inserting after “physician” the following: “(as defined in subsection (r)(1)) or a physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in subsection (aa)(5))”;
(2) in paragraph (3)(A), by striking “physician-prescribed exercise” and inserting “exercise prescribed by a physician (as defined in subsection (r)(1)) or a physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in subsection (aa)(5))”; and
(3) in paragraph (5), by inserting after “physician” the following: “(as defined in subsection (r)(1)) or a physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in subsection (aa)(5))”.
(b) Pulmonary rehabilitation programs.—Section 1861(fff) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(fff)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (2)(A), by striking “physician-prescribed exercise” and inserting “exercise prescribed by a physician (as defined in subsection (r)(1)) or a physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in subsection (aa)(5))”; and
(2) in paragraph (3), by inserting after “physician” the following: “(as defined in subsection (r)(1)) or a physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in subsection (aa)(5))”.
SEC. 102. Permitting nurse practitioners and physician assistants to satisfy Medicare documentation requirement for coverage of certain shoes for individuals with diabetes.
Section 1861(s)(12) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(s)(12)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (A), by inserting “, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant” after “physician”; and
(2) in subparagraph (C), by inserting “, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant” after each occurrence of “physician”.
SEC. 103. Improvements to the assignment of beneficiaries under the Medicare shared savings program.
Section 1899(c)(1) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395jjj(c)(1)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (A), by striking “and” at the end;
(2) in subparagraph (B), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(C) in the case of performance years beginning on or after January 1, 2026, primary care services provided under this title by an ACO professional described in subsection (h)(1)(B).”.
SEC. 104. Expanding the availability of medical nutrition therapy service Medicare program.
Section 1861(vv)(1) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(vv)(1)) is amended by inserting “ or a nurse practitioner, a clinical nurse specialist, or a physician assistant (as such terms are defined in subsection (aa)(5))” before the period at the end.
SEC. 105. Preserving access to home infusion therapy.
(a) Allowing applicable providers To establish home infusion therapy plans.—Section 1861(iii)(1)(B) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(iii)(1)(B)) is amended—
(1) by striking “a physician (as defined in subsection (r)(1))” and inserting “an applicable provider (as defined in paragraph (3)(A))”; and
(2) by striking “a physician (as so defined)” and inserting “an applicable provider (as so defined)”.
(b) Conforming amendment.—Section 1834(u)(6) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395m(u)(6)) is amended by striking “physician” and inserting “applicable provider (as defined in section 1861(iii)(3)(A))”.
SEC. 106. Increasing access to hospice care services.
(a) In general.—Section 1814(a)(7)(A) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395f(a)(7)(A)) is amended—
(1) in clause (i)—
(A) in subclause (I), by striking “a nurse practitioner or”;
(B) in subclause (II), by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “physician”; and
(C) in the flush matter following subclause (II), by inserting “, nurse practitioner’s,” after “physician’s”; and
(2) in clause (ii), by striking “or physician” and inserting “, physician, or nurse practitioner”.
(b) Hospice care definition.—Section 1861(dd)(1)(C) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(dd)(1)(C)) is amended by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “physician”.
(c) Nurse practitioner billing.—Not later than 90 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall revise section 418.304 of title 42, Code of Federal Regulations, to allow nurse practitioners to bill for services not described in paragraph (a) of such section in the same manner as physicians may bill for such services in accordance with paragraph (b) of such section. Such revision shall provide that such services furnished by a nurse practitioner shall be payable at the percent of the physician fee schedule specified in section 1833(a)(1)(O) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395l(a)(1)(O)).
SEC. 107. Streamlining care delivery in skilled nursing facilities and nursing facilities; authorizing Medicare and Medicaid inpatient hospital patients to be under the care of a nurse practitioner.
(a) Medicare.—
(1) CERTIFICATION OF POST-HOSPITAL EXTENDED CARE SERVICES.—Section 1814(a)(2) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395f(a)(2)) is amended, in the matter preceding subparagraph (A), by striking “, or a nurse practitioner,” and inserting “or a nurse practitioner (in accordance with State law), or”.
(2) CERTIFICATION AUTHORITY FOR NURSE PRACTITIONERS.—Section 1814(a)(3) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395f(a)(3)) is amended by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “physician”.
(3) SUPERVISION REQUIREMENT IN SKILLED NURSING FACILITY SERVICES AND RESIDENT’S RIGHTS.—Section 1819 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395i–3(b)(6)) is amended—
(A) in subsection (b)—
(i) in paragraph (2)(B), by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “attending physician”; and
(ii) in paragraph (6)—
(I) in the heading, by striking “Physician supervision” and inserting “Supervision”; and
(II) in subparagraph (A), by inserting “or a nurse practitioner, in accordance with State law” after “physician”; and
(B) in subsection (c)—
(i) in subparagraph (1)(A)(i), by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “attending physician”;
(ii) in the flush matter at the end of subparagraph (2)(A), by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “physician” in each occurrence; and
(iii) in subparagraph (3)(A), by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “physician”.
(4) ADMINISTRATION OF PART B.—Section 1842(b)(2)(C) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395u(b)(2)(C)) is amended, in the second sentence—
(A) by inserting “or a nurse practitioner” after “a physician”; and
(B) by striking “or a nurse practitioner working in collaboration with that physician, or both”.
(5) PROVISION OF MEDICAL AND OTHER HEALTH SERVICES.—Section 1861(s)(2)(K)(ii) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(s)(2)(K)(ii)) is amended by striking “or clinical nurse specialist (as defined in subsection (aa)(5)) working in collaboration (as defined in subsection (aa)(6)) with a physician (as defined in subsection (r)(1))” and inserting “(as defined in subsection (aa)(5)(A)), or by a clinical nurse specialist (as defined in subsection (aa)(5)(B)) working in collaboration with a physician (as defined in subsection (r)(1)),”.
(6) PRIVILEGES FOR NURSE PRACTITIONERS.—Section 1861 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x) is amended—
(A) in subsection (e)(4), by inserting “(or nurse practitioner, in accordance with State law)” after “physician”;
(B) in subsection (f)(1), by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “physician”; and
(C) in each of subparagraphs (B) and (F) of subsection (ee)(2), by inserting “or nurse practitioner” after “physician”.
(b) Medicaid.—
(1) CERTIFICATION AUTHORITY FOR NURSE PRACTITIONERS.—Section 1902(a)(44) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396a(a)(44)) is amended to read as follows:
“(44) in each case for which payment for inpatient hospital services, skilled nursing facility services, services in an intermediate care facility described in section 1905(d), or inpatient mental hospital services is made under the State plan—
“(A) a physician or nurse practitioner (or, in the case of skilled nursing facility services or intermediate care facility services, a physician or nurse practitioner, or a clinical nurse specialist who is not an employee of the facility but is working in collaboration with a physician) certifies at the time of admission, or, if later, the time the individual applies for medical assistance under the State plan (and a physician or nurse practitioner, or a physician assistant under the supervision of a physician, or, in the case of skilled nursing facility services or intermediate care facility services, a physician or nurse practitioner, or a clinical nurse specialist who is not an employee of the facility but is working in collaboration with a physician, recertifies, where such services are furnished over a period of time, in such cases, at least as often as required under section 1903(g)(6) (or, in the case of services that are services provided in an intermediate care facility, every year), and accompanied by such supporting material, appropriate to the case involved, as may be provided in regulations of the Secretary), that such services are or were required to be given on an inpatient basis because the individual needs or needed such services, and
“(B) such services were furnished under a plan established and periodically reviewed and evaluated by a physician or nurse practitioner, or, in the case of skilled nursing facility services or intermediate care facility services, by a physician or nurse practitioner, or a clinical nurse specialist who is not an employee of the facility but is working in collaboration with a physician;”.
(2) NURSING FACILITY SERVICES SUPERVISION AND CLINICAL RECORDS.—Section 1919(b)(6)(A) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396r(b)(6)(A)) is amended to read as follows:
“(A) require that the health care of every resident be provided under the supervision of a physician or nurse practitioner (or, at the option of a State, under the supervision of a clinical nurse specialist or physician assistant who is not an employee of the facility but who is working in collaboration with a physician);”.
SEC. 108. Improving access to Medicaid clinic services.
Section 1905(a)(9) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396d(a)(9)) is amended by adding “or nurse practitioner” after “physician” in both places that it appears.
TITLE II—Removal of Barriers to Practice on Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists
SEC. 201. Clarifying that certified registered nurse anesthetists can be reimbursed by Medicare for evaluation and management services.
Section 1861(bb)(1) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(bb)(1)) is amended by inserting “, including pre-anesthesia evaluation and management services,” after “and related care”.
SEC. 202. Revision of conditions of payment relating to services ordered and referred by certified registered nurse anesthetists.
Not later than 3 months after the date of enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall revise section 410.69 of title 42, Code of Federal Regulations, to clarify that, for purposes of payment under part B of title XVIII of the Social Security Act—
(1) certified registered nurse anesthetists are authorized to order, certify, and refer services to the extent allowed under the law of the State in which the services are furnished; and
(2) payment shall be made under such part for such services so ordered, certified, or referred by certified registered nurse anesthetists.
SEC. 203. Special payment rule for teaching student registered nurse anesthetists.
Section 1848(a)(6) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–4(a)(6)) is amended, in the matter preceding subparagraph (A), by inserting “or student registered nurse anesthetists” after “physician residents”.
SEC. 204. Removing unnecessary and costly supervision of certified registered nurse anesthetists.
Section 1861(bb)(2) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(bb)(2)) is amended—
(1) in the second sentence, by inserting “, but may not require that certified registered nurse anesthetists provide services under the supervision of a physician” after “certification of nurse anesthetists”; and
(2) in the third sentence, by inserting “under the supervision of an anesthesiologist” after “an anesthesiologist assistant”.
SEC. 205. CRNA services as a Medicaid-required benefit.
(a) In general.—Section 1905(a)(5) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396d(a)(5)) is amended—
(1) by striking “and (B)” and inserting “(B)”; and
(2) by inserting before the semicolon at the end the following: “, and (C) services furnished by a certified registered nurse anesthetist (as defined in section 1861(bb)(2)), which such certified registered nurse anesthetist is authorized to perform under State law (or the State regulatory mechanism as provided by State law)”.
(b) Payment.—Section 1902(a) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396d(a)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (86), by striking “and” at the end;
(2) in paragraph (87), by striking the period and inserting “; and”; and
(3) by inserting after paragraph (87) the following new paragraph:
“(88) provide for payment for the services of a certified registered nurse anesthetist (as defined in section 1861(bb)(1)) in amounts no lower than the amounts, using the same methodology, used for payment for amounts under section 1833(a)(1)(H).”.
TITLE III—Removal of Barriers to Practice on Certified Nurse-Midwives
SEC. 301. Improving access to training in maternity care.
(a) Medicare payments for supervision by certified nurse-Midwives.—Paragraph (1) of section 1861(gg) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(gg)) is amended to read as follows:
“(1) The term ‘certified nurse-midwife services’ means—
“(A) such services furnished by a certified nurse-midwife (as defined in paragraph (2)); and
“(B) such services (and such supplies and services furnished as an incident to the nurse-midwife’s service) which—
“(i) the certified nurse-midwife is legally authorized to perform under State law (or the State regulatory mechanism provided by State law) as would otherwise be covered if furnished by a physician;
“(ii) are furnished under the supervision of a certified-nurse midwife by an intern or resident-in-training (as described in subsection (b)(6));
“(iii) would otherwise be described in subparagraph (A) if furnished by a certified nurse-midwife; and
“(iv) would otherwise be covered if furnished under the supervision of a physician.”.
(b) Clarifying permissibility of using certain grants for clinical training by certified nurse-Midwives.—Section 811(a)(1) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 296j(a)(1)) is amended by inserting “, including clinical training,” after “projects”.
SEC. 302. Improving Medicare patient access to home health services provided by certified nurse-midwives.
(a) In general.—Section 1835(a) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395n(a)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (2)—
(A) in the matter preceding subparagraph (A), by inserting “or a certified nurse-midwife (as defined in section 1861(gg)),” after “or a physician assistant (as defined in section 1861(aa)(5)) who is working in accordance with State law,”; and
(B) in subparagraph (A)—
(i) in each of clauses (ii) and (iii), by striking “or a physician assistant (as the case may be)” and inserting “a physician assistant, or a certified nurse-midwife (as the case may be)”; and
(ii) in clause (iv), by—
(I) inserting “or by a certified nurse-midwife (as defined in section 1861(gg))” after “(but in no case later than the date that is 6 months after the date of the enactment of the CARES Act)”; and
(II) by striking “(as defined in section 1861(gg))”; and
(2) in the matter following paragraph (2), by striking “or physician assistant (as the case may be)” and inserting “physician assistant, or certified nurse-midwife (as the case may be)” each place it appears.
(b) Conforming amendments.—Section 1895 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395(fff)) is amended—
(1) in subsection (c)(1), by inserting “the certified nurse-midwife (as defined in section 1861(gg)),” after “clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in section 1861(aa)(5)),”; and
(2) in subsection (e)(1)(A), by striking “a physician a nurse practitioner or clinical nurse specialist,” and inserting “a physician, a nurse practitioner, a clinical nurse specialist, a certified nurse-midwife,”.
SEC. 303. Improving access to DMEPOS for Medicare beneficiaries.
Section 1834(a) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395m(a)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1)(E)(ii) by striking “or a clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in section 1861(aa)(5))” and inserting “, a clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in section 1861(aa)(5)), or a certified nurse-midwife (as defined in section 1861(gg))”; and
(2) in paragraph (11)(B)(ii)—
(A) by striking “or a clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in section 1861(aa)(5))” and inserting “a clinical nurse specialist (as those terms are defined in section 1861(aa)(5)), or a certified nurse-midwife (as defined in section 1861(gg))”; and
(B) by striking “or specialist” and inserting “specialist, or nurse-midwife”.
SEC. 304. Technical changes to qualifications and conditions with respect to the services of certified nurse-midwives.
Section 1861(gg)(2) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395x(gg)(2)) is amended by striking “, or has been certified by an organization recognized by the Secretary” and inserting “and has been certified by the American Midwifery Certification Board (or a successor organization)”.
TITLE IV—Improving Federal Health Programs for All Advanced Practice Registered Nurses
SEC. 401. Revising the local coverage determination process under the Medicare program.
(a) In general.—Section 1862(l)(5) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395y(l)(5)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (D), by adding at the end the following new clauses:
“(vi) Identification of any medical or scientific experts whose advice was obtained by such contractor during the development of such determination, whether or not such contractor relied on such advice in developing such determination.
“(vii) A hyperlink to any written communication between such contractor and another entity that such contractor relied on when developing such determination.
“(viii) A hyperlink to any rule, guideline, protocol, or other criterion that such contractor relied on when developing such determination.”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following new subparagraphs:
“(E) PROHIBITION ON IMPOSITION OF PRACTITIONER QUALIFICATIONS.—The Secretary shall prohibit a Medicare administrative contractor that develops a local coverage determination from imposing such determination on any coverage limitation with respect to the qualifications of a physician (as defined in section 1861(r)) or a practitioner described in section 1842(b)(18)(C) who may furnish the item or service that is the subject of such determination.
“(F) CIVIL MONETARY PENALTY.—A Medicare administrative contractor that develops a local coverage determination that fails to make information described in subparagraph (D) available as required by the Secretary under such subparagraph or comply with the prohibition under subparagraph (E) is subject to a civil monetary penalty of not more than $10,000 for each such failure. The provisions of section 1128A (other than subsections (a) and (b)) shall apply to a civil money penalty under the previous sentence in the same manner as such provisions apply to a penalty or proceeding under section 1128A(a).”.
(b) Timing of review.—Section 1869(f)(2) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395ff(f)(2)) is amended by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(D) TIMING OF REVIEW.—An aggrieved party may file a complaint described in subparagraph (A) with respect to a local coverage determination on or after the date that such determination is posted, in accordance with section 1862(l)(5)(D), on the Internet website of the Medicare administrative contractor making such determination, whether or not such determination has taken effect.”.
(c) Effective date.—The amendments made by this section shall apply to local coverage determinations made available on the internet website of a Medicare administrative contractor and on the Medicare internet website on or after the date of the enactment of this Act.
SEC. 402. Locum tenens.
Section 1842(b)(6) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395u(b)(6)) is amended, in the first sentence—
(1) by striking “and (J)” and inserting “(J)”; and
(2) by inserting before the period at the end the following: “, and (K) in the case of services furnished by a certified registered nurse anesthetist (as defined in section 1861(bb)(2)), nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist (as defined in section 1861(aa)(5)), or a certified nurse midwife (as defined in section 1861(gg)(2)), subparagraph (D) of this sentence shall apply to such services and such anesthetist, practitioner, specialist, or nurse-midwife in the same manner as such subparagraph applies to physicians’ services furnished by physicians”.
SEC. 501. Effective date.
The provisions of, including the amendments made by, this Act (other than sections 103 and 401) shall apply with respect to items and services furnished on or after the date that is 90 days after the date of the enactment of this Act. Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall implement such provisions, including such amendments, through interim final rule or subregulatory guidance if the Secretary determines such implementation to be necessary for purposes of complying with the preceding sentence or with any other effective date provided in this Act.
Nutrition
S.561 – Healthy SNAP Act of 2025
A bill to amend the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 to require the Secretary to designate food and food products to be made available under the supplemental nutrition assistance program, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Food under supplemental nutrition assistance program.
(a) Definition of food.—Section 3(k)(1) of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 2012(k)(1)) is amended—
(1) by striking “except alcoholic beverages, tobacco” and inserting “designated by the Secretary under section 4(d), except any alcoholic beverages, tobacco, soft drinks, candy, ice cream, prepared desserts such as cakes, pies, cookies, or similar products”; and
(2) by striking “clauses” and inserting “paragraphs”.
(b) Designated food.—Section 4 of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 2013) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(d) Designated food.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this subsection, the Secretary shall designate by regulation the foods and food products that shall be included in the definition of the term ‘food’ under section 3(k)(1).
“(2) CONSIDERATIONS.—In carrying out paragraph (1), the Secretary shall—
“(A) take into consideration food and food products that—
“(i) based on nutrition research, contain nutrients lacking in the diets of people in the United States; and
“(ii) promote the health of the population served by the supplemental nutrition assistance program, based on relevant nutrition science, public health concerns, and cultural eating patterns; and
“(B) to the maximum extent practicable, ensure that the fat, sugar, and salt content of the food and food products is appropriate.
“(3) REVIEW OF AVAILABLE FOODS.—As frequently as determined by the Secretary to be necessary to reflect the most recent scientific knowledge, but not less frequently than once every 5 years, the Secretary shall—
“(A) conduct a scientific review of the food and food products designated under paragraph (1); and
“(B) amend those foods and food products, as necessary, to reflect nutrition science, public health concerns, and cultural eating patterns.
“(4) PREPARED MEALS.—Prepared meals described in section 3(k) shall have nutritional values consistent with regulations developed by the Secretary under this subsection.
“(5) CULTURAL CUISINES.—To allow for different cultural eating patterns, State agencies may, with the approval of the Secretary, substitute different food for food designated under paragraph (1) subject to the condition that the different food is nutritionally equivalent to the substituted food.”.
S.813 – SHOPP Act of 2025 or the Supporting all Healthy Options when Purchasing Produce Act of 2025
A bill to amend the Food, Conservation, and Energy Act of 2008 to provide families year-round access to nutrition incentives under the Gus Schumacher Nutrition Incentive Program, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Nutrition incentives under Gus Schumacher Nutrition Incentive Program.
Section 4405 of the Food, Conservation, and Energy Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 7517) is amended—
(1) in subsection (b)(2)(B)—
(A) by redesignating clauses (ix) and (x) as clauses (x) and (xi), respectively; and
(B) by inserting after clause (viii) the following:
“(ix) increase the year-round availability of the incentive described in subparagraph (A)(ii)(II) by offering fresh frozen fruits or vegetables;”; and
(2) in subsection (c)—
(A) in paragraph (1)(A), by striking “fruits and vegetables” and inserting “fruits, vegetables, and legumes”; and
(B) in paragraph (3), by striking “fresh fruits and vegetables” each place it appears and inserting “fresh or fresh frozen fruits, vegetables, and legumes”.
S.1021 – Dairy Nutrition Incentive Program Act of 2025
A bill to amend the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 to establish a dairy nutrition incentive program, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Dairy nutrition incentive program.
(a) In general.—The Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 2011 et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 31. Dairy nutrition incentive program.
“(a) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) DAIRY PRODUCT.—The term ‘dairy product’ means a product for which cow’s milk is listed as—
“(A) the first ingredient on the labeled ingredients list of the product; or
“(B) the second ingredient on the labeled ingredients list of the product, if the first listed ingredient is water.
“(2) ELIGIBLE ENTITY.—The term ‘eligible entity’ means—
“(A) a State or local governmental entity; and
“(B) a nonprofit organization.
“(3) FLUID MILK.—The term ‘fluid milk’ means any variety of pasteurized cow’s milk that—
“(A) is packaged in liquid form; and
“(B) contains vitamins A and D at levels consistent with the Food and Drug Administration standards, and applicable State and local standards, for fluid milk.
“(4) NATURALLY NUTRIENT-RICH DAIRY.—The term ‘naturally nutrient-rich dairy’ means—
“(A) fluid milk;
“(B) yogurt and other cultured cow’s milk dairy products; and
“(C) cheese (including nonstandardized cheese) made from cow’s milk.
“(5) PROGRAM.—The term ‘program’ means the dairy nutrition incentive program established under subsection (b).
“(b) Establishment.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this section, the Secretary shall establish a dairy nutrition incentive program under which the Secretary shall develop and test methods to increase the purchase and consumption of naturally nutrient-rich dairy by members of households that receive benefits under the supplemental nutrition assistance program by providing an incentive for the purchase of naturally nutrient-rich dairy at the point of purchase to members of households purchasing food using those benefits.
“(c) Grants or cooperative agreements.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—To carry out the program, the Secretary shall enter into cooperative agreements with, or provide grants to, eligible entities, on a competitive basis, for projects that meet the purpose of the program described in subsection (b).
“(2) APPLICATION.—An eligible entity seeking to enter into a cooperative agreement or receive a grant under the program shall submit to the Secretary an application at such time, in such manner, and containing such information as the Secretary may require.
“(3) SELECTION CRITERIA.—The Secretary shall develop and make public criteria for evaluating proposed projects in applications submitted under paragraph (2), which shall incorporate a scientifically based strategy designed to improve diet quality and nutritional outcomes through the increased purchase of naturally nutrient-rich dairy.
“(4) PRIORITY.—In entering into cooperative agreements and awarding grants under the program, the Secretary shall give priority to projects that—
“(A) maximize the percentage of funds used for direct incentives for participants in the supplemental nutrition assistance program;
“(B) include a project design—
“(i) that provides incentives when naturally nutrient-rich dairy is purchased using benefits under the supplemental nutrition assistance program; and
“(ii) in which the incentives earned may be used only to purchase naturally nutrient-rich dairy;
“(C) include project sites that serve members of households that participate in the supplemental nutrition assistance program; and
“(D) incorporate the use of point-of-sale systems that can electronically issue incentives earned under the program.
“(5) ADDITIONAL FINANCIAL ASSISTANCE.—An eligible entity may request funds from the Secretary, pursuant to section 16, to offset initial costs to enable electronic benefits transfer technology for electronic point-of-sale systems described in paragraph (4)(D) for project sites selected under the program.
“(d) Evaluation.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary shall provide for an independent evaluation of each project carried out under the program that measures, to the maximum extent practicable, the effect of incentives on purchases of naturally nutrient-rich dairy by members of households that receive benefits under the supplemental nutrition assistance program.
“(2) METHODOLOGY REQUIREMENT.—The independent evaluation under paragraph (1) shall use rigorous methodologies, such as random assignment or other methods that are capable of producing scientifically valid information regarding activities that are effective.
“(3) DISCONTINUANCE.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Except as provided in subparagraph (B), subject to availability of funds, nothing in this section shall limit the continuation of a project carried out under the program.
“(B) NONCOMPLIANCE.—The Secretary may discontinue a project or close a project site under the program if the project—
“(i) does not comply with the requirements under this section;
“(ii) does not comply with the requirements of the grant awarded or cooperative agreement entered into under the program, as applicable; or
“(iii) if the Secretary determines that the results of the independent evaluation of the project under paragraph (1) are not satisfactory.
“(4) PUBLIC DISSEMINATION.—The Secretary shall make publicly available the results of each independent evaluation carried out under paragraph (1).
“(e) Report.—Not later than December 31 of the first full calendar year following the date of establishment of the program, and biennially thereafter, the Secretary shall submit to the Committee on Agriculture, Nutrition, and Forestry of the Senate and the Committee on Agriculture of the House of Representatives a report that includes a description of—
“(1) the status of each project carried out under the program; and
“(2) the results of each completed evaluation under paragraph (1) during the period covered by the report.
“(f) Funding.—
“(1) MANDATORY FUNDING.—There is appropriated to the Secretary, out of any funds in the Treasury not otherwise appropriated, $10,000,000 for each fiscal year to carry out this section.
“(2) AUTHORIZATION OF APPROPRIATIONS.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—In addition to the funds made available under paragraph (1), there is authorized to be appropriated to the Secretary to carry out this section $10,000,000 for fiscal year 2025 and each fiscal year thereafter.
“(B) APPROPRIATIONS IN ADVANCE.—With respect to any funds made available under subparagraph (A), only funds appropriated in advance specifically to carry out this section shall be available to carry out this section.
“(3) EVALUATION COSTS.—Of the funds made available to carry out this section for a fiscal year, the Secretary shall use not more than 7 percent to carry out subsection (d).
“(4) LIMITATION ON USE.—Funds made available to carry out this section shall not be used for any project that limits the use of benefits under the supplemental nutrition assistance program.”.
(b) Transition from healthy fluid milk incentives projects.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary of Agriculture (referred to in this subsection as the “Secretary”) shall transition projects carried out under section 4208 of the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018 (7 U.S.C. 2026a) to be carried out as part of the dairy nutrition incentive program established under section 31 of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008.
(2) NO INTERRUPTION.—In carrying out paragraph (1), the Secretary shall ensure that—
(A) there is no interruption in projects being carried out under section 4208 of the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018 (7 U.S.C. 2026a) during the transition described in that paragraph; and
(B) any additional authorities or flexibilities under the dairy nutrition incentive program established under section 31 of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 shall be applied to the projects described in subparagraph (A).
(3) REPEAL.—Effective 1 year after the date on which the Secretary certifies that the Secretary has completed carrying out paragraph (1), section 4208 of the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018 (7 U.S.C. 2026a) is repealed.
S.1100 – A bill to amend the Food and Nutrition Act to modify the definition of food under the supplemental nutrition assistance program, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Definition of food; waiver of eligibility of certain food.
(a) Definition of food.—Section 3(k) of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 2012(k)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1), by striking “home consumption” and inserting “home consumption, subject to section 11(y),”; and
(2) by inserting “, any nonalcoholic beverage that is not water, cow’s milk, a milk-substitute beverage (such as almond milk, soy milk, and coconut milk), or 100 percent juice, snack and dessert food items (as described in the supplemental guidance document of the Food and Nutrition Service, effective as of March 5, 2018, entitled ‘Accessory Foods List’),” before “tobacco”.
(b) Waiver of eligibility of certain food.—Section 11 of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 (7 U.S.C. 2020) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(y) Waiver of eligibility of certain food.—The Secretary shall permit a State agency, on request of the State agency, to prohibit the use of benefits to purchase food that the applicable State nutrition agency determines to be unhealthy food.”.
S.1129 – Dietary Guidelines Reform Act of 2025
A bill to amend the National Nutrition Monitoring and Related Research Act of 1990 to improve the dietary guidelines, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Establishment of dietary guidelines.
(a) In general.—Section 301(a) of the National Nutrition Monitoring and Related Research Act of 1990 (7 U.S.C. 5341(a)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1)—
(A) by striking the paragraph designation and heading and all that follows through “five years” in the first sentence and inserting the following:
“(1) IN GENERAL.—At least every 10 years,”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following: “Rulemaking requirements under section 553 of title 5, United States Code, shall apply to the development of each report under this paragraph.”;
(2) by indenting paragraphs (2) and (3) appropriately;
(3) in paragraph (2), by striking “shall” and all that follows through the period at the end and inserting the following: “shall—
“(A) be based on significant scientific agreement that is determined by evidence-based review (as defined in paragraph (9)(A));
“(B) be current at the time that the report is prepared;
“(C) be derived from the questions generated under paragraph (5)(E);
“(D) address high-priority areas of concern to advance health outcomes;
“(E) be designed to achieve nutritional adequacy and promote health, as specified by the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, through the consumption of food, including nutrients and bioactive food components occurring naturally and in fortified foods;
“(F) include nutritional and dietary information relevant to individuals with common nutrition-related chronic diseases, as defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; and
“(G) include recommendations that are affordable, available, and accessible for the general population.”;
(4) by redesignating paragraph (3) as paragraph (8);
(5) by inserting after paragraph (2) the following:
“(3) FREQUENCY.—The Secretaries may publish the report required under paragraph (1) more frequently than required under that paragraph if the Secretaries determine that more frequent publication is necessary to promote health based on updated dietary reference intake values specified by—
“(A) the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; and
“(B) other relevant scientific advancements based on continuous review of the totality of publicly available scientific evidence.
“(4) NOTIFICATION OF UPDATE.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 90 days before the Secretaries plan to update a report under paragraph (1), the Secretaries shall submit notification of that plan, in writing, to the Committees on Agriculture, Nutrition, and Forestry and Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions of the Senate and the Committees on Agriculture and Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives.
“(B) JUSTIFICATION.—The notification under subparagraph (A) shall include a justification for updating the report.
“(5) INDEPENDENT ADVISORY BOARD.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 90 days after the Secretaries submit a notification under paragraph (4)(A), the Secretaries shall establish an Independent Advisory Board (referred to in this paragraph as the ‘Board’).
“(B) MEMBERS.—The Board shall comprise not more than 8 members, of which—
“(i) 4 shall be appointed by the Secretaries, 2 of whom shall not be Federal employees; and
“(ii) 1 shall be appointed by each of the highest-ranking Member on each Committee described in paragraph (4)(A) of the opposite political party of the President of the United States.
“(C) EXPERTISE.—Each member appointed to the Board shall have expertise in nutrition science or food science, including academic and applied experience.
“(D) MEETINGS.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—The first meeting of the Board shall take place on or after the date that is 90 days after the Secretaries submit a notification under paragraph (4)(A).
“(ii) QUORUM.—A 6⁄8 majority of the members shall constitute a quorum for the transaction of the business of the Board.
“(E) DUTIES.—Not later than 1 year after the establishment of the Board, the Board shall submit to the Secretaries and the Committees described in paragraph (4)(A) a list of scientific questions based on the proposed report under paragraph (1), which questions shall be used to inform the work of the Secretaries on that report and any relevant work of the Committees described in paragraph (4)(A).
“(F) TERMINATION.—The authority of the Board shall terminate, and the Board shall disband, immediately after carrying out subparagraph (E).
“(6) DIETARY REFERENCE INTAKE UPDATES.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The Secretaries shall coordinate with the Joint United States-Canada Dietary Reference Intake Working Group to ensure that the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine update the dietary reference intake values to represent the most up-to-date understanding of nutritional science.
“(B) UPDATES.—The Joint United States-Canada Dietary Reference Intake Working Group is encouraged—
“(i) to initiate at least 1 dietary reference intake update per year; and
“(ii) to identify updates that are of highest priority and necessitate review.
“(7) EXCLUSION.—The information and guidelines contained in each report required under paragraph (1) shall not be based on or include topics that are not relevant to dietary guidance, as determined by the Secretaries, in consultation with the Independent Advisory Board established under paragraph (5), including taxation, social welfare policies, purchases under Federal feeding programs, food and agricultural production practices, food labeling, socioeconomic status, race, religion, ethnicity, culture, or regulations relating to nutrition.”; and
(6) by adding at the end the following:
“(9) EVIDENCE-BASED REVIEW.—
“(A) DEFINITION OF EVIDENCE-BASED REVIEW.—In this paragraph, the term ‘evidence-based review’ means a process under which—
“(i) the totality of the scientific evidence relevant to a question of interest is collected, analyzed, and evaluated;
“(ii) scientific studies, conclusions, and recommendations are rated, adhering strictly to standardized, generally accepted evidence-based review methods; and
“(iii) external peer review is conducted by nongovernment experts with recognized expertise in quality-of-evidence evaluation.
“(B) STRENGTH OF EVIDENCE.—Each guideline contained in a report published under paragraph (1) shall be assigned a rating by the Secretaries for the strength of evidence used, including the extent to which the guideline will improve the Healthy Eating Index.
“(10) TRANSPARENCY.—
“(A) DISCLOSURE.—Any individual appointed to the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee or an Independent Advisory Board established under paragraph (5) shall provide full disclosure of all financial and nonfinancial conflicts of interest relevant to their membership using the Office of Government Ethics Form 450 (or successor form).
“(B) PUBLICATION.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, not later than 30 days after the date on which a Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee is established, the Secretaries shall make publicly available—
“(i) the disclosures required under subparagraph (A), categorized by the name of the individual; and
“(ii) a detailed plan for managing any disclosed conflicts of interest, including financial or ethical conflicts of interest, preferences, values, and beliefs.
“(11) FUNDING.—Of the funds made available by section 32 of the Act of August 24, 1935 (7 U.S.C. 612c), the Secretary of Agriculture shall make available to carry out this subsection $5,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2025 through 2029, to remain available until expended.”.
(b) Controlling report.—The 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans published by the Secretaries under section 301(a)(1) of the National Nutrition Monitoring and Related Research Act of 1990 (7 U.S.C. 5341(a)(1)) (as in effect before the date of enactment of this Act) shall be considered the most recent Dietary Guidelines for Americans until the publication of the first report under that section (as amended by subsection (a)).
S.1202 – A bill to amend the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 to permit supplemental nutrition assistance program benefits to be used to purchase additional types of food items.
S.1236 – A bill to amend the Richard B. Russell National School Lunch Act to require schools to offer a variety of milk to students participating in the school lunch program, and for other purposes.
Mental Health
S.683 – More Behavioral Health Providers Act of 2025
A bill to amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to expand eligibility for incentives under the Medicare health professional shortage area bonus program to practitioners furnishing mental health and substance use disorder services.
SEC. 2. Expanding eligibility for incentives under the Medicare health professional shortage area bonus program to practitioners furnishing mental health and substance use disorder services.
Section 1833(m) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395l(m)) is amended—
(1) by striking paragraph (1) and inserting the following new paragraph:
“(1) In the case of—
“(A) physicians’ services (other than specified health services that are eligible for the additional payment under subparagraph (B)) furnished in a year to an individual, who is covered under the insurance program established by this part and who incurs expenses for such services, in an area that is designated (under section 332(a)(1)(A) of the Public Health Service Act) as a health professional shortage area as identified by the Secretary prior to the beginning of such year, in addition to the amount otherwise paid under this part, there also shall be paid to the physician (or to an employer or facility in the cases described in clause (A) of section 1842(b)(6)) (on a monthly or quarterly basis) from the Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Fund an amount equal to 10 percent of the payment amount for the service under this part; and
“(B) specified health services (as defined in paragraph (5)) furnished in a year to an individual, who is covered under the insurance program established by this part and who incurs expenses for such services, in an area that is designated (under such section 332(a)(1)(A)) as a mental health professional shortage area as identified by the Secretary prior to the beginning of such year, in addition to the amount otherwise paid under this part, there also shall be paid to the physician or applicable practitioner (as defined in paragraph (6)) (or to an employer or facility in the cases described in clause (A) of section 1842(b)(6)) (on a monthly or quarterly basis) from such Trust Fund an amount equal to 15 percent of the payment amount for the service under this part.”;
(2) in paragraph (2)—
(A) by striking “in paragraph (1)” and inserting “in subparagraph (A) or (B) of paragraph (1)”; and
(B) by inserting “or, in the case of specified health services, the physician or applicable practitioner” after “physician”;
(3) in paragraph (3), by striking “paragraph (1)” each place it appears and inserting “subparagraph (A) or (B) of paragraph (1)”;
(4) in paragraph (4)—
(A) in subparagraph (B), by inserting “or applicable practitioner” after “physician”; and
(B) in subparagraph (C), by inserting “or applicable practitioner” after “physician”; and
(5) by adding at the end the following new paragraphs:
“(5) In this subsection, the term ‘specified health services’ means services otherwise covered under this part that are furnished on or after January 1, 2024, by a physician or an applicable practitioner to an individual—
“(A) for purposes of diagnosis, evaluation, or treatment of a mental health disorder, as determined by the Secretary; or
“(B) with a substance use disorder diagnosis for purposes of treatment of such disorder or co-occurring mental health disorder, as determined by the Secretary.
“(6) In this subsection, the term ‘applicable practitioner’ means the following:
“(A) A physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist (as defined in section 1861(aa)(5)).
“(B) A clinical social worker (as defined in section 1861(hh)(1)).
“(C) A clinical psychologist (as defined by the Secretary for purposes of section 1861(ii)).
“(D) A marriage and family therapist (as defined in section 1861(lll)(2)).
“(E) A mental health counselor (as defined in section 1861(lll)(4)).”.
S.779 – EARLY Minds Act or Early Action and Responsiveness Lifts Youth Minds Act
A bill to amend title XIX of the Public Health Service Act to provide for prevention and early intervention services under the Block Grants for Community Mental Health Services program, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Early intervention.
(a) State plan option.—Section 1912(b)(1)(A)(vii) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 300x–1(b)(1)(A)(vii)) is amended—
(1) in subclause (III), by striking “and” at the end;
(2) in subclause (IV), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(V) a description of any evidence-based prevention and early intervention strategies and programs the State provides to prevent, delay, or reduce the severity and onset of mental illness and behavioral problems, including for children and adolescents, irrespective of experiencing a serious mental illness or serious emotional disturbance, as defined under subsection (c)(1).”.
(b) Allocation allowance; reports.—Section 1920 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 300x–9) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(e) Prevention and early intervention services.—In the case of a State with a State plan that provides for strategies and programs specified in section 1912(b)(1)(A)(vii)(V), such State may expend not more than 5 percent of the amount of the allotment of the State pursuant to a funding agreement under section 1911 for each fiscal year to support such strategies and programs.
“(f) Reports to congress.—Not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of the EARLY Minds Act, and biennially thereafter, the Secretary shall submit to Congress a report on the prevention and early intervention strategies and programs pursued by States pursuant to subsection (e). Each such report shall include—
“(1) a list of the States that utilized the option to provide prevention and early intervention services;
“(2) a description of the prevention and early intervention activities of each such State;
“(3) the population served, including information on demographics, including age;
“(4) the outcomes of such activities, including—
“(A) how such activities reduced delays in access to mental and behavioral health care for children and adults; and
“(B) how such activities reduced the severity of onset of serious mental illness and serious emotional disturbance; and
“(5) any other relevant information the Secretary determines necessary.”.
S.825 – Fighting Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Act of 2025
A bill to require the Attorney General to propose a program for making treatment for post-traumatic stress disorder and acute stress disorder available to public safety officers, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) Public safety officers serve their communities with bravery and distinction in order to keep their communities safe.
(2) Public safety officers, including police officers, firefighters, emergency medical technicians, and 911 dispatchers, are on the front lines of dealing with situations that are stressful, graphic, harrowing, and life-threatening.
(3) The work of public safety officers puts them at risk for developing post-traumatic stress disorder and acute stress disorder.
(4) It is estimated that 30 percent of public safety officers develop behavioral health conditions at some point in their lifetimes, including depression and post-traumatic stress disorder, in comparison to 20 percent of the general population that develops such conditions.
(5) Victims of post-traumatic stress disorder and acute stress disorder are at a higher risk of dying by suicide.
(6) Firefighters have been reported to have higher suicide attempt and ideation rates than the general population.
(7) It is estimated that between 125 and 300 police officers die by suicide every year.
(8) In 2019, pursuant to section 2(b) of the Law Enforcement Mental Health and Wellness Act of 2017 (Public Law 115–113; 131 Stat. 2276), the Director of the Office of Community Oriented Policing Services of the Department of Justice developed a report (referred to in this section as the “LEMHWA report”) that expressed that many law enforcement agencies do not have the capacity or local access to the mental health professionals necessary for treating their law enforcement officers.
(9) The LEMHWA report recommended methods for establishing remote access or regional mental health check programs at the State or Federal level.
(10) Individual police and fire departments generally do not have the resources to employ full-time mental health experts who are able to treat public safety officers with state-of-the-art techniques for the purpose of treating job-related post-traumatic stress disorder and acute stress disorder.
SEC. 3. Programming for post-traumatic stress disorder.
(a) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICER.—The term “public safety officer”—
(A) has the meaning given the term in section 1204 of title I of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10284); and
(B) includes Tribal public safety officers.
(2) PUBLIC SAFETY TELECOMMUNICATOR.—The term “public safety telecommunicator” means an individual who—
(A) operates telephone, radio, or other communication systems to receive and communicate requests for emergency assistance at 911 public safety answering points and emergency operations centers;
(B) takes information from the public and other sources relating to crimes, threats, disturbances, acts of terrorism, fires, medical emergencies, and other public safety matters; and
(C) coordinates and provides information to law enforcement and emergency response personnel.
(b) Report.—Not later than 150 days after the date of enactment of this Act, the Attorney General, acting through the Director of the Office of Community Oriented Policing Services of the Department of Justice, shall submit to the Committee on the Judiciary of the Senate and the Committee on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives a report on—
(1) not fewer than 1 proposed program, if the Attorney General determines it appropriate and feasible to do so, to be administered by the Department of Justice for making state-of-the-art treatments or preventative care available to public safety officers and public safety telecommunicators with regard to job-related post-traumatic stress disorder or acute stress disorder by providing public safety officers and public safety telecommunicators access to evidence-based trauma-informed care, peer support, counselor services, and family supports for the purpose of treating or preventing post-traumatic stress disorder or acute stress disorder;
(2) a draft of any necessary grant conditions required to ensure that confidentiality is afforded to public safety officers on account of seeking the care or services described in paragraph (1) under the proposed program;
(3) how each proposed program described in paragraph (1) could be most efficiently administered throughout the United States at the State, Tribal, territorial, and local levels, taking into account in-person and telehealth capabilities;
(4) a draft of legislative language necessary to authorize each proposed program described in paragraph (1); and
(5) an estimate of the amount of annual appropriations necessary for administering each proposed program described in paragraph (1).
(c) Development.—In developing the report required under subsection (b), the Attorney General shall consult relevant stakeholders, including—
(1) Federal, State, Tribal, territorial, and local agencies employing public safety officers and public safety telecommunicators; and
(2) non-governmental organizations, international organizations, academies, or other entities, including organizations that support the interests of public safety officers and public safety telecommunicators and the interests of family members of public safety officers and public safety telecommunicators.
S.931 – COMPLETE Care Act or the Connecting Our Medical Providers with Links to Expand Tailored and Effective Care
A bill to amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to provide incentives for behavioral health integration.
SEC. 2. Medicare incentives for behavioral health integration with primary care.
(a) Incentives.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 1848(b) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–4(b)) is amended by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(13) INCENTIVES FOR BEHAVIORAL HEALTH INTEGRATION.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—For services described in subparagraph (B) that are furnished during 2027, 2028, or 2029, instead of the payment amount that would otherwise be determined under this section for such year, the payment amount shall be equal to the applicable percent (as defined in subparagraph (C)) of such payment amount for such year.
“(B) SERVICES DESCRIBED.—The services described in this subparagraph are services identified, as of January 1, 2024, by HCPCS codes 99484, 99492, 99493, 99494, G2214, and G0323 (and any successor or similar codes as determined appropriate by the Secretary).
“(C) APPLICABLE PERCENT.—In this paragraph, the term ‘applicable percent’ means, with respect to a service described in subparagraph (A), the following:
“(i) For services furnished during 2027 , 175 percent.
“(ii) For services furnished during 2028, 150 percent.
“(iii) For services furnished during 2029, 125 percent.”.
(2) WAIVER OF BUDGET NEUTRALITY.—Section 1848(c)(2)(B)(iv) of such Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–4(c)(2)(B)(iv)) is amended—
(A) in subclause (V), by striking “and” at the end;
(B) in subclause (VI), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and” and
(C) by adding at the end the following new subclause:
“(VII) the increase in payment amounts as a result of the application of subsection (b)(13) shall not be taken into account in applying clause (ii)(II) for 2027, 2028, or 2029.”.
(b) Technical assistance for the adoption of behavioral health integration.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than January 1, 2026, the Secretary of Health and Human Services (in this subsection referred to as the “Secretary”) shall enter into contracts or agreements with appropriate entities to offer technical assistance to primary care practices that are seeking to adopt behavioral health integration models in such practices.
(2) BEHAVIORAL HEALTH INTEGRATION MODELS.—For purposes of paragraph (1), behavioral health integration models include the Collaborative Care Model (with services identified as of January 1, 2024, by HCPCS codes 99492, 99493, 99494, and G2214 (and any successor codes)), the Primary Care Behavioral Health model (with services identified as of January 1, 2024, by HCPCS codes 99484 and G0323 (and any successor code)), and other models identified by the Secretary.
(3) IMPLEMENTATION.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Secretary may implement the provisions of this subsection by program instruction or otherwise.
(4) FUNDING.—In addition to amounts otherwise available, there is appropriated to the Secretary for each of fiscal years 2025 through 2029, out of any money in the Treasury not otherwise appropriated, such sums as are necessary, to remain available until expended, for purposes of carrying out this subsection.
S.1264 – A bill to amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to establish a demonstration program to promote collaborative treatment of mental and physical health comorbidities under the Medicare program.
S.1266 – A bill to establish a Youth Mental Health Research Initiative in the National Institutes of Health for purposes of encouraging collaborative research to improve youth mental health.
A bill to establish a Youth Mental Health Research Initiative in the National Institutes of Health for purposes of encouraging collaborative research to improve youth mental health.
Pharmacy
S.526 – Pharmacy Benefit Manager Transparency Act of 2025
A bill to prevent unfair and deceptive acts or practices and the dissemination of false information related to pharmacy benefit management services for prescription drugs, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Prohibition on unfair or deceptive prescription drug pricing practices.
(a) Conduct prohibited.—Except as provided in subsection (b), it shall be unlawful for any pharmacy benefit manager (or affiliate, subsidiary, or agent of a pharmacy benefit manager), directly or indirectly, to engage in any of the following activities related to pharmacy benefit management services:
(1) Charge a health plan or payer a different amount for a prescription drug’s ingredient cost or dispensing fee than the amount the pharmacy benefit manager reimburses a pharmacy for the prescription drug’s ingredient cost or dispensing fee where the pharmacy benefit manager retains the amount of any such difference.
(2) Arbitrarily, unfairly, or deceptively, by contract or any other means, reduce, rescind, or otherwise claw back any reimbursement payment, in whole or in part, to a pharmacist or pharmacy for a prescription drug’s ingredient cost or dispensing fee, unless—
(A) the original claim was submitted fraudulently;
(B) the original claim payment was inconsistent with the reimbursement terms in the contract; or
(C) the pharmacist services were not rendered by the pharmacy or pharmacist.
(3) Arbitrarily, unfairly, or deceptively, by contract or any other means, increase fees or lower reimbursement to a pharmacy in order to offset reimbursement changes instructed by the Federal Government under any health plan funded by the Federal Government.
(b) Exceptions.—A pharmacy benefit manager shall not be in violation of paragraph (1) or (3) of subsection (a) if the pharmacy benefit manager meets the following conditions:
(1) The pharmacy benefit manager, affiliate, subsidiary, or agent passes along or returns 100 percent of any price concession to a health plan or payer, including any rebate, discount, or other price concession.
(2) The pharmacy benefit manager, affiliate, subsidiary, or agent provides full and complete disclosure of—
(A) the cost, price, and reimbursement of a prescription drug to each health plan, payer, and pharmacy with which the pharmacy benefit manager, affiliate, subsidiary, or agent has a contract or agreement to provide pharmacy benefit management services;
(B) each fee, markup, and discount charged or imposed by the pharmacy benefit manager, affiliate, subsidiary, or agent to each health plan, payer, and pharmacy with which the pharmacy benefit manager, affiliate, subsidiary, or agent has a contract or agreement for pharmacy benefit management services; or
(C) the aggregate amount of all remuneration the pharmacy benefit manager receives from a prescription drug manufacturer for a prescription drug, including any rebate, discount, administration fee, and any other payment or credit obtained or retained by the pharmacy benefit manager, or affiliate, subsidiary, or agent of the pharmacy benefit manager, pursuant to a contract or agreement for pharmacy benefit management services to a health plan, payer, or any Federal agency (upon the request of the agency).
SEC. 3. Prohibition on false information.
It shall be unlawful for any person to report information related to pharmacy benefit management services to a Federal department or agency if—
(1) the person knew, or reasonably should have known, the information to be false or misleading;
(2) the information was required by law to be reported; and
(3) the false or misleading information reported by the person would affect analysis or information compiled by the Federal department or agency for statistical or analytical purposes with respect to the market for pharmacy benefit management services.
SEC. 4. Transparency.
(a) Reporting by pharmacy benefit managers.—Subject to subsection (d), not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of this Act, and annually thereafter, each pharmacy benefit manager (or affiliate, subsidiary, or agent of a pharmacy benefit manager) shall report to the Commission and the Secretary of Health and Human Services the following information:
(1) The aggregate amount of the difference between the amount the pharmacy benefit manager was paid by each health plan and the amount that the pharmacy benefit manager paid each pharmacy on behalf of the health plan for prescription drugs.
(2) The aggregate amount of any—
(A) generic effective rate fee charged to each pharmacy;
(B) direct and indirect remuneration fee charged or other price concession to each pharmacy; and
(C) payment rescinded or otherwise clawed back from a reimbursement made to each pharmacy.
(3) If, during the reporting year, the pharmacy benefit manager moved or reassigned a prescription drug to a formulary tier that has a higher cost, higher copayment, higher coinsurance, or higher deductible to a consumer, or a lower reimbursement to a pharmacy, an explanation of the reason why the drug was moved or reassigned from 1 tier to another, including whether the move or reassignment was determined or requested by a prescription drug manufacturer or other entity.
(4) With respect to any pharmacy benefit manager that owns, controls, or is affiliated with a pharmacy, a report regarding any difference in reimbursement rates or practices, direct and indirect remuneration fees or other price concessions, and clawbacks between a pharmacy that is owned, controlled, or affiliated with the pharmacy benefit manager and any other pharmacy.
(b) Report to Congress.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of this Act, and annually thereafter, the Commission shall submit to the Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation of the Senate and the Committee on Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives a report that addresses, at a minimum—
(A) the number actions brought by the Commission during the reporting year to enforce this Act and the outcome of each such enforcement action;
(B) the number of open investigations or inquiries into potential violations of this Act as of the time the report is submitted;
(C) the number and nature of complaints received by the Commission relating to an allegation of a violation of this Act during the reporting year;
(D) an anonymized summary of the reports filed with the Commission pursuant to subsection (a) for the reporting year;
(E) an analysis of the requirements of this Act and whether the implementation of such requirements leads to mergers (including horizontal mergers or vertical mergers) amongst any pharmacy benefit managers, or any pharmacy benefit manager that owns, controls, or is affiliated with a pharmacy, or any pharmacy benefit manager that owns, controls, or is affiliated with a health plan, and the effect of such merger (including the likelihood of a substantial decrease in competition or the potential for a monopoly); and
(F) policy or legislative recommendations to strengthen any enforcement action relating to a violation of this Act, including recommendations to include additional prohibited conduct in section 2(a), and recommendations to encourage more competition and decrease the likelihood of a monopoly in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
(2) FORMULARY DESIGN OR PLACEMENT PRACTICES.—Not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of this Act, the Commission shall submit to the Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation of the Senate, the Committee on Finance of the Senate, the Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions of the Senate, the Committee on Ways and Means of the House of Representatives, and the Committee on Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives a report that addresses the policies, practices, and role of pharmacy benefit managers (including their affiliates, subsidiaries, and agents) regarding formulary design or placement, including—
(A) whether pharmacy benefit managers (including their affiliates, subsidiaries, and agents) use formulary design or placement to increase their gross revenue without an accompanying increase in patient access or decrease in patient cost; or
(B) recommendations to Congress for legislative action addressing such policies, practices, and role of pharmacy benefit managers (including their affiliates, subsidiaries, and agents).
(3) CONSTRUCTION.—Nothing in this section shall be construed as authorizing the Commission to disclose any information that is a trade secret or confidential information described in section 552(b)(4) of title 5, United States Code, except as necessary to enforce this Act.
(4) CONFIDENTIALITY.—The Commission may disclose the information in a form which does not disclose the identity of a specific pharmacy benefit manager, pharmacy, or health plan for the following purposes:
(A) To permit the Comptroller General of the United States to review the information provided to carry out this Act.
(B) To permit the Director of the Congressional Budget Office to review the information provided.
(c) GAO study.—Not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of this Act, the Comptroller General of the United States shall submit to the Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation, the Committee on Finance, and the Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions of the Senate and to the Committee on Ways and Means and the Committee on Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives a report that—
(1) addresses, at minimum—
(A) the role that pharmacy benefit managers play in the pharmaceutical supply chain;
(B) the state of competition among pharmacy benefit managers, including the market share for the Nation’s 10 largest pharmacy benefit managers;
(C) the use of rebates and fees by pharmacy benefit managers, including data for each of the 10 largest pharmacy benefit managers that reflects, for each drug in the formulary of each such pharmacy benefit manager—
(i) the amount of the rebate passed on to patients;
(ii) the amount of the rebate passed on to payors;
(iii) the amount of the rebate kept by the pharmacy benefit manager; and
(iv) the role of fees charged by the pharmacy benefit manager;
(D) whether pharmacy benefit managers structure their formularies in favor of high-rebate prescription drugs over lower-cost, lower-rebate alternatives;
(E) the average prior authorization approval time for each of the 10 largest pharmacy benefit managers;
(F) factors affecting the use of step therapy in each of the 10 largest pharmacy benefit managers;
(G) the extent to which the price that pharmacy benefit managers charge payors, such as the Medicare program under title XXVIII of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395 et seq.), State Medicaid programs under title XIX of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396 et seq.), the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program under chapter 89 of title 5, United States Code, or private payors, for a drug is more than such pharmacy benefit managers pay the pharmacy for the drug; and
(H) the competitive impact of pharmacy benefit managers’ business practices, including the impact that such business practices have on the cost of health plan premiums or prescription drugs for consumers; and
(2) provides recommendations for legislative action to lower the cost of prescription drugs for consumers and payors, improve the efficiency of the pharmaceutical supply chain by lowering intermediary costs, improve competition in pharmacy benefit management, and provide transparency in pharmacy benefit management.
(d) Privacy requirements.—Any entity shall provide information under subsection (a) in a manner consistent with the privacy, security, and breach notification regulations promulgated under section 264(c) of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (42 U.S.C. 1320d–2 note) (or any successor regulation), and shall restrict the use and disclosure of such information according to such regulations.
SEC. 5. Whistleblower protections.
(a) In general.—A pharmacy benefit manager, health plan, pharmaceutical manufacturer, pharmacy, or any affiliate, subsidiary, or agent thereof shall not, directly or indirectly, discharge, demote, suspend, diminish, or withdraw benefits from, threaten, harass, or in any other manner discriminate against or adversely impact a covered individual because—
(1) the covered individual, or anyone perceived as assisting the covered individual, takes (or is suspected to have taken or will take) a lawful action in providing to Congress, an agency of the Federal Government, the attorney general of a State, a State regulator with authority over the distribution or insurance coverage of prescription drugs, or a law enforcement agency relating to any act or omission that the covered individual reasonably believes to be a violation of this Act;
(2) the covered individual provides information that the covered individual reasonably believes evidences such a violation to—
(A) a person with supervisory authority over the covered individual at the pharmacy benefit manager, health plan, pharmaceutical manufacturer, pharmacy, or any affiliate, subsidiary, or agent thereof; or
(B) another individual working for the pharmacy benefit manager, health plan, pharmaceutical manufacturer, pharmacy, or any affiliate, subsidiary, or agent thereof who the covered individual reasonably believes has the authority to investigate, discover, or terminate the violation or to take any other action to address the violation;
(3) the covered individual testifies (or it is suspected that the covered individual will testify) in an investigation or judicial or administrative proceeding concerning such a violation; or
(4) the covered individual assists or participates (or it is expected that the covered individual will assist or participate) in such an investigation or judicial or administrative proceeding.
(b) Enforcement.—An individual who alleges any adverse action in violation of subsection (a) may bring an action for a jury trial in the appropriate district court of the United States for the following relief:
(1) Temporary relief while the case is pending.
(2) Reinstatement with the same seniority status that the individual would have had, but for the discharge or discrimination.
(3) Twice the amount of back pay otherwise owed to the individual, with interest.
(4) Consequential and compensatory damages, and compensation for litigation costs, expert witness fees, and reasonable attorneys’ fees.
(c) Waiver of rights and remedies.—The rights and remedies provided for in this section shall not be waived by any policy form or condition of employment, including by a predispute arbitration agreement.
(d) Predispute arbitration agreements.—No predispute arbitration agreement shall be valid or enforceable if the agreement requires arbitration of a dispute arising under this section.
SEC. 6. Enforcement.
(a) Enforcement by the Commission.—
(1) UNFAIR AND DECEPTIVE ACTS OR PRACTICES.—A violation of this Act shall be treated as a violation of a rule defining an unfair or deceptive act or practice under section 18(a)(1)(B) of the Federal Trade Commission Act (15 U.S.C. 57a(a)(1)(B)).
(2) POWERS OF THE COMMISSION.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—Except as provided in subparagraph (C), the Commission shall enforce this Act in the same manner, by the same means, and with the same jurisdiction, powers, and duties as though all applicable terms and provisions of the Federal Trade Commission Act (15 U.S.C. 41 et seq.) were incorporated into and made a part of this Act.
(B) PRIVILEGES AND IMMUNITIES.—Subject to paragraph (3), any person who violates this Act shall be subject to the penalties and entitled to the privileges and immunities provided in the Federal Trade Commission Act (15 U.S.C. 41 et seq.).
(C) NONPROFIT ORGANIZATIONS AND INSURANCE.—Notwithstanding section 4 or 6 of the Federal Trade Commission Act (15 U.S.C. 44, 46), section 2 of McCarran-Ferguson Act (15 U.S.C. 1012), or any other jurisdictional limitation of the Commission, the Commission shall also enforce this Act, in the same manner provided in subparagraphs (A) and (B) of this paragraph, with respect to—
(i) organizations not organized to carry on business for their own profit or that of their members; and
(ii) the business of insurance, and persons engaged in such business.
(D) AUTHORITY PRESERVED.—Nothing in this section shall be construed to limit the authority of the Commission under any other provision of law.
(3) PENALTIES.—
(A) ADDITIONAL CIVIL PENALTY.—In addition to any penalty applicable under the Federal Trade Commission Act (15 U.S.C. 41 et seq.), any person that violates this Act shall be liable for a civil penalty of not more than $1,000,000.
(B) METHOD.—The penalties provided by subparagraph (A) shall be obtained in the same manner as civil penalties imposed under section 18(a)(1)(B) of the Federal Trade Commission Act (15 U.S.C. 57a(a(1)(B).
(C) MULTIPLE OFFENSES; MITIGATING FACTORS.—In assessing a penalty under subparagraph (A)—
(i) each day of a continuing violation shall be considered a separate violation; and
(ii) the court shall take into consideration, among other factors—
(I) the seriousness of the violation;
(II) the efforts of the person committing the violation to remedy the harm caused by the violation in a timely manner; and
(III) whether the violation was intentional.
(b) Enforcement by States.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—If the attorney general of a State has reason to believe that an interest of the residents of the State has been or is being threatened or adversely affected by a practice that violates this Act, the attorney general of the State may bring a civil action on behalf of the residents of the State in an appropriate district court of the United States to obtain appropriate relief.
(2) RIGHTS OF THE COMMISSION.—
(A) NOTICE TO THE COMMISSION.—
(i) IN GENERAL.—Except as provided in clause (iii), the attorney general of a State, before initiating a civil action under paragraph (1), shall provide written notification to the Commission that the attorney general intends to bring such civil action.
(ii) CONTENTS.—The notification required under clause (i) shall include a copy of the complaint to be filed to initiate the civil action.
(iii) EXCEPTION.—If it is not feasible for the attorney general of a State to provide the notification required under clause (i) before initiating a civil action under paragraph (1), the attorney general shall notify the Commission immediately upon instituting the civil action.
(B) INTERVENTION BY THE COMMISSION.—The Commission may—
(i) intervene in any civil action brought by the attorney general of a State under paragraph (1); and
(ii) upon intervening—
(I) be heard on all matters arising in the civil action; and
(II) file petitions for appeal of a decision in the civil action.
(3) CONSTRUCTION.—
(A) POWERS CONFERRED ON THE ATTORNEY GENERAL OF A STATE.—Nothing in this subsection may be construed to prevent the attorney general of a State from exercising the powers conferred on the attorney general by the laws of the State to conduct investigations, to administer oaths or affirmations, or to compel the attendance of witnesses or the production of documentary or other evidence.
(B) ERISA.—No civil action brought pursuant to this subsection shall conflict with the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (29 U.S.C. 1001 et seq.).
(4) VENUE; SERVICE OF PROCESS.—
(A) VENUE.—Any action brought under paragraph (1) may be brought in—
(i) the district court of the United States that meets applicable requirements relating to venue under section 1391 of title 28, United States Code; or
(ii) another court of competent jurisdiction.
(B) SERVICE OF PROCESS.—In an action brought under paragraph (1), process may be served in any district in which—
(i) the defendant is an inhabitant, may be found, or transacts business; or
(ii) venue is proper under section 1391 of title 28, United States Code.
(5) ACTIONS BY OTHER STATE OFFICIALS.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—If an attorney general lacks appropriate jurisdiction to bring a civil action under paragraph (1), any other officer of a State who is authorized by the State to do so may bring a civil action under paragraph (1), subject to the same requirements and limitations that apply under this subsection to civil actions brought by attorneys general.
(B) CLARIFICATION OF AUTHORITY.—The authority provided by subparagraph (A) shall supplant, and not supplement, the authorities of State attorneys general under paragraph (1).
(C) SAVINGS PROVISION.—Nothing in this subsection may be construed to prohibit an authorized official of a State from initiating or continuing any proceeding in a court of the State for a violation of any civil or criminal law of the State.
(c) Affirmative defense.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—In an action brought under this section to enforce section 2, it shall be an affirmative defense, on which the defendant has the burden of persuasion by a preponderance of the evidence, that the conduct alleged to be a violation of section 2 was nonpretextual and reasonably necessary to—
(A) prevent a violation of, or comply with, Federal or State law;
(B) protect patient safety; or
(C) protect patient access.
(2) CLARIFICATION.—Nothing in this subsection shall be construed to prohibit a defendant from raising any other affirmative defense available.
SEC. 7. Protection of personal health information.
In making any disclosure or report required by this Act, a pharmacy benefit manager (including their affiliates, subsidiaries, and agents) shall not include any information that would identify a patient or a provider that issued a prescription.
SEC. 8. Effect on State laws.
Nothing in this Act shall be construed to preempt, displace, or supplant any State laws, rules, regulations, or requirements, or the enforcement thereof.
SEC. 9. Definitions.
In this Act:
(1) COMMISSION.—The term “Commission” means the Federal Trade Commission.
(2) COVERED INDIVIDUAL.—The term “covered individual” means a current or former employee, contractor, subcontractor, service provider, or agent of a pharmacy benefit manager, health plan, pharmaceutical manufacturer, pharmacy, or any affiliate, subsidiary, or agent thereof.
(3) HEALTH PLAN.—The term “health plan” means any group or individual health insurance plan or coverage, including any health insurance plan or coverage sponsored or funded by the Federal Government or the government of any State, Territory, or subdivision thereof.
(4) PHARMACY BENEFIT MANAGER.—The term “pharmacy benefit manager” means any entity that provides pharmacy benefit management services on behalf of a health plan, a payer, or health insurance issuer.
(5) PHARMACY BENEFIT MANAGEMENT SERVICES.—The term “pharmacy benefit management services” means, pursuant to a written agreement with a payer or health plan offering group or individual health insurance coverage, directly or through an intermediary, the service of—
(A) negotiating terms and conditions, including rebates and price concessions, with respect to a prescription drug on behalf of the health plan, coverage, or payer; or
(B) managing the prescription drug benefits provided by the health plan, coverage, or payer, which may include formulary management the processing and payment of claims for prescription drugs, the performance of drug utilization review, the processing of drug prior authorization requests, the adjudication of appeals or grievances related to the prescription drug benefit, contracting with network pharmacies, or the provision of related services.
(6) PRESCRIPTION DRUG.—The term “prescription drug” means—
(A) a drug, as that term is defined in section 201(g) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 321(g)), that is—
(i) approved by the Food and Drug Administration under section 505 of such Act (21 U.S.C. 355); and
(ii) subject to the requirements of section 503(b)(1) of such Act (21 U.S.C. 353(b)(1));
(B) a biological product as that term is defined in section 351 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 262(i)(1)); or
(C) a product that is biosimilar to, or interchangeable with, a biologic product under section 351 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 262(i)).
S.882 – Patients Before Middlemen Act
A bill to amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to assure pharmacy access and choice for beneficiaries under prescription drug plans and MA-PD plans and to establish requirements of pharmacy benefit managers under Medicare part D.
SEC. 2. Assuring pharmacy access and choice for Medicare beneficiaries.
(a) In general.—Section 1860D–4(b)(1) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–104(b)(1)) is amended by striking subparagraph (A) and inserting the following:
“(A) IN GENERAL.—
“(i) PARTICIPATION OF ANY WILLING PHARMACY.—A PDP sponsor offering a prescription drug plan shall permit any pharmacy that meets the standard contract terms and conditions under such plan to participate as a network pharmacy of such plan.
“(ii) CONTRACT TERMS AND CONDITIONS.—
“(I) IN GENERAL.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, for plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2028, in accordance with clause (i), contract terms and conditions offered by such PDP sponsor shall be reasonable and relevant according to standards established by the Secretary under subclause (II).
“(II) STANDARDS.—Not later than the first Monday in April of 2027, the Secretary shall establish standards for reasonable and relevant contract terms and conditions for purposes of this clause.
“(III) REQUEST FOR INFORMATION.—Not later than April 1, 2026, for purposes of establishing the standards under subclause (II), the Secretary shall issue a request for information to seek input on trends in prescription drug plan and network pharmacy contract terms and conditions, current prescription drug plan and network pharmacy contracting practices, whether pharmacy reimbursement and dispensing fees paid by PDP sponsors to network pharmacies sufficiently cover the ingredient and operational costs of such pharmacies, the use and application of pharmacy quality measures by PDP sponsors for network pharmacies, PDP sponsor restrictions or limitations on the dispensing of covered part D drugs by network pharmacies (or any subsets of such pharmacies), PDP sponsor auditing practices for network pharmacies, areas in current regulations or program guidance related to contracting between prescription drug plans and network pharmacies requiring clarification or additional specificity, factors for consideration in determining the reasonableness and relevance of contract terms and conditions between prescription drug plans and network pharmacies, and other issues as determined appropriate by the Secretary.”.
(b) Essential retail pharmacies.—Section 1860D–42 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–152) is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(e) Essential retail pharmacies.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—With respect to plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2028, the Secretary shall publish reports, at least once every 2 years until 2034, and periodically thereafter, that provide information, to the extent feasible, on—
“(A) trends in ingredient cost reimbursement, dispensing fees, incentive payments and other fees paid by PDP sponsors offering prescription drug plans and MA organizations offering MA–PD plans under this part to essential retail pharmacies (as defined in paragraph (2)) with respect to the dispensing of covered part D drugs, including a comparison of such trends between essential retail pharmacies and pharmacies that are not essential retail pharmacies;
“(B) trends in amounts paid to PDP sponsors offering prescription drug plans and MA organizations offering MA–PD plans under this part by essential retail pharmacies with respect to the dispensing of covered part D drugs, including a comparison of such trends between essential retail pharmacies and pharmacies that are not essential retail pharmacies;
“(C) trends in essential retail pharmacy participation in pharmacy networks and preferred pharmacy networks for prescription drug plans offered by PDP sponsors and MA–PD plans offered by MA organizations under this part, including a comparison of such trends between essential retail pharmacies and pharmacies that are not essential retail pharmacies;
“(D) trends in the number of essential retail pharmacies, including variation in such trends by geographic region or other factors;
“(E) a comparison of cost-sharing for covered part D drugs dispensed by essential retail pharmacies that are network pharmacies for prescription drug plans offered by PDP sponsors and MA–PD plans offered by MA organizations under this part and cost-sharing for covered part D drugs dispensed by other network pharmacies for such plans located in similar geographic areas that are not essential retail pharmacies;
“(F) a comparison of the volume of covered part D drugs dispensed by essential retail pharmacies that are network pharmacies for prescription drug plans offered by PDP sponsors and MA–PD plans offered by MA organizations under this part and such volume of dispensing by network pharmacies for such plans located in similar geographic areas that are not essential retail pharmacies, including information on any patterns or trends in such comparison specific to certain types of covered part D drugs, such as generic drugs or drugs specified as specialty drugs by a PDP sponsor under a prescription drug plan or an MA organization under an MA–PD plan; and
“(G) a comparison of the information described in subparagraphs (A) through (F) between essential retail pharmacies that are network pharmacies for prescription drug plans offered by PDP sponsors under this part and essential retail pharmacies that are network pharmacies for MA–PD plans offered by MA organizations under this part.
“(2) DEFINITION OF ESSENTIAL RETAIL PHARMACY.—In this subsection, the term ‘essential retail pharmacy’ means, with respect to a plan year, a retail pharmacy that—
“(A) is not a pharmacy that is an affiliate as defined in paragraph (4); and
“(B) is located in—
“(i) a medically underserved area (as designated pursuant to section 330(b)(3)(A) of the Public Health Service Act);
“(ii) a rural area in which there is no other retail pharmacy within 10 miles, as determined by the Secretary;
“(iii) a suburban area in which there is no other retail pharmacy within 2 miles, as determined by the Secretary; or
“(iv) an urban area in which there is no other retail pharmacy within 1 mile, as determined by the Secretary.
“(3) LIST OF ESSENTIAL RETAIL PHARMACIES.—
“(A) PUBLICATION OF LIST OF ESSENTIAL RETAIL PHARMACIES.—For each plan year (beginning with plan year 2028), the Secretary shall publish, on a publicly available internet website of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, a list of pharmacies that meet the criteria described in subparagraphs (A) and (B) of paragraph (2) to be considered an essential retail pharmacy.
“(B) REQUIRED SUBMISSIONS FROM PDP SPONSORS.—For each plan year (beginning with plan year 2028), each PDP sponsor offering a prescription drug plan and each MA organization offering an MA–PD plan shall submit to the Secretary, for the purposes of determining retail pharmacies that meet the criterion specified in subparagraph (A) of paragraph (2), a list of retail pharmacies that are affiliates of such sponsor or organization, or are affiliates of a pharmacy benefit manager acting on behalf of such sponsor or organization, at a time, and in a form and manner, specified by the Secretary.
“(C) REPORTING BY PDP SPONSORS AND MA ORGANIZATIONS.—For each plan year beginning with plan year 2027, each PDP sponsor offering a prescription drug plan and each MA organization offering an MA–PD plan under this part shall submit to the Secretary information on incentive payments and other fees paid by such sponsor or organization to pharmacies, insofar as any such payments or fees are not otherwise reported, at a time, and in a form and manner, specified by the Secretary.
“(D) IMPLEMENTATION.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Secretary may implement this paragraph by program instruction or otherwise.
“(E) NONAPPLICATION OF PAPERWORK REDUCTION ACT.—Chapter 35 of title 44, United States Code, shall not apply to the implementation of this paragraph.
“(4) DEFINITION OF AFFILIATE.—In this subsection, the term ‘affiliate’ means any entity that is owned by, controlled by, or related under a common ownership structure with a pharmacy benefit manager or a managed care entity or other specified entity (as such terms are defined in section 1903(m)(9)(D)).”.
(c) Enforcement.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 1860D–4(b)(1) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–104(b)(1)) is amended by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(F) ENFORCEMENT OF STANDARDS FOR REASONABLE AND RELEVANT CONTRACT TERMS AND CONDITIONS.—
“(i) ALLEGATION SUBMISSION PROCESS.—
“(I) IN GENERAL.—Not later than January 1, 2028, the Secretary shall establish a process through which a pharmacy may submit to the Secretary an allegation of a violation by a PDP sponsor offering a prescription drug plan of the standards for reasonable and relevant contract terms and conditions under subparagraph (A)(ii), or of subclause (VIII) of this clause.
“(II) FREQUENCY OF SUBMISSION.—
“(aa) IN GENERAL.—Except as provided in item (bb), the allegation submission process under this clause shall allow pharmacies to submit any allegations of violations described in subclause (I) not more frequently than once per plan year per contract between a pharmacy and a PDP sponsor.
“(bb) ALLEGATIONS RELATING TO CONTRACT MODIFICATIONS.—In the case where a contract between a pharmacy and a PDP sponsor is modified following the submission of allegations by a pharmacy with respect to such contract and plan year, the allegation submission process under this clause shall allow such pharmacy to submit an additional allegation related to those modifications with respect to such contract and plan year.
“(III) ACCESS TO RELEVANT DOCUMENTS AND MATERIALS.—A PDP sponsor subject to an allegation under this clause—
“(aa) shall provide documents or materials, as specified by the Secretary, including contract offers made by such sponsor to such pharmacy or correspondence related to such offers, to the Secretary at a time, and in a form and manner, specified by the Secretary; and
“(bb) shall not prohibit or otherwise limit the ability of a pharmacy to submit such documents or materials to the Secretary for the purpose of submitting an allegation or providing evidence for such an allegation under this clause.
“(IV) STANDARDIZED TEMPLATE.—The Secretary shall establish a standardized template for pharmacies to use for the submission of allegations described in subclause (I). Such template shall require that the submission include a certification by the pharmacy that the information included is accurate, complete, and true to the best of the knowledge, information, and belief of such pharmacy.
“(V) PREVENTING FRIVOLOUS ALLEGATIONS.—In the case where the Secretary determines that a pharmacy has submitted frivolous allegations under this clause on a routine basis, the Secretary may temporarily prohibit such pharmacy from using the allegation submission process under this clause, as determined appropriate by the Secretary.
“(VI) EXEMPTION FROM FREEDOM OF INFORMATION ACT.—Allegations submitted under this clause shall be exempt from disclosure under section 552 of title 5, United States Code.
“(VII) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION.—Nothing in this clause shall be construed as limiting the ability of a pharmacy to pursue other legal actions or remedies, consistent with applicable Federal or State law, with respect to a potential violation of a requirement described in this subparagraph.
“(VIII) ANTI-RETALIATION AND ANTI-COERCION.—Consistent with applicable Federal or State law, a PDP sponsor shall not—
“(aa) retaliate against a pharmacy for submitting any allegations under this clause; or
“(bb) coerce, intimidate, threaten, or interfere with the ability of a pharmacy to submit any such allegations.
“(ii) INVESTIGATION.—The Secretary shall investigate, as determined appropriate by the Secretary, allegations submitted pursuant to clause (i).
“(iii) ENFORCEMENT.—
“(I) IN GENERAL.—In the case where the Secretary determines that a PDP sponsor offering a prescription drug plan has violated the standards for reasonable and relevant contract terms and conditions under subparagraph (A)(ii), the Secretary may use authorities under sections 1857(g) and 1860D–12(b)(3)(E) to impose civil monetary penalties or other intermediate sanctions.
“(II) APPLICATION OF CIVIL MONETARY PENALTIES.—The provisions of section 1128A (other than subsections (a) and (b)) shall apply to a civil monetary penalty under this clause in the same manner as such provisions apply to a penalty or proceeding under section 1128A(a).”.
(2) CONFORMING AMENDMENT.—Section 1857(g)(1) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–27(g)(1)) is amended—
(A) in subparagraph (J), by striking “or” after the semicolon;
(B) by redesignating subparagraph (K) as subparagraph (L);
(C) by inserting after subparagraph (J), the following new subparagraph:
“(K) fails to comply with the standards for reasonable and relevant contract terms and conditions under subparagraph (A)(ii) of section 1860D–4(b)(1); or”;
(D) in subparagraph (L), as redesignated by subparagraph (B), by striking “through (J)” and inserting “through (K)”; and
(E) in the flush matter following subparagraph (L), as so redesignated, by striking “subparagraphs (A) through (K)” and inserting “subparagraphs (A) through (L)”.
(d) Accountability of pharmacy benefit managers for violations of reasonable and relevant contract terms and conditions.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 1860D–12(b) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–112) is amended by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(9) ACCOUNTABILITY OF PHARMACY BENEFIT MANAGERS FOR VIOLATIONS OF REASONABLE AND RELEVANT CONTRACT TERMS AND CONDITIONS.—For plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2028, each contract entered into with a PDP sponsor under this part with respect to a prescription drug plan offered by such sponsor shall provide that any pharmacy benefit manager acting on behalf of such sponsor has a written agreement with the PDP sponsor under which the pharmacy benefit manager agrees to reimburse the PDP sponsor for any amounts paid by such sponsor under section 1860D–4(b)(1)(F)(iii)(I) to the Secretary as a result of a violation described in such section if such violation is related to a responsibility delegated to the pharmacy benefit manager by such PDP sponsor.”.
(2) MA–PD PLANS.—Section 1857(f)(3) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–27(f)(3)) is amended by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(F) ACCOUNTABILITY OF PHARMACY BENEFIT MANAGERS FOR VIOLATIONS OF REASONABLE AND RELEVANT CONTRACT TERMS.—For plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2028, section 1860D–12(b)(9).”.
(e) Biennial report on enforcement and oversight of pharmacy access requirements.—Section 1860D–42 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–152), as amended by subsection (b), is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(f) Biennial report on enforcement and oversight of pharmacy access requirements.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 2 years after the date of enactment of this subsection, and at least once every 2 years thereafter, the Secretary shall publish a report on enforcement and oversight actions and activities undertaken by the Secretary with respect to the requirements under section 1860D–4(b)(1).
“(2) LIMITATION.—A report under paragraph (1) shall not disclose—
“(A) identifiable information about individuals or entities unless such information is otherwise publicly available; or
“(B) trade secrets with respect to any entities.”.
SEC. 3. Requirements of pharmacy benefit managers under Medicare part D.
(a) Prescription drug plans.—Section 1860D–12 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–112) is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(h) Requirements relating to pharmacy benefit managers.—For plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2028:
“(1) AGREEMENTS WITH PHARMACY BENEFIT MANAGERS.—Each contract entered into with a PDP sponsor under this part with respect to a prescription drug plan offered by such sponsor shall provide that any pharmacy benefit manager acting on behalf of such sponsor has a written agreement with the PDP sponsor under which the pharmacy benefit manager, and any affiliates of such pharmacy benefit manager, as applicable, agree to meet the following requirements:
“(A) NO INCOME OTHER THAN BONA FIDE SERVICE FEES.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—The pharmacy benefit manager and any affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager shall not derive any remuneration with respect to any services provided on behalf of any entity or individual, in connection with the utilization of covered part D drugs, from any such entity or individual other than bona fide service fees, subject to clauses (ii) and (iii).
“(ii) INCENTIVE PAYMENTS.—For the purposes of this subsection, an incentive payment (as determined by the Secretary) paid by a PDP sponsor to a pharmacy benefit manager that is performing services on behalf of such sponsor shall be deemed a ‘bona fide service fee’ (even if such payment does not otherwise meet the definition of such term under paragraph (7)(B)) if such payment is a flat dollar amount, is consistent with fair market value (as specified by the Secretary), is related to services actually performed by the pharmacy benefit manager or affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager, on behalf of the PDP sponsor making such payment, in connection with the utilization of covered part D drugs, and meets additional requirements, if any, as determined appropriate by the Secretary.
“(iii) CLARIFICATION ON REBATES AND DISCOUNTS USED TO LOWER COSTS FOR COVERED PART D DRUGS.—Rebates, discounts, and other price concessions received by a pharmacy benefit manager or an affiliate of a pharmacy benefit manager from manufacturers, even if such price concessions are calculated as a percentage of a drug’s price, shall not be considered a violation of the requirements of clause (i) if they are fully passed through to a PDP sponsor and are compliant with all regulatory and subregulatory requirements related to direct and indirect remuneration for manufacturer rebates under this part, including in cases where a PDP sponsor is acting as a pharmacy benefit manager on behalf of a prescription drug plan offered by such PDP sponsor.
“(iv) EVALUATION OF REMUNERATION ARRANGEMENTS.—Components of subsets of remuneration arrangements (such as fees or other forms of compensation paid to or retained by the pharmacy benefit manager or affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager), as determined appropriate by the Secretary, between pharmacy benefit managers or affiliates of such pharmacy benefit managers, as applicable, and other entities involved in the dispensing or utilization of covered part D drugs (including PDP sponsors, manufacturers, pharmacies, and other entities as determined appropriate by the Secretary) shall be subject to review by the Secretary, in consultation with the Office of the Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services, as determined appropriate by the Secretary. The Secretary, in consultation with the Office of the Inspector General, shall review whether remuneration under such arrangements is consistent with fair market value (as specified by the Secretary) through reviews and assessments of such remuneration, as determined appropriate.
“(v) DISGORGEMENT.—The pharmacy benefit manager shall disgorge any remuneration paid to such pharmacy benefit manager or an affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager in violation of this subparagraph to the PDP sponsor.
“(vi) ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS.—The pharmacy benefit manager shall—
“(I) enter into a written agreement with any affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager, under which the affiliate shall identify and disgorge any remuneration described in clause (v) to the pharmacy benefit manager; and
“(II) attest, subject to any requirements determined appropriate by the Secretary, that the pharmacy benefit manager has entered into a written agreement described in subclause (I) with any relevant affiliate of the pharmacy benefit manager.
“(B) TRANSPARENCY REGARDING GUARANTEES AND COST PERFORMANCE EVALUATIONS.—The pharmacy benefit manager shall—
“(i) define, interpret, and apply, in a fully transparent and consistent manner for purposes of calculating or otherwise evaluating pharmacy benefit manager performance against pricing guarantees or similar cost performance measurements related to rebates, discounts, price concessions, or net costs, terms such as—
“(I) ‘generic drug’, in a manner consistent with the definition of the term under section 423.4 of title 42, Code of Federal Regulations, or a successor regulation;
“(II) ‘brand name drug’, in a manner consistent with the definition of the term under section 423.4 of title 42, Code of Federal Regulations, or a successor regulation;
“(III) ‘specialty drug’;
“(IV) ‘rebate’; and
“(V) ‘discount’;
“(ii) identify any drugs, claims, or price concessions excluded from any pricing guarantee or other cost performance measure in a clear and consistent manner; and
“(iii) where a pricing guarantee or other cost performance measure is based on a pricing benchmark other than the wholesale acquisition cost (as defined in section 1847A(c)(6)(B)) of a drug, calculate and provide a wholesale acquisition cost-based equivalent to the pricing guarantee or other cost performance measure.
“(C) PROVISION OF INFORMATION.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—Not later than July 1 of each year, beginning in 2028, the pharmacy benefit manager shall submit to the PDP sponsor, and to the Secretary, a report, in accordance with this subparagraph, and shall make such report available to such sponsor at no cost to such sponsor in a format specified by the Secretary under paragraph (5). Each such report shall include, with respect to such PDP sponsor and each plan offered by such sponsor, the following information with respect to the previous plan year:
“(I) A list of all drugs covered by the plan that were dispensed including, with respect to each such drug—
“(aa) the brand name, generic or non-proprietary name, and National Drug Code;
“(bb) the number of plan enrollees for whom the drug was dispensed, the total number of prescription claims for the drug (including original prescriptions and refills, counted as separate claims), and the total number of dosage units of the drug dispensed;
“(cc) the number of prescription claims described in item (bb) by each type of dispensing channel through which the drug was dispensed, including retail, mail order, specialty pharmacy, long term care pharmacy, home infusion pharmacy, or other types of pharmacies or providers;
“(dd) the average wholesale acquisition cost, listed as cost per day’s supply, cost per dosage unit, and cost per typical course of treatment (as applicable);
“(ee) the average wholesale price for the drug, listed as price per day’s supply, price per dosage unit, and price per typical course of treatment (as applicable);
“(ff) the total out-of-pocket spending by plan enrollees on such drug after application of any benefits under the plan, including plan enrollee spending through copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles;
“(gg) total rebates paid by the manufacturer on the drug as reported under the Detailed DIR Report (or any successor report) submitted by such sponsor to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services;
“(hh) all other direct or indirect remuneration on the drug as reported under the Detailed DIR Report (or any successor report) submitted by such sponsor to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services;
“(ii) the average pharmacy reimbursement amount paid by the plan for the drug in the aggregate and disaggregated by dispensing channel identified in item (cc);
“(jj) the average National Average Drug Acquisition Cost (NADAC); and
“(kk) total manufacturer-derived revenue, inclusive of bona fide service fees, attributable to the drug and retained by the pharmacy benefit manager and any affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager.
“(II) In the case of a pharmacy benefit manager that has an affiliate that is a retail, mail order, or specialty pharmacy, with respect to drugs covered by such plan that were dispensed, the following information:
“(aa) The percentage of total prescriptions that were dispensed by pharmacies that are an affiliate of the pharmacy benefit manager for each drug.
“(bb) The interquartile range of the total combined costs paid by the plan and plan enrollees, per dosage unit, per course of treatment, per 30-day supply, and per 90-day supply for each drug dispensed by pharmacies that are not an affiliate of the pharmacy benefit manager and that are included in the pharmacy network of such plan.
“(cc) The interquartile range of the total combined costs paid by the plan and plan enrollees, per dosage unit, per course of treatment, per 30-day supply, and per 90-day supply for each drug dispensed by pharmacies that are an affiliate of the pharmacy benefit manager and that are included in the pharmacy network of such plan.
“(dd) The lowest total combined cost paid by the plan and plan enrollees, per dosage unit, per course of treatment, per 30-day supply, and per 90-day supply, for each drug that is available from any pharmacy included in the pharmacy network of such plan.
“(ee) The difference between the average acquisition cost of the affiliate, such as a pharmacy or other entity that acquires prescription drugs, that initially acquires the drug and the amount reported under subclause (I)(jj) for each drug.
“(ff) A list inclusive of the brand name, generic or non-proprietary name, and National Drug Code of covered part D drugs subject to an agreement with a covered entity under section 340B of the Public Health Service Act for which the pharmacy benefit manager or an affiliate of the pharmacy benefit manager had a contract or other arrangement with such a covered entity in the service area of such plan.
“(III) Where a drug approved under section 505(c) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (referred to in this subclause as the ‘listed drug’) is covered by the plan, the following information:
“(aa) A list of currently marketed generic drugs approved under section 505(j) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act pursuant to an application that references such listed drug that are not covered by the plan, are covered on the same formulary tier or a formulary tier typically associated with higher cost-sharing than the listed drug, or are subject to utilization management that the listed drug is not subject to.
“(bb) The estimated average beneficiary cost-sharing under the plan for a 30-day supply of the listed drug.
“(cc) Where a generic drug listed under item (aa) is on a formulary tier typically associated with higher cost-sharing than the listed drug, the estimated average cost-sharing that a beneficiary would have paid for a 30-day supply of each of the generic drugs described in item (aa), had the plan provided coverage for such drugs on the same formulary tier as the listed drug.
“(dd) A written justification for providing more favorable coverage of the listed drug than the generic drugs described in item (aa).
“(ee) The number of currently marketed generic drugs approved under section 505(j) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act pursuant to an application that references such listed drug.
“(IV) Where a reference product (as defined in section 351(i) of the Public Health Service Act) is covered by the plan, the following information:
“(aa) A list of currently marketed biosimilar biological products licensed under section 351(k) of the Public Health Service Act pursuant to an application that refers to such reference product that are not covered by the plan, are covered on the same formulary tier or a formulary tier typically associated with higher cost-sharing than the reference product, or are subject to utilization management that the reference product is not subject to.
“(bb) The estimated average beneficiary cost-sharing under the plan for a 30-day supply of the reference product.
“(cc) Where a biosimilar biological product listed under item (aa) is on a formulary tier typically associated with higher cost-sharing than the reference product, the estimated average cost-sharing that a beneficiary would have paid for a 30-day supply of each of the biosimilar biological products described in item (aa), had the plan provided coverage for such products on the same formulary tier as the reference product.
“(dd) A written justification for providing more favorable coverage of the reference product than the biosimilar biological product described in item (aa).
“(ee) The number of currently marketed biosimilar biological products licensed under section 351(k) of the Public Health Service Act, pursuant to an application that refers to such reference product.
“(V) Total gross spending on covered part D drugs by the plan, not net of rebates, fees, discounts, or other direct or indirect remuneration.
“(VI) The total amount retained by the pharmacy benefit manager or an affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager in revenue related to utilization of covered part D drugs under that plan, inclusive of bona fide service fees.
“(VII) The total spending on covered part D drugs net of rebates, fees, discounts, or other direct and indirect remuneration by the plan.
“(VIII) An explanation of any benefit design parameters under such plan that encourage plan enrollees to fill prescriptions at pharmacies that are an affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager, such as mail and specialty home delivery programs, and retail and mail auto-refill programs.
“(IX) The following information:
“(aa) A list of all brokers, consultants, advisors, and auditors that receive compensation from the pharmacy benefit manager or an affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager for referrals, consulting, auditing, or other services offered to PDP sponsors related to pharmacy benefit management services.
“(bb) The amount of compensation provided by such pharmacy benefit manager or affiliate to each such broker, consultant, advisor, and auditor.
“(cc) The methodology for calculating the amount of compensation provided by such pharmacy benefit manager or affiliate, for each such broker, consultant, advisor, and auditor.
“(X) A list of all affiliates of the pharmacy benefit manager.
“(XI) A summary document submitted in a standardized template developed by the Secretary that includes such information described in subclauses (I) through (X).
“(ii) WRITTEN EXPLANATION OF CONTRACTS OR AGREEMENTS WITH DRUG MANUFACTURERS.—
“(I) IN GENERAL.—The pharmacy benefit manager shall, not later than 30 days after the finalization of any contract or agreement between such pharmacy benefit manager or an affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager and a drug manufacturer (or subsidiary, agent, or entity affiliated with such drug manufacturer) that makes rebates, discounts, payments, or other financial incentives related to one or more covered part D drugs or other prescription drugs, as applicable, of the manufacturer directly or indirectly contingent upon coverage, formulary placement, or utilization management conditions on any other covered part D drugs or other prescription drugs, as applicable, submit to the PDP sponsor a written explanation of such contract or agreement.
“(II) REQUIREMENTS.—A written explanation under subclause (I) shall—
“(aa) include the manufacturer subject to the contract or agreement, all covered part D drugs and other prescription drugs, as applicable, subject to the contract or agreement and the manufacturers of such drugs, and a high-level description of the terms of such contract or agreement and how such terms apply to such drugs; and
“(bb) be certified by the Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, or General Counsel of such pharmacy benefit manager, or affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager, as applicable, or an individual delegated with the authority to sign on behalf of one of these officers, who reports directly to the officer.
“(III) DEFINITION OF OTHER PRESCRIPTION DRUGS.—For purposes of this clause, the term ‘other prescription drugs’ means prescription drugs covered as supplemental benefits under this part or prescription drugs paid outside of this part.
“(D) AUDIT RIGHTS.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—Not less than once a year, at the request of the PDP sponsor, the pharmacy benefit manager shall allow for an audit of the pharmacy benefit manager to ensure compliance with all terms and conditions under the written agreement described in this paragraph and the accuracy of information reported under subparagraph (C).
“(ii) AUDITOR.—The PDP sponsor shall have the right to select an auditor. The pharmacy benefit manager shall not impose any limitations on the selection of such auditor.
“(iii) PROVISION OF INFORMATION.—The pharmacy benefit manager shall make available to such auditor all records, data, contracts, and other information necessary to confirm the accuracy of information provided under subparagraph (C), subject to reasonable restrictions on how such information must be reported to prevent redisclosure of such information.
“(iv) TIMING.—The pharmacy benefit manager must provide information under clause (iii) and other information, data, and records relevant to the audit to such auditor within 6 months of the initiation of the audit and respond to requests for additional information from such auditor within 30 days after the request for additional information.
“(v) INFORMATION FROM AFFILIATES.—The pharmacy benefit manager shall be responsible for providing to such auditor information required to be reported under subparagraph (C) or under clause (iii) of this subparagraph that is owned or held by an affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager.
“(2) ENFORCEMENT.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Each PDP sponsor shall—
“(i) disgorge to the Secretary any amounts disgorged to the PDP sponsor by a pharmacy benefit manager under paragraph (1)(A)(v);
“(ii) require, in a written agreement with any pharmacy benefit manager acting on behalf of such sponsor or affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager, that such pharmacy benefit manager or affiliate reimburse the PDP sponsor for any civil money penalty imposed on the PDP sponsor as a result of the failure of the pharmacy benefit manager or affiliate to meet the requirements of paragraph (1) that are applicable to the pharmacy benefit manager or affiliate under the agreement; and
“(iii) require, in a written agreement with any such pharmacy benefit manager acting on behalf of such sponsor or affiliate of such pharmacy benefit manager, that such pharmacy benefit manager or affiliate be subject to punitive remedies for breach of contract for failure to comply with the requirements applicable under paragraph (1).
“(B) REPORTING OF ALLEGED VIOLATIONS.—The Secretary shall make available and maintain a mechanism for manufacturers, PDP sponsors, pharmacies, and other entities that have contractual relationships with pharmacy benefit managers or affiliates of such pharmacy benefit managers to report, on a confidential basis, alleged violations of paragraph (1)(A) or subparagraph (C).
“(C) ANTI-RETALIATION AND ANTI-COERCION.—Consistent with applicable Federal or State law, a PDP sponsor shall not—
“(i) retaliate against an individual or entity for reporting an alleged violation under subparagraph (B); or
“(ii) coerce, intimidate, threaten, or interfere with the ability of an individual or entity to report any such alleged violations.
“(3) CERTIFICATION OF COMPLIANCE.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Each PDP sponsor shall furnish to the Secretary (at a time and in a manner specified by the Secretary) an annual certification of compliance with this subsection, as well as such information as the Secretary determines necessary to carry out this subsection.
“(B) IMPLEMENTATION.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Secretary may implement this paragraph by program instruction or otherwise.
“(4) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION.—Nothing in this subsection shall be construed as—
“(A) prohibiting flat dispensing fees or reimbursement or payment for ingredient costs (including customary, industry-standard discounts directly related to drug acquisition that are retained by pharmacies or wholesalers) to entities that acquire or dispense prescription drugs; or
“(B) modifying regulatory requirements or sub-regulatory program instruction or guidance related to pharmacy payment, reimbursement, or dispensing fees.
“(5) STANDARD FORMATS.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Not later than June 1, 2027, the Secretary shall specify standard, machine-readable formats for pharmacy benefit managers to submit annual reports required under paragraph (1)(C)(i).
“(B) IMPLEMENTATION.—Notwithstanding any other provision of law, the Secretary may implement this paragraph by program instruction or otherwise.
“(6) CONFIDENTIALITY.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Information disclosed by a pharmacy benefit manager, an affiliate of a pharmacy benefit manager, a PDP sponsor, or a pharmacy under this subsection that is not otherwise publicly available or available for purchase shall not be disclosed by the Secretary or a PDP sponsor receiving the information, except that the Secretary may disclose the information for the following purposes:
“(i) As the Secretary determines necessary to carry out this part.
“(ii) To permit the Comptroller General to review the information provided.
“(iii) To permit the Director of the Congressional Budget Office to review the information provided.
“(iv) To permit the Executive Director of the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission to review the information provided.
“(v) To the Attorney General for the purposes of conducting oversight and enforcement under this title.
“(vi) To the Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services in accordance with its authorities under the Inspector General Act of 1978 (section 406 of title 5, United States Code), and other applicable statutes.
“(B) RESTRICTION ON USE OF INFORMATION.—The Secretary, the Comptroller General, the Director of the Congressional Budget Office, and the Executive Director of the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission shall not report on or disclose information disclosed pursuant to subparagraph (A) to the public in a manner that would identify—
“(i) a specific pharmacy benefit manager, affiliate, pharmacy, manufacturer, wholesaler, PDP sponsor, or plan; or
“(ii) contract prices, rebates, discounts, or other remuneration for specific drugs in a manner that may allow the identification of specific contracting parties or of such specific drugs.
“(7) DEFINITIONS.—For purposes of this subsection:
“(A) AFFILIATE.—The term ‘affiliate’ means, with respect to any pharmacy benefit manager or PDP sponsor, any entity that, directly or indirectly—
“(i) owns or is owned by, controls or is controlled by, or is otherwise related in any ownership structure to such pharmacy benefit manager or PDP sponsor; or
“(ii) acts as a contractor, principal, or agent to such pharmacy benefit manager or PDP sponsor, insofar as such contractor, principal, or agent performs any of the functions described under subparagraph (C).
“(B) BONA FIDE SERVICE FEE.—The term ‘bona fide service fee’ means a fee that is reflective of the fair market value (as specified by the Secretary, through notice and comment rulemaking) for a bona fide, itemized service actually performed on behalf of an entity, that the entity would otherwise perform (or contract for) in the absence of the service arrangement and that is not passed on in whole or in part to a client or customer, whether or not the entity takes title to the drug. Such fee must be a flat dollar amount and shall not be directly or indirectly based on, or contingent upon—
“(i) drug price, such as wholesale acquisition cost or drug benchmark price (such as average wholesale price);
“(ii) the amount of discounts, rebates, fees, or other direct or indirect remuneration with respect to covered part D drugs dispensed to enrollees in a prescription drug plan, except as permitted pursuant to paragraph (1)(A)(ii);
“(iii) coverage or formulary placement decisions or the volume or value of any referrals or business generated between the parties to the arrangement; or
“(iv) any other amounts or methodologies prohibited by the Secretary.
“(C) PHARMACY BENEFIT MANAGER.—The term ‘pharmacy benefit manager’ means any person or entity that, either directly or through an intermediary, acts as a price negotiator or group purchaser on behalf of a PDP sponsor or prescription drug plan, or manages the prescription drug benefits provided by such sponsor or plan, including the processing and payment of claims for prescription drugs, the performance of drug utilization review, the processing of drug prior authorization requests, the adjudication of appeals or grievances related to the prescription drug benefit, contracting with network pharmacies, controlling the cost of covered part D drugs, or the provision of related services. Such term includes any person or entity that carries out one or more of the activities described in the preceding sentence, irrespective of whether such person or entity calls itself a ‘pharmacy benefit manager’.”.
(b) MA–PD plans.—Section 1857(f)(3) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–27(f)(3)), as amended by section 2(d)(2), is amended by adding at the end the following new subparagraph:
“(G) REQUIREMENTS RELATING TO PHARMACY BENEFIT MANAGERS.—For plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2028, section 1860D–12(h).”.
(c) Nonapplication of Paperwork Reduction Act.—Chapter 35 of title 44, United States Code, shall not apply to the implementation of this subsection.
Veterans
S.609 – BRAVE Act of 2025 or the Building Resources and Access for Veterans’ Mental Health Engagement Act of 2025
To improve mental health services of the Department of Veterans Affairs, and for other purposes.
(b) Table of contents.—The table of contents for this Act is as follows:
Sec. 1. Short title; table of contents.
TITLE I—IMPROVEMENT OF WORKFORCE IN SUPPORT OF MENTAL HEALTH CARE
Sec. 101. Report on market pay surveys for Readjustment Counseling Service positions.
Sec. 102. Qualifications of appointees in occupations that support mental health programs.
Sec. 103. Report on coordination of Veterans Health Administration with Readjustment Counseling Service.
TITLE II—IMPROVEMENT OF VET CENTER INFRASTRUCTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Sec. 201. Vet Center defined.
Sec. 202. Comptroller General report on Readjustment Counseling Service model for expansion of Vet Center footprint.
Sec. 203. Improvement of guidance and information to improve veteran outreach efforts by Vet Centers.
Sec. 204. Report on information technology system of Readjustment Counseling Service.
Sec. 301. Study on effectiveness of suicide prevention and mental health outreach programs of Department of Veterans Affairs for women veterans.
Sec. 302. Requirement for Department of Veterans Affairs to modify the REACH VET program to incorporate risk factors weighted for women veterans.
Sec. 303. Review of and report on reintegration and readjustment services for veterans and family members in group retreat settings.
Sec. 401. Extension of Staff Sergeant Parker Gordon Fox Suicide Prevention Grant Program.
Sec. 402. Access to mental health residential rehabilitation treatment programs for veterans with spinal cord injury or disorder.
Sec. 403. Mental health consultations and outreach on mental health services for veterans receiving compensation for disabilities relating to mental health diagnoses.
Sec. 404. Joint report on effectiveness of programs of Department of Veterans Affairs and Department of Defense that promote access to mental health services for transitioning members of the Armed Forces.
TITLE I—Improvement of workforce in support of mental health care
SEC. 101. Report on market pay surveys for Readjustment Counseling Service positions.
(a) Findings.—Congress finds that the Secretary of Veterans Affairs, through the Chief Readjustment Counseling Officer, reviews market pay surveys in each Readjustment Counseling Service District to compare the salaries of employees in the Readjustment Counseling Service of the Department of Veterans Affairs, including licensed professional mental health counselors, social workers, and marriage and family therapists, to the salaries of similarly situated employees within the Department and the private sector.
(b) Report.—Not later than 180 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary shall submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report on the findings specified in subsection (a), which shall—
(1) include an assessment of pay disparities between employees of the Readjustment Counseling Service of the Department and similarly situated employees within the Department and the private sector; and
(2) identify if pay-related staffing challenges exist, and if so, determine if each Readjustment Counseling Service District has initiated a review of third-party survey data for the identified occupations.
(c) Districts.—Each report submitted under subsection (b) shall include reports from all Readjustment Counseling Service Districts of the Department, including—
(1) areas that are geographically diverse;
(2) rural areas;
(3) highly rural areas;
(4) urban areas; and
(5) areas with health care shortages.
(d) Assessment of pay.—Each report submitted under subsection (b) shall include an assessment of pay based on the following factors:
(1) Third-party survey data.
(2) Geographic location.
(3) Equivalent qualifications (licensure, education level, or experience).
(4) Short-term incentives.
SEC. 102. Qualifications of appointees in occupations that support mental health programs.
(a) Psychologists.—Section 7402(b)(8)(C) of title 38, United States Code, is amended by striking “for a period not to exceed” and all that follows through the period at the end and inserting “for a reasonable period of time recommended by the Under Secretary for Health.”.
(b) Licensed professional mental health counselors.—Section 7402(b)(11)(B) of title 38, United States Code, is amended by striking the period at the end and inserting “, except that the Secretary may waive the requirement of licensure or certification for an individual licensed professional mental health counselor for a reasonable period of time recommended by the Under Secretary for Health.”.
SEC. 103. Report on coordination of Veterans Health Administration with Readjustment Counseling Service.
(a) In general.—Not later than 60 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report regarding coordination between the clinical care system of the Veterans Health Administration and the Readjustment Counseling Service of the Department of Veterans Affairs.
(b) Assessment.—The report required by subsection (a) shall include an assessment of the adherence by each Director of a Veterans Integrated Service Network to policies of the Veterans Health Administration, which require each such Director to ensure that a support facility of the Department of Veterans Affairs is aligned laterally with each Vet Center to provide supportive administrative and clinical collaboration to better serve veterans eligible for services from Vet Centers, particularly those at high risk for suicide.
(c) Analysis.—The report required by subsection (a) shall include an analysis of—
(1) whether staff at Vet Centers in the local area of a medical facility of the Department have the updated contact information for appropriate staff at the medical facility to ensure proper coordination of care;
(2) whether the external clinical consultant and suicide prevention coordinator of a medical facility of the Department are providing counseling staff of each Vet Center in the local area of the medical facility professional consultation not less frequently than monthly through regularly scheduled peer case presentations onsite at the Vet Center or via virtual or telephone consultation as necessary to fully support the coordination of care of patients, particularly those at high risk for suicide;
(3) whether the external clinical consultant and suicide prevention coordinator are documenting any consultation conducted under paragraph (2); and
(4) whether the Under Secretary for Health is coordinating with the Outreach Specialist at each Vet Center to ensure active duty members of the Armed Forces who are participating in the Transition Assistance Program of the Department of Defense are provided information regarding Vet Centers and the services provided at Vet Centers.
(d) Vet Center defined.—In this section, the term “Vet Center” has the meaning given that term in section 1712A(h) of title 38, United States Code.
TITLE II—Improvement of Vet Center infrastructure and technology
SEC. 201. Vet Center defined.
In this title, the term “Vet Center” has the meaning given that term in section 1712A(h) of title 38, United States Code.
SEC. 202. Comptroller General report on Readjustment Counseling Service model for expansion of Vet Center footprint.
(a) In general.—Not later than one year after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Comptroller General of the United States shall submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report assessing the model used by the Readjustment Counseling Service of the Department of Veterans Affairs to guide the expansion of the real property footprint of Vet Centers.
(b) Elements.—The report required by subsection (a) shall assess—
(1) whether the model described in such subsection adequately accounts for the demand for Vet Center services in rural areas;
(2) whether the frequency with which the Secretary of Veterans Affairs is reassessing areas for potential expansion of Vet Center services is often enough to address any population shifts;
(3) whether such model adequately considers the needs of veterans in areas with high rates of calls to the Veterans Crisis Line or high rates of suicide by veterans or members of the Armed Forces;
(4) whether such model adequately accounts for trends in usage of mobile Vet Centers in a given area; and
(5) whether such model takes into account the unique needs of veterans and members of the Armed Forces in areas being assessed.
(c) Veterans Crisis Line.—In this section, the term “Veterans Crisis Line” means the toll-free hotline for veterans established under section 1720F(h) of title 38, United States Code.
SEC. 203. Improvement of guidance and information to improve veteran outreach efforts by Vet Centers.
Not later than 180 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall—
(1) ensure each Vet Center has demographic data, such as age, gender, race, and ethnicity, for individuals eligible for Vet Center services in the service area of such Vet Center to be used to tailor outreach activities, including data on veterans who have recently transitioned from service in the Armed Forces;
(2) provide Vet Centers with guidance for assessing the effectiveness of outreach activities, including guidance on metrics for those activities and targets against which to assess those metrics to determine effectiveness;
(3) develop and implement a process to periodically assess the extent to which veterans and members of the Armed Forces who are eligible for services from Vet Centers experience barriers to obtaining such services, including a lack of awareness about Vet Centers and challenges accessing Vet Center services; and
(4) develop and implement a process to periodically assess the extent to which staff of Vet Centers may encounter barriers to providing services.
SEC. 204. Report on information technology system of Readjustment Counseling Service.
Not later than 60 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs, through the Chief Readjustment Counseling Officer of the Veterans Health Administration, shall submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report identifying—
(1) whether the Department of Veterans Affairs is retaining or replacing the current information technology platform of the Department, commonly referred to as “RCSNet”, which is currently used to manage certain parts of the daily work of employees of the Readjustment Counseling Service and operational data and management functions of the Readjustment Counseling Service;
(2) if the Department intends to keep RCSNet, the rationale for that decision and an identification of the steps the Department is taking to maintain or improve the functionality of RCSNet and the timeline for those steps; and
(3) if the Department intends to replace RCSNet, the rationale for that decision and an identification of the steps the Department is taking to implement that replacement, including a timeline and the estimated cost for that replacement.
SEC. 301. Study on effectiveness of suicide prevention and mental health outreach programs of Department of Veterans Affairs for women veterans.
(a) In general.—Not later than 240 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall conduct surveys and host listening sessions with women veterans to determine the extent to which—
(1) suicide prevention, lethal-means safety, and mental health resources and messaging campaigns of the Department of Veterans Affairs are perceived and accepted by women veterans;
(2) women veterans find those resources and messaging campaigns effective and sufficiently tailored to women veterans;
(3) the integration into those resources and messaging campaigns of information pertaining to military sexual trauma, intimate partner violence, and trauma-informed health care would make those resources and messaging campaigns more effective for women veterans;
(4) the Department could make additional improvements to those resources and messaging campaigns, including the Women’s Health Transition Training Program, to make those resources and messaging campaigns more effective for women veterans; and
(5) programs and services of the Department are targeted at women veterans of different ages and eras of services, racial and ethnic backgrounds, and geographical areas.
(b) Population studied.—The Secretary shall conduct the surveys and listening sessions required under subsection (a) in urban and rural areas and shall ensure such surveys and listening sessions are targeted at different demographics.
(c) Report.—Not later than one year after the surveys and listening sessions required under subsection (a) are complete, the Secretary shall submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report on the findings of such surveys and listening sessions, which shall document the steps the Secretary intends to take to refine the suicide prevention, lethal-means safety, and mental health resources and messaging campaigns of the Department based on the feedback from such surveys and listening sessions to ensure the Secretary is utilizing the most effective strategies.
SEC. 302. Requirement for Department of Veterans Affairs to modify the REACH VET program to incorporate risk factors weighted for women veterans.
Not later than 60 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall initiate efforts to modify the Recovery Engagement and Coordination for Health–Veterans Enhanced Treatment program (“REACH VET”) to incorporate into such program risk factors weighted for women, such as military sexual trauma and intimate partner violence.
SEC. 303. Review of and report on reintegration and readjustment services for veterans and family members in group retreat settings.
(a) Review.—Not later than 60 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall review all requests for reintegration and readjustment services for veterans and family members of veterans in group retreat program settings under section 1712A(a)(1)(B)(ii) of title 38, United States Code, to determine if current retreat programming meets demand, specifically requests for—
(1) women only retreats;
(2) disabled access retreats, particularly wheelchair accessible retreats; and
(3) retreats for veterans with specific medical needs.
(b) Report.—Not later than 120 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary shall submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report on whether the provision by the Secretary of reintegration and readjustment services for veterans and family members of veterans in group retreat program settings should be increased and made permanent, including—
(1) women only retreats;
(2) disabled access retreats, particularly wheelchair accessible retreats; and
(3) retreats for veterans with specific medical needs.
SEC. 401. Extension of Staff Sergeant Parker Gordon Fox Suicide Prevention Grant Program.
Section 201 of the Commander John Scott Hannon Veterans Mental Health Care Improvement Act of 2019 (Public Law 116–171; 38 U.S.C. 1720F note) is amended—
(1) in subsection (c)(2)(A), by striking “$750,000” and inserting “$1,000,000”; and
(2) in subsection (j), by striking “three years” and inserting “six years”.
SEC. 402. Access to mental health residential rehabilitation treatment programs for veterans with spinal cord injury or disorder.
(a) Plan.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 60 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a plan to ensure access to mental health residential treatment programs of the Department of Veterans Affairs for veterans with a spinal cord injury or disorder.
(2) ELEMENTS.—The plan required under paragraph (1) shall include—
(A) a staffing plan, which shall include a plan for how the Department will—
(i) incorporate staff from other facilities to support the pilot program required under subsection (b); and
(ii) ensure adequate staffing to support the needs of veterans with a spinal cord injury or disorder;
(B) an assessment of medical equipment needs; and
(C) an assessment of the best location to deliver treatment and health care under the mental health residential treatment programs of the Department, including through the use of spinal cord injury or disorder centers and spinal cord injury or disorder spokes.
(b) Pilot program.—Commencing not later than 120 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary shall carry out a pilot program to provide access to mental health residential treatment programs of the Department for veterans with a spinal cord injury or disorder at not fewer than three medical facilities of the Department.
(c) Report.—Not later than one year after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary shall submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report on—
(1) the implementation of the plan required under subsection (a);
(2) the initial results from the pilot program under subsection (b); and
(3) plans to expand the mental health residential treatment programs of the Department to additional medical facilities of the Department to address demand for the highly specialized treatment provided under such programs for veterans with a spinal cord injury or disorder.
SEC. 403. Mental health consultations and outreach on mental health services for veterans receiving compensation for disabilities relating to mental health diagnoses.
(a) Technical corrections.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The section 1167 of title 38, United States Code, relating to mental health consultations, is redesignated as section 1169.
(2) CLERICAL AMENDMENTS.—The table of sections at the beginning of chapter 11 is amended—
(A) by striking the item relating to the section 1167 relating to mental health consultations; and
(B) adding after the item relating to section 1168 the following new item:
“1169. Mental health consultations.”.
(b) Improvements.—Section 1169 of such title, as redesignated by subsection (a), is amended—
(1) in subsection (a), in the subsection heading, by striking “In general” and inserting “Initial mental health consultations”;
(2) by redesignating subsection (b) and (c) as subsections (c) and (d), respectively;
(3) by inserting after subsection (a) the following new subsection (b):
“(b) Annual mental health consultations and outreach.—Not less frequently than once each year, the Secretary shall—
“(1) offer to each veteran who is receiving compensation under this chapter for a service-connected disability relating to a mental health diagnosis a mental health consultation to assess the mental health needs of, and discuss other mental health care options for, the veteran; and
“(2) conduct outreach to each veteran described in paragraph (1) regarding the availability of consultations described in such paragraph and other mental health services from the Department.”;
(4) in subsection (c), as redesignated by paragraph (2), by inserting “or (b)” after “under subsection (a)” both places it appears; and
(5) in subsection (d), as redesignated by paragraph (2), by inserting “or as requiring reevaluation of any entitlement of the veteran to compensation under this chapter” before the period at the end.
(c) Biennial reports.—Such section, as amended by subsection (b), is further amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(e) Biennial reviews and reports.— (1) Not later than one year after the date of the enactment of the BRAVE Act of 2025, and not less frequently than once every two years thereafter, the Secretary shall—
“(A) review the efficacy of the outreach of the Department with respect to consultations offered under this section; and
“(B) submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report on—
“(i) the findings of the Secretary with respect to the most recent review conducted pursuant to subparagraph (A); and
“(ii) the plans of the Secretary to address the findings described in clause (i).
“(2) In order to facilitate reviews conducted under paragraph (1)(A), the Secretary shall—
“(A) ensure veterans can provide feedback to the Secretary on outreach described in paragraph (1) and the consultations offered under this section; and
“(B) analyze the feedback described in subparagraph (A) that is provided to the Secretary.
“(3) Each review conducted pursuant to paragraph (1)(A) shall cover the following:
“(A) The feedback collected under paragraph (2).
“(B) Consultations sought pursuant to offers under this section.
“(C) Matters that deter veterans from seeking consultations offered under this section.”.
SEC. 404. Joint report on effectiveness of programs of Department of Veterans Affairs and Department of Defense that promote access to mental health services for transitioning members of the Armed Forces.
(a) In general.—Not later than 180 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs and the Secretary of Defense shall jointly submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives a report on the actions taken or that will be taken by each such Secretary, either independently or jointly, to improve the effectiveness of programs of the Department of Veterans Affairs and the Department of Defense that promote access to mental health services for members of the Armed Forces transitioning from service in the Armed Forces to civilian life.
(b) Status of response to Comptroller General recommendations.—The report required under subsection (a) shall include an assessment of the status of the response by the Secretary of Veterans Affairs and the Secretary of Defense to the recommendations of the Comptroller General of the United States set forth in the July 2024 report entitled “DOD AND VA HEALTH CARE: Actions Needed to Better Facilitate Access to Mental Health Services During Military to Civilian Transitions” (GAO–24–106189).
(c) Identification of duplicative efforts.—The report required under subsection (a) shall identify any duplicative efforts or gaps in services and recommend changes to programs of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the Department of Defense to address such duplicative efforts or gaps, including recommendations for legislative action.
S.702 – Veterans Mental Health and Addiction Therapy Quality of Care Act
A bill to require a study on the quality of care difference between mental health and addiction therapy care provided by health care providers of the Department of Veterans Affairs compared to non-Department providers, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Study on quality of care difference between mental health and addiction therapy care provided by health care providers of Department of Veterans Affairs compared to non-Department providers.
(a) In general.—Not later than 90 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs shall seek to enter into an agreement with an independent and objective organization outside the Department of Veterans Affairs under which that organization shall—
(1) conduct a study on the quality of care difference between mental health and addiction therapy care under the laws administered by the Secretary provided by health care providers of the Department compared to non-Department providers across various modalities, such as telehealth, in-patient, intensive out-patient, out-patient, and residential treatment; and
(2) submit to the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs of the House of Representatives and publish on a publicly available website a report containing the final results of such study.
(b) Timing.—The Secretary shall ensure that the organization with which the Secretary enters into an agreement pursuant to subsection (a) is able to complete the requirements under such subsection by not later than 18 months after the date on which the agreement is entered into.
(c) Elements.—The report submitted pursuant to subsection (a)(2) shall include an assessment of the following:
(1) The amount of improvement in health outcomes from start of treatment to completion, including symptom scores and suicide risk using evidence-based scales, including the Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
(2) Whether providers of the Department and non-Department providers are using evidence-based practices in the treatment of mental health and addiction therapy care, including criteria set forth by the American Society of Addiction Medicine.
(3) Potential gaps in coordination between providers of the Department and non-Department providers in responding to individuals seeking mental health or addiction therapy care, including the sharing of patient health records.
(4) Implementation of veteran-centric care, including the level of satisfaction of patients with care and the competency of providers with the unique experiences and needs of the military and veteran population.
(5) Whether veterans with co-occurring conditions receive integrated care to holistically address their needs.
(6) Whether providers monitor health outcomes continually throughout treatment and at regular intervals for up to three years after treatment.
(7) The average length of time to initiate services, which shall include a comparison of the average length of time between the initial point of contact after patient outreach to the point of initial service, as measured or determined by the Secretary.
S.1134 – A bill to amend title 38, United States Code, to improve the Office of Patient Advocacy of the Department of Veterans Affairs.
S.1139 – A bill to amend the Commander John Scott Hannon Veterans Mental Health Care Improvement Act of 2019 to modify and reauthorize the Staff Sergeant Parker Gordon Fox Suicide Prevention Grant Program of the Department of Veterans Affairs, and for other purposes.
Pain
S.475 – Alternatives to PAIN Act or the Alternatives to Prevent Addiction In the Nation Act
A bill to amend title XVIII of the Social Security Act to ensure appropriate access to non-opioid pain management drugs under part D of the Medicare program.
SEC. 2. Appropriate cost-sharing for qualifying non-opioid pain management drugs under Medicare part D.
(a) Medicare part D.—Section 1860D–2 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–102) is amended—
(1) in subsection (b)—
(A) in paragraph (1)(A), in the matter preceding clause (i), by striking “paragraphs (8) and (9)” and inserting “paragraphs (8), (9), and (10)”;
(B) in paragraph (2)(A), in the matter preceding clause (i), by striking “paragraphs (8) and (9)” and inserting “paragraphs (8), (9), and (10)”; and
(C) by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(10) TREATMENT OF COST-SHARING FOR QUALIFYING NON-OPIOID PAIN MANAGEMENT DRUGS.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—For plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2026, with respect to a covered part D drug that is a qualifying non-opioid pain management drug (as defined in subparagraph (B))—
“(i) the deductible under paragraph (1) shall not apply; and
“(ii) such drug shall be placed on the lowest cost-sharing tier, if any, for purposes of determining the maximum co-insurance or other cost-sharing for such drug.
“(B) QUALIFYING NON-OPIOID PAIN MANAGEMENT DRUGS.—In this paragraph, the term ‘qualifying non-opioid pain management drug’ means a drug or biological product—
“(i) that has a label indication approved by the Food and Drug Administration to reduce postoperative pain or any other form of acute pain;
“(ii) that does not act upon the body’s opioid receptors;
“(iii) for which there is no other drug or product that is—
“(I) rated as therapeutically equivalent (under the Food and Drug Administration’s most recent publication of ‘Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations’); and
“(II) sold or marketed in the United States; and
“(iv) for which the wholesale acquisition cost (as defined in section 1847A(c)(6)(B)), for a monthly supply does not exceed the monthly specialty-tier cost threshold as determined by the Secretary from time to time.”; and
(2) in subsection (c), by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(7) TREATMENT OF COST-SHARING FOR QUALIFYING NON-OPIOID PAIN MANAGEMENT DRUGS.—The coverage is provided in accordance with subsection (b)(10).”.
(b) Conforming amendments to cost-Sharing for low-Income individuals.—Section 1860D–14(a) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–114(a)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1)(D), in each of the clauses (ii) and (iii), by striking “Subject to paragraph (6)” and inserting “Subject to paragraphs (6) and (7)”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following new paragraph:
“(7) TREATMENT OF COST-SHARING OR DEDUCTIBLE FOR QUALIFYING NON-OPIOID PAIN MANAGEMENT DRUGS.—For plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2026, with respect to a covered part D drug that is a qualifying non-opioid pain management drug (as defined in section 1860D–2(b)(10)(B))—
“(A) the deductible under section 1860D–2(b)(1) shall not apply; and
“(B) such drug shall be placed on the lowest cost-sharing tier, if any, for purposes of determining the maximum co-insurance or other cost-sharing for such drug.”.
SEC. 3. Prohibition on the use of step therapy and prior authorization for qualifying non-opioid pain management drugs under medicare part D.
Section 1860D–4(c) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395w–104) is amended—
(1) by redesignating paragraph (6), as added by section 50354 of division E of the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (Public Law 115–123), as paragraph (7); and
(2) by adding at the end the following paragraph:
“(8) PROHIBITION ON USE OF STEP THERAPY AND PRIOR AUTHORIZATION FOR QUALIFYING NON-OPIOID PAIN MANAGEMENT DRUGS.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—For plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2026, a prescription drug plan or an MA–PD plan may not, with respect to a qualifying non-opioid pain management drug (as defined in section 1860D–2(b)(10)(B)) for which coverage is provided under such plan, impose any—
“(i) step therapy requirement under which an individual enrolled under such plan is required to use an opioid prior to receiving such drug; or
“(ii) prior authorization requirement.
“(B) STEP THERAPY.—In this paragraph, the term ‘step therapy’ means a drug therapy utilization management protocol or program that requires use of an alternative, preferred prescription drug or drugs before the plan approves coverage for the non-preferred drug therapy prescribed.
“(C) PRIOR AUTHORIZATION.—In this paragraph, the term ‘prior authorization’ means any requirement to obtain approval from a plan prior to the furnishing of a drug.”.
Substance Misuse, Addiction
Substance Misuse
S. 139 – FASD Respect Act or the Advancing FASD Research, Services and Prevention Act
A bill to amend the Public Health Service Act to reauthorize and extend the Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Prevention and Services program, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Support for individuals and families impacted by fetal alcohol spectrum disorder.
(a) In general.—Part O of title III of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 280f et seq.) is amended—
(1) by amending the part heading to read as follows: “Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Prevention and Services Program”;
(2) in section 399H (42 U.S.C. 280f)—
(A) in the section heading, by striking “Establishment of fetal alcohol syndrome prevention” and inserting “Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders prevention, intervention,”;
(B) by striking “Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Effect” each place it appears and inserting “FASD”;
(C) in subsection (a)—
(i) by amending the heading to read as follows: “In general”;
(ii) in the matter preceding paragraph (1)—
(I) by inserting “or continue activities to support” after “shall establish”;
(II) by striking “FASD” (as amended by subparagraph (B)) and inserting “fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (referred to in this section as ‘FASD’)”;
(III) by striking “prevention, intervention” and inserting “awareness, prevention, identification, intervention,”; and
(IV) by striking “that shall” and inserting “, which may”;
(iii) in paragraph (1)—
(I) in subparagraph (A)—
(aa) by striking “medical schools” and inserting “health professions schools”; and
(bb) by inserting “infants,” after “provision of services for”; and
(II) in subparagraph (D), by striking “medical and mental” and inserting “agencies providing”;
(iv) in paragraph (2)—
(I) in the matter preceding subparagraph (A), by striking “a prevention and diagnosis program to support clinical studies, demonstrations and other research as appropriate” and inserting “supporting and conducting research on FASD, as appropriate, including”;
(II) in subparagraph (B)—
(aa) by striking “prevention services and interventions for pregnant, alcohol-dependent women” and inserting “culturally and linguistically appropriate evidence-based or evidence-informed interventions and appropriate societal supports for preventing prenatal alcohol exposure, which may co-occur with exposure to other substances”; and
(bb) by striking “; and” and inserting a semicolon;
(v) by striking paragraph (3) and inserting the following:
“(3) integrating into surveillance a case definition for FASD and, in collaboration with other Federal and outside partners, supporting organizations of appropriate medical and mental health professionals in their development and refinement of evidence-based clinical diagnostic guidelines and criteria for all FASD; and
“(4) building State and Tribal capacity for the identification, treatment, and support of individuals with FASD and their families, which may include—
“(A) utilizing and adapting existing Federal, State, or Tribal programs to include FASD identification and FASD-informed support;
“(B) developing and expanding screening and diagnostic capacity for FASD;
“(C) developing, implementing, and evaluating targeted FASD-informed intervention programs for FASD;
“(D) increasing awareness of FASD;
“(E) providing training with respect to FASD for professionals across relevant sectors; and
“(F) disseminating information about FASD and support services to affected individuals and their families.”;
(D) in subsection (b)—
(i) by striking “described in section 399I”;
(ii) by striking “The Secretary” and inserting the following:
“(1) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary”; and
(iii) by adding at the end the following:
“(2) ELIGIBLE ENTITIES.—To be eligible to receive a grant, or enter into a cooperative agreement or contract, under this section, an entity shall—
“(A) be a State, Indian Tribe or Tribal organization, local government, scientific or academic institution, or nonprofit organization; and
“(B) prepare and submit to the Secretary an application at such time, in such manner, and containing such information as the Secretary may require, including a description of the activities that the entity intends to carry out using amounts received under this section.
“(3) ADDITIONAL APPLICATION CONTENTS.—The Secretary may require that an eligible entity include in the application submitted under paragraph (2)(B)—
“(A) a designation of an individual to serve as a FASD State or Tribal coordinator of activities such eligible entity proposes to carry out through a grant, cooperative agreement, or contract under this section; and
“(B) a description of an advisory committee the entity will establish to provide guidance for the entity on developing and implementing a statewide or Tribal strategic plan to prevent FASD and provide for the identification, treatment, and support of individuals with FASD and their families.”; and
(E) by striking subsections (c) and (d); and
(F) by adding at the end the following:
“(c) Definition of FASD-Informed.—For purposes of this section, the term ‘FASD-informed’, with respect to support or an intervention program, means that such support or intervention program uses culturally and linguistically informed evidence-based or practice-based interventions and appropriate societal supports to support an improved quality of life for an individual with FASD and the family of such individual.”; and
(3) by striking sections 399I, 399J, and 399K (42 U.S.C. 280f–1, 280f–2, 280f–3) and inserting the following:
“SEC. 399I. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders Centers for Excellence.
“(a) In general.—The Secretary shall, as appropriate, award grants, cooperative agreements, or contracts to public or nonprofit private entities with demonstrated expertise in the prevention of, identification of, and intervention services with respect to, fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (referred to in this section as ‘FASD’) and other related adverse conditions. Such awards shall be for the purposes of establishing Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Centers for Excellence to build local, Tribal, State, and nationwide capacities to prevent the occurrence of FASD and other related adverse conditions, and to respond to the needs of individuals with FASD and their families by carrying out the programs described in subsection (b).
“(b) Programs.—An entity receiving an award under subsection (a) may use such award for the following purposes:
“(1) Initiating or expanding diagnostic capacity for FASD by increasing screening, assessment, identification, and diagnosis.
“(2) Developing and supporting public awareness and outreach activities, including the use of a range of media and public outreach, to raise public awareness of the risks associated with alcohol consumption during pregnancy, with the goals of reducing the prevalence of FASD and improving the developmental, health (including mental health), and educational outcomes of individuals with FASD and supporting families caring for individuals with FASD.
“(3) Acting as a clearinghouse for evidence-based resources on FASD prevention, identification, and culturally and linguistically appropriate best practices, including the maintenance of a national data-based directory on FASD-specific services in States, Indian Tribes, and local communities, and disseminating ongoing research and developing resources on FASD to help inform systems of care for individuals with FASD across their lifespan.
“(4) Increasing awareness and understanding of efficacious, evidence-based screening tools and culturally and linguistically appropriate evidence-based intervention services and best practices, which may include by conducting nationwide, regional, State, Tribal, or peer cross-State webinars, workshops, or conferences for training community leaders, medical and mental health and substance use disorder professionals, education and disability professionals, families, law enforcement personnel, judges, individuals working in financial assistance programs, social service personnel, child welfare professionals, and other service providers.
“(5) Improving capacity for State, Tribal, and local affiliates dedicated to FASD awareness, prevention, and identification and family and individual support programs and services.
“(6) Providing technical assistance to recipients of grants, cooperative agreements, or contracts under section 399H, as appropriate.
“(7) Carrying out other functions, as appropriate.
“(c) Application.—To be eligible for a grant, contract, or cooperative agreement under this section, an entity shall submit to the Secretary an application at such time, in such manner, and containing such information as the Secretary may require.
“(d) Subcontracting.—A public or private nonprofit entity may carry out the following activities required under this section through contracts or cooperative agreements with other public and private nonprofit entities with demonstrated expertise in FASD:
“(1) Prevention activities.
“(2) Screening and identification.
“(3) Resource development and dissemination, training and technical assistance, administration, and support of FASD partner networks.
“(4) Intervention and treatment services.
“SEC. 399J. Authorization of appropriations.
“There are authorized to be appropriated to carry out this part such sums as may be necessary for each of fiscal years 2025 through 2029.”.
(b) Report.—Not later than 4 years after the date of enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall submit to the Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions of the Senate and the Committee on Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives a report on the efforts of the Department of Health and Human Services to advance public awareness of, and facilitate the identification of best practices related to, fetal alcohol spectrum disorders identification, prevention, treatment, and support.
(c) Technical amendment.—Section 519D of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 290bb–25d) is repealed.
S. 329 – Keeping Drugs Out of Schools Act of 2025
A bill to authorize grants to implement school-community partnerships for preventing substance use and misuse among youth.
SEC. 2. Grant program.
(a) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) DIRECTOR.—The term “Director” means the Director of the Office of National Drug Control Policy.
(2) DRUG-FREE COMMUNITIES FUNDED COALITION.—The term “Drug-Free Communities funded coalition” means a recipient of a grant under section 1032 of the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988 (21 U.S.C. 1532).
(3) EFFECTIVE DRUG PREVENTION PROGRAMS.—The term “effective drug prevention programs”, with respect to a school-community partnership between a Drug-Free Communities funded coalition and a local school, means strategies, policies, and activities that—
(A) are tailored to meet the needs of the student population of the school, based on the environment of the school and the community surrounding the school; and
(B) prevent and reduce substance use and misuse among local youth.
(4) ELIGIBLE ENTITY.—The term “eligible entity” means a coalition (within the meaning of section 1032 of the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988 (21 U.S.C. 1532)) that—
(A) receives or has received a grant under subchapter I of chapter 2 of title I of the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988 (21 U.S.C. 1523 et seq.); and
(B) has a memorandum of understanding in effect with not less than 1 local school to establish a school-community partnership.
(5) LOCAL SCHOOL.—The term “local school” means an elementary, middle, or high school located in an area served by an eligible entity.
(6) SCHOOL-COMMUNITY PARTNERSHIP.—The term “school-community partnership” means a partnership between a Drug-Free Communities funded coalition and not less than 1 local school for the purpose of implementing effective drug prevention programs.
(7) SUBSTANCE USE AND MISUSE.—The term “substance use and misuse”—
(A) has the meaning given the term in paragraph (9) of section 1023 of the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988 (21 U.S.C. 1523); and
(B) includes the use of electronic or other delivery mechanisms to consume a substance described in subparagraph (A), (B), or (C) of that paragraph.
(b) Grants authorized.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—
(A) INITIAL GRANTS.—Subject to paragraph (2), the Director may award grants to eligible entities for the purpose of implementing a school-community partnership.
(B) RENEWAL GRANTS.—Subject to paragraph (2), the Director may award to an eligible entity who has received a grant under subparagraph (A) an additional grant for each fiscal year during the 3-fiscal-year period following the fiscal year for which the grant was awarded under subparagraph (A), for the purpose of continuing the school-community partnership.
(2) LIMITATIONS.—
(A) AMOUNT.—The amount of a grant under this subsection may not exceed $75,000 for a fiscal year.
(B) RECIPIENTS.—Not more than 1 eligible entity may receive a grant under this subsection to establish a school-community partnership with a particular local school.
(c) Interagency agreement.—The Director may enter into an interagency agreement with a National Drug Control Program agency, as defined in section 702 of the Office of National Drug Control Policy Reauthorization Act of 1998 (21 U.S.C. 1701), to delegate authority for—
(1) the execution of grants under this section; and
(2) other activities necessary to carry out the responsibilities of the Director under this section.
(d) Application.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—An eligible entity desiring a grant under this section, in coordination with each local school with which the eligible entity has a school-community partnership, shall submit to the Director an application at such time, in such manner, and accompanied by such information as the Director may require.
(2) PLAN.—The application submitted under paragraph (1) shall include a detailed, comprehensive plan for the school-community partnership to implement effective drug prevention programs.
(e) Use of funds.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—An eligible entity receiving a grant under this section shall use funds from the grant—
(A) to implement the plan described in subsection (d)(2); and
(B) if necessary, to obtain specialized training and assistance from the organization receiving the grant under section 4(a) of Public Law 107–82 (21 U.S.C. 1521 note).
(2) SUPPLEMENT NOT SUPPLANT.—Grants provided under this section shall be used to supplement, and not supplant, Federal and non-Federal funds that are otherwise available for drug prevention programs in local schools.
(f) Evaluation.—Section 1032(a)(6) of the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988 (21 U.S.C. 1532(a)(6)) shall apply to a grant under this section in the same manner as that section applies to a grant under subchapter I of chapter 2 of subtitle A of title I of that Act (21 U.S.C. 1531 et seq.).
(g) Authorization of appropriations.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—There are authorized to be appropriated to carry out this section $7,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2026 through 2031.
(2) ADMINISTRATIVE COSTS.—Not more than 8 percent of the funds appropriated pursuant to paragraph (1) may be used by the Director for administrative expenses associated with the responsibilities of the Director under this section.
Addiction
S.500 – CAREER Act of 2025 or Comprehensive Addiction Recovery through Effective Employment and Reentry Act of 2025
A bill to reauthorize certain programs under the SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Act, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Reauthorization of the CAREER Act; treatment, recovery, and workforce support grants.
(a) In general.—Section 7183 of the SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Act (42 U.S.C. 290ee–8) is amended—
(1) in the section heading, by inserting “; treatment, recovery, and workforce support grants” after “CAREER Act”;
(2) in subsection (b), by inserting “each” before “for a period”;
(3) in subsection (c)—
(A) in paragraph (1), by striking “the rates described in paragraph (2)” and inserting “the average rates for calendar years 2018 through 2022 described in paragraph (2)”; and
(B) by amending paragraph (2) to read as follows:
“(2) RATES.—The rates described in this paragraph are the following:
“(A) The highest age-adjusted average rates of drug overdose deaths for calendar years 2018 through 2022 based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, including, if necessary, provisional data for calendar year 2022.
“(B) The highest average rates of unemployment for calendar years 2018 through 2022 based on data provided by the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
“(C) The lowest average labor force participation rates for calendar years 2018 through 2022 based on data provided by the Bureau of Labor Statistics.”;
(4) in subsection (g)—
(A) in each of paragraphs (1) and (3), by redesignating subparagraphs (A) and (B) as clauses (i) and (ii), respectively, and adjusting the margins accordingly;
(B) by redesignating paragraphs (1) through (3) as subparagraphs (A) through (C), respectively, and adjusting the margins accordingly;
(C) in the matter preceding subparagraph (A) (as so redesignated), by striking “An entity” and inserting the following:
“(1) IN GENERAL.—An entity”; and
(D) by adding at the end the following:
“(2) TRANSPORTATION SERVICES.—An entity receiving a grant under this section may use not more than 5 percent of the funds for providing transportation for individuals to participate in an activity supported by a grant under this section, which transportation shall be to or from a place of work or a place where the individual is receiving vocational education or job training services or receiving services directly linked to treatment of or recovery from a substance use disorder.
“(3) LIMITATION.—The Secretary may not require an entity to, or give priority to an entity that plans to, use the funds of a grant under this section for activities that are not specified in this subsection.”;
(5) in subsection (i)(2), by inserting “, which shall include employment and earnings outcomes described in subclauses (I) and (III) of section 116(b)(2)(A)(i) of the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (29 U.S.C. 3141(b)(2)(A)(i)) with respect to the participation of such individuals with a substance use disorder in programs and activities funded by the grant under this section” after “subsection (g)”;
(6) in subsection (j)—
(A) in paragraph (1), by inserting “for grants awarded prior to the date of enactment of the Comprehensive Addiction Recovery through Effective Employment and Reentry Act of 2025” after “grant period under this section”; and
(B) in paragraph (2)—
(i) in the matter preceding subparagraph (A), by striking “2 years after submitting the preliminary report required under paragraph (1)” and inserting “September 30, 2030”; and
(ii) in subparagraph (A), by striking “(g)(3)” and inserting “(g)(1)(C)”; and
(7) in subsection (k), by striking “$5,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2019 through 2023” and inserting “$12,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2026 through 2030”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of contents in section 1(b) of the SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Act (Public Law 115–271; 132 Stat. 3894) is amended by striking the item relating to section 7183 and inserting the following:
“Sec. 7183. CAREER Act; treatment, recovery, and workforce support grants.”.
SEC. 3. Reauthorization of the CAREER Act; Recovery Housing Pilot Program.
(a) In general.—Section 8071 of the SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Act (42 U.S.C. 5301 note; Public Law 115–271) is amended—
(1) by striking the section heading and inserting “CAREER Act; Recovery Housing Pilot Program”;
(2) in subsection (a), by striking “through 2023” and inserting “through 2030”;
(3) in subsection (b)—
(A) in paragraph (1), by striking “not later than 60 days after the date of enactment of this Act” and inserting “not later than 60 days after the date of enactment of the Comprehensive Addiction Recovery through Effective Employment and Reentry Act of 2025”; and
(B) in paragraph (2)(B)(i)—
(i) in subclause (I)—
(I) by striking “for calendar years 2013 through 2017”; and
(II) by inserting “for calendar years 2018 through 2022” after “rates of unemployment”;
(ii) in subclause (II)—
(I) by striking “for calendar years 2013 through 2017”; and
(II) by inserting “for calendar years 2018 through 2022” after “participation rates”; and
(iii) by striking subclause (III) and inserting the following:
“(III) The highest age-adjusted average rates of drug overdose deaths for calendar years 2018 through 2022 based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, including, if necessary, provisional data for calendar year 2022.”; and
(4) in subsection (f), by striking “For the 2-year period following the date of enactment of this Act, the” and inserting “The”.
(b) Conforming amendment.—Subtitle F of title VIII of the SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Act (Public Law 115–271; 132 Stat. 4095) is amended by striking the subtitle heading and inserting the following:
“subtitle F—CAREER Act; Recovery Housing Pilot Program”.
(c) Clerical amendments.—The table of contents in section 1(b) of the SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Act (Public Law 115–271; 132 Stat. 3894) is amended—
(1) by striking the item relating to subtitle F of title VIII and inserting the following:
“Subtitle F—CAREER Act; Recovery Housing Pilot Program
and
(2) by striking the item relating to section 8071 and inserting the following:
“Sec. 8071. CAREER Act; Recovery Housing Pilot Program.”.
S.665 – Fatal Overdose Reduction Act of 2025
A bill to amend title XIX of the Social Security Act to establish the Health Engagement Hub Demonstration Program to increase access to treatment for opioid use disorder and other substance use disorders, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Health Engagement Hub Demonstration Program under Medicaid.
Section 1903 of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1396b) is amended by adding at the end the following new subsection:
“(cc) Health Engagement Hub Demonstration Program.—
“(1) AUTHORITY.—The Secretary shall conduct a demonstration program (referred to in this subsection as the ‘demonstration program’) for the purpose of increasing access to treatment for opioid use disorder and other substance use disorders through the establishment of Health Engagement Hubs that meet the criteria published by the Secretary under paragraph (2)(A).
“(2) PUBLICATION OF GUIDANCE.—Not later than 6 months after the date of enactment of this subsection, the Secretary shall publish the following:
“(A) CERTIFICATION CRITERIA.—The criteria described in paragraph (3)(A) (which may be further defined and interpreted by the Secretary as necessary to carry out the demonstration program) for an organization to be certified by a State as a Health Engagement Hub for purposes of participating in the demonstration program.
“(B) PROSPECTIVE PAYMENT SYSTEM.—Guidance for States selected to participate in the demonstration program to use to establish a prospective payment system for the required items and services described in paragraph (3)(B) (which may be further defined and interpreted by the Secretary as necessary to carry out the demonstration program) that are provided by a certified Health Engagement Hub participating in the demonstration program to individuals who are eligible for medical assistance under a State plan under this title or under a waiver of such plan. Such guidance shall specify that the prospective payment system established by a State shall only apply to the required items and services described in paragraph (3)(B)(i) that are provided in accordance with the requirements applicable under this title to the provision of such services to individuals who are eligible for medical assistance under the State plan under this title or under a waiver of such plan.
“(C) CLARIFICATION REGARDING PAYMENT FOR FURNISHING MEDICAL ASSISTANCE FOR PRESCRIBED DRUGS OR COVERED OUTPATIENT DRUGS.—Statements that, with respect to the provision of medical assistance for prescribed drugs or covered outpatient drugs (as defined in section 1927(k)) by a certified Health Engagement Hub to individuals who are eligible for medical assistance under the State plan under this title or under a waiver of such plan and in accordance with the requirements applicable under this title—
“(i) the prospective payment system established by a State for purposes of the demonstration program shall not include payment for such medical assistance (other than with respect to the service of providing a prescription or administering a drug if needed); and
“(ii) a certified Health Engagement Hub that provides medical assistance for prescribed drugs or covered outpatient drugs (as so defined) shall not be precluded from receiving payment under the State plan under this title or under a waiver of such plan for the provision of such medical assistance, that is in addition to, and separate from, any payment made to the certified Health Engagement Hub under such prospective payment system.
“(D) ELIGIBILITY OF AN INDIAN TRIBE, TRIBAL ORGANIZATION, URBAN INDIAN ORGANIZATION, OR CONSORTIA.—Such requirements as the Secretary determines appropriate for an Indian Tribe or Tribal organization, (as such terms are defined in section 4 of the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act), a tribal consortia, or an Urban Indian organization (as defined in section 4 of the Indian Health Care Improvement Act), to apply for, and be selected to participate in, the demonstration program. To the extent practicable, such requirements shall be similar to the requirements applicable to a State desiring to participate in the demonstration program.
“(3) CRITERIA FOR CERTIFICATION OF HEALTH ENGAGEMENT HUBS.—
“(A) GENERAL REQUIREMENTS.—In order to be certified as a Health Engagement Hub, an organization shall satisfy the following requirements:
“(i) The organization demonstrates that the organization is equipped to serve individuals who are eligible for medical assistance under a State plan under this title or under a waiver of such plan (including individuals who are eligible for such assistance but are not enrolled in such State plan or waiver), as well as uninsured individuals (as defined in section 1902(ss)), and provide such populations with access to a range of social and medical services, in a drop-in manner and without prior appointment.
“(ii) The organization provides (in a manner reflecting person-centered care) the services specified in subparagraph (B) which, if not available directly through the organization, are provided or referred through partnerships or formal contracts with other providers.
“(iii) The organization demonstrates that in selecting the location for the Health Engagement Hub, the organization prioritized placement in communities disproportionately impacted by overdose and other harms related to substance use disorder (as further defined by the Secretary), including rural areas, geographically isolated areas within the State, tribal areas, urban centers with under-resourced behavioral health infrastructure, communities with significant numbers of individuals experiencing homelessness, and communities negatively impacted by the criminal-legal system.
“(iv) The organization uses evidence-based models to increase engagement and improve outcomes for individuals with opioid use disorder or other substance use disorders, such as social work empowerment models, motivational interviewing models, shared decision-making models, and other evidence-based recovery and support services.
“(v) The organization demonstrates that the organization is equipped to provide—
“(I) overdose education and distribution of a drug or device approved or cleared under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act for emergency reversal of known or suspected opioid overdose (such as naloxone);
“(II) safer substance use education and supplies;
“(III) safer-sex supplies;
“(IV) emotional support and counseling services to reduce harms associated with substance use, using a trauma-informed approach; and
“(V) access, within 4 hours of the arrival of an individual with opioid use disorder or other substance use disorder at a Health Engagement Hub, to drugs approved under section 505 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and biological products licensed under section 351 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 262) for treatment of opioid use disorder or substance use disorder with a strong evidence base of significantly reducing mortality, directly or through partnerships or formal contracts with other providers in a manner that insures consistency of care and care coordination.
“(vi) The organization demonstrates that the organization is equipped to provide, as selected by the organization, 1 or more services to address health-related social needs, which may include—
“(I) identification services (such as assistance with obtaining a government-recognized form of identification);
“(II) employment counseling;
“(III) recovery support services, including services that promote a process of change through which individuals improve their health and wellness, live self-directed lives, and strive to reach their full potential through career, education, or community-building;
“(IV) family reunification services, including services that help the reunification of family members separated by the legal system or foster system; and
“(V) criminal-legal services, including the provision of legal clinical consultation, legal information and advice, legal referrals, and legal advocacy or retainer.
“(vii) The organization demonstrates that the organization is equipped to meet—
“(I) the minimum staffing requirements described in subparagraph (C);
“(II) the experience requirement described in subparagraph (D); and
“(III) the community advisory board requirement described in subparagraph (E).
“(viii) The organization agrees to provide services to an uninsured individual (as defined in section 1902(ss)), with fees for such services imposed on a sliding scale basis that—
“(I) is developed at the discretion of a certified Health Engagement Hub or the State;
“(II) is based on an individual’s ability to pay; and
“(III) provides that the organization shall not reject or limit services on the basis of an individual’s ability to pay or place of residence.
“(B) SCOPE OF ITEMS AND SERVICES.—The items and services specified in this subparagraph are the following, subject to the requirements applicable under this title to the provision of such items and services:
“(i) REQUIRED ITEMS AND SERVICES PAID FOR THROUGH THE PROSPECTIVE PAYMENT SYSTEM.—
“(I) Harm reduction services and supplies.
“(II) Patient-centered and patient-driven physical and behavioral health care that has walk-in availability, is offered during non-traditional hours, including evenings and weekends, and includes—
“(aa) primary mental health and substance use disorder services, as defined by the Secretary, including screening, assessment, and referrals to higher levels of care;
“(bb) shared decision-making for patients and providers for opioid use disorder or substance use disorder under which a patient and provider discuss the patient’s diagnosis and condition together and evaluate treatment options together;
“(cc) wound care and supplies;
“(dd) infectious disease vaccination, screening, testing, and, to the extent practicable, treatment (including for HIV, sexually transmitted infections, and hepatitis);
“(ee) sexual and reproductive health services provided directly or through partnerships or formal contracts with other providers; and
“(ff) secure medication storage and inventory policies and procedures for patients experiencing homelessness or housing insecurity.
“(III) Medication management, as specified by the State, including with respect to the types of conditions for which medication management must be at a minimum available.
“(IV) Targeted case management.
“(V) Peer support services.
“(VI) Community health outreach and navigation services, including services that guide patients through social and health care systems to connect with services and service providers that the patients need.
“(ii) PRESCRIBED DRUGS AND COVERED OUTPATIENT DRUGS PAID SEPARATE FROM THE PROSPECTIVE PAYMENT SYSTEM.—Directly or through partnerships or formal contracts with other providers, prescribed drugs and covered outpatient drugs (as defined in section 1927(k)) for which medical assistance is available under the State plan under this title or under a waiver of such plan that are provided in accordance with requirements applicable under this title and, if applicable, a rebate agreement in effect under section 1927.
“(C) MINIMUM STAFFING REQUIREMENTS.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—The minimum staffing requirements specified in this subparagraph are the following:
“(I) At least 1 part-time or full-time health care provider who is licensed to practice in the State where the Health Engagement Hub is located and is licensed, registered, or otherwise permitted, by the United States to prescribe controlled substances (as defined in section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act) in the course of professional practice.
“(II) At least 1 part-time or full-time registered nurse or licensed practical nurse who can provide or supervise staff providing medication management, targeted case management, wound care, and vaccine administration.
“(III) At least 1 part-time or full-time licensed behavioral health staff who is qualified to assess or provide counseling about potential treatment options or about the need for treatment.
“(IV) At least 1 full-time equivalent staff who is a peer support specialist, community health worker, or recovery coach, with priority for hiring staff for such positions who are individuals with lived and living experience with substance use.
“(V) Full-time outreach, engagement, and ongoing care navigation staff, including peer support specialists, community health workers, and recovery coaches. At least 50 percent of such staff shall be individuals with lived and living experience with substance use.
“(ii) STAFFING THROUGH CONTRACTUAL ARRANGEMENTS WITH PARTNER AGENCIES.—An organization may enter into a contractual arrangement with a partner agency, such as a Federally-qualified health center, to satisfy the minimum staffing requirements specified in clause (i) with staff who are on-site at the Health Engagement Hub.
“(D) EXPERIENCE.—An organization shall have a demonstrated history of at least 12 months of providing opioid use disorder or substance use disorder treatment services to individuals.
“(E) COMMUNITY ADVISORY BOARD.—An organization shall have a community advisory board composed of individuals with lived and living experience with substance use that meets, at a minimum—
“(i) on a monthly basis, to review program utilization data and provide feedback to the organization; and
“(ii) on a quarterly basis, with the executives or board of directors of the organization to provide input on service delivery and receive feedback on actions taken based on previous feedback provided by the community advisory board.
“(4) PLANNING GRANTS; ADMINISTRATION.—There is appropriated, out of any funds in the Treasury not otherwise appropriated, $60,000,000 to the Secretary for purposes of implementing, administering, and making planning grants to States as soon as practicable for purposes of developing proposals to participate in the demonstration program and obtaining technical assistance from the Secretary with respect to the design and implementation of the demonstration program, for expenditures attributable to collecting and reporting the information and data required under paragraph (6)(B), and for administrative expenses of the Secretary to carry out this subsection, to remain available until expended.
“(5) STATE DEMONSTRATION PROGRAMS.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 9 months after the date on which the Secretary first awards a planning grant under paragraph (4), the Secretary shall solicit applications to participate in the demonstration program solely from States awarded such a grant.
“(B) APPLICATION REQUIREMENTS.—An application to participate in the demonstration program shall include the following:
“(i) A description of the target population (including the estimated number of individuals in such population) to be served by the State under the demonstration program.
“(ii) An assurance that at least 50 percent of the Health Engagement Hubs in the State shall be located in—
“(I) a county (or municipality or other unit of local government, if not contained within any county) where the mean drug overdose death rate per 100,000 people over the past 3 years for which official data are available from the State, is higher than the most recent available national average overdose death rate per 100,000 people over the past 3 years, as reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; or
“(II) an area of the State that is designated under section 332(a)(1)(A) of the Public Health Service Act as a mental health professional shortage area.
“(iii) A description of the prospective payment system that is to be tested under the demonstration program.
“(iv) A list of the certified Health Engagement Hubs located in the State that will participate in the demonstration program.
“(v) Verification that each such certified Health Engagement Hub satisfies the requirements described in paragraph (3).
“(vi) Verification that the State has agreed to pay for the items and services required to be paid for through the prospective payment system at the rate established under the prospective payment system.
“(vii) Any other information that the Secretary may require relating to the demonstration program with respect to determining the soundness of the proposed prospective payment system.
“(C) SELECTION CRITERIA.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary shall select from among the applications submitted up to 10 States to participate in the demonstration program.
“(ii) PRIORITY.—In selecting States to participate in the demonstration program, the Secretary shall prioritize selecting States—
“(I) with the highest opioid- or stimulant-involved overdose death rates; and
“(II) in a manner that ensures, to the extent practicable, geographic diversity across the United States.
“(D) LENGTH OF DEMONSTRATION PROGRAMS.—A State selected to participate in the demonstration program shall participate in the program for a 5-year period.
“(E) WAIVER OF CERTAIN REQUIREMENTS.—The Secretary shall waive section 1902(a)(1) (relating to statewideness) and section 1902(a)(10)(B) (relating to comparability) as may be necessary for a State to participate in the demonstration program in accordance with this paragraph.
“(F) PAYMENTS TO STATES.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—For each quarter occurring during the period for which the demonstration program is conducted, the Secretary shall pay a State participating in the demonstration program an amount equal to 90 percent (or, if higher, the Federal medical assistance percentage otherwise applicable to the State and year under section 1905 (without regard to this subparagraph)) of the amounts expended by the State for the quarter for items and services provided by certified Health Engagement Hubs (directly or through partnerships or formal contracts with other providers) at the rate established under the prospective payment system established by the State for purposes of the demonstration program to individuals who are eligible for, and enrolled under, the State plan or under a waiver of such plan.
“(ii) ENSURING NO DUPLICATE PPS PAYMENTS.—The guidance required under paragraph (2)(B) shall include guidance on how the Secretary will determine, if 2 or more prospective payment systems may apply to a service provided by a certified Health Engagement Hub (directly or through partnerships or formal contracts with other providers) to an individual who is eligible for, and enrolled under, the State plan or under a waiver of such plan, which prospective payment systems shall apply for purposes of determining the amount to be paid to a State for a quarter under clause (i).
“(iii) APPLICATION.—Payments made to States made under this subparagraph shall be considered to have been made under, and are subject to, the requirements of this section.
“(6) REPORTS.—
“(A) INITIAL IMPLEMENTATION.—During the first 2 years in which a State participates in the demonstration program under paragraph (5), the State shall submit to the Secretary such information as the Secretary may require relating to the implementation and initial operation of the demonstration program.
“(B) ANNUAL STATE REPORTS.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—Beginning with the 3rd year in which a State participates in the demonstration program under paragraph (5), the State shall submit an annual report to the Secretary on the demonstration program that includes the following:
“(I) An assessment of the extent to which Health Engagement Hubs funded under the demonstration program have increased access to treatment for opioid use disorder and other substance use disorders, health services for individuals who use drugs, and other social services under the State’s plan under this title or under a waiver of such plan in the area or areas of the State targeted by the demonstration program, as compared to other areas of the State.
“(II) An assessment of the extent to which Health Engagement Hubs are reducing opioid and stimulant overdose mortality rates and the rate of adherence to prescribed medication for opioid use, hospitalization rates, recovery rates, and housing status for the populations served by the Health Engagement Hubs as compared to populations that are not served by the Health Engagement Hubs.
“(III) Data and information comparing for populations served by the Health Engagement Hubs the racial and socioeconomic demographics, housing status, employment, and other metrics, as recommended by the Secretary, of such populations.
“(IV) A description of the successes of the demonstration program.
“(V) Recommendations for improvements to the demonstration program, including whether the demonstration program should be continued, expanded, modified, or terminated.
“(ii) DATA AVAILABILITY.—Each State selected to participate in the demonstration program under paragraph (5) shall agree, as a condition of such selection, to cooperate with data collection for purposes of the national implementation evaluation under paragraph (7).
“(iii) INFORMATION AND DATA COLLECTION AND REPORTING EXPENDITURES.—From amounts made available under paragraph (4)(A)(i), the Secretary shall make payments to States for expenditures attributable to collecting and reporting the information and data required under this subparagraph.
“(C) REPORTS TO CONGRESS AND THE COMPTROLLER GENERAL.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—Beginning with the 3rd year in which a State participates in the demonstration program under paragraph (5), the Secretary shall submit to Congress and the Comptroller General of the United States, and make publicly available, an annual report that describes the information, findings, and recommendations in the annual State reports submitted to the Secretary under subparagraph (A).
“(ii) IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION RESULTS.—The Secretary shall include with the first 3 annual reports submitted by the Secretary under this subparagraph the findings and conclusions of the national implementation evaluation required by paragraph (7).
“(7) NATIONAL IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION.—
“(A) IN GENERAL.—The Secretary shall contract with an entity that meets the requirements of subparagraph (B)(ii) to solicit public input and conduct a national implementation evaluation of the planning grants awarded under paragraph (4) and the State demonstration programs under paragraph (5) to determine the reach, effectiveness, adoption, and implementation of the demonstration program in each such State and to allow for a complete assessment of the impact of Health Engagement Hubs in each State participating in the demonstration program.
“(B) REQUIREMENTS.—
“(i) INFORMATION.—The evaluation shall include information on the characteristics of the individuals who received services, service utilization metrics over time (including by staff role), and input from interviews with such individuals and staff.
“(ii) ELIGIBLE ENTITIES.—In order to be eligible to conduct the evaluation, an entity shall—
“(I) have documented experience conducting implementation evaluations of health and social services programs; and
“(II) satisfy such additional eligibility criteria as the Secretary may establish.”.
SEC. 3. Government Accountability Office report.
Not later than 18 months after receipt of the annual State reports and the findings and conclusions of the national implementation evaluation under paragraph (6)(C) of section 1903(cc) of the Social Security Act (as added by section 2), the Comptroller General of the United States shall provide to the Committee on Finance of the Senate and the Committee on Energy and Commerce of the House of Representatives a report assessing the Secretary’s evaluation of the Health Engagement Hub Demonstration Program established under such section.
S.1004 – Pregnant and Postpartum Women Treatment Reauthorization Act
A bill to reauthorize the program to support residential treatment programs for pregnant and postpartum women, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Reauthorization of program.
Section 508 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 290bb–1) is amended—
(1) in subsection (d)(11)(C), by striking “providing health services” and inserting “providing health care services”;
(2) in subsection (g)—
(A) by inserting “a plan describing” after “will provide”; and
(B) by adding at the end the following: “Such plan may include a description of how such applicant will target outreach to women disproportionately impacted by maternal substance use disorder.”; and
(3) in subsection (s), by striking “$29,931,000 for each of fiscal years 2019 through 2023” and inserting “$38,931,000 for each of fiscal years 2025 through 2029”.
S.1022 – Strengthening Communities of Recovery Act
A bill to reauthorize the program for strengthening communities of recovery for individuals with substance use disorders.
SEC. 2. Strengthening communities of recovery.
Section 547 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 290ee–2) is amended—
(1) in the section heading, by striking “Building” and inserting “Strengthening”;
(2) in subsection (d)(2)(A), in the matter preceding clause (i), by inserting “or strengthen” after “build”; and
(3) in subsection (f), by striking “$5,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2019 through 2023” and inserting “$16,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2025 through 2029”.
S.1036 – Improving Access to Addiction Medicine Providers Act
SEC. 2. Minority Fellowship Program.
Section 597 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 290ll) is amended—
(1) in subsection (a)(1), by inserting “diagnosis,” after “related to”; and
(2) in subsection (b), by inserting “addiction medicine,” after “psychiatry,”.
S.1074 – A bill to provide for a study on the accessibility of substance use disorder treatment and mental health care providers and services for farmers and ranchers, and for other purposes.
S.1132 – A bill to amend the Older Americans Act of 1965 to include peer supports as a supportive service within the National Family Caregiver Support Program, to require States to consider the unique needs of caregivers whose families have been impacted by substance use disorder, including opioid use disorder, in providing services under such program, and for other purposes.
Controlled Substances
Opioids
S.617 – OPIOIDS Act or the Overcoming Prevalent Inadequacies in Overdose Information Data Sets Act
A bill to permit the Attorney General to award grants for accurate data on opioid-related overdoses, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Accurate data on opioid-related overdoses.
The Attorney General may award grants to States, territories, and localities to support improved data and surveillance on opioid-related overdoses, including for activities to improve postmortem toxicology testing, data linkage across data systems throughout the United States, electronic death reporting, or the comprehensiveness of data on fatal and nonfatal opioid-related overdoses.
SEC. 3. Law enforcement grants.
(a) In general.—The Attorney General shall make grants to local law enforcement agencies and forensic laboratories in communities with high rates of drug overdoses for the purpose of—
(1) training to help officers identify overdoses;
(2) upgrading essential systems for tracing drugs and processing samples in forensic laboratories to provide timely, accurate, and standard data reporting to the National Forensic Laboratory Information System; or
(3) training to better trace criminals through the darknet.
(b) Mandatory reporting.—None of the funds made under subsection (a) may be used by grantees that do not submit to the National Forensic Laboratory Information System reports on overdose data.
(c) Federal Law Enforcement Training Centers.—Federal Law Enforcement Training Centers shall provide training to State and local law enforcement agencies on how to best coordinate with State and Federal partners for tracking drug-related activity.
(d) COPS grants.—Section 1701(b) of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10381) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (23), by striking “and” at the end;
(2) in paragraph (24), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(24) to provide training and resources for containment devices to prevent secondary exposure to fentanyl and other substances for first responders.”.
SEC. 4. Office of National Drug Control Policy reform.
(a) In general.—The Drug Enforcement Administration shall develop uniform reporting standards for inputting data into the National Forensic Laboratory Information System for purity, formulation, and weight to allow for better comparison across jurisdictions and between agencies and the sharing of data.
(b) Clarification.—Nothing in subsection (a) may be construed to require the creation of new or increased obligations or reporting requirements on State or local laboratories.
SEC. 5. DEA testing.
The Drug Enforcement Administration shall submit to Congress, as part of the annual budget process, a specific line item for the level of funding necessary for the Fentanyl Signature Profiling Program.
S.938 – Joint Task Force to Counter Illicit Synthetic Narcotics Act of 2025
A bill to establish the Joint Task Force to Counter the Illicit Synthetic Narcotics.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) The United States is experiencing a crisis of substance abuse and addiction resulting in the deaths of hundreds of thousands of people of the United States. Most of these deaths involve some form of opioids.
(2) There are many elements of Federal, State, territorial, Tribal, and local governments working to combat the opioid epidemic.
(3) No central entity exists at the appropriate level whereby different agencies can share information and coordinate efforts to combat the opioid crisis.
SEC. 3. Definitions.
In this Act:
(1) CONTROLLED SUBSTANCE; LISTED CHEMICAL.—The terms “controlled substance” and “listed chemical” have the meanings given the terms in section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 802).
(2) DIRECTOR.—The term “Director” means the Director of the JTF–ISN.
(3) ILLICIT SYNTHETIC NARCOTIC.—The term “illicit synthetic narcotic” means—
(A) a controlled substance with the exception of—
(i) a substance of natural origin; or
(ii) a medication—
(I) that is lawful under the laws of the United States; and
(II) for which the Drug Enforcement Administration has provided an import permit to the importing organization for the import of the medication;
(B) a listed chemical; and
(C) an active pharmaceutical ingredient or chemical that is used in the production of a controlled substance or listed chemical in subparagraphs (A) and (B).
(4) JTF–ISN.—The term “JTF–ISN” means the Joint Task Force to Counter Illicit Synthetic Narcotics established under section 4.
SEC. 4. Establishment of joint task force to counter illicit synthetic narcotics.
(a) In general.—There is established a Joint Task Force to Counter Illicit Synthetic Narcotics.
(b) Membership.—The JTF–ISN shall be composed of representatives of the following entities:
(1) The Department of Justice, including—
(A) the Drug Enforcement Administration;
(B) the Federal Bureau of Investigation; and
(C) assistant United States attorneys and trial attorneys, as the Director determines are appropriate.
(2) The Department of the Treasury, including—
(A) the Counter-Fentanyl Strike Force;
(B) the Internal Revenue Service Criminal Investigation;
(C) the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network;
(D) the Office of Foreign Assets Control; and
(E) Office of Intelligence and Analysis.
(3) The Department of Homeland Security, including—
(A) Homeland Security Investigations;
(B) U.S. Customs and Border Protection, including the National Targeting Center;
(C) Immigration and Customs Enforcement; and
(D) the United States Coast Guard.
(4) The Department of State.
(5) The Department of Commerce.
(6) The Department of Defense.
(7) The Office of the Director of National Intelligence.
(8) Any other agency the Director deems appropriate.
(c) Director.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The JTF–ISN shall be led by a Director who shall be appointed by the President, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate.
(2) COMPENSATION.—The Director shall be compensated at the rate of basic pay prescribed for level II of the Executive Schedule under section 5313 of title 5, United States Code.
(d) Reporting.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The Director shall report to the Attorney General.
(2) REPORTS AND BRIEFINGS.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this Act, and every 180 days thereafter, the Director shall submit to the Committee on the Judiciary and the Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs of the Senate and the Committee on the Judiciary and the Committee on Homeland Security of the House of Representatives a report, and upon request of the chairman or ranking member of any such committee, a briefing that includes—
(A) a comprehensive plan covering the 2-year period beginning on the date on which the report is submitted or the briefing is made, as applicable, that includes—
(i) a description of the goals of the JTF–ISN;
(ii) description of areas of improvement with respect to collaboration among the participating agencies; and
(iii) an estimate of the funding and staff needed for the continued work of the JTF–ISN;
(B) a statement of the budget priorities of the JTF–ISN for each year in the 2-year period;
(C) a description of the efforts of the JTF–ISN to investigate and prosecute illicit synthetic narcotics trafficking crimes, including raids conducted, assets seized, assets forfeited and indictments brought and convictions; and
(D) efforts of the JTF–ISN to address matters related to the role of the People’s Republic of China in the opioids crisis.
SEC. 5. Primary missions of JTF–ISN.
The primary mission of the JTF–ISN shall be to direct counter opioid and synthetic narcotics activities, including disruption activities and associated investigations, and provide strategic coordination on related activities, including sanctions enforcement, conducting joint operations, raids, and other tactical actions in coordination with Federal, State, territorial, Tribal, and local law enforcement agencies through memorandums of understanding such as legal actions against traffickers and foreign entities, particularly in the People’s Republic of China, complicit in the opioid trade.
SEC. 6. Authority and limitations.
(a) Authority.—The JTF–ISN shall be vested with power and authority to—
(1) investigate and prosecute violations of Federal law relating to—
(A) the trafficking of illicit synthetic narcotics and related offenses, such as money laundering and other financial crimes; and
(B) smuggling, false statements, and any matter that arises or might arises directly from its investigations;
(2) in the case of a prosecution relating to non-United States persons outside of the United States, bring a case—
(A) in the district where the crime was committed;
(B) in the district where the Drug Enforcement Administration is located; or
(C) in a district described in section 3238 of title 18, United States Code;
(3) facilitate the sharing of information between members of the JTF–ISN in a timely manner;
(4) establish protocols for interagency referrals and procedures for referring cases to prosecuting and sanctions designating authorities as appropriate;
(5) develop strategies to address the role of the People’s Republic of China in the illicit synthetic narcotics crisis;
(6) work cooperatively with State, territorial, Tribal, and local law enforcement agencies to combat and prosecute trafficking of illicit synthetic narcotics;
(7) assess and improve existing methods of investigating and prosecuting illicit synthetic narcotics trafficking crimes; and
(8) conduct direct operational activities, including joint operations, raids, and other tactical actions, to disrupt illicit synthetic narcotics trafficking networks and bring offenders to justice.
(b) Limitation.—The Director may not direct the execution of operational activities outside the scope of counter-opioid efforts related to illicit synthetic narcotics suppliers and their networks pursuant to the primary missions of the JTF–ISN.
SEC. 7. Internal structure of JTF–ISN.
(a) Intelligence coordination.—The Director shall establish and maintain within the JTF–ISN an intelligence coordination element, which shall have primary responsibility within the United States Government for analysis of illicit synthetic narcotics and related trafficking organizations from all sources of intelligence, whether collected inside or outside the United States.
(b) Strategic operational planning.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—The Director shall establish and maintain within the JTF–ISN a strategic operational planning element, which shall provide strategic operational plans for counter-opioid operations conducted by the United States Government, and include the mission, objectives to be achieved, tasks to be performed, interagency coordination of operational activities, and the assignment of roles and responsibilities.
(2) MONITORING.—The Director shall monitor the implementation of strategic operational plans and shall obtain information from each element of the intelligence community, and from each other department, agency, or element of the United States Government relevant for monitoring the progress of such entity in implementing such plans.
(c) Office of General Counsel.—The Director shall establish and maintain within the JTF–ISN an Office of General Counsel, which shall provide legal advice in support of the JTF–ISN and its directorates.
(d) Office of Congressional Coordination.—The Director shall establish and maintain within the JTF–ISN an Office of Congressional Coordination, which shall coordinate communications of the JTF–ISN with Congress and ensure compliance with reporting and briefing obligations under this Act.
SEC. 8. Retention of existing authorities.
Each member of the JTF–ISN shall maintain their existing authorities to investigate and prosecute trafficking crimes relating to illicit synthetic narcotics.
SEC. 9. Rule of construction.
Nothing in this Act shall be construed to authorize the JTF–ISN to investigate, target, or prosecute individuals for personal drug use or to pursue enforcement actions against low-level drug dealing that does not involve significant connections to larger trafficking networks.
S.1098 – A bill to amend the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 to enhance the Comprehensive Opioid Abuse Grant Program, and for other purposes.
S.1258 – A bill to prohibit the sale of food that is, or contains, unsafe poppy seeds.
Other Drugs
S.545 – Combating Illicit Xylazine Act
A bill to prohibit certain uses of xylazine, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Definitions.
(a) In general.—In this title, the term “xylazine” has the meaning given the term in paragraph (60) of section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act, as added by subsection (b) of this section.
(b) Controlled substances act.—Section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 802) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(60) The term ‘xylazine’ means the substance xylazine, including its salts, isomers, and salts of isomers whenever the existence of such salts, isomers, and salts of isomers is possible.”.
SEC. 3. Adding xylazine to schedule III.
Schedule III of section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(f) Unless specifically excepted or unless listed in another schedule, any material, compound, mixture, or preparation which contains any quantity of xylazine.”.
SEC. 4. Amendments.
(a) Amendment.—Section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 802) is amended by striking paragraph (27) and inserting the following:
“(27) (A) Except as provided in subparagraph (B), the term ‘ultimate user’ means a person who has lawfully obtained, and who possesses, a controlled substance for the use by the person or for the use of a member of the household of the person or for an animal owned by the person or by a member of the household of the person.
“(B) (i) In the case of xylazine, other than for a drug product approved under subsection (b) or (j) of section 505 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355), the term ‘ultimate user’ means a person—
“(I) to whom xylazine was dispensed by—
“(aa) a veterinarian registered under this Act; or
“(bb) a pharmacy registered under this Act pursuant to a prescription of a veterinarian registered under this Act; and
“(II) who possesses xylazine for—
“(aa) an animal owned by the person or by a member of the household of the person;
“(bb) an animal under the care of the person;
“(cc) use in government animal-control programs authorized under applicable Federal, State, Tribal, or local law; or
“(dd) use in wildlife programs authorized under applicable Federal, State, Tribal, or local law.
“(ii) In this subparagraph, the term ‘person’ includes—
“(I) a government agency or business where animals are located; and
“(II) an employee or agent of an agency or business acting within the scope of their employment or agency.”.
(b) Facilities.—An entity that manufactures xylazine, as of the date of enactment of this Act, shall not be required to make capital expenditures necessary to install the security standard required of schedule III of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 801 et seq.) for the purposes of manufacturing xylazine.
(c) Labeling.—The requirements related to labeling, packaging, and distribution logistics of a controlled substance in schedule III of section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812(c)) shall not take effect for xylazine until the date that is 1 year after the date of enactment of this Act.
(d) Practitioner registration.—The requirements related to practitioner registration, inventory, and recordkeeping of a controlled substance in schedule III of section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812(c)) shall not take effect for xylazine until the date that is 60 days after the date of enactment of this Act. A practitioner that has applied for registration during the 60-day period beginning on the date of enactment of this Act may continue their lawful activities until such application is approved or denied.
(e) Manufacturer transition.—The Food and Drug Administration and the Drug Enforcement Administration shall facilitate and expedite the relevant manufacturer submissions or applications required by the placement of xylazine on schedule III of section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812(c)).
(f) Clarification.—Nothing in this title, or the amendments made by this title, shall be construed to require the registration of an ultimate user of xylazine under the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 801 et seq.) in order to possess xylazine in accordance with subparagraph (B) of section 102(27) of that Act (21 U.S.C. 802(27)), as added by subsection (a) of this section.
SEC. 5. Arcos tracking.
Section 307(i) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 827(i)) is amended—
(1) in the matter preceding paragraph (1)—
(A) by inserting “or xylazine” after “gamma hydroxybutyric acid”;
(B) by inserting “or 512” after “section 505”; and
(C) by inserting “respectively,” after “the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act,”; and
(2) in paragraph (6), by inserting “or xylazine” after “gamma hydroxybutyric acid”.
SEC. 6. Sentencing Commission.
Pursuant to its authority under section 994(p) of title 28, United States Code, the United States Sentencing Commission shall review and, if appropriate, amend its sentencing guidelines, policy statements, and official commentary applicable to persons convicted of an offense under section 401 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 841) or section 1010 of the Controlled Substances Import and Export Act (21 U.S.C. 960) to provide appropriate penalties for offenses involving xylazine that are consistent with the amendments made by this title. In carrying out this section, the Commission should consider the common forms of xylazine as well as its use alongside other scheduled substances.
SEC. 7. Report to Congress on xylazine.
(a) Initial report.—Not later than 18 months after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Attorney General, acting through the Administrator of the Drug Enforcement Administration and in coordination with the Commissioner of Food and Drugs, shall submit to Congress a report on the prevalence of illicit use of xylazine in the United States and the impacts of such use, including—
(1) where the drug is being diverted;
(2) where the drug is originating; and
(3) whether any analogues to xylazine, or related or derivative substances, exist and present a substantial risk of abuse.
(b) Additional report.—Not later than 4 years after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Attorney General, acting through the Administrator of the Drug Enforcement Administration and in coordination with the Commissioner of Food and Drugs, shall submit to Congress a report updating Congress on the prevalence and proliferation of xylazine trafficking and misuse in the United States.
S.548 – Caribbean Border Counternarcotics Strategy Act
A bill to amend the Office of National Drug Control Policy Reauthorization Act of 1998 to require a Caribbean border counternarcotics strategy, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Caribbean Border Counternarcotics Strategy Act.
(a) Definitions.—Section 702 of the Office of National Drug Control Policy Reauthorization Act of 1998 (21 U.S.C. 1701) is amended—
(1) by redesignating paragraphs (15) through (17) as paragraphs (16) through (18), respectively;
(2) by inserting after paragraph (14) the following:
“(15) STATE.—The term ‘State’ means each of the several States of the United States, the District of Columbia, and each territory or possession of the United States.”;
(3) by amending paragraph (18), as redesignated—
(A) by redesignating subparagraphs (G) and (H) as subparagraphs (H) and (I), respectively; and
(B) by inserting after subparagraph (F) the following:
“(G) activities to map, track, dismantle, and disrupt the financial networks of drug trafficking organizations, transnational criminal organizations, and money laundering organizations involved in the manufacture and trafficking of drugs in the United States and in foreign countries;”; and
(4) by adding at the end the following:
“(19) UNITED STATES.—The term ‘United States’, when used in a geographical sense, means all of the States, the District of Columbia, and the territories and possessions of the United States, and any waters within the jurisdiction of the United States.”.
(b) Requirement for Caribbean Border Counternarcotics Strategy.—Section 706(c)(3) of the Office of National Drug Control Policy Reauthorization Act of 1998 (21 U.S.C. 1705(c)(3)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(D) REQUIREMENT FOR CARIBBEAN BORDER COUNTERNARCOTICS STRATEGY.—
“(i) PURPOSES.—The Caribbean Border Counternarcotics Strategy shall—
“(I) set forth the strategy of the Federal Government for preventing the illegal trafficking of drugs through the Caribbean region into the United States, including through ports of entry, between ports of entry, and across air and maritime approaches;
“(II) describe the specific roles and responsibilities of each relevant National Drug Control Program agency for implementing such strategy;
“(III) identify the specific resources required to enable the relevant National Drug Control Program agencies to implement such strategy; and
“(IV) be designed to promote, and not to hinder, legitimate trade and travel.
“(ii) SPECIFIC CONTENT RELATED TO PUERTO RICO AND THE UNITED STATES VIRGIN ISLANDS.—The Caribbean Border Counternarcotics Strategy shall include—
“(I) a strategy to prevent the illegal trafficking of drugs to or through Puerto Rico or the United States Virgin Islands, including measures to substantially reduce drug-related violent crime on such islands; and
“(II) recommendations for additional assistance or authorities, if any, needed by Federal, State, and local law enforcement agencies relating to the strategy, including an evaluation of Federal technical and financial assistance, infrastructure capacity building, and interoperability deficiencies.”.
S.767 – HIDTA Enhancement Act
A bill to amend the Office of National Drug Control Prevention Act of 1998 to include new requirements for assessments and reports, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Office of National Drug Control Policy.
The Office of National Drug Control Policy Reauthorization Act of 1998 (21 U.S.C. 1701 et seq.) is amended—
(1) in section 706(g)(3) (21 U.S.C. 1705(g)(3))—
(A) in subparagraph (C), by striking “and” at the end;
(B) in subparagraph (D), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(C) by adding at the end the following:
“(E) a report describing the use of HIDTA funds to investigate organizations and individuals trafficking in fentanyl or fentanyl-related substances, including any resulting prosecution, in the prior calendar year, including—
“(i) the amounts of fentanyl or fentanyl-related substances seized by a HIDTA-funded initiative in the area during the previous year; and
“(ii) law enforcement and predictive data from regional HIDTA threat assessments showing patterns and trends in substance abuse, trafficking, and transportation of fentanyl and fentanyl-related substances.”;
(2) in section 707 (21 U.S.C. 1706)—
(A) in subsection (l)(2)—
(i) in subparagraph (F), by striking “and” at the end;
(ii) in subparagraph (G), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(iii) by adding at the end the following:
“(H) any limitations of the ability of a high intensity drug trafficking area to meet the purpose or goals of the area and recommendations to address any such limitations, including through resource allocation, partnerships, or a change in authority or law.”;
(B) in subsection (p)—
(i) in paragraph (5), by striking “and” at the end;
(ii) in paragraph (6), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(iii) by adding at the end the following:
“(7) $333,000,000 for each of fiscal years 2025 through 2030.”;
(C) in subsection (s)—
(i) in the matter preceding paragraph (1), by striking “$10,000,000” and inserting “$14,224,000”;
(ii) in paragraph (2), by striking “and” at the end;
(iii) in paragraph (3), by striking the period at the end and inserting a semicolon; and
(iv) by adding at the end the following:
“(4) providing assistance to Federal, State, local, and Tribal law enforcement agencies in investigations and activities related to the interdiction of fentanyl and other substances; and
“(5) any additional purpose the Director determines is appropriate to enhance fentanyl prevention, seizure, and interdiction activities.”; and
(D) by adding at the end the following:
“(t) Additional prosecutorial resources.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—The Attorney General shall make available sufficient investigative and prosecution resources as may be practicable for the purposes described in this section, including temporary reassignment under subsection (b)(2) for fiscal years 2024 through 2030, during which such an assistant United States attorney shall prioritize the investigation and prosecution of organizations and individuals trafficking in fentanyl and fentanyl-related substances. Such temporary reassignment may be extended by the Attorney General for such time as may be necessary to conclude any ongoing investigation or prosecution in which the assistant United States attorney is engaged.
“(2) PROCESS FOR TEMPORARY REASSIGNMENT.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this subsection, the Attorney General shall establish a process under which the Director, in consultation with the Executive Boards of each designated high intensity drug trafficking area, may request an assistant United States attorney to be so temporarily reassigned in accordance with this subsection.”.
Marijuana
S.471 – No Deductions for Marijuana Businesses Act
A bill to amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to maintain the prohibition on allowing any deduction or credit associated with a trade or business involved in trafficking marijuana.
SEC. 2. Expenditures in connection with the sale of marijuana.
(a) In general.—Section 280E of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to read as follows:
“SEC. 280E. Expenditures in connection with the illegal sale of drugs.
“No deduction or credit shall be allowed for any amount paid or incurred during the taxable year in carrying on any trade or business if such trade or business (or the activities which comprise such trade or business) consists of trafficking in—
“(1) marijuana (as defined in section 102(16) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 802(16))), or
“(2) controlled substances (within the meaning of schedule I and II of the Controlled Substances Act),
which is prohibited by Federal law or the law of any State in which such trade or business is conducted.”.
(b) Effective date.—The amendment made by this section shall apply to amounts paid or incurred after the date of the enactment of this Act in taxable years ending after such date.
Fentanyl
S. 63 -CBW Fentanyl Act
A bill to amend the Chemical and Biological Weapons Control and Warfare Elimination Act of 1991 to impose sanctions on foreign countries in response to acts concerning chemical or biological programs that cause injury to other foreign countries, and for other purposes.
S. 165 – Stopping Overdoses of Fentanyl Analogues Act
A bill to amend the Controlled Substances Act to list fentanyl-related substances as schedule I controlled substances
SEC. 2. Fentanyl-related substances.
(a) In general.—Schedule I of section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812(c)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(e) (1) Unless specifically exempted or unless listed in another schedule, any material, compound, mixture, or preparation which contains any quantity of fentanyl-related substances, including their isomers, esters, ethers, salts, and salts of isomers, esters, and ethers, whenever the existence of such isomers, esters, ethers, and salts is possible within the specific chemical designation.
“(2) In paragraph (1), the term ‘fentanyl-related substances’ includes any substance that is structurally related to fentanyl by 1 or more of the following modifications:
“(A) By replacement of the phenyl portion of the phenethyl group by any monocycle, whether or not further substituted in or on the monocycle.
“(B) By substitution in or on the phenethyl group with alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyl, hydroxyl, halo, haloalkyl, amino, or nitro groups.
“(C) By substitution in or on the piperidine ring with alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyl, ester, ether, hydroxyl, halo, haloalkyl, amino, or nitro groups.
“(D) By replacement of the aniline ring with any aromatic monocycle whether or not further substituted in or on the aromatic monocycle.
“(E) By replacement of the N-propionyl group by another acyl group.”.
(b) Effective date.—This Act shall take effect 1 day after the date of enactment of this Act.
S. 331 – HALT Fentanyl Act or the Halt All Lethal Trafficking of Fentanyl Act
A bill to amend the Controlled Substances Act with respect to the scheduling of fentanyl-related substances, and for other purposes
This bill permanently places fentanyl-related substances as a class into schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act. A schedule I controlled substance is a drug, substance, or chemical that has a high potential for abuse; has no currently accepted medical value; and is subject to regulatory controls and administrative, civil, and criminal penalties under the Controlled Substances Act.
Under the bill, offenses involving fentanyl-related substances are triggered by the same quantity thresholds and subject to the same penalties as offenses involving fentanyl analogues (e.g., offenses involving 100 grams or more trigger a 10-year mandatory minimum prison term).
Additionally, the bill establishes a new, alternative registration process for certain schedule I research.
The bill also makes several other changes to registration requirements for conducting research with controlled substances, including
- permitting a single registration for related research sites in certain circumstances,
- waiving the requirement for a new inspection in certain situations, and
- allowing a registered researcher to perform certain manufacturing activities with small quantities of a substance without obtaining a manufacturing registration.
Finally, the bill expresses the sense that Congress agrees with the interpretation of the Controlled Substances Act in United States v. McCray, a 2018 case decided by the U.S. District Court for the Western District of New York. In that case, the court held that butyryl fentanyl, a controlled substance, can be considered an analogue of fentanyl even though, under the Controlled Substances Act, the term controlled substance analogue specifically excludes a controlled substance.
SEC. 2. Class scheduling of fentanyl-related substances.
Section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812(c)) is amended by adding at the end of schedule I the following:
“(e) (1) Unless specifically exempted or unless listed in another schedule, any material, compound, mixture, or preparation which contains any quantity of a fentanyl-related substance, or which contains the salts, isomers, and salts of isomers of a fentanyl-related substance whenever the existence of such salts, isomers, and salts of isomers is possible within the specific chemical designation.
“(2) For purposes of paragraph (1), except as provided in paragraph (3), the term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ means any substance that is structurally related to fentanyl by 1 or more of the following modifications:
“(A) By replacement of the phenyl portion of the phenethyl group by any monocycle, whether or not further substituted in or on the monocycle.
“(B) By substitution in or on the phenethyl group with alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyl, hydroxyl, halo, haloalkyl, amino, or nitro groups.
“(C) By substitution in or on the piperidine ring with alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyl, ester, ether, hydroxyl, halo, haloalkyl, amino, or nitro groups.
“(D) By replacement of the aniline ring with any aromatic monocycle whether or not further substituted in or on the aromatic monocycle.
“(E) By replacement of the N-propionyl group with another acyl group.
“(3) A substance that satisfies the definition of the term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ in paragraph (2) shall nonetheless not be treated as a fentanyl-related substance subject to this schedule if the substance—
“(A) is controlled by action of the Attorney General under section 201; or
“(B) is otherwise expressly listed in a schedule other than this schedule.
“(4) (A) The Attorney General may by order publish in the Federal Register a list of substances that satisfy the definition of the term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ in paragraph (2).
“(B) The absence of a substance from a list published under subparagraph (A) does not negate the control status of the substance under this schedule if the substance satisfies the definition of the term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ in paragraph (2).”.
SEC. 3. Registration requirements related to research.
(a) Alternative registration process for schedule I research.—Section 303 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 823) is amended—
(1) by redesignating the second subsection (l) (relating to required training for prescribers) as subsection (m); and
(2) by adding at the end the following:
“(n) Special provisions for practitioners conducting certain research with schedule I controlled substances.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Notwithstanding subsection (g), a practitioner may conduct research described in paragraph (2) of this subsection with 1 or more schedule I substances in accordance with subparagraph (A) or (B) of paragraph (3) of this subsection.
“(2) RESEARCH SUBJECT TO EXPEDITED PROCEDURES.—Research described in this paragraph is research that—
“(A) is with respect to a drug that is the subject of an investigational use exemption under section 505(i) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355(i)); or
“(B) is—
“(i) conducted by the Department of Health and Human Services, the Department of Defense, or the Department of Veterans Affairs; or
“(ii) funded partly or entirely by a grant, contract, cooperative agreement, or other transaction from the Department of Health and Human Services, the Department of Defense, or the Department of Veterans Affairs.
“(3) EXPEDITED PROCEDURES.—
“(A) RESEARCHER WITH A CURRENT SCHEDULE I OR II RESEARCH REGISTRATION.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—If a practitioner is registered to conduct research with a controlled substance in schedule I or II, the practitioner may conduct research under this subsection on and after the date that is 30 days after the date on which the practitioner sends a notice to the Attorney General containing the following information, with respect to each substance with which the practitioner will conduct the research:
“(I) The chemical name of the substance.
“(II) The quantity of the substance to be used in the research.
“(III) Demonstration that the research is in the category described in paragraph (2), which demonstration may be satisfied—
“(aa) in the case of a grant, contract, cooperative agreement, or other transaction, or intramural research project, by identifying the sponsoring agency and supplying the number of the grant, contract, cooperative agreement, other transaction, or project; or
“(bb) in the case of an application under section 505(i) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355(i)), by supplying the application number and the sponsor of record on the application.
“(IV) Demonstration that the researcher is authorized to conduct research with respect to the substance under the laws of the State in which the research will take place.
“(ii) VERIFICATION OF INFORMATION BY HHS OR VA.—Upon request from the Attorney General, the Secretary of Health and Human Services, the Department of Defense, or the Secretary of Veterans Affairs, as appropriate, shall verify information submitted by an applicant under clause (i)(III).
“(B) RESEARCHER WITHOUT A CURRENT SCHEDULE I OR II RESEARCH REGISTRATION.—
“(i) IN GENERAL.—If a practitioner is not registered to conduct research with a controlled substance in schedule I or II, the practitioner may send a notice to the Attorney General containing the information listed in subparagraph (A)(i), with respect to each substance with which the practitioner will conduct the research.
“(ii) ATTORNEY GENERAL ACTION.—The Attorney General shall—
“(I) treat notice received under clause (i) as a sufficient application for a research registration; and
“(II) not later than 45 days of receiving such a notice that contains all information required under subparagraph (A)(i)—
“(aa) register the applicant; or
“(bb) serve an order to show cause upon the applicant in accordance with section 304(c).
“(4) ELECTRONIC SUBMISSIONS.—The Attorney General shall provide a means to permit a practitioner to submit a notification under paragraph (3) electronically.
“(5) LIMITATION ON AMOUNTS.—A practitioner conducting research with a schedule I substance under this subsection may only possess the amounts of schedule I substance identified in—
“(A) the notification to the Attorney General under paragraph (3); or
“(B) a supplemental notification that the practitioner may send if the practitioner needs additional amounts for the research, which supplemental notification shall include—
“(i) the name of the practitioner;
“(ii) the additional quantity needed of the substance; and
“(iii) an attestation that the research to be conducted with the substance is consistent with the scope of the research that was the subject of the notification under paragraph (3).
“(6) IMPORTATION AND EXPORTATION REQUIREMENTS NOT AFFECTED.—Nothing in this subsection alters the requirements of part A of title III, regarding the importation and exportation of controlled substances.
“(7) INSPECTOR GENERAL REPORT.—Not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of the Halt All Lethal Trafficking of Fentanyl Act, the Inspector General of the Department of Justice shall complete a study, and submit to Congress a report thereon, about research described in paragraph (2) of this subsection with fentanyl.”.
(b) Separate registrations not required for additional researcher in same institution.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 302(c) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822(c)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(4) An agent or employee of a research institution that is conducting research with a controlled substance if—
“(A) the agent or employee is acting within the scope of the professional practice of the agent or employee;
“(B) another agent or employee of the institution is registered to conduct research with a controlled substance in the same schedule;
“(C) the researcher who is so registered—
“(i) informs the Attorney General of the name, position title, and employing institution of the agent or employee who is not separately registered;
“(ii) authorizes that agent or employee to perform research under the registration of the registered researcher; and
“(iii) affirms that any act taken by that agent or employee involving a controlled substance shall be attributable to the registered researcher, as if the researcher had directly committed the act, for purposes of any proceeding under section 304(a) to suspend or revoke the registration of the registered researcher; and
“(D) the Attorney General does not, within 30 days of receiving the information, authorization, and affirmation described in subparagraph (C), refuse, for a reason listed in section 304(a), to allow the agent or employee to possess the substance without a separate registration.”.
(2) TECHNICAL CORRECTION.—Section 302(c)(3) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822(c)(3)) is amended by striking “(25)” and inserting “(27)”.
(c) Single registration for related research sites.—Section 302(e) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822(e)) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(4) (A) Notwithstanding paragraph (1), a person registered to conduct research with a controlled substance under section 303(g) may conduct the research under a single registration if—
“(i) the research occurs exclusively on sites all of which are—
“(I) within the same city or county; and
“(II) under the control of the same institution, organization, or agency; and
“(ii) before commencing the research, the researcher notifies the Attorney General of each site where—
“(I) the research will be conducted; or
“(II) the controlled substance will be stored or administered.
“(B) A site described in subparagraph (A) shall be included in a registration described in that subparagraph only if the researcher has notified the Attorney General of the site—
“(i) in the application for the registration; or
“(ii) before the research is conducted, or before the controlled substance is stored or administered, at the site.
“(C) The Attorney General may, in consultation with the Secretary, issue regulations addressing, with respect to research sites described in subparagraph (A)—
“(i) the manner in which controlled substances may be delivered to the research sites;
“(ii) the storage and security of controlled substances at the research sites;
“(iii) the maintenance of records for the research sites; and
“(iv) any other matters necessary to ensure effective controls against diversion at the research sites.”.
(d) New inspection not required in certain situations.—Section 302(f) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822(f)) is amended—
(1) by striking “(f) The” and inserting “(f)(1) The”; and
(2) by adding at the end the following:
“(2) (A) If a person is registered to conduct research with a controlled substance and applies for a registration, or for a modification of a registration, to conduct research with a second controlled substance that is in the same schedule as the first controlled substance, or is in a schedule with a higher numerical designation than the schedule of the first controlled substance, a new inspection by the Attorney General of the registered location is not required.
“(B) Nothing in subparagraph (A) shall prohibit the Attorney General from conducting an inspection that the Attorney General determines necessary to ensure that a registrant maintains effective controls against diversion.”.
(e) Continuation of research on substances newly added to schedule I.—Section 302 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(h) Continuation of research on substances newly added to schedule I.—If a person is conducting research on a substance when the substance is added to schedule I, and the person is already registered to conduct research with a controlled substance in schedule I—
“(1) not later than 90 days after the scheduling of the newly scheduled substance, the person shall submit a completed application for registration or modification of existing registration, to conduct research on the substance, in accordance with regulations issued by the Attorney General for purposes of this paragraph;
“(2) the person may, notwithstanding subsections (a) and (b), continue to conduct the research on the substance until—
“(A) the person withdraws the application described in paragraph (1) of this subsection; or
“(B) the Attorney General serves on the person an order to show cause proposing the denial of the application under section 304(c);
“(3) if the Attorney General serves an order to show cause as described in paragraph (2)(B) and the person requests a hearing, the hearing shall be held on an expedited basis and not later than 45 days after the request is made, except that the hearing may be held at a later time if so requested by the person; and
“(4) if the person sends a copy of the application described in paragraph (1) to a manufacturer or distributor of the substance, receipt of the copy by the manufacturer or distributor shall constitute sufficient evidence that the person is authorized to receive the substance.”.
(f) Treatment of certain manufacturing activities as coincident to research.—Section 302 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 822), as amended by subsection (e), is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(i) Treatment of certain manufacturing activities as coincident to research.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Except as provided in paragraph (3), a person who is registered to perform research on a controlled substance may perform manufacturing activities with small quantities of that substance, including activities described in paragraph (2), without being required to obtain a manufacturing registration, if—
“(A) the activities are performed for the purpose of the research; and
“(B) the activities and the quantities of the substance involved in the activities are stated in—
“(i) a notification submitted to the Attorney General under section 303(n);
“(ii) a research protocol filed with an application for registration approval under section 303(g); or
“(iii) a notification to the Attorney General that includes—
“(I) the name of the registrant; and
“(II) an attestation that the research to be conducted with the small quantities of manufactured substance is consistent with the scope of the research that is the basis for the registration.
“(2) ACTIVITIES INCLUDED.—Activities permitted under paragraph (1) include—
“(A) processing the substance to create extracts, tinctures, oils, solutions, derivatives, or other forms of the substance consistent with—
“(i) the information provided as part of a notification submitted to the Attorney General under section 303(n); or
“(ii) a research protocol filed with an application for registration approval under section 303(g); and
“(B) dosage form development studies performed for the purpose of requesting an investigational new drug exemption under section 505(i) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 355(i)).
“(3) EXCEPTION REGARDING MARIHUANA.—The authority under paragraph (1) to manufacture substances does not include the authority to grow marihuana.”.
(g) Transparency regarding special procedures.—Section 303 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 823), as amended by subsection (a), is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(o) Transparency regarding special procedures.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—If the Attorney General determines, with respect to a controlled substance, that an application by a practitioner to conduct research with the substance should be considered under a process, or subject to criteria, different from the process or criteria applicable to applications to conduct research with other controlled substances in the same schedule, the Attorney General shall make public, including by posting on the website of the Drug Enforcement Administration—
“(A) the identities of all substances for which such determinations have been made;
“(B) the process and criteria that shall be applied to applications to conduct research with those substances; and
“(C) how the process and criteria described in subparagraph (B) differ from the process and criteria applicable to applications to conduct research with other controlled substances in the same schedule.
“(2) TIMING OF POSTING.—The Attorney General shall make information described in paragraph (1) public upon making a determination described in that paragraph, regardless of whether a practitioner has submitted such an application at that time.”.
SEC. 4. Technical correction on controlled substances dispensing.
Effective as if included in the enactment of Public Law 117–328—
(1) section 1252(a) of division FF of Public Law 117–328 (136 Stat. 5681) is amended, in the matter being inserted into section 302(e) of the Controlled Substances Act, by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”;
(2) section 1262 of division FF of Public Law 117–328 (136 Stat. 5681) is amended—
(A) in subsection (a)—
(i) in the matter preceding paragraph (1), by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”;
(ii) in the matter being stricken by subsection (a)(2), by striking “(g)(1)” and inserting “(h)(1)”; and
(iii) in the matter being inserted by subsection (a)(2), by striking “(g) Practitioners” and inserting “(h) Practitioners”; and
(B) in subsection (b)—
(i) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (1), by striking “303(g)(1)” and inserting “303(h)(1)”;
(ii) in the matter being inserted by paragraph (1), by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”;
(iii) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (2)(A), by striking “303(g)(2)” and inserting “303(h)(2)”;
(iv) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (3), by striking “303(g)(2)(B)” and inserting “303(h)(2)(B)”;
(v) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (5), by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”; and
(vi) in the matter being stricken by paragraph (6), by striking “303(g)” and inserting “303(h)”; and
(3) section 1263(b) of division FF of Public Law 117–328 (136 Stat. 5685) is amended—
(A) by striking “303(g)(2)” and inserting “303(h)(2)”; and
(B) by striking “(21 U.S.C. 823(g)(2))” and inserting “(21 U.S.C. 823(h)(2))”.
SEC. 5. Rulemaking.
(a) Interim final rules.—The Attorney General—
(1) shall, not later than 6 months after the date of enactment of this Act, issue rules to implement this Act and the amendments made by this Act; and
(2) may issue the rules under paragraph (1) as interim final rules.
(b) Procedure for final rule.—
(1) EFFECTIVENESS OF INTERIM FINAL RULES.—A rule issued by the Attorney General as an interim final rule under subsection (a) shall become immediately effective as an interim final rule without requiring the Attorney General to demonstrate good cause therefor, notwithstanding subparagraph (B) of the undesignated matter following paragraph (4) of section 553(b) of title 5, United States Code.
(2) OPPORTUNITY FOR COMMENT AND HEARING.—An interim final rule issued under subsection (a) shall give interested persons the opportunity to comment and to request a hearing.
(3) FINAL RULE.—After the conclusion of such proceedings, the Attorney General shall issue a final rule to implement this Act and the amendments made by this Act in accordance with section 553 of title 5, United States Code.
SEC. 6. Penalties.
(a) In general.—Section 401(b)(1) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 841(b)(1)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (A)(vi), by inserting “or a fentanyl-related substance” after “any analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide”; and
(2) in subparagraph (B)(vi), by inserting “or a fentanyl-related substance” after “any analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide”.
(b) Importation and exportation.—Section 1010(b) of the Controlled Substances Import and Export Act (21 U.S.C. 960(b)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1)(F), by inserting “or a fentanyl-related substance” after “any analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide”; and
(2) in paragraph (2)(F), by inserting “or a fentanyl-related substance” after “any analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide”.
(c) Definition of fentanyl-related substance.—Section 102 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 802) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“(60) The term ‘fentanyl-related substance’ has the meaning given the term in subsection (e)(2) of schedule I of section 202(c).”.
SEC. 7. Applicability; other matters.
(a) In general.—Irrespective of the date on which the rules required by section 5 are finalized, the amendments made by this Act apply beginning as of the date of enactment of this Act.
(b) Rule of construction.—Nothing in the amendments made by this Act may be construed as evidence that, in applying sections 401(b)(1) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 841(b)(1)) and 1010(b) of the Controlled Substances Import and Export Act (21 U.S.C. 960(b)) with respect to conduct occurring before the date of the enactment of this Act, a fentanyl-related substance (as defined by such amendments) is not an analogue of N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide.
(c) Sense of Congress.—Congress agrees with the interpretation of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 801 et seq.) in United States v. McCray, 346 F. Supp. 3d 363 (W.D.N.Y. 2018).
S. 477 – Fairness in Fentanyl Sentencing Act of 2025
A bill to amend the Controlled Substances Act and the Controlled Substances Import and Export Act to modify the offenses relating to fentanyl, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Controlled Substances Act amendments.
Section 401(b)(1) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 841(b)(1)) is amended—
(1) in subparagraph (A)(vi)—
(A) by striking “400” and inserting “20”;
(B) by striking “100” and inserting “5”; and
(C) by inserting “scheduled or unscheduled” before “analogue of”; and
(2) in subparagraph (B)(vi)—
(A) by striking “40” and inserting “2”;
(B) by striking “10” and inserting “0.5”; and
(C) by inserting “scheduled or unscheduled” before “analogue of”.
SEC. 3. Controlled Substances Import and Export Act amendments.
Section 1010(b) of the Controlled Substances Import and Export Act (21 U.S.C. 960(b)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1)(F)—
(A) by striking “400” and inserting “20”;
(B) by striking “100” and inserting “5”; and
(C) by inserting “scheduled or unscheduled” before “analogue of”; and
(2) in paragraph (2)(F)—
(A) by striking “40” and inserting “2”;
(B) by striking “10” and inserting “0.5”; and
(C) by inserting “scheduled or unscheduled” before “analogue of”.
SEC. 4. Directive to the Sentencing Commission.
(a) Definition.—In this section, the term “Commission” means the United States Sentencing Commission.
(b) Directive to the United States Sentencing Commission.—Pursuant to the authority of the Commission under section 994(p) of title 28, United States Code, and in accordance with this section, the Commission shall review and amend, if appropriate, the guidelines and policy statements of the Commission applicable to a person convicted of an offense under section 401 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 841) or section 1010 of the Controlled Substances Import and Export Act (21 U.S.C. 960) to ensure that the guidelines and policy statements are consistent with the amendments made by sections 2 and 3 of this Act.
(c) Emergency authority.—The Commission shall—
(1) promulgate the guidelines, policy statements, or amendments provided for in this Act as soon as practicable, and in any event not later than 120 days after the date of enactment of this Act, in accordance with the procedure set forth in section 21(a) of the Sentencing Act of 1987 (28 U.S.C. 994 note), as though the authority under that Act had not expired; and
(2) pursuant to the emergency authority provided under paragraph (1), make such conforming amendments to the Federal sentencing guidelines as the Commission determines necessary to achieve consistency with other guideline provisions and applicable law.
SEC. 5. Interdiction of fentanyl, other synthetic opioids, and other narcotics and psychoactive substances.
(a) Definitions.—In this section—
(1) the term “chemical screening device” means an immunoassay, narcotics field test kit, infrared spectrophotometer, mass spectrometer, nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, Raman spectrophotometer, or other scientific instrumentation able to collect data that can be interpreted to determine the presence of fentanyl, other synthetic opioids, and other narcotics and psychoactive substances;
(2) the term “express consignment operator or carrier” has the meaning given the term in section 128.1 of title 19, Code of Federal Regulations, or any successor thereto; and
(3) the term “Postmaster General” means the Postmaster General of the United States Postal Service.
(b) Interdiction of fentanyl, other synthetic opioids, and other narcotics and psychoactive substances.—
(1) CHEMICAL SCREENING DEVICES.—The Postmaster General shall—
(A) increase the number of chemical screening devices that are available to the United States Postal Service; and
(B) make additional chemical screening devices available to the United States Postal Service as the Postmaster General determines are necessary to interdict fentanyl, other synthetic opioids, and other narcotics and psychoactive substances that are illegally imported into the United States, including such substances that are imported through the mail or by an express consignment operator or carrier.
(2) PERSONNEL TO INTERPRET DATA.—The Postmaster General shall dedicate the appropriate number of personnel of the United States Postal Service, including scientists, so that those personnel are available during all operational hours to interpret data collected by chemical screening devices.
(c) Authorization of appropriations.—There is authorized to be appropriated to the Postmaster General $9,000,000 to ensure that the United States Postal Service has resources, including chemical screening devices, personnel, and scientists, available during all operational hours to prevent, detect, and interdict the unlawful importation of fentanyl, other synthetic opioids, and other narcotics and psychoactive substances.
S. 690 – Overdose RADAR Act or Overdose Response Action Data for Actionable Reforms Act
A bill to combat the fentanyl crisis.
SEC. 2. Accurate data on opioid-related overdoses.
Part D of title V of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 290dd et seq.) is amended by adding at the end the following:
“SEC. 554. Accurate data on opioid-related overdoses.
“The Secretary may award grants to States, territories, and localities to support improved data and surveillance on opioid-related overdoses, including for activities to improve postmortem toxicology testing, data linkage across data systems throughout the United States, electronic death reporting, or the comprehensiveness of data on fatal and nonfatal opioid-related overdoses.”.
SEC. 3. Office of National Drug Control Policy reform.
(a) Sense of Congress.—It is the sense of Congress that—
(1) the Director of the Office of National Drug Control Policy shall be a Cabinet-level position; and
(2) nothing in this section shall affect the reporting structure of agencies with drug enforcement responsibilities.
(b) Requirements.—The Office of National Drug Control Policy shall—
(1) document strategies for ensuring prevention of duplicating services and grant funding within National Drug Control Program agencies;
(2) collaborate with the National Center for Health Statistics and the National Forensic Laboratory Information System, including by working with the Department of Justice to create national standards for the submission of data to ensure uniformity across the United States, including data from cases in which the defendant pleads guilty; and
(3) issue guidance that States and localities should record overdose deaths as homicides if there is sufficient evidence that the overdose was not self-induced and intentional.
(c) Interagency coordinating council.—The Office of National Drug Control Policy, the Department of Justice, the Department of Health and Human Services, and other National Drug Control Program agencies shall coordinate to limit duplication and ensure uniform reporting standards and improve relationships between the agencies.
(d) Congressional Review Act.—If the Office of National Drug Control Policy does not certify that a final rule made by a National Drug Control Program participant is consistent with the National Drug Control Policy, the rule shall be deemed to be submitted under section 801(a)(1) of title 5, United States Code.
(e) Reprogramming and transfer requests.—Section 704(c)(4)(A) of the Office of National Drug Control Policy Reauthorization Act of 1998 (21 U.S.C. 1703(c)(4)(A)) is amended by striking “deemed approved” and inserting “deemed denied”.
SEC. 4. State opioid response grants.
Section 1003 of the 21st Century Cures Act (42 U.S.C. 290ee–3a) is amended—
(1) in subsection (f)—
(A) in paragraph (2), by striking “; and” and inserting a semicolon;
(B) in paragraph (3), by striking the period and inserting “; and”; and
(C) by adding at the end the following:
“(4) an assessment of the challenges of such recipients in addressing opioid misuse and use disorders and, as applicable and appropriate, stimulant misuse and use disorders, accounting for variations in implementation of the grant funds.”; and
(2) in subsection (g)—
(A) in the subsection heading, by inserting “and best practices” after “Technical assistance”;
(B) by striking “with technical assistance” and inserting “with—
“(1) technical assistance”; and
(C) by striking the period at the end and inserting “; and”; and
(D) by adding at the end the following:
“(2) best practices on how to address opioid-related overdoses.”.
SEC. 5. Wastewater pilot program.
The Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in collaboration with the Attorney General, shall carry out a 3-year pilot program to award grants on a competitive basis to municipal wastewater treatment facilities in order to conduct wastewater analysis to determine the prevalence of certain illicit substances, such as fentanyl or xylazine, as determined by the Director, in collaboration with the Attorney General, in the communities served by such facilities.
SEC. 6. Grants for reducing opioid overdose deaths.
(a) Use of funds.—Section 544(c) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 290dd–3(c)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1), by inserting “or administering” after “prescribing”; and
(2) in paragraph (2), by inserting “or on the administration of” after “prescribing of”.
(b) Authorization of appropriations.—Section 544(g) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 290dd–3(g)) is amended by striking “to carry out this section” and inserting “to carry out this section and section 544A”.
SEC. 7. Grants for reducing opioid overdose deaths in elementary and secondary schools.
Title V of the Public Health Service Act is amended by inserting after section 544 of such Act (42 U.S.C. 290dd–3) the following:
“SEC. 544A. Reducing opioid overdose deaths in elementary and secondary schools.
“(a) In general.—The Secretary may award grants to eligible entities to provide for the administration, at public and private elementary and secondary schools under the jurisdiction of the eligible entity, of drugs and devices for emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose.
“(b) Applications.—To seek a grant under this section, an eligible entity shall submit to the Secretary an application at such time, in such manner, and containing—
“(1) the information required under section 544(b);
“(2) the certifications specified in subsection (c); and
“(3) such other information as the Secretary shall require.
“(c) Certifications.—The certifications specified in this subsection, with respect to each elementary school and secondary school under the jurisdiction of the eligible entity, are the following:
“(1) The school has in place a program under which the school will permit trained personnel of the school to administer drugs or devices for purposes of providing emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose.
“(2) The school will maintain a supply of such drugs and devices in a location that is easily accessible to trained personnel of the school for the purpose of administering such drugs and devices.
“(3) The school has in place a plan for having on the premises of the school during all operating hours one or more individuals who are such trained personnel.
“(4) The State attorney general of the State in which the school is located certifies that the State—
“(A) has reviewed any applicable civil liability protection law to determine the application of such law with regard to elementary and secondary school trained personnel who may administer drugs and devices for emergency treatment in the case of a known or suspected opioid overdose; and
“(B) has concluded that such law provides adequate civil liability protection applicable to such trained personnel.
“(d) Definitions.—In this section:
“(1) The term ‘civil liability protection law’ means a State law offering legal protection to individuals who give aid in an emergency to an individual who is ill, in peril, or otherwise incapacitated.
“(2) The term ‘eligible entity’ has the meaning given such term in section 544(a)(2).
“(3) The term ‘trained personnel’, with respect to an elementary or secondary school, means an individual—
“(A) who is a school nurse or other individual designated by the principal or other appropriate administrative staff of the school to administer drugs or devices for emergency treatment in the case of a known or suspected opioid overdose;
“(B) who has received training in the administration of such drugs or devices; and
“(C) whose training in the administration of such drugs or devices meets appropriate medical standards and has been documented by appropriate administrative staff of the school.”.
SEC. 8. Fentanyl test strips.
Section 422(f) of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 862(f)) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1), by striking “or” at the end;
(2) in paragraph (2), by striking the period at the end and inserting “; or”; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(3) fentanyl test strips.”.
S. 86o – BUST FENTANYL Act or the Break Up Suspicious Transactions of Fentanyl Act.
To modify the information about countries exporting methamphetamine that is included in the annual International Narcotics Control Strategy Report, to require a report to Congress on the seizure and production of certain illicit drugs, to impose sanctions with respect to the production and trafficking into the United States, of synthetic opioids, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. International Narcotics Control Strategy Report.
Section 489(a) of the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961 (22 U.S.C. 2291h(a)) is amended—
(1) in the matter preceding paragraph (1), by striking “March 1” and inserting “June 1”; and
(2) in paragraph (8)(A)(i), by striking “pseudoephedrine” and all that follows through “chemicals)” and inserting “chemical precursors used in the production of methamphetamine that significantly affected the United States”.
SEC. 3. Study and report on efforts to address fentanyl trafficking from the People’s Republic of China and other relevant countries.
(a) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) APPROPRIATE COMMITTEES OF CONGRESS.—The term “appropriate committees of Congress” means—
(A) the Committee on the Judiciary of the Senate;
(B) the Committee on Foreign Relations of the Senate;
(C) the Committee on the Judiciary of the House of Representatives; and
(D) the Committee on Foreign Affairs of the House of Representatives.
(2) DEA.—The term “DEA” means the Drug Enforcement Administration.
(3) PRC.—The term “PRC” means the People’s Republic of China.
(b) Study and report on addressing trafficking of fentanyl and other synthetic opioids from the PRC and other relevant countries.—Not later than 180 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of State and the Attorney General shall jointly submit to the appropriate committees of Congress an unclassified written report, with a classified annex, that includes—
(1) a description of United States Government efforts to gain a commitment from the Government of the PRC to submit unregulated fentanyl precursors, such as 4–AP, to controls;
(2) a plan for future steps the United States Government will take to urge the Government of the PRC to combat the production and trafficking of illicit fentanyl and synthetic opioids from the PRC, including the trafficking of precursor chemicals used to produce illicit narcotics in Mexico and in other countries;
(3) a detailed description of cooperation by the Government of the PRC to address the role of the PRC financial system and PRC money laundering organizations in the trafficking of fentanyl and synthetic opioid precursors;
(4) an assessment of the expected impact that the designation of principal corporate officers of PRC financial institutions for facilitating narcotics-related money laundering would have on PRC money laundering organizations;
(5) an assessment of whether the Trilateral Fentanyl Committee, which was established by the United States, Canada, and Mexico during the January 2023 North American Leaders’ Summit, is improving cooperation with law enforcement and financial regulators in Canada and Mexico to combat the role of PRC financial institutions and PRC money laundering organizations in narcotics trafficking;
(6) an assessment of the effectiveness of other United States bilateral and multilateral efforts to strengthen international cooperation to address the PRC’s role in the trafficking of fentanyl and synthetic opioid precursors, including through the Global Coalition to Address Synthetic Drug Threats;
(7) an update on the status of commitments made by third countries through the Global Coalition to Address Synthetic Drug Threats to combat the synthetic opioid crisis and progress towards the implementation of such commitments;
(8) a plan for future steps to further strengthen bilateral and multilateral efforts to urge the Government of the PRC to take additional actions to address the PRC’s role in the trafficking of fentanyl and synthetic opioid precursors, particularly in coordination with countries in East Asia and Southeast Asia that have been impacted by such activities;
(9) an assessment of how actions the Government of the PRC has taken since November 15, 2023 has shifted relevant supply chains for fentanyl and synthetic opioid precursors, if at all; and
(10) the items described in paragraphs (1) through (4) pertaining to India, Mexico, and other countries the Secretary of State determines to have a significant role in the production or trafficking of fentanyl and synthetic opioid precursors for purposes of this report.
(c) Establishment of DEA offices in the PRC.—Not later than 180 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of State and the Attorney General shall jointly provide to the appropriate committees of Congress a classified briefing on—
(1) outreach and negotiations undertaken by the United States Government with the Government of the PRC that was aimed at securing the approval of the Government of the PRC to establish of United States Drug Enforcement Administration offices in Shanghai and Guangzhou, the PRC; and
(2) additional efforts to establish new partnerships with provincial-level authorities in the PRC to counter the illicit trafficking of fentanyl, fentanyl analogues, and their precursors.
SEC. 4. Prioritization of identification of persons from the People’s Republic of China.
Section 7211 of the Fentanyl Sanctions Act (21 U.S.C. 2311) is amended—
(1) in subsection (a)—
(A) by redesignating paragraphs (3) and (4) as paragraphs (4) and (5), respectively; and
(B) by inserting after paragraph (2) the following:
“(3) PRIORITIZATION.—
“(A) DEFINED TERM.—In this paragraph, the term ‘person of the People’s Republic of China’ means—
“(i) an individual who is a citizen or national of the People’s Republic of China; or
“(ii) an entity organized under the laws of the People’s Republic of China or otherwise subject to the jurisdiction of the Government of the People’s Republic of China.
“(B) IN GENERAL.—In preparing the report required under paragraph (1), the President shall prioritize, to the greatest extent practicable, the identification of persons of the People’s Republic of China involved in the shipment of fentanyl, fentanyl analogues, fentanyl precursors, precursors for fentanyl analogues, pre-precursors for fentanyl and fentanyl analogues, and equipment for the manufacturing of fentanyl and fentanyl-laced counterfeit pills to Mexico or any other country that is involved in the production of fentanyl trafficked into the United States, including—
“(i) any entity involved in the production of pharmaceuticals; and
“(ii) any person that is acting on behalf of any such entity.
“(C) TERMINATION OF PRIORITIZATION.—The President shall continue the prioritization required under subparagraph (B) until the President certifies to the appropriate congressional committees that the People’s Republic of China is no longer the primary source for the shipment of fentanyl, fentanyl analogues, fentanyl precursors, precursors for fentanyl analogues, pre-precursors for fentanyl and fentanyl analogues, and equipment for the manufacturing of fentanyl and fentanyl-laced counterfeit pills to Mexico or any other country that is involved in the production of fentanyl trafficked into the United States.”; and
(2) in subsection (c), by striking “the date that is 5 years after such date of enactment” and inserting “December 31, 2030”.
SEC. 5. Expansion of sanctions under the Fentanyl Sanctions Act.
Section 7212 of the Fentanyl Sanctions Act (21 U.S.C. 2312) is amended—
(1) in paragraph (1), by striking “or” at the end;
(2) in paragraph (2), by striking the period at the end and inserting a semicolon; and
(3) by adding at the end the following:
“(3) the President determines has knowingly engaged in, on or after the date of the enactment of the BUST FENTANYL Act, a significant activity or significant financial transaction that has materially contributed to opioid trafficking; or
“(4) the President determines—
“(A) has received any property or interest in property that the foreign person knows—
“(i) constitutes or is derived from the proceeds of an activity or transaction described in paragraph (3); or
“(ii) was used or intended to be used to commit or to facilitate such an activity or transaction;
“(B) has knowingly provided significant financial, material, or technological support for, including through the provision of goods or services in support of—
“(i) any activity or transaction described in paragraph (3); or
“(ii) any foreign person described in paragraph (3); or
“(C) is or has been owned, controlled, or directed by any foreign person described in subparagraph (A) or (B) or in paragraph (3), or has knowingly acted or purported to act for or on behalf of, directly or indirectly, such a foreign person.”.
SEC. 6. Imposition of sanctions with respect to agencies or instrumentalities of foreign states.
(a) Definitions.—In this section, the terms “knowingly” and “opioid trafficking” have the meanings given such terms in section 7203 of the Fentanyl Sanctions Act (21 U.S.C. 2302).
(b) In general.—The President may—
(1) impose one or more of the sanctions described in section 7213 of the Fentanyl Sanctions Act (21 U.S.C. 2313) with respect to each political subdivision, agency, or instrumentality of a foreign government, including any financial institution owned or controlled by a foreign government, that the President determines has knowingly, on or after the date of the enactment of this Act—
(A) engaged in a significant activity or a significant financial transaction that has materially contributed to opioid trafficking; or
(B) provided financial, material, or technological support for (including through the provision of goods or services in support of) any significant activity or significant financial transaction described in subparagraph (A); and
(2) impose one or more of the sanctions described in section 7213(a)(6) of the Fentanyl Sanctions Act (21 U.S.C. 2313(a)(6)) with respect to each senior official of a political subdivision, agency, or instrumentality of a foreign government that the President determines has knowingly, on or after the date of the enactment of this Act, facilitated a significant activity or a significant financial transaction described in paragraph (1).
SEC. 7. Annual report on efforts to prevent the smuggling of methamphetamine into the United States from Mexico.
Section 723(c) of the Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act of 2005 (22 U.S.C. 2291 note) is amended by striking the period at the end and inserting the following “, which shall—
“(1) identify the significant source countries for methamphetamine that significantly affect the United States, and
“(2) describe the actions by the governments of the countries identified pursuant to paragraph (1) to combat the diversion of relevant precursor chemicals and the production and trafficking of methamphetamine.”.
S. 724 – Temporary Extension of Fentanyl-Related Substances Scheduling Act.
A bill to extend the temporary scheduling order for fentanyl-related substances for 6 months.
SEC. 2. Extension of temporary order for fentanyl-related substances.
Section 2 of the Temporary Reauthorization and Study of the Emergency Scheduling of Fentanyl Analogues Act (Public Law 116–114; 134 Stat. 103) is amended by striking “March 31, 2025” and inserting “September 30, 2025”.
S. 921 – Tyler’s Law
A bill to direct the Secretary of Health and Human Services to issue guidance on whether hospital emergency departments should implement fentanyl testing as a routine procedure for patients experiencing an overdose, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Testing for fentanyl in hospital emergency departments.
(a) Study.—Not later than 1 year after the date of enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall complete a study to determine—
(1) how frequently hospital emergency departments test for fentanyl (in addition to testing for other substances such as amphetamines, phencyclidine, cocaine, opiates, and marijuana) when a patient is experiencing an overdose;
(2) the costs associated with such testing for fentanyl;
(3) the potential benefits and risks for patients receiving such testing for fentanyl; and
(4) how fentanyl testing in hospital emergency departments may impact the experience of the patient, including—
(A) protections for the confidentiality and privacy of the patient’s personal health information; and
(B) the patient-physician relationship.
(b) Guidance.—Not later than 6 months after completion of the study under subsection (a), based on the results of such study, the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall issue guidance on the following:
(1) Whether hospital emergency departments should implement fentanyl testing as a routine procedure for patients experiencing an overdose.
(2) How hospitals can ensure that clinicians in their hospital emergency departments are aware of which substances are being tested for in their routinely-administered drug tests, regardless of whether those tests screen for fentanyl.
(3) How the administration of fentanyl testing in hospital emergency departments may affect the future risk of overdose and general health outcomes.
(c) Definition.—In this section, the term “hospital emergency department” means a hospital emergency department as such term is used in section 1867(a) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395dd(a)).
Other Bills
S. 210 – SWAG Act or the Stop Wasteful Advertising by the Government Act
A bill to prohibit agencies from using Federal Funds for publicity or propaganda purposes, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Definitions.
In this Act—
(1) the term “advertising” means the placement of messages in media that are intended to inform or persuade an audience, including placement in television, radio, a magazine, a newspaper, digital media, direct mail, a tangible product, an exhibit, or a billboard;
(2) the term “agency” has the meaning given the term in section 551 of title 5, United States Code;
(3) the term “mascot” means an individual, animal, or object adopted by an agency as a symbolic figure to represent the agency, the mission of the agency, or a program within the agency, including a costumed character;
(4) the term “public relations” means communications by an agency that are directed to the public, including activities dedicated to maintaining the image of the governmental unit or maintaining or promoting understanding and favorable relations with the community or the public;
(5) the term “return on investment” means, with respect to the public relations and advertising spending by an agency, a positive return in achieving agency or program goals relative to the investment in advertising and marketing materials; and
(6) the term “swag”—
(A) means a tangible product or merchandise distributed at no cost with the sole purpose of advertising or promoting an agency, organization, or program;
(B) includes blankets, buttons, candy, clothing, coloring books, graphic novels, cups, fidget spinners, hats, holiday ornaments, jar grip openers, keychains, koozies, magnets, neckties, snuggies, stickers, stress balls, stuffed animals, thermoses, tote bags, trading cards, and writing utensils; and
(C) does not include—
(i) an item presented as an honorary or informal recognition award related to the Armed Forces of the United States, such as a challenge coin or medal issued for sacrifice or meritorious service;
(ii) a brochure or pamphlet purchased or distributed for informational purposes; or
(iii) an item distributed for diplomatic purposes, including a gift for a foreign leader.
SEC. 3. Prohibitions; public relations and advertising spending.
(a) Prohibitions.—Except as provided in subsection (c), and unless otherwise expressly authorized by law—
(1) an agency or other entity of the Federal Government may not use Federal funds to purchase or otherwise acquire or distribute swag; and
(2) an agency or other entity of the Federal Government may not use Federal funds to manufacture or use a mascot to promote an agency, organization, program, or agenda.
(b) Public relations and advertising spending.—Each agency shall, as part of the annual budget justification submitted to Congress, report on the public relations and advertising spending of the agency for the preceding fiscal year, which may include an estimate of the return on investment for the agency.
(c) Exceptions.—
(1) SWAG.—Subsection (a)(1) shall not apply with respect to—
(A) an agency program that supports the mission and objectives of the agency that is initiating the public relations or advertising spending, provided that the spending generates a positive return on investment for the agency;
(B) recruitment relating to—
(i) enlistment or employment with the Armed Forces; or
(ii) employment with the Federal Government; or
(C) an item distributed by the Bureau of the Census to assist the Bureau in conducting a census of the population of the United States.
(2) MASCOTS.—Subsection (a)(2) shall not apply with respect to—
(A) a mascot that is declared the property of the United States under a provision of law, including under section 2 of Public Law 93–318 (16 U.S.C. 580p–1); or
(B) a mascot used—
(i) for the purpose of recruitment of individuals to enlist in the Armed Forces of the United States; or
(ii) in support of a military academy athletic team.
(d) Regulations.—Not later than 180 days after the date of enactment of this Act, the Director of the Office of Management and Budget shall issue regulations to carry out this Act.
S. 459 – Amateur Radio Emergency Preparedness Act.
A bill to amend the Communications Act of 1934 to prohibit the application of certain private land use restrictions to amateur station antennas, and for other purposes.
Related Bill: H. 1094
S. 634 – Korematsu-Takai Civil Liberties Protection Act of 2025
A bill to ensure due process protections of individuals in the United States against unlawful detention based solely on a protected characteristic.
SEC. 2. Prohibition against unlawful detention.
Section 4001 of title 18, United States Code, is amended—
(1) by redesignating subsection (b) as subsection (c); and
(2) by inserting after subsection (a) the following:
“(b) Prohibition on detention based on protected characteristics.—
“(1) DEFINITION.—In this subsection, the term ‘protected characteristic’ includes each of the following:
“(A) Race.
“(B) Ethnicity.
“(C) National origin.
“(D) Religion.
“(E) Sex.
“(F) Gender identity.
“(G) Sexual orientation.
“(H) Disability.
“(I) Any additional characteristic that the Attorney General determines to be a protected characteristic.
“(2) PROHIBITION.—No individual may be imprisoned or otherwise detained based solely on an actual or perceived protected characteristic of the individual.
“(3) RULE OF CONSTRUCTION.—Nothing in this subsection shall be construed to allow the Attorney General to remove a characteristic described in subparagraphs (A) through (H) of paragraph (1).”.
S. 698 – Federal Prisons Accountability Act of 2025
A bill to require the Director of the Bureau of Prisons to be appointed by and with the advice and consent of the Senate.
SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds the following:
(1) The Director of the Bureau of Prisons leads a law enforcement component of the Department of Justice with a budget that exceeded $8,390,000,000 for fiscal year 2024.
(2) With the exception of the Federal Bureau of Investigation, the Bureau of Prisons had the largest operating budget of any unit within the Department of Justice for fiscal year 2024.
(3) As of 2025, the Director of the Bureau of Prisons oversaw 122 facilities and was responsible for the welfare of more than 155,000 Federal inmates.
(4) As of 2025, the Director of the Bureau of Prisons supervised more than 35,000 employees, many of whom operate in hazardous environments that involve regular interaction with violent offenders.
(5) Within the Department of Justice, in addition to those officials who oversee litigating components, the Director of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, the Director of the Community Relations Service, the Director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation, the Director of the Office on Violence Against Women, the Administrator of the Drug Enforcement Administration, the Deputy Administrator of the Drug Enforcement Administration, the Director of the United States Marshals Service, 94 United States Marshals, the Inspector General of the Department of Justice, and the Special Counsel for Immigration Related Unfair Employment Practices, are all appointed by the President by and with the advice and consent of the Senate.
(6) Despite the significant budget of the Bureau of Prisons and the vast number of people under the responsibility of the Director of the Bureau of Prisons, the Director is not appointed by and with the advice and consent of the Senate.
SEC. 3. Director of the Bureau of Prisons.
(a) In general.—Section 4041 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking “appointed by and serving directly under the Attorney General.” and inserting the following: “who shall be appointed by the President, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate. The Director shall serve directly under the Attorney General.”.
(b) Incumbent.—Notwithstanding the amendment made by subsection (a), the individual serving as the Director of the Bureau of Prisons on the date of enactment of this Act may serve as the Director of the Bureau of Prisons until the date that is 3 months after the date of enactment of this Act.
(c) Rule of construction.—Nothing in this Act shall be construed to limit the ability of the President to appoint the individual serving as the Director of the Bureau of Prisons on the date of enactment of this Act to the position of Director of the Bureau of Prisons in accordance with section 4041 of title 18, United States Code, as amended by subsection (a).
(d) Term.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Section 4041 of title 18, United States Code, as amended by subsection (a), is amended by inserting after “consent of the Senate.” the following: “The Director shall be appointed for a term of 10 years, except that an individual appointed to the position of Director may continue to serve in that position until another individual is appointed to that position, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate. An individual may not serve more than 1 term as Director.”.
(2) APPLICABILITY.—The amendment made by paragraph (1) shall apply to appointments made on or after the date of enactment of this Act.
S. 1102 – Providing a Quality Defense Act of 2025
A bill to incentivize States and localities to improve access to justice, and for other purposes.
SEC. 2. Purposes.
The purposes of this Act are—
(1) to protect the constitutional rights to due process and a fair criminal prosecution under the Fifth, Sixth, and Fourteenth Amendments to the Constitution of the United States, including the right to counsel, in State and local courts, as articulated by the Supreme Court of the United States in Gideon v. Wainwright, 372 U.S. 335 (1963), and its progeny;
(2) to protect the right to counsel for juveniles in delinquency proceedings, including the determination of whether a juvenile should be tried as an adult, under the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment as articulated by the Supreme Court in In re Gault, 387 U.S. 1 (1967);
(3) to collect data related to public defense in order to facilitate evidence-based reforms and improvements; and
(4) to ensure that compensation for public defenders and panel attorneys reflects the constitutional guarantee of the right to counsel and does not disincentivize attorneys from pursuing a career in public defense.
SEC. 3. Definitions.
In this Act, except as otherwise provided in section 7:
(1) APPLICABLE PUBLIC DEFENDER’S OFFICE.—The term “applicable public defender’s office”, with respect to an eligible entity that is—
(A) a public defender’s office, means the eligible entity;
(B) a State or unit of local government, means—
(i) the public defender’s office of the eligible entity; and
(ii) a public defender’s office of a unit of local government within the eligible entity; and
(C) a Tribal organization, means the public defender’s office of the Tribal organization.
(2) ASSIGNED COUNSEL PROGRAM.—The term “assigned counsel program” means a program or procedure by which a court assigns a panel attorney to provide quality legal representation to a client.
(3) CASE.—The term “case” includes all charges against an individual involved in a single incident of alleged criminal or delinquent conduct.
(4) CASE TYPE.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—The term “case type” means the classification of a client’s case into 1 of the following categories, as defined under State or local law:
(i) Juvenile.
(ii) Misdemeanor.
(iii) Felony for which the death penalty may be imposed.
(iv) Felony for which a sentence of up to life imprisonment may be imposed.
(v) Felony not described in clause (iii) or (iv).
(vi) Violation of probation or parole.
(vii) School proceeding.
(viii) Other.
(B) MULTIPLE CHARGES.—If a case involves multiple charges, the case type shall be determined according to the most serious charge under the applicable State or local law.
(5) CORRESPONDING PROSECUTOR’S OFFICE.—The term “corresponding prosecutor’s office”, with respect to a public defender’s office or panel attorneys, means a prosecutorial unit that appears adverse to the public defender’s office or panel attorneys in criminal proceedings.
(6) DATA GRANT.—The term “data grant” means a grant awarded under section 4(a)(1).
(7) ELIGIBLE ENTITY.—The term “eligible entity” means a State, unit of local government, Tribal organization, public defender’s office, or assigned counsel program that—
(A) in the case of an application for a data grant, has not, as of the date of application, developed and implemented a data collection process that meets the requirements under section 4(b)(2); and
(B) in the case of an application for a hiring grant, as of the date of the application, has—
(i) received a data grant; and
(ii) fulfilled the requirements of the data grant.
(8) HIRING GRANT.—The term “hiring grant” means a grant awarded under section 4(a)(2).
(9) MOST SERIOUS CHARGE.—The term “most serious charge”, with respect to a case that involves multiple charges, means the charge that carries the most severe or lengthy maximum penalty.
(10) PANEL ATTORNEY.—The term “panel attorney” means a private attorney assigned by the court who serves the same function as a public defender, without regard to whether the role is full-time or part-time.
(11) PROSECUTOR.—The term “prosecutor”—
(A) has the meaning given the term in section 3001(b) of title I of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10671(b)); and
(B) includes a full-time employee of a Tribal organization who—
(i) is continually licensed to practice law; and
(ii) carries out activities equivalent to those of a prosecutor referred to in subparagraph (A).
(12) PUBLIC DEFENDER.—The term “public defender”—
(A) has the meaning given the term in section 3001(b) of title I of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10671(b)); and
(B) includes an attorney employed by a Tribal organization who—
(i) is continually licensed to practice law; and
(ii) carries out activities equivalent to those of a public defender referred to in subparagraph (A).
(13) PROSECUTOR’S OFFICE; PUBLIC DEFENDER’S OFFICE.—The terms “prosecutor’s office” and “public defender’s office” mean an agency or office of a State, unit of local government, or Tribal organization that employs prosecutors or public defenders, respectively.
(14) RESOLUTION.—The term “resolution”, with respect to a case, means the manner in which the case concludes, including by—
(A) dismissal by the prosecutor;
(B) dismissal based on a motion, such as a motion to suppress evidence;
(C) a plea agreement at first appearance;
(D) a plea agreement entered into at any point in the criminal prosecution other than first appearance;
(E) diversion; or
(F) a bench or jury trial and the outcome of the trial, including the sentence if the defendant is convicted of any offense charged.
(15) SECONDARY CHARGE.—The term “secondary charge”, with respect to a case that involves multiple charges, means any charge that is not the most serious charge.
(16) STATE.—The term “State” has the meaning given the term in section 901 of title I of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10251).
(17) TRIBAL ORGANIZATION.—The term “Tribal organization” has the meaning given the term “tribal organization” in section 4(l) of the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act (25 U.S.C. 5304(l)).
(18) UNIT OF LOCAL GOVERNMENT.—The term “unit of local government” has the meaning given the term in section 901 of title I of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10251).
SEC. 4. Public defense grant program.
(a) Grant authority.—The Attorney General may award a grant to an eligible entity to—
(1) develop, implement, and update a data collection process under subsection (b)(2); or
(2) hire additional public defense attorneys or carry out related activities under subsection (c)(3).
(b) Data grants.—
(1) TERM.—The term of a data grant shall be 3 fiscal years.
(2) REQUIRED DATA COLLECTION.—An eligible entity that receives a data grant shall develop and implement a process for collecting the following data for attorneys employed by each applicable public defender’s office, and for panel attorneys within the jurisdiction of the eligible entity, during each fiscal year of the grant period:
(A) The mean number of hours per month worked per attorney.
(B) The mean number of hours spent per month by an attorney on—
(i) discovery and investigation, including witness interviews;
(ii) court time, including preparation and appearances;
(iii) client communication and care;
(iv) research and writing, including motions practice; and
(v) administrative work.
(C) The number of cases handled, broken down by—
(i) case type, including by—
(I) the most serious charge; and
(II) each secondary charge;
(ii) the race, ethnicity, age, and gender of the client;
(iii) the date on which the attorney was appointed to the case;
(iv) whether the case remained open as of the last day of the fiscal year, and if not, the date on which the case was closed; and
(v) the resolution of the case, if the case was concluded by the last day of the fiscal year.
(D) Any other information as the Attorney General determines appropriate.
(3) RENEWAL.—Upon application from an eligible entity that received a data grant, the Attorney General may award a subsequent data grant to the eligible entity for an additional term that may begin upon termination of the initial data grant.
(c) Hiring grants.—
(1) APPLICATION REQUIREMENTS.—An eligible entity desiring a hiring grant shall submit to the Attorney General an application that includes, as of the date of the application—
(A) the caseload and number of, and pay scale for, attorneys and other staff of each applicable public defender’s office; and
(B) (i) the number of panel attorneys within the jurisdiction of the eligible entity;
(ii) the total number of cases assigned to the attorneys described in clause (i); and
(iii) the average number of hours spent on a case by an attorney described in clause (i).
(2) TERM.—The term of a hiring grant shall be 3 years.
(3) USE OF FUNDS.—An eligible entity may use a hiring grant to—
(A) hire additional public defenders;
(B) increase compensation for public defenders or panel attorneys to achieve pay parity with corresponding prosecutor’s offices;
(C) hire case workers, social workers, investigators, or paralegals; or
(D) establish or fund a loan assistance program for public defenders.
(4) SUPPLEMENT, NOT SUPPLANT.—An eligible entity may not use a hiring grant to supplant funds that the eligible entity would otherwise have used for any authorized purpose described in paragraph (3) during the grant period.
(5) REQUIRED DATA COLLECTION.—During each fiscal year of the grant period, an eligible entity that receives a hiring grant shall collect the data described in subsection (b)(2).
(d) Submission requirement.—Not later than 60 days after the end of a fiscal year, an eligible entity that receives a data grant or hiring grant shall submit to the Attorney General the data described in subsection (b)(2) for that fiscal year.
(e) Multiple defendants.—If a prosecutor’s charging document states that multiple defendants were involved in a single incident of alleged criminal or delinquent conduct, each defendant shall be considered a separate case for purposes of the collection of data described in subsection (b)(2).
(f) Authorization of appropriations.—There are authorized to be appropriated to the Attorney General to carry out this section—
(1) $250,000,000 for each of the first 5 fiscal years beginning after the date of enactment of this Act; and
(2) such sums as may be necessary for each fiscal year thereafter.
SEC. 5. Studies.
(a) Studies.—
(1) CASELOAD LIMITS STUDY.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—After the end of the first fiscal year for which data grants are awarded, the Attorney General, acting through the Director of the Bureau of Justice Assistance and the Director of the Office for Access to Justice, shall—
(i) conduct a study to analyze the data submitted to the Attorney General under section 4(d) for that fiscal year related to public defender and panel attorney caseloads and correlated outcomes;
(ii) review studies, reports, and other data published or provided by professional organizations, legal associations, and bar associations related to public defender and panel attorney caseloads; and
(iii) develop and publish best practices and recommendations for setting public defender and panel attorney caseloads based on the information described in clauses (i) and (ii) to ensure—
(I) reasonably effective assistance of counsel pursuant to constitutional standards and prevailing professional norms; and
(II) competent representation pursuant to applicable rules of professional responsibility.
(B) CONTINUING STUDY.—Not less frequently than once every 5 years, the Attorney General shall—
(i) study and review new studies, reports, or other data as described in subparagraph (A)(ii); and
(ii) update the best practices and recommendations under subparagraph (A)(iii).
(2) COMPENSATION STUDY.—Not later than 3 years after the date of enactment of this Act, the Attorney General, acting through the Director of the Bureau of Justice Assistance and the Director of the Office for Access to Justice, shall—
(A) conduct a national study of public defender salaries and panel attorney rates, using prosecutors’ salaries as one benchmark; and
(B) develop and publish best practices and recommendations relating to compensation of public defenders and panel attorneys.
(b) Authorization of appropriations.—There are authorized to be appropriated to the Attorney General such sums as may be necessary to carry out this section.
SEC. 6. State data collection.
(a) In general.—For any fiscal year beginning after the date of enactment of this Act, a State that receives funds under subpart 1 of part E of title I of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10151 et seq.) may submit to the Office for Access to Justice of the Department of Justice data on, with respect to criminal cases heard by a court of the State or of a unit of local government in the State during that fiscal year, the number of cases for which a defendant was represented in court by a public defender or panel attorney, broken down by—
(1) the most serious charge and the total number of secondary charges in each case; and
(2) race, ethnicity, age, and gender of the defendant.
(b) Applicable criminal offenses.—A State that elects to submit data under subsection (a) shall include data with respect to—
(1) criminal offenses for which a term of imprisonment of more than 1 year may be imposed;
(2) criminal offenses for which a term of imprisonment of 1 year or less may be imposed, including misdemeanors, traffic violations, and violations of municipal ordinances; and
(3) acts of juvenile delinquency or juvenile status offenses for which any term of detention may be imposed.
(c) Funding.—A State that receives funds under subpart 1 of part E of title I of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (34 U.S.C. 10151 et seq.) may apply for, and the Attorney General may award, a 5 percent increase in those funds, to be used by the State to collect and provide to the Office for Access to Justice of the Department of Justice the data described in subsection (a) of this section.
SEC. 7. Funding for educational programs.
(a) Definition.—In this section, the term “eligible entity” means an entity that is—
(1) an organization—
(A) described in paragraph (3) or (6) of section 501(c) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 and exempt from taxation under section 501(a) of such Code; or
(B) funded by a State or unit of local government; or
(2) a State, unit of local government, Indian Tribal government, or political subdivision of an Indian Tribe.
(b) Grants.—The Attorney General shall award grants to eligible entities to provide a comprehensive educational program to public defenders and panel attorneys that offers—
(1) ongoing training and support; and
(2) programming that includes—
(A) skills training, including pretrial practice, negotiation skills, trial skills, and sentencing advocacy;
(B) client-centered values;
(C) implicit bias training;
(D) leadership development; and
(E) ongoing support to reinforce the training curriculum.
(c) Authorization of appropriations.—There are authorized to be appropriated to the Attorney General to carry out this section $5,000,000 for each of the first 5 fiscal years beginning after the date of enactment of this Act.
S. 1148 – A bill to terminate the Department of Education.
S.1157 – A bill to direct the Secretary of Health and Human Services to conduct a review to evaluate the status of research on lung cancer in women and underserved populations, and for other purposes.
S.1189 – A bill to provide block grants to assign armed law enforcement officers to elementary and secondary schools.
S.1208 – A bill to amend title 5, United States Code, to address records maintained on individuals, and for other purposes.
S. 1232 A bill to direct the Secretary of Labor to issue an occupational safety and health standard that requires covered employers within the health care and social service industries to develop and implement a comprehensive workplace violence prevention plan, and for other purposes.
S.1295 – A bill to require the Director of the Bureau of Prisons to develop and implement a strategy to interdict fentanyl and other synthetic drugs in the mail at Federal correctional facilities.
It is imperative that every American communicate with the health issues staff person for their legislators. If you don't have that contact information, you can get it by filling out the contact form below.
For the purpose of this communication campaign, I will provide the health staffer contacts for the entire state. In order to get the health staffer contacts for the entire country, you have to be a supporting member of Doctorsofcourage.
Who Are My Health Issues Staff?
Ambassadors, Advertise Here
Ambassadors, if you have any skills, products, that you are using to make a living during your attack, please share with us and we will support you, spread the word, and do everything we can to help.
DoC Membership Provides YOU:
Point and Click Connections to all Legislators' email, health staff, Facebook and Twitter accounts.
A Website to tell the world what is happening to innocent citizens-both patients and doctors.

A personal contact to meet with legislators in Washington
Linda Cheek is a teacher and disenfranchised medical doctor, turned activist, author, and speaker. A victim of prosecutorial misconduct and outright law-breaking of the government agencies DEA, DHHS, and DOJ, she hopes to be a part of exonerating all doctors illegally attacked through the Controlled Substance Act. She holds the key to success, as she can offset the government propaganda that drugs cause addiction with the truth: The REAL Cause of Drug Abuse.
Get a free gift to learn how the government is breaking the law to attack your doctor: Click here to get my free gift
